Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
OOS调差
Transféré par
Smartishag BediakoDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
OOS调差
Transféré par
Smartishag BediakoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Page: SOP#: Eff.
Date: Supersedes:
1/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
/
Author
Date
Dept. Head Approval
Date
QA
Approved by QA
Date
Distribution:
QA, QC OOTOOS Analytical results obtained could be atypical (out of trend, OOT) or out-of-specification (OOS). These aberrant results require verification and, if verified, investigation into their root cause. This procedure provides detailed instructions for consistent and thorough evaluation and investigation of such analytical results. OOS OOT This procedure covers handling of data, investigation and documentation of final results. QC laboratory has responsibility for the evaluation of all investigations of laboratory data associated with potential OOS or OOT results. This procedure applies to all testing against approved specification. It applies, but not limited to, analytical and physical testing of the following materials: Incoming raw materials Intermediates, In-process samples and final products Stability samples Process and cleaning validation samples This procedure does not apply to: OOS/OOT Potential OOS/OOT results obtained during process development (includes stress or accelerated study), where some results are expected to fall outside of established limits. Method validation and verification Method transfer
PURPOSE:
SCOPE:
SCOPE: (Cont.)
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
2/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
Analyst qualification / Equipment qualification/calibration
REFERENCE AND ATTACHMENT:
SOP/ SOP/TITLE 1-3002 Deviation Investigation
// FORMS/ATTACHMENTS/TITLE 1 Attachment 1: Laboratory Investigation Flow Chart 2 Attachment 2: Aid to Analyst/Supervisor Review in Initial Laboratory Investigation F-03-001 Laboratory Investigation Report --Initial Investigation by QC Laboratory F-03-002 Laboratory Investigation Report --Further Investigation by QC Laboratory F-03-003 Laboratory Investigation Report Distribution Log F-03-004 KLE Known Laboratory Error Log F-03-005 OOS Laboratory OOS Log
N/A Any laboratory test result (including individual data point when replicate are determined) that fails a stated specification limit, either descriptive or numerical limit. An unusual, atypical or unexpected test result within specification limit, which, on inspection and in consideration of previous testing results, may not be reasonably expected to occur. OOT OOS Note: Analytical results arising from description mentioned above are also known as aberrant results until these results are investigated and classified as either OOT or OOS.
DEFINITIONS:
OOS Out-ofSpecification Result (OOS) OOT Out of Trend (OOT)
:
DEFINITIONS: (Cont.)
Established Specification
A value or range of values that define the acceptance criteria for a given test, material or product.
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
3/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
Assignable Cause Sample Original Sample Preparation
A detailed and scientifically sound explanation of laboratory error or other cause that lead to occurrence of aberrant result. A representative quantity of material taken from a defined bulk (by a known method), clearly identified and logged into laboratory for analysis. Aliquot of sample prepared according to test method for analysis, which includes dilution and any solution prepared from the ORIGINAL sample.
Original Result Test value obtained on analysis of original sample preparation according to specified test method. Invalid Result Result found to be incorrect following a documented investigation based on sound scientific evidence, which indicates that the result produced under incorrect condition or from an improper sample. Examples of data considered invalid are: Incorrect start and stop integration locations Failure to properly follow instructions as required in test methodology Error in preparation HPLC Instrument malfunction, e.g. HPLC auto sampler miss-injection Sample deterioration is suspected due to long queue time before testing is completed. Sample exceeds storage time as per methodology (Includes sample solution preparation as well as bulk raw material sample) / Incorrect storage of sample/standard
:
DEFINITIONS: (Cont.)
Invalid Result
/ Note: When data/results are invalidated due to a factor that affects a number of analytical results tested at the same time using the same method, all data that are affected by that factor must be invalidated. Invalid data/results should be crossed out.
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
4/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
Investigation
A systematic documented process by which the potential causes for error are identified and the appropriated follow-up work that may be undertaken (e.g. scientifically sound and justifiable experiments, gathering of evidence from other sources) to enable the identification of assignable or most probable cause of error. Any scientifically sound and justifiable experiments undertaken, as part of an investigation, must be described in an approved protocol. An error occurring in the testing process, caused by an analyst, a piece of equipment, the test materials, etc. that can be proven through investigation, that enables the invalidation of the result to be declared. Examples of Known Laboratory Error includes: Calculation error Measurement error (weights, volumes, etc.) Use of incorrect, expired, or otherwise defective standards Manipulation error (pipetting, transferring, etc.) Failure to follow test method as written Use of non-validated or inadequately validated method Use of unapproved method or modified method
KLE Known Laboratory Error (KLE)
:
DEFINITIONS: (Cont.)
