Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture4 Control Charts
Transféré par
Melissa JohnDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lecture4 Control Charts
Transféré par
Melissa JohnDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
STATISTICAL QUALITY CONTROL AND IMPROVEMENT
Lecture 4 Control Charts Shashikant Sathaye Polytechnic Institute of NYU
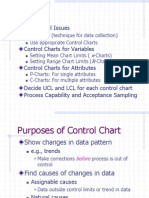
Variable Control Charts
How to Use the Process Control Charts
A process is said to be in control when the performance of the process falls within the statistically calculated control limits and exhibits only random variation due to chance causes Process under control does not mean that the process meets design specifications Identifying Patterns:
Trends are changes in levels; for e.g the center line might be drifting downwards Change or jump in level can be detected if a consecutive set of observations are consistently above(below) the center line.
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 2
Variable Control Charts
Example: Printer Assembly
An assembly area has been experiencing serious delays in the manufacture of computer printers. As a quality assurance manager you are asked to investigate and determine the cause of delays and fix the problems. Given the limited time, you get together with the representatives from all the departments and develop an cause and effect diagram Set the quality characteristic to measured length of a shaft
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 3
Variable Control Charts
Example: Printer Assembly
Choose a rational sub-group to sample needs to be homogeneous
Sub-group should be at least 4. Normally use range R for estimating std dev. If sub-group size is more than 10, then use s.
Collect the data Determine the trial central line for the X chart. X= Xi m
where X = average of the subgroup averages Xi = average of the ith group m = number of subgroups
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement Polytechnic Institute of NYU Lecture 4 MN611 4
Variable Control Charts
Determine the Trial Control Limits for the Xbar Chart UCLx = X + 3 x LCLx = X - 3 x Since the std deviation, is not known and we have a small sample size for each subgroup (4), we use the range R as a proxy for the std deviation and a factor A2 as the multiplier for the 99% confidence limit. A2 depends on the sample size. Thus UCLx = X + A2R LCLx = X A2R So for our example: X = (11.99+12.00,+12.00)/21 = 11.99 and R = (.08+.07_.04+.+.04)/21 = 0.05 UCLx = X + A2R = 11.99 + .577(.05) = 12.02 LCLx = X A2R = 11.99 - .577(.05) = 11.96
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 5
Variable Control Charts
Determine the Trial Control Limits for the R Chart R = Ri = .05 m The upper and lower control limits are determined using another set of multiplier D3 and D4; for a sample of n=5, D3 and D4 are 0 and 2.114. Thus UCLR = D4R = 2.114(.05) = 0.11 LCLR = D3R = 0(.05) = 0
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 6
Variable Control Charts
X
bar
12.04 12.02 12.00 11.98
UCLr CLine LCLr
C H A R T R C H A R T
11.96 11.94 11.92 11.90 11.88
0.12 0.10 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02
UCLr
CL
LCLr
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 7
Variable Control Charts
Examine the process: Control Chart Interpretation
Avoid misinterpretations
Blaming people for problems they cannot control Spending time and money on process adjustments that are not necessary Asking for workers to improve when it the equipment that needs fixing
State of Process Control Process is under control when the performance falls within the statistically calculated control and exhibits only chance or random causes. +/-3 limits 99.73% of the measurements will be within the limits. Based upon the normal curve
Region A = 68.3% Region B = 27.2% Region C = 4.2%
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 8
Variable Control Charts
Examine the process: Control Chart Interpretation Thus the basic guidelines for a process under control are:
Two thirds of the points are close to center A few points on or near the center line Points equally spread around the center No points outside the control limits No patterns or trends on the chart
The range chart reveals the amount of variation in the process; so look for amount of variation in addition to the rules listed above. Types of patterns (non random variations)
Trends (upward or downward) Change or shift in level Runs Recurring cycles Non homogenous data
