Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Unidad 5 - Transmission Mechanisms - Word Problems
Transféré par
bemdasTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Unidad 5 - Transmission Mechanisms - Word Problems
Transféré par
bemdasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Colegio Ntra.
Seora del Prado (Ciudad Real)
3 ESO Tecnologa
UNIT 5
FRICTION WHEELS
TRANSMITTING ROTARY MOTION
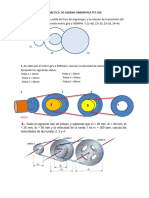
1. In the following picture you have friction wheel system. Wheel A is the driver one, while wheel B is the driven one. If the driver one rotates clock-wise, in which direction will wheel C rotate? Put the wheels in decreasing speed order.
2. We have a friction wheel system in which the 15 cm diameter driver wheel is rotating at 120 rpm and a driven one with 60 cm of diameter. a) Draw the system indicating which is the driver and the driven wheel. b) Calculate the transmission ratio and the speed ratio. c) Calculate the speed of the driven wheel. d) If the driven wheel rotates clockwise, how will the driver one will do? e) Is it an increasing speed mechanism or a decreasing speed mechanism? 3. In a friction wheel system the driver wheel has a diameter of 80 cm while the driven one has 20 cm. a) Draw the system indicating which is the driver and the driven wheel. b) Calculate the speed of the driven wheel if the driver one rotates at 100 rpm. c) If the driver wheel rotates anti-clockwise, how will the driven one will do? d) Calculate transmission and speed ratio. e) When the driven wheel rotates 20 turns, how many turns are given by the driver one? f) Is it an increasing speed mechanism or a decreasing speed mechanism? BELT DRIVES 1. In the belt drive system of the figure, what will the speed be in the driven pulley if the driver one is running at 250 rpm?
2. We have three pulleys with diameters 20, 40 and 60 mm. Use them to build a pulley train so the driven pulley speed is nine times the speed for the driver one. Draw the mechanism and explain the results using numbers.
1
Colegio Ntra. Seora del Prado (Ciudad Real)
3 ESO Tecnologa
3. In the belt drive system of the figure, please indicate the direction of the motions in the different pulleys when the driver (A) rotates clock-wise.
4. The engine of a washing machine is linked to 8 cm diameter pulley, while the container is linked to a 32 cm diameter pulley. If the highest speed for the engine is 1,500 rpm: a) Which is the highest speed for the container? b) If we change the engine pulley for another one which is twice the size, how will this affect to the container speed? 5. Indicate the direction of the motion for the following mechanisms.
6. Indicate the direction of the motion for the following mechanisms when the first pulley on the left rotates clockwise.
Colegio Ntra. Seora del Prado (Ciudad Real)
3 ESO Tecnologa
7. We have an engine rotating at 1,000 rpm which is linked to a 20 cm diameter pulley. This pulley is linked using a belt to another pulley with 60 cm of diameter. a) Draw the system indicating which is the driver and the driven pulley. b) Calculate the transmission ratio and the speed ratio. c) Calculate the speed of the driven pulley. d) Is it an increasing speed mechanism or a decreasing speed mechanism? 8. In the following mechanism, calculate the transmission ratio, the speed ratio and the numbers of turns in the driven pulley when the driver one is rotating at 100 rpm.
9. Calculate the speed of the pulley 6 when the diameter of the big pulleys is 30 cm and for the small ones is 5 cm. The speed for the pulley 1 is 150 rpm.
10. In a pulley train with diameters d1 = 10 mm, d2 = 30 mm, d3 = 20 mm and d4 = 50 mm, calculate the speed for the pulley 4 when pulley 1 is rotating at 20 rpm. Draw the mechanism and calculate the speed ratio for all the steps. 11. Calculate the final speed (pulley 6) of the mechanism in the figure when the driver pulley rotates at 50 rpm.
Colegio Ntra. Seora del Prado (Ciudad Real)
3 ESO Tecnologa
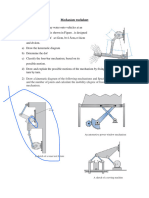
GEARS 1. Indicate the direction of the motion for the following gear mechanisms.