Additional replicate analysis performed using an aliquot or additional portion of material from the original analytical sample.
Retest
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
5/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
Note: Retest may not always be possible, e.g. testing a sample from a dynamic process (in-process testing of a reaction mixture), where testing is destructive of the material tested, or where testing is compromised by previously opened container e.g. determination of moisture of a hygroscopic material. QA A further sample taken from the same batch or lot of material from which the original sample was taken. Note that resample is not taken from the same sample originally submitted to the laboratory. Resample should be taken in compliance with a clearly defined sampling procedure or an approved investigation protocol, to provide a new sample for analysis. Resample is only allowed when original analytical sample used for testing is shown, by investigation, to be: --- Not representative of the batch or lot --- Or because it has been used up --- Or compromised in some manner Note: A retained sample is not considered a resample. There must always be a documented rationale, QA approved, for resample. Control Sample A sample of material that has been previously characterized and tested and results obtained been found to be consistent with similar historical results for that material. Any product that has previously been well characterized may also be used; typically, a stability sample with a prior historical trend is a good source of control samples. Process Error OOS/OOT An error occurred in or related to the manufacturing process, where root cause is known or determined or attributed to the process, which may result in OOS / OOT results.
Resample
:
DEFINITIONS: (Cont.)
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
6/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
Re-dilution
Repeating any dilution or treatment of original sample and its accompanying standard solution for repeating the analysis or test measurement to confirm result obtained. This is used to identify a possible sample preparation problem and is not considered a retest. A re-aliquot is justified when an intermediate step in the sample preparation is suspect (e.g. dilution, digestion, pipetting etc.). Note: Re-dilution is dependant upon suitable solution/sample stability from the time of preparation and its storage.
/ Re-injection / Re-read
OOS/OOT / Re-examination of the same aliquot or dilution that produced OOS / OOT result in order to confirm the actual result obtained. Note: As above, this may not be possible where the prepared aliquot or dilution is known to be unstable after a given time period.
Valid Result
A result from testing carried out under approved, scientifically suitable conditions, whether within specification or outside, and there is no sound scientific grounds for invalidating this result.
ACTION
PROCEDURE:
RESPONSIBILIT Y
1. Analyst 1.1
INITIAL INVESTIGATION BY QC LABORATORY
Immediately notify Supervisor when an aberrant result is obtained Note that notification should be done after calculations have been checked.
RESPONSIBILIT Y
ACTION
QC
1.2
QC QC
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
7/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
Analyst & QC Supervisor
When the reason for aberrant result is easily and completely explained, e.g. calculation, clerical, or transcription error, and the Supervisor is satisfied that the reason is valid and no further practical work needs to be carried out, then the analyst should enter the reason for the error and the correct value(s) in the notebook. Supervisor countersigns these entries. 1.3 QC LIR When calculation of result is found to be accurate, a formal investigation is required and this initial investigation should be recorded in the Laboratory Investigation Report (LIR) Form - Initial Investigation by QC Supervisor. QC LIR LIR First, analyst should obtain the next sequential LIR Number from the Logbook and obtain an authorized copy of the LIR Initial Investigation Form from QC Supervisor or designee. 1.4.1 The initial Laboratory Investigation involves investigating, within the laboratory, for known errors during testing of the sample. This Initial Laboratory Investigation should be completed within one work-day when aberrant result is reported. LIR 2005 LIR 2005-001 Assign unique LIR Number using numeric full year designation followed by a sequential number corresponding to the occurrence in that year. For example, the first occurrence of 2005 would be assigned an LIR Number of 2005-001.
QC QC Supervisor
Analyst
1.4
1.4.2 1.4.3
QC Analyst & QC Supervisor
1.5
QC LIR Working together with Supervisor, analyst should perform a preliminary assessment of the data and result(s) obtained (including a visual check on pipettes, flasks used, weights, numbers calculations, equipment used, etc.) to establish whether there is any identifiable laboratory or clerical error (Known Laboratory Error, KLE). Analyst and Supervisor should complete the LIR Initial Investigation Form as they undertake this phase of the investigation.