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 9
Variable Control Charts
Revising the charts
R chart should be under control (it appear so) Isolate the cause of out of control and fix the problem
12.04
X
ba r
12.02 12.00 11.98 11.96
UCLr CLine LCLr
C H A R T R C H A R T
11.94 11.92 11.90 11.88
0.12 0.10 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02
UCLr
CL
LCLr
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 10
Variable Control Charts
Revise the charts
Eliminate the out of control points from both the charts and re-calculate the center line and control limits Eliminate the three points Xnew = and Rnew =
Xi - Xd m - md Ri - Rd m - md
= (251.77-11.94-11.95-11.95)/(21-3) = 12 = Xo
= (1.06-.04-.05-.6)(21-3) = .05
New Control Limits o = Rnew/d2 = .05/2.326 = 0.02 UCLx = Xo + A o = 12 + 1.342(.02) = 12.03 LCLx = Xo - A o = 12 - 1.342(.02) = 11.97
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 11
Variable Control Charts
Revising the control charts
12.04 12.02 12.00 11.98 11.96 11.94 11.92
UCLx UCLo Center Lineo LCLo
11.90 11.88
LCLx
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN6113 - 12
Variable Control Charts
Xandscharts
schartismoreprecisethanRchartsbutrequirelargersample subgroupsize(>10) ThecontrollimitsarecalculatedinasimilarmannerasXandR chartsexceptthatthe controllimitsarebasedupons. s=
si m
=(.03+.029+..+.011)/21=0.414/21=.02
UCLx =X+A3s=11.99+1.427(.02)=12.02 LCLx =XA3s=11.99 1.427(.02)=11.96 UCLs =B4s=2.089(.02)=.04 LCLs =B3s=0(.02)=0
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN6113 - 13
Variable Control Charts (Xbar and s charts)
X
bar
12.04 12.02 12.00 11.98
UCLr CLine LCLr
C H A R T S C H A R T
11.96 11.94 11.92 11.90 11.88
0.05 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01
UCLs
CL
LCLs
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 14
Variable Control Charts
Statistical Quality Control and Improvement
Polytechnic Institute of NYU
Lecture 4 MN611 15
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Practical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsD'EverandPractical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsPas encore d'évaluation
- DocxDocument3 pagesDocxMikey MadRat0% (1)
- Which Control Charts To Use WhereDocument115 pagesWhich Control Charts To Use Whereanbarasuar1964Pas encore d'évaluation
- Variation: The Presence of VariationDocument17 pagesVariation: The Presence of VariationHarris ChackoPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Quality Control 2Document34 pagesStatistical Quality Control 2Tech_MXPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics For Business and Economics: Bab 20Document43 pagesStatistics For Business and Economics: Bab 20balo100% (1)
- Statistical Quality ControlDocument18 pagesStatistical Quality ControluzaimyPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Charts: Walter A. ShewhartDocument28 pagesControl Charts: Walter A. Shewhartmimossmart26036Pas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Quality Control: By: Vilas PathakDocument45 pagesStatistical Quality Control: By: Vilas Pathakgazala100% (2)
- Operations Management: Quality Control - Concept of Quality - Quality Planning - Statistical Quality ControlDocument37 pagesOperations Management: Quality Control - Concept of Quality - Quality Planning - Statistical Quality ControlDrisya M NambiarPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Control ChartsDocument30 pagesQuality Control ChartsLibyaFlowerPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Quality ControlDocument13 pagesStatistical Quality ControlsekelanilunguPas encore d'évaluation
- 06control Chart 1Document37 pages06control Chart 1abishank09100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Control Charts For VariablesDocument44 pagesChapter 4 Control Charts For Variablesgeletaw mitawPas encore d'évaluation
- 06control Chart 1Document37 pages06control Chart 1Ashok SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Quality Control (S.Q.C.) Presented By-: Nikhil Garg ROLL NO-0129626Document38 pagesStatistical Quality Control (S.Q.C.) Presented By-: Nikhil Garg ROLL NO-0129626jolaakPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Process ControlDocument42 pagesStatistical Process ControlErick Bok Cang YeongPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Four Control Charts For Variables-I: Implementing SPC in A Quality Improvement ProgramDocument10 pagesChapter Four Control Charts For Variables-I: Implementing SPC in A Quality Improvement ProgramComputer Maintainance Hardware and softwarePas encore d'évaluation
