Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchi
Transféré par
inamaliitDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchi
Transféré par
inamaliitDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi (chronic obstructive bronchitis) causes increase mucus production and chronic
cough. The clinical manifestations of Chronic Bronchitis continue for at least 3 months of the year for 2 consecutive years. Chronic bronchitis is also known the blue bloater. It is characterized by the following:
y y y
An increase in the size and number of submucous glands in the large bronchi which causes increase mucus production An increased number of globlet cells, which also secrete mucus Impaired ciliary function, which reduces mucus clearance
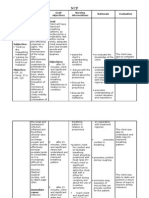
1 Ineffective Airway Clearance
COPD is an inflammatory response to the offending microorganism. The defense mechanisms of the lungs lose effectiveness and allow organisms to penetrate the sterile respiratory tract, as a result inflammation develops. The inflammation and increased secretions make it difficult to maintain a patent airway. Assessment S:O: The may patient manifest the ffg.:>with wheezes/crackle s upon auscultation on the BLF >with subcostal retraction >with nasal flaring >presence of non-productive cough >increase RR above normal range Nursing Planning Diagnosis Ineffectiv Short e airway term:After 4-5 clearance hours of related to nursing retained interventions and the patient will excessive demonstrate secretions effective and clearing of ineffective secretions.Lon coughing g term:After 2 days of nursing interventions, the patient will maintain effective airway clearance. Nursing InterExpected Rationale ventions Outcome >Establish rapport >To gain trust Short to the pt. and and active term:The SO>Assess the participation>T patient shall patient o know the have condition>Monito condition of the demonstrated r and record pt>To have a effective V/S>Position head baseline clearing of midline with data.>To gain or secretions.Lon flexion on maintain open g term:The appropriate for airway patient shall age/condition have >To decrease maintained pressure on the effective >Elevate HOB diaphragm and airway clearance. >Observe S/Sx of enhancing drainage infections >Auscultate breath sounds & assess air movt >To identify infectious process
>To ascertain >Instruct the patient to increase status & note progress fluid intake >To help to >Demonstrate effective coughing liquefy
and deepbreathing techniques. >Keep back dry
secretions. >To maximize effort
>To prevent >Turn the patient further q 2 hours complications >Demonstrate chest physiotherapy, such as bronchial tapping when in cough, proper postural drainage. >Administer bronchodilators if prescribed. >More aggressive measures to maintain airway patency. >To prevent possible aspirations >These techniques will prevent possible aspirations and prevent any untoward complications
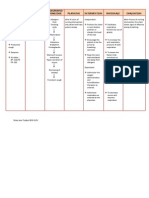
2 Ineffective Breathing Pattern
The presence of microorganisms in the lungs causes body to increase the secretory activity of goblet cells to get rid of the invading organism but the mechanism is not enough which allows the stasis of mucus secretion leading to ineffective breathing pattern. Nursing NursingInterExpected Planning Rationale Dx ventions Outcome S: Reports Ineffective Short >Establish rapport >To gain trust Short of breathing term:After to the pt. and and active term:The dyspneaO: pattern 4-5 hours of SO>Assess the participation>To patient shall The patient related to nursing patient know the have may retained interventions condition>Monitor condition of the improved manifest mucus the patient and record V/S pt>To have a breathing the secretions will improve especially baseline pattern.Long manifest breathing RR>Provide rest data.>To reduce term:The the ffg.:> pattern.Long periods fatigue and patient shall with term:After 2 obtain rest have Assessment
wheezes /crackles upon auscultation on BLF> increase RR above normal range >presence of productive cough >use of accessory muscle when breathing >presence of nasal flaring and retractions
days of nursing >Place pt in semiinterventions fowlers position the patient will >Increase fluid maintain a intake respiratory rate within >Keep patient normal back dry limits. >Change position every 2 hours >Perform CPT
maintained a respiratory >To have a maximum lung rate within normal expansion limits. >To liquefy secretions >To avoid stasis of secretions and avoid further complication
>To facilitate secretion movt >Place a pillow when the client is and drainage sleeping >To loosen >Instruct how to secretion splint the chest wall with a pillow >To provide for comfort during adequate lung expansion while coughing and elevation of head sleeping. over body as >To promote appropriate physiological >Maintain a patent ease of maximal airway, suctioning inspiration of secretions may be done as ordered >To remove secretions that obstructs the >Provide airway respiratory support. Oxygen >To aid in inhalation is relieving patient provided per from dyspnea doctors order >To promote >Administer prescribed cough deeper suppressants and respirations and analgesics and be cough cautious, however, because opioids
may depress respirations more than desired.