RESPONSIBILIT Y
ACTION
QC Analyst & QC Supervisor
a QC 2 / Notes: Analyst and Supervisor shall use checklist given in Attachment 2 (Aid to Analyst / Supervisor Review in Initial Laboratory Investigation) as an aid to undertake this initial investigation.
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
8/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
b HPLC/GC 1.2 When investigating an aberrant result involving a HPLC/GC auto sampler and it is clearly obvious that there is a stable system and that one injection of replicate injection is clearly miss-inject, it is permissible, in this case, to re-inject the original solution to confirm results. However, this re-injection needs to be clearly documented and signed by the Supervisor as in 1.2 above. 2. Analyst & Supervisor 2.1
REVIEW OF INITIAL INVESTIGATION
If the conclusion of the Initial Investigation is that the aberrant results was due to laboratory error, then: 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 2.1.4 2.1.5 2.1.6 No further investigation needs to be performed The original results are invalided The analysis must be repeated either by re-dilution or in its entirety according to assigned cause. LIR / Complete the Initial Investigation Review section of the LIR Initial Investigation Form, sign and date. New results should be reported. Record laboratory error in the KLE logbook
2.2
LIR / The LIR Initial Investigation Form should be filed with each Data Recording Sheet/laboratory notebook, or stability file covering the product analysis in question. KLE QA Notify QA at the end of the Initial Laboratory Investigation if no KLE could be found, and the result considered valid.
Analyst & Supervisor
RESPONSIBILIT Y
2.3
ACTION
QA
2.4
Note:
a KLE QC QAQA In the case of new incoming raw material analysis, at the end of the Initial Laboratory Investigation and if analytical result is confirmed as not being due to a KLE, QC should notify QA. QA should then Reject the batch of raw material, notify Purchasing and arrange for material to be returned to the supplier.
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
9/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
bQA SOP 1-3002 In the case of retested raw material that have been stored at site, QA may decide to undertake further investigation. In such case, SOP 1-3002 should be followed. 3. QA 3.1
CROSS FUNCTIONAL MEETING
QC QA Upon receiving the notification from QC, QA should notify the relevant Production, Engineering and Material to alert people to possibility of a product quality problem. QA QA 3 Note: QA may decide to call a cross functional meeting to discuss the aberrant result and require Production, Engineering or Material Management to undertake investigations in their respective areas to identify potential causes of aberrant result. This meeting to initiate further investigation must be undertaken within 3 work days from the date event reported to QA.
QC QA
3.2
QC If aberrant result is due to a potential processing error and this is confirmed by Production, then no further investigation needs to be carried out by the laboratory. Then QC reports the results. The batch shall be rejected. LIR / The LIR Initial Investigation Form should be filed with each Data Recording Sheet/laboratory notebook, or stability file covering the product analysis in question.
RESPONSIBILIT Y
ACTION
QC
3.3
LIR If it is decided that further QC work is required, this must be documented in a LIR --- Further Investigation. QC If it is decided that no further QC work is required, then QC reports the results, and Deviation Investigation procedure shall be initiated. QA
QC QA
3.4
QA
3.5
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
10/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
QA should write meeting minutes or memo, the investigation report of relevant department shall be attached to the minutes or memo. 3.6 LIR The minutes or memo should be attached to the LIR Investigation Protocol or Deviation Investigation Report (if applicable).
FURTHER QC INVESTIGATION
4. QC 4.1
QC LIR If further work is required, analyst should obtain an authorized copy of the LIR Further Investigation by QC Laboratory from QC Supervisor or designee. These documents are to be regards as the minimal level of documentation required for Further Investigation. / A more comprehensive protocol / report may need to be developed on additional pages to these Forms as required. QC QA Note: QA must approve all protocols before QC carries out any additional work.
QC
4.2
QC Using the Further Investigation form, QC Supervisor and analyst must define possible causes for the problem and design an investigation protocol aimed at determining the assignable or most probable cause of the aberrant result via available data.
RESPONSIBILIT Y
ACTION
QC
4.3
Using the protocol, a pre-defined number of retests should be documented using scientifically sound judgment and rationale, and should be approved PRIOR to any testing activity. Note: Retesting may not be necessary if all of the results outside of the specification are expected (e.g. a stability interval result obtained after batch expiration or on accelerated stability).