- SQCDocument36 pagesSQCMandeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Control ChartDocument25 pagesControl ChartSURYAPRAKASH GPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Charts - MBADocument30 pagesControl Charts - MBAShivangi Dhamija100% (1)
- Operations Management: Processes and Supply ChainsDocument82 pagesOperations Management: Processes and Supply ChainsMustafa MangalPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Charts For Variable Data: STAT8010 Applied Statistical TechniquesDocument22 pagesControl Charts For Variable Data: STAT8010 Applied Statistical TechniquesIsha BPas encore d'évaluation
- Control ChartsDocument29 pagesControl Chartsmbstutextile100% (1)
- Control ChartsDocument38 pagesControl ChartsHassan MirzaPas encore d'évaluation
- 9a. Statistical Quality ControlDocument21 pages9a. Statistical Quality ControlNikhil PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistic ProcessDocument39 pagesStatistic ProcessxredjokerxPas encore d'évaluation
- Manajemen Kualitas - Process ControlDocument4 pagesManajemen Kualitas - Process ControlAli PahlevyPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Quality Control: Simple Applications of Statistics in TQMDocument57 pagesStatistical Quality Control: Simple Applications of Statistics in TQMHarpreet Singh PanesarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 5 Variables Control ChartDocument48 pagesLec 5 Variables Control ChartAldwin Angelo Culing MontañezPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 SPCDocument53 pages4 SPCShubham AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- PPT3-Quality in ProductionDocument55 pagesPPT3-Quality in ProductionK3L PLN WKSKTPas encore d'évaluation
- 6e ControlchartsforvariablesDocument39 pages6e ControlchartsforvariablesdeepikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocess Ontrol Tatistical: C C I P P S E EDocument71 pagesRocess Ontrol Tatistical: C C I P P S E EalwaleedrPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical QCDocument57 pagesStatistical QCJigar NagvadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Six Sigma BooK Part2Document83 pagesSix Sigma BooK Part2foofoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Satistical Quality ControlDocument21 pagesSatistical Quality Controladitya v s sPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Control Chart For VariablesDocument66 pagesChapter 3 Control Chart For VariablesRitam PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Iem PDFDocument11 pagesIem PDFNalabolu Eshwari EshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Quality Control PDFDocument82 pagesStatistical Quality Control PDFInshal KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Metrology Control ChartsDocument14 pagesMetrology Control ChartsRaghu KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Quality ControlDocument82 pagesStatistical Quality ControlShahmirBalochPas encore d'évaluation
- TQM Unit 3Document26 pagesTQM Unit 3Anurag KushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- SQC (Chapter 2)Document59 pagesSQC (Chapter 2)Yitages kefelewPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Notes On SQCDocument12 pagesFinal Notes On SQCShashank Srivastava100% (1)
- Statistical Quality ControlDocument6 pagesStatistical Quality ControlAtish JitekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3Document18 pagesUnit 3ankit03shukla15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Sub: STD: Roll No: : Chandni K Jadav ARA 14Document15 pagesName: Sub: STD: Roll No: : Chandni K Jadav ARA 14Nirav JadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Quality Control (SQC) FinalDocument47 pagesStatistical Quality Control (SQC) FinalSagar DhagePas encore d'évaluation
- Process Capability and SPC : Operations ManagementDocument43 pagesProcess Capability and SPC : Operations ManagementRahul KhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Process Control: Using Control Charts To Monitor "Quality"Document26 pagesStatistical Process Control: Using Control Charts To Monitor "Quality"Ajay SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Control GuideDocument43 pagesQuality Control GuideBhanu Chander100% (1)
- 22 - Control ChartshghgyugyuDocument5 pages22 - Control ChartshghgyugyuBishnu Ram GhimirePas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Quality ControlDocument3 pagesStatistical Quality ControlHunson Abadeer100% (1)