3 Impaired Gas Exchange
The disruption of the mechanical defenses of cough and ciliary motility leads to colonization of the lungs and subsequent infection leading to inflammation and accumulation of secretions. Inflamed and fluid-filled alveolar sacs cannot exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide effectively. Nursing Dx S:O: The Impaired patient may gas manifest the exchange ffg.:>Appearance related to of bluish altered extremities when oxygen in cough (cyanosis), lips>Lethargy Assessment >Restlessness >Hypercapnea >Hypoxemia >Abnormal rate, rhythm, depth of breathing >Diaphoresis NursingInterExpected Rationale ventions Outcome Short >Establish rapport >To gain trustand Short term:After to the pt. and active term:The 4-5 hours of SO>Assess the participation>To patient shall nursing patient know the condition have interventions condition>Monitor of the pt>To have improved the patient and record a baseline data. ventilation will improve V/S>Monitor level and ventilation of consciousness >Restlessness, adequate and or mental status oxygenation adequate of anxiety, oxygenation >Assist the client tissuesLong of into the Highterm:The confusion, tissuesLong Fowlers position somnolence are patient shall term:After 2 have common days of >Increase patients manifestation of minimized nursing or totally be fluid intake hypoxia and interventions free of hypoxemia. the patient >Encourage symptoms will of expectoration >The upright minimize or position allows full respiratory totally be lung excursion and distress. >Encourage free of frequent position enhances air symptoms of changes exchange respiratory distress. >Encourage >To help liquefy adequate rest & secretions limit activities to within client >To eliminate tolerance thick, tenacious, copious secretions which contribute >Promote for the impairment calm/restful Planning
environments >Administer supplemental oxygen judiciously as indicated
of gas exchange. >To promote drainage of secretions >Helps limit oxygen
>Administer meds as indicated such needs/consumption as bronchodilators >To correct/improve existing deficiencies >May correct or prevent worsening of hypoxia. >To treat the underlying condition
4 Sleep Pattern Disturbance
COPD patients need a comfortable position such as the High-Fowlers position during sleeping in order to promote lung expansion. Lying flat on bed promotes the occurrence of DOB and makes the patient uncomfortable due to the impaired alveolar ventilation which the body processes at night cant be controlled Nursing Dx S:O: The patient may Sleep manifest the pattern ffg.:>irritability>restlessn disturban ess ce related to difficulty >lethargy of breathing >changes in posture Assessment >difficulty of breathing which worsens at night NursingInterRationale ventions Short >Establish >To gain trust term:After rapport to the pt. and active 4-5 hours of and SO>Assess participation>T nursing the patient o know the intervention condition>Monit condition of the s the patient or and record pt>To have a will identify V/S>Monitor baseline individually level of data>Restlessne appropriate consciousness or ss, anxiety, intervention mental status s to promote confusion, sleep.Long >Promote somnolence are Planning Expected Outcome Short term:The patient shall have identified individually appropriate intervention s to promote sleepLong term:The patient shall
term:After 2 comfort days of measures such nursing as back rub and intervention change in s, the patient position as will be able necessary to report improvemen >Observe ts in provision of sleep/rest emotional pattern. support >Provide quiet environment. >Increase patients fluid intake >Encourage expectoration >Limit the fluid intake in evening if nocturia is a problem >Obtain feedback from SO regarding usual bedtime, rituals/routines
common manifestation of hypoxia and hypoxemia. >To provide non pharmagcologic management >Lack of knowledge and problems, relationships may create tension. Interfering with sleep routines based on adult schedules may not meet childs needs. >To promote an environment conducive to sleep. >To help liquefy secretions
have reported improvemen ts in pt.s sleep/rest
>To eliminate thick, tenacious, >Provide safety copious for patient sleep secretions which contribute for time safety the DOB >Recommend midmorning nap >To reduce if one required need for nighttime elimination >Administer pain medication >To determine as ordered. usual sleep
patterns & provide comparative baseline >To promote comfort/safety >Napping esp. in the afternoon can disrupt normal sleep pattern >To relieve discomfort and take maximum advantage of sedative effect
5 Risk for Spread of Infection