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
11/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
QC Analyst & QC Supervisor
4.4
Each investigation needs to be evaluated on a case-by-case basis and documented in the protocol using scientifically sound justification. The applicability of a Second Analyst should be evaluated. A second analyst is not always required. A second analyst could however be an effective tool in finding an assignable cause and could improve the power of the retest data. The use of a control sample could assist in finding the likely root cause and when used, acceptance criteria for the control should be pre-defined. A control sample could be a stability sample or previously well-characterized material. QC The QC Supervisor should always ensure that any further analyses are undertaken in accordance with the defined and approved investigational protocol, and assess if results meet acceptance criteria of the protocol. If the results meet the acceptance criteria of the protocol, then a decision could be taken with respect to compliance to specification and the data reported. LIR If not, further investigational work may be carried out in accordance with additional approved protocols and these should be cross-referenced to the original LIR Number. The protocols must clearly state at what point testing will be stopped, and a decision reached on whether or not the material under test complies with specification.
4.5
QC QC Supervisor
4.6
4.7
RESPONSIBILIT Y
ACTION
5. QC QC Supervisor 5.1
EVALUATIONS AND REPORTING OF RESULTS
LIR Investigational reports must be generated using the issued LIR Further Investigation by QC Laboratory for each completed protocol, minimally describing: 5.1.1 5.1.2 Clear chronology of the investigation and determination of the assignable cause Corrective and preventative actions
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
12/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
5.1.3 5.1.4 5.1.5 5.1.6
The final result to be taken as the reported value The justification for invalidating any data and QC QA Appropriate approvals --- QC Supervisor, QA Manager - as necessary. 30 QA QA These reports must be completed within 30 calendar days from date aberrant result is found. If investigational work requires longer time, QA should be notified. If appropriate, QA could a grant extension to the investigation underway. a / When averaging results for reporting purpose, careful consideration should be given to this process. Any re-injection / re-reads of a preparation should be treated as sub sets of a preparation. Redilutions may also be treated as a sub set of a preparation. All Retests should be weighted the same as the original preparation. The documentation should clearly present the averaging process used in reporting results. b/ Use of averaging depends on sample / purpose. If the sample could be assumed to be homogenous and a number of discrete measurements are taken (e.g. in Specific Rotation tests), then the average of all valid data points could be reported as test result.
Note:
RESPONSIBILIT Y
ACTION
c SD RSD Unless the test method or Investigational Protocol specifies averaging, all individual test results should be reported; it may be appropriate to report an assessment of the variability of the data such as the Standard Deviation and Relative Standard Deviation. d To use averaged results for assay or related substances reporting, all individual test results must conform to specification. QC QA 5.2 QA
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
13/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
QC Supervisor QA
Ensure that the Investigation is complete and that all data has been documented in the Investigation Report in compliance with the procedure. If a Deviation is initially raised, QA may need to close the Report through the Site Deviations Procedure. QA Ensure clear conclusions are reached including the status and / or fate of the batch(es) in question (production batch testing only) and pass the Report to QA for final approval. QC QA LIR On periodic basis (but a least annually), QC Supervisor and the QA Manager should formally review all LIRs for trends with respect to analyst, product, method, and equipment. This review should be reported as part of the notification to Senior Management. OOS OOT SOP In the event that an aberrant result is confirmed as an OOS or OOT, the material must be rejected using the relevant SOPs. OOS OOS In the event that an aberrant result is confirmed as an OOS, it should assign the OOS Number and document in the logbook. 5.6.1 OOS OOS 2005 OOS OOS 200501 Assign unique OOS Numbers using the numeric full year designation followed by a sequential number corresponding to the occurrence in that year. For example, the first occurrence of 2005 would be assigned an OOS Number of 200501.
SUMMARY OF CHANGES
5.3 QC QA QC Supervisor QA 5.4 QC QA QC Supervisor QA Manager
QA
5.5
QC QA 5.6 QC Supervisor QA
CC No. Revision No. Effective Date Summary
N/A 2006-0034 .00 .01
2005.12.1 2006.7.20
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
14/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
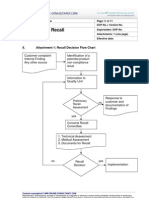
Aberrant Result
Easily and completely explained?