- Topic 14Document21 pagesTopic 14lucasPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality ManagementDocument10 pagesQuality ManagementTifarie Luesas33% (3)
- Six Sigma Green Belt, Round 2: Making Your Next Project Better than the Last OneD'EverandSix Sigma Green Belt, Round 2: Making Your Next Project Better than the Last OnePas encore d'évaluation
- Economic Control of Quality of Manufactured ProductD'EverandEconomic Control of Quality of Manufactured ProductPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan BRM - Even Sem - Feb - May - 2020Document3 pagesLesson Plan BRM - Even Sem - Feb - May - 2020Manu Mallikarjun NelagaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Deepa AnwarDocument17 pagesDeepa AnwarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpPas encore d'évaluation
- Examples: Data Mining & Business IntelligenceDocument15 pagesExamples: Data Mining & Business IntelligenceAshish PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 41 3 Tests Two SamplesDocument22 pages41 3 Tests Two SamplesvignanarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Week1 Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesWeek1 Questions and AnswersThanh LePas encore d'évaluation
- Multivariate Statistical Analysis: Old SchoolDocument319 pagesMultivariate Statistical Analysis: Old SchoolVivek11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 ClassificationDocument87 pagesUnit 4 Classificationhetvi DharshandiaPas encore d'évaluation
- (Analysis of Variance) : AnovaDocument22 pages(Analysis of Variance) : AnovaJoanne Bernadette IcaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Accuracy Comparison Between GPS and DGPS A Field SDocument13 pagesAccuracy Comparison Between GPS and DGPS A Field SAshique AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Artikel TesisDocument9 pagesArtikel TesisUsman SpadPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4 - Hypothesis TestingDocument23 pagesLecture 4 - Hypothesis TestingAyodele OgundipePas encore d'évaluation
- Two-Sample Tests of Hypothesis: ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2008 Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument38 pagesTwo-Sample Tests of Hypothesis: ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2008 Mcgraw-Hill/Irwiniracahyaning tyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 013Document141 pagesChap 013theluckless77750% (2)
- Assignment Jawapan 1Document31 pagesAssignment Jawapan 1drbobhcPas encore d'évaluation
- MeanDocument3 pagesMeanBaby MacPas encore d'évaluation
- Eregress Predict - Predict After Eregress and XteregressDocument6 pagesEregress Predict - Predict After Eregress and XteregressBienvenu KakpoPas encore d'évaluation
- 137 Take Home FinalDocument10 pages137 Take Home FinalHasan ReichPas encore d'évaluation
- Kitten Length (CM) Weight (G) : SolutionDocument4 pagesKitten Length (CM) Weight (G) : SolutionCyndi CascaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Sesi 4 - Distribusi NormalDocument21 pagesSesi 4 - Distribusi NormalAstrid FebriyantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Studi Kasus Pengaruh-Motivasi-Kerja-Terhadap-Kinerja - 2 PDFDocument14 pagesStudi Kasus Pengaruh-Motivasi-Kerja-Terhadap-Kinerja - 2 PDFdianjabalPas encore d'évaluation
- EE2101 Unit5Document2 pagesEE2101 Unit5Sadyant HbpPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowchart On Statistical TechniqueDocument3 pagesFlowchart On Statistical TechniqueRoma MalasartePas encore d'évaluation
- ProbabilityDocument6 pagesProbabilityPreethi VictorPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 Lesson 4 Mean and Variance of The Sampling Distribution of Sample MeansDocument64 pagesModule 5 Lesson 4 Mean and Variance of The Sampling Distribution of Sample Meanssantiagorachel445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Inference SyllabusDocument1 pageStatistical Inference Syllabusognobogvoshno100% (1)
- MGT 2070 Assignment 2 - Solutions: T t-1 t-1 t-1Document5 pagesMGT 2070 Assignment 2 - Solutions: T t-1 t-1 t-1Nadya AzzuraPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 9Document81 pagesCH 9AbhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Tendency Module - 10Document64 pagesCentral Tendency Module - 10rueljp5thPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic Data Analysis: HeteroskedasticityDocument8 pagesEconomic Data Analysis: HeteroskedasticityhishamsaukPas encore d'évaluation