Once the bacteria, virus, or fungus enter the lungs, they usually settle in the air sacs of the lung where they rapidly grow in number. This area of the lung then becomes filled with fluid and pus as the body attempts to fight the infection. Disruption of the mechanical defenses of cough and ciliary motility leads to colonization of the lungs and subsequent infection Nursing NursingInterExpected Planning Rationale Dx ventions Outcome S:O: The patient Risk for Short >Establish rapport >To gain trust and Short may spread of term:After 4- to the pt. and active term:The manifest:>Body infection 5 hours of SO>Assess the participation>To shall have temperature above related to nursing patient know the condition identified normal stasis of interventions condition>Monitor of the pt>To have interventions range>dehydration secretions the patient & record a baseline data and to prevent and will identify V/S>Review fever may be and/or reduce >increase WBC decreased interventions importance of present because of the risk of ciliary to prevent breathing infection and/or infectionLong count action. and/or reduce exercises, dehydration>These term:The the risk of effective cough, activities promote patient shall >presence of infectionLong frequent position mobilization and have increase mucus term:After 2 changes, and expectoration of minimized or production days of adequate fluid secretions to totally be free nursing intake reduce the risk of from the risk interventions developing of infection. Assessment
the patient will have >Turn the patient minimize or q 2 hours totally be free from the risk >Encourage of infection. increase fluid intake >Stress the importance of handwashing to SOs >Teach the SOs how to care for and clean respiratory equipment
pulmonary infection. >To facilitate secretion movt and drainage >To liquefy secretions >Handwashing is the primary defense against the spread of infection >Water in respiratory equipment is a common source of bacterial growth
>Teach the SOs the manifestations >Early recognition of pulmonary infections (change of manifestations in color of sputum, can lead to a rapid fever, chills) , self- diagnosis. care and when to call the physician >To prevent risk of oral candidiasis. >Recommend rinsing mouth with >Given water prophylactically to reduce any possible >Administer antimicrobial such complications as cefuroxime as indicated. Other nursing diagnoses:
y y y y y
6 High risk for suffocation 7 High risk for aspiration 8 Anxiety RT acute breathing difficulties 9 Activity Intolerance RT inadequate oxygenation 10 Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than body requirements RT reduced appetite and dyspnea (for empysema)
Once the bacteria, virus, or fungus enter the lungs, they usually settle in the air sacs of the lung where they rapidly grow in number. This area of the lung then becomes filled with fluid and pus as the body attempts to fight the infection. Disruption of the mechanical defenses of cough and ciliary motility leads to colonization of the lungs and subsequent infection
Filed in: Nursing Care Plans Tags: impaired gas exchange, ineffective airway clearance, ineffective breathing pattern, respiratory system, risk for infection diagnostic tests done for ineffective airway clearance, labs ordered for pt with copd, ineffective airway clearance mechanical vent copd ncp, teaching plan for cough, ncp sample of wound debridement, impaired gas exchange related to copd, nursing care plan for ineffective airway clearance related to accumulation of mucus secretions Related Posts :
7 Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plans 6 More Bronchopneumonia Nursing Care Plans
Legionnaire's Disease Nursing Management
Pneumothorax/Hemothorax Nursing Care Plan: In...
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Concept Map - Abby !Document2 pagesConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Rapid Review Hematology PDFDocument155 pagesRapid Review Hematology PDFBaguma Michael100% (3)
- Copd NCPDocument16 pagesCopd NCPSuperMaye100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Case Study - EmphysemaDocument6 pagesCase Study - Emphysemamackie_041992Pas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeBenedicto RosalPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesRenal Failure Nursing Care Planemman_abz33% (3)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Insurance BookDocument3 pagesHealth Insurance BookHarish SiharePas encore d'évaluation
- Automobile Air Conditioning SystemDocument8 pagesAutomobile Air Conditioning SystemAyyan Gaonkhadkar100% (1)
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP BaiaeDocument7 pagesNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 NCP's FinalDocument9 pages4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHanya Bint PotawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP CopdDocument4 pagesNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- NCP PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP Pneumoniakaiserdominick100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document1 pageChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeNader AbdurasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 page(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goals Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goals Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationIngrid Nicolas100% (1)
- Pneumonia Case StudyDocument5 pagesPneumonia Case StudycrisolandPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma Nanda DiagnosesDocument4 pagesAsthma Nanda DiagnosesZinya RobinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma NCPDocument3 pagesAsthma NCPjaijai magbanuaPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTHMADocument9 pagesASTHMAmildred alidonPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Tissue PerfusionLisa Tandog100% (1)
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study and NCP!Document8 pagesDrug Study and NCP!Abegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and OxygenationDocument2 pagesNursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and Oxygenationlodeth100% (2)