Y
Record in Data Recording Sheet/Notebook
N
Initial Investigation
Review of Initial Investigation
KLE
No KLE can be confirmed or No assignable cause is found
KLE
Invalidate Original Result
QA
Notify QA
Repeat Test
Cross Functional Meeting
1 Attachment 1: Laboratory Investigation Flow Chart Complete Initial Investigation Review
Production
Engineering
QC
Material
Other relevant Department
Confirmed process error
Further QC investigation required?
Report Original results
Complete Initial Investigation Review
Y LIR
LIR Investigation Protocol
Close the Report through Deviation procedure
LIR
LIR result of Investigation Protocol
Evaluations and reporting of results
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
15/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
21 Attachment 2: Aid to Analyst/Supervisor Review in Initial Laboratory Investigation (1) This guide is provided to aid analyst and supervisor in investigating the validity of analytical test results. This list is NOT all-inclusive; other parameters should be evaluated as needed. General Items Analyst training Testing procedure Calculations Reagents Standards Environment Lab equipment Instrument performance Filters Volumetric flasks Shakers Instrument calibration HPLC HPLC Items System suitability Peak shape Tailing Shoulders Baseline trend Peak integration Retention times Mobile phase Lamp energy Wavelength Column ID Column pressure / UV/VIS Items Raw data information Spectra ID Baseline correction Blank reading Cell quality Wavelength Lamp energy Bubble Performance record
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
16/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
Balance used Pipettes
Seal leak Bubble Injection time
22 Attachment 2: Aid to Analyst/Supervisor Review in Initial Laboratory Investigation (2) The following (which are not exclusive) are example of questions that should be considered during deviation investigation of the QC Microbiological Laboratory following a deviation: 1 Date unacceptably high microbiological results were recorded? 2 Sample reference and Date sample taken? 3 Batch numbers / material impacted by or in production at time of high results being recorded. 4 Did sampler observe anything different when taking the sample for analysis? 5 SOP Reference of SOP(s) used by sampler. 6 SOP SOP in date and current? 7 SOP Sampler trained in the sampling technique / SOP requirements? 8 Microbiological Laboratory Aspects: 1 Expiry date of media used? 2
Page: SOP#: Eff. Date: Supersedes:
17/17 3-0002.01 2006.7.20 2005.12.1
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Title
OOS
INVESTIGATION OF OUT-OF-SPECIFICATION RESULTS
Correctly stored? 3 Media receipt and media preparation logs satisfactory? 4 Are media preparation records satisfactory? 5 Growth promotion on batch of media used satisfactory? 6 Are incubators used operating correctly? 7 Are incubators within calibration date? 8 Have temperature monitoring charts been checked. 9 Any additional information relevant to the investigation.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Nursing Practice Skills: Adult Intensive Care Unit PatientsDocument10 pagesNursing Practice Skills: Adult Intensive Care Unit PatientsMona Doria67% (3)
- Sterile Drug Insp CPGM 7356-002a - Ora - Lao-Nm 9-10-15 - Emc Lao FinalDocument54 pagesSterile Drug Insp CPGM 7356-002a - Ora - Lao-Nm 9-10-15 - Emc Lao Finaltito1628100% (1)
- Avoiding Errors With The Batch Release ProcessDocument11 pagesAvoiding Errors With The Batch Release ProcessAnthony CollierPas encore d'évaluation
- Why The Swab Matters in Cleaning ValidationDocument3 pagesWhy The Swab Matters in Cleaning ValidationYehuda Rahmanu PuteraPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationD'EverandPractical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Resistance Training GP5Document20 pagesBasic Resistance Training GP5matt.tubieron23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Metrics Poster PDA March 2016Document1 pageQuality Metrics Poster PDA March 2016Anthony CollierPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Reddy's Laboratories LTD CTO India 01-20 Through 28-2020 - 483 PDFDocument8 pagesDr. Reddy's Laboratories LTD CTO India 01-20 Through 28-2020 - 483 PDFBrian WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Conducting Audits Gap Assessments Volume IIDocument139 pagesConducting Audits Gap Assessments Volume IIDoan Chi ThienPas encore d'évaluation
- First Periodical Exam Math 8Document2 pagesFirst Periodical Exam Math 8Joanne88% (8)
- Wire Rope Forensics Letter PDFDocument50 pagesWire Rope Forensics Letter PDFAshley DeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic or Skip Testing in Pharmaceutical Industry Us and Europe Perspective 2153 2435.1000283 PDFDocument5 pagesPeriodic or Skip Testing in Pharmaceutical Industry Us and Europe Perspective 2153 2435.1000283 PDFnsk79in@gmail.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Oos SopDocument10 pagesOos SopSolomonPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP-000038295 Laboratory InvestigationsDocument16 pagesSOP-000038295 Laboratory InvestigationsSebastian LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 LC Vibratory Sifter 01Document2 pages01 LC Vibratory Sifter 01Ravi YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- IVT Network - The FDA CGMP Inspection Is Coming - Make The Best of It - 2016-02-05Document18 pagesIVT Network - The FDA CGMP Inspection Is Coming - Make The Best of It - 2016-02-05marwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Recall FlowchartDocument1 pageProduct Recall FlowchartSmartishag Bediako100% (3)
- Risk Based Environmental Monitoring (Em) and em Data Management and TrendingDocument65 pagesRisk Based Environmental Monitoring (Em) and em Data Management and TrendingIsabelle PlourdePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Aspects of Process Validation of Solid Oral Dosage FormsDocument15 pagesBasic Aspects of Process Validation of Solid Oral Dosage FormsAbeer TamimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Handling of Out of Specification Results: International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance April 2015Document8 pagesHandling of Out of Specification Results: International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance April 2015Pavana KharwalPas encore d'évaluation
- American National Standard Safety Signs: ANSI Z535.1-2016Document42 pagesAmerican National Standard Safety Signs: ANSI Z535.1-2016Luis Enrique GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hold Time Stability Studies in Pharmaceutical Industry Review 2167 7689.1000104Document8 pagesHold Time Stability Studies in Pharmaceutical Industry Review 2167 7689.1000104iloveit52252Pas encore d'évaluation
- FDA Sterile Product Manufacturing GuidelinesDocument63 pagesFDA Sterile Product Manufacturing GuidelinesSmartishag Bediako100% (2)
- SOP-000182638 Phase 1b Investigation ChecklistDocument3 pagesSOP-000182638 Phase 1b Investigation ChecklistSebastian LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP-BDTO-QA021-10-Guideline For Personnel Training & Maintenance of Training Records - UnlockedDocument26 pagesSOP-BDTO-QA021-10-Guideline For Personnel Training & Maintenance of Training Records - UnlockedRasel Uddin ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- QCD-036-01 Good Chromatography PracticesDocument12 pagesQCD-036-01 Good Chromatography Practicesarnab rayPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP For Reduce Testing For Raw MaterialDocument3 pagesSOP For Reduce Testing For Raw MaterialMubarak Patel100% (1)
- SOP-000182637 Phase 1a Investigation ChecklistDocument2 pagesSOP-000182637 Phase 1a Investigation ChecklistSebastian LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP-000182636 Phase 1 InvestingationDocument3 pagesSOP-000182636 Phase 1 InvestingationSebastian LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Nomenclature and Sources of DrugsDocument36 pagesNomenclature and Sources of DrugsSmartishag Bediako100% (1)
- Oos Form Ud6Document10 pagesOos Form Ud6Mina Maher MikhailPas encore d'évaluation
- Commnets@39-02.SOP QC Investigation of (OOS)Document34 pagesCommnets@39-02.SOP QC Investigation of (OOS)systacare remediesPas encore d'évaluation
- Water System Validation ExampleDocument6 pagesWater System Validation ExampleBhuwan SPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling in Cleaning Validation in Pharmaceutical Industry - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDocument2 pagesSampling in Cleaning Validation in Pharmaceutical Industry - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesASHOK KUMAR LENKAPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP For Yield Range For TV Batches With CommentsDocument5 pagesSOP For Yield Range For TV Batches With CommentsPurushothaman SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Bulk Hold Time Study 1657011635Document6 pagesBulk Hold Time Study 1657011635Huỳnh Ngọc SángPas encore d'évaluation