- NCP Copd FinalDocument3 pagesNCP Copd FinalGiselle EstoquiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesNursing Care PlanZhel Geron MercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxDocument8 pagesCase Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxJansen Arquilita RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Far Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageFar Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationSarah CarreteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study COPDDocument16 pagesCase Study COPDRegine Cimafranca Macalaguing100% (5)
- NCP AidsDocument16 pagesNCP AidstferdianingsihPas encore d'évaluation
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP CopdDocument2 pagesNCP CopdJane Umali TulabotPas encore d'évaluation
- Bronchitis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchitis PathophysiologyFerry Reyes0% (1)
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizellePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP TBDocument7 pagesNCP TBLorraine CilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationAziil LiizaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP NminDocument5 pagesNCP NminkrizziajPas encore d'évaluation
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPPrincess Camille ArceoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Baby DDocument3 pagesNCP Baby DYna LafuentePas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPRyan Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceEsel Mae DinamlingPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearancejancel_bollaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananPas encore d'évaluation
- Zook Rupture Disc URADocument2 pagesZook Rupture Disc URAmd_taheriPas encore d'évaluation
- Scala: Service InstructionsDocument16 pagesScala: Service Instructionsmario_turbinadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gardobond 24d Imu Sds Ver1Document6 pagesGardobond 24d Imu Sds Ver1stuart3962Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1101259L 580.752830 Pressure Washer ManualDocument64 pages1101259L 580.752830 Pressure Washer Manualgork1roguesPas encore d'évaluation
- J Jacadv 2022 100034Document14 pagesJ Jacadv 2022 100034Rui FontePas encore d'évaluation
- Convecc Ao Forc Ada Externa: Vicente Luiz ScalonDocument18 pagesConvecc Ao Forc Ada Externa: Vicente Luiz ScalonMaria VitóriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fulltext PDFDocument55 pagesFulltext PDFManikandan VpPas encore d'évaluation
- ND 0108 SpongeDiver SymiDocument2 pagesND 0108 SpongeDiver SymiPoki MokiPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam G-9 CookeryDocument5 pagesExam G-9 Cookeryaileenarcabal01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bycatch Reduction Devices - PresentationDocument92 pagesBycatch Reduction Devices - PresentationSujit Shandilya0% (1)
- Numerical Modelling of Brine Dispersion in Shallow Coastal WatersDocument13 pagesNumerical Modelling of Brine Dispersion in Shallow Coastal WatersIAEME PublicationPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 - Flexible Operation of Thermal Power Plants - OEM Perspective and Experiences PDFDocument22 pages06 - Flexible Operation of Thermal Power Plants - OEM Perspective and Experiences PDFRavishankarPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.4324 9781315717289 PreviewpdfDocument179 pages10.4324 9781315717289 PreviewpdfMahdi GargouriPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Natural Sore Throat RemediesDocument5 pages5 Natural Sore Throat Remedieslisa smithis100% (1)
- L-2 Single and Composite Heat TransferDocument44 pagesL-2 Single and Composite Heat Transfer271758 ktr.chem.18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Multicultural Aspects of Communication Disorders - CH 12Document21 pagesMulticultural Aspects of Communication Disorders - CH 12Maitry PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Diana ACCOMPLISHMENTDocument8 pagesDiana ACCOMPLISHMENTMarycon MaapoyPas encore d'évaluation
- AT-502 - AT-504 - OM-0-Introduction-1 - 10-12-2019Document6 pagesAT-502 - AT-504 - OM-0-Introduction-1 - 10-12-2019Vinicius RodriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental Health Activity ProposalDocument2 pagesMental Health Activity ProposalJustin Tagumasi Agustin100% (1)
- Juri Ferrer - Ws - WeatherDocument4 pagesJuri Ferrer - Ws - WeathersJIqsPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 4 Centrifugal CompressorDocument11 pagesExp 4 Centrifugal CompressorFaris HamirPas encore d'évaluation
- English 10-1 Personal Response EssayDocument2 pagesEnglish 10-1 Personal Response Essayapi-467840192Pas encore d'évaluation
- Composition Solidus Temperature Liquidus Temperature: (WT% Si) (°C) (°C)Document7 pagesComposition Solidus Temperature Liquidus Temperature: (WT% Si) (°C) (°C)Muhammad Ibkar YusranPas encore d'évaluation
- LaserDocument12 pagesLasercabe79Pas encore d'évaluation
- JSA - Bolt TensioningDocument5 pagesJSA - Bolt TensioningRaju KhalifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocabulary June v22Document2 pagesVocabulary June v22Wiston TonwisPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Design II: Prof. K.Gopinath & Prof. M.M.MayuramDocument4 pagesMachine Design II: Prof. K.Gopinath & Prof. M.M.Mayurampredrag10Pas encore d'évaluation