- Temp Mapping Protocol For Reefer TrucksDocument15 pagesTemp Mapping Protocol For Reefer TrucksJewel HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 CGMP Meeting d1s2 Quality-Overview Iser v3Document57 pages1 CGMP Meeting d1s2 Quality-Overview Iser v3Roberto TorrezPas encore d'évaluation
- PE4 ExamDocument3 pagesPE4 ExamEugene ColotPas encore d'évaluation
- DIST-GAM-SOP-011-02 Cleaning Operation at DCDocument8 pagesDIST-GAM-SOP-011-02 Cleaning Operation at DCImran KarimPas encore d'évaluation
- Deviation Report Guidance in Pharma in Engineering DepartmentDocument24 pagesDeviation Report Guidance in Pharma in Engineering DepartmentShiva Sai BuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pe009 Pics Guide GMP Medicinal Products PDFDocument68 pagesPe009 Pics Guide GMP Medicinal Products PDFhuykhiemPas encore d'évaluation
- SMF LAW Online2017 enDocument31 pagesSMF LAW Online2017 enAnonymous cZ0Sn4hxF100% (1)
- Ceftrioxne Injection 250 DossiorDocument133 pagesCeftrioxne Injection 250 DossiorMohammed Zubair100% (1)
- Excipient Master File GuideDocument30 pagesExcipient Master File GuideVanna Alyssa YuPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigation of Out of Specification ResultsDocument75 pagesInvestigation of Out of Specification ResultsAmit MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Out of Specification: Mhra Medicine and Healthcare Products Regulatory AgencyDocument91 pagesOut of Specification: Mhra Medicine and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agencymunny000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Put Your Continued Process VerificationDocument9 pagesPut Your Continued Process VerificationMinh LePas encore d'évaluation
- Omgoing Stability Testing - Innovations - in - Pharmaceutical - TechnologyDocument3 pagesOmgoing Stability Testing - Innovations - in - Pharmaceutical - TechnologyJuan RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm E3219 20Document11 pagesAstm E3219 20ehsan050628100% (1)
- ПЕТ Центар- Производство и Контрола На Квалитет- Е. ЈанеевиќDocument30 pagesПЕТ Центар- Производство и Контрола На Квалитет- Е. ЈанеевиќEmilija Janevik100% (1)
- Forced DegradationDocument8 pagesForced DegradationBiyaya San PedroPas encore d'évaluation
- Canada Health Auth Draft Validation Guide GUI 0029 en For Comment 20 Nov 2018 1Document34 pagesCanada Health Auth Draft Validation Guide GUI 0029 en For Comment 20 Nov 2018 1atulbsPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Breakout D-Quality Risk Management-Key MessagesDocument26 pages06 Breakout D-Quality Risk Management-Key Messageshenrykayode4100% (1)
- USFDA A To Z DefinationDocument26 pagesUSFDA A To Z DefinationRishikesh ChakorPas encore d'évaluation
- VP-08-107 - Protocol For Hold Time of Softgel EquipmentsDocument7 pagesVP-08-107 - Protocol For Hold Time of Softgel EquipmentsprakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Arco Pharma Pvt. LTDDocument16 pagesArco Pharma Pvt. LTDnimeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Integrity Guidance For RussiaDocument37 pagesData Integrity Guidance For RussiaAmbadas RautPas encore d'évaluation
- CHECKLIST Q3-2 2013b PDFDocument13 pagesCHECKLIST Q3-2 2013b PDFJoe Luis Villa MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Materi Workshop CAPA BPOMDocument53 pagesMateri Workshop CAPA BPOMRidwan ArifandiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 6 Sampling WHO GuidelinesDocument22 pages2 6 Sampling WHO GuidelinesPepeArandaPas encore d'évaluation
- ASQ On DIDocument70 pagesASQ On DIRia DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- White Paper Tga Audit ReadinessDocument10 pagesWhite Paper Tga Audit ReadinessFaraz Haider100% (1)
- 2018年FDA 483表缺陷之六大系统分类Document183 pages2018年FDA 483表缺陷之六大系统分类van roadman100% (1)
- Dissolution Case StudiesDocument70 pagesDissolution Case Studieslhthang1990100% (1)
- Ensuring The Air Suplly Rate To A Cleanroom Complies With The Eu GGMP and Iso 14644-3 Recovery Rate RequirementsDocument3 pagesEnsuring The Air Suplly Rate To A Cleanroom Complies With The Eu GGMP and Iso 14644-3 Recovery Rate RequirementsluisPas encore d'évaluation
- F Deviation Investigation ReportDocument4 pagesF Deviation Investigation ReportBilal AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- In-Use Stability TestingDocument3 pagesIn-Use Stability TestingIsabelLópezPas encore d'évaluation
- Residual Solvents USP 467Document10 pagesResidual Solvents USP 467Shridhar AnishettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Deklarasi Helsinki PDFDocument5 pagesDeklarasi Helsinki PDFMazterMaztermaztermazter MaztermaztermazterYande100% (1)
- Drug Discovery and Development: - Ian Hughes, I.e.hughes@leeds - Ac.ukDocument31 pagesDrug Discovery and Development: - Ian Hughes, I.e.hughes@leeds - Ac.ukRakesh Kumar DixitPas encore d'évaluation
- Metronidazole AFTinfDocument8 pagesMetronidazole AFTinfSmartishag BediakoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ringer Lactate Infusion Product InsertDocument1 pageRinger Lactate Infusion Product InsertSmartishag BediakoPas encore d'évaluation
- C.E. 324 - Ethics - 1.0Document103 pagesC.E. 324 - Ethics - 1.0dela rosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Davao Region Slogan Reflective EssayDocument4 pagesDavao Region Slogan Reflective EssayDonna Elaine OrdoñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Dense Ball PackingDocument334 pagesDense Ball PackingLucas RibeiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Marcelo - GarciaDocument6 pagesMarcelo - GarciaNancy FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document3 pages1Pradeep PunterPas encore d'évaluation
- MS2040 Constitution Parts ListDocument6 pagesMS2040 Constitution Parts ListTemptationPas encore d'évaluation
- BTS "Whalien 52" Lyrics Romanization, English and Indonesian TranslationDocument11 pagesBTS "Whalien 52" Lyrics Romanization, English and Indonesian TranslationEmaFediFeniPas encore d'évaluation
- SUNANDA Hack Aid Plast SPL PDFDocument2 pagesSUNANDA Hack Aid Plast SPL PDFSheezan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- AngelDocument21 pagesAngelNoj ZachPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit II Construction PracticesDocument61 pagesUnit II Construction PracticesiploguPas encore d'évaluation
- Scan&SolveDocument24 pagesScan&SolveAtul ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Draf Model LC 2024 Non TransferableDocument3 pagesDraf Model LC 2024 Non TransferablepresidenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Carcass Strength Relationships Conveyor BeltsDocument9 pagesCarcass Strength Relationships Conveyor Beltseduardo_chaban100% (1)
- Crimin Q and A Set 1Document6 pagesCrimin Q and A Set 1Marc angelo RegnerPas encore d'évaluation
- DSE MC G11 G12 Equations Straight Lines 2023Document6 pagesDSE MC G11 G12 Equations Straight Lines 2023ernestchan501Pas encore d'évaluation
- Federal Bylaw 12 Air Pollution 2006 English Translation v2 OCRDocument63 pagesFederal Bylaw 12 Air Pollution 2006 English Translation v2 OCRIsmail SultanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quick Start Guide For The Remote Access Dial-In Multiport Ethernet ModemDocument16 pagesQuick Start Guide For The Remote Access Dial-In Multiport Ethernet ModemdilipPas encore d'évaluation
- Manuel Alava 01-12-10 PLDocument3 pagesManuel Alava 01-12-10 PLAshley RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexowell® Replacement-Belts enDocument3 pagesFlexowell® Replacement-Belts enrerererererererererePas encore d'évaluation
- Rediscovery' Revised - The Cooperation of Erich and Armin Von Tschermak-Seysenegg in The Context of The Rediscovery' of Mendel's Laws in 1899-1901Document7 pagesRediscovery' Revised - The Cooperation of Erich and Armin Von Tschermak-Seysenegg in The Context of The Rediscovery' of Mendel's Laws in 1899-1901lacisagPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspirating Smoke Detector: Technical DescriptionDocument115 pagesAspirating Smoke Detector: Technical DescriptionSecuriton ArgentinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual African Airstrip Adventures EnglDocument46 pagesManual African Airstrip Adventures EnglDele Jnr EriboPas encore d'évaluation
- Fact Sheeton Canola OilDocument15 pagesFact Sheeton Canola OilMonika ThadeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Term English Exam: Level TCST June 2021Document6 pagesSecond Term English Exam: Level TCST June 2021benfaresPas encore d'évaluation