2. A gear train is formed by three gears linked. The first one has 90 teeth, the second one 274 and the third one 180. If the first one rotates at 400 rpm, which will the speed be for the third one? 3. We have an engine rotating at 3,000 rpm which is linked to a 20 teeth gear. This gear is linked to another gear with 60 teeth. a) Draw the system indicating which is the driver and the driven gear. b) Calculate the transmission ratio and the speed ratio. c) Calculate the speed of the driven gear. 4. You have a mechanism in which the driver gear has 14 teeth and rotates at 4,000 rpm, while the driven gear has 56 teeth. a) Is it an increasing speed mechanism or a decreasing speed mechanism? b) Calculate the speed for the driven gear. c) If the driven gear rotates clockwise, how will the driver one will do? d) Calculate the number of turns given by the driven wheel in half an hour. 5. In the following figure you can find the transmission system for a bicycle. When we pedal one turn, the pinion moves three turns.
a) Calculate the transmission ratio and the speed ratio. b) When we pedal at 50 rpm, calculate the speed of the wheel.
Colegio Ntra. Seora del Prado (Ciudad Real)
3 ESO Tecnologa
6. In the following system the driver gear is rotating at 40 rpm while the driven one is doing it at 120 rpm.
a) Indicate which is the driven and the driver gears. b) Is it an increasing speed mechanism or a decreasing speed mechanism? c) Calculate the speed ratio and the transmission ratio. d) Calculate the speed of the driven gear if the driver one is rotating at 100 rpm. 7. In the following system the speed is reduced in two steps. The two gears are exactly the same and the transmission ratio for the two of them is 1/3.
a) Calculate the speed ratio and the transmission ratio for the whole mechanism. b) If the driver gear (first one on the left) rotates at 45 rpm, calculate the speed for the driven one (last one on the right). 8. In the gear train of the figure:
a) Indicate the direction of the motion of the driven gear when the driver one rotates clockwise. b) What is the function of the idler gear? c) When the speed of the driver gear is 100 rpm, calculate the speed for both the idler gear and the driven one. d) Calculate speed ratio and transmission ratio for the steps and the total system. e) When the driven gear rotates at 60 rpm, calculate the speed for the idler gear and the driver one. f) Is it an increasing speed mechanism or a decreasing speed mechanism?
5
Colegio Ntra. Seora del Prado (Ciudad Real)
3 ESO Tecnologa
9. Answer the following questions about the mechanism of the figure: a) When gear A moves, how many gears will move too? b) Indicate the direction of motion for gear I. c) Indicate the direction of motion for gear K.
10. For the system in the figure, z1 = 40, z2 = 10, z3 = 20 and z4 = 40:
a) Calculate the final speed (gear 4) b) Indicate the direction of the motion for gears 2, 3 and 4. c) When the final speed is 60 rpm, calculate the speed for gear 1.
6
Colegio Ntra. Seora del Prado (Ciudad Real)
3 ESO Tecnologa
11. For the system in the figure, zA = 45, zB = zD = 15 and zC = 30:
a) Indicate the direction of the motion when gear A rotates clockwise. b) Calculate the speed for all the gears when gear A rotates at 40 rpm. c) Transmission ratio and speed ratio for all the steps and for the total system. d) Is it an increasing speed mechanism or a decreasing speed mechanism? 12. For the gear train in the figure:
a) Indicate the direction of the motion of all the gears when the driver one rotates anti-clockwise. b) Calculate the speed of all the gears. c) Calculate speed ratio and transmission ratio for the steps and the total system. d) When the driven gear rotates at 60 rpm, calculate the speed for all the gears. e) Is it an increasing speed mechanism or a decreasing speed mechanism? 13. In a gear system where the two gears have the same number of teeth, calculate: a) Transmission ratio and speed ratio. b) Speed for the driven gear when the driver one rotates at 200 rpm. c) When the driven gear rotates clockwise, how will the driver one do? 14. In the transmission system of the figure, calculate the speed for gear 5.
Colegio Ntra. Seora del Prado (Ciudad Real)
3 ESO Tecnologa
15. A simple gear is shown in the figure. Driver gear A has 20 teeth. When shaft A has rotated 10 times, shaft B rotates 5 times. a) How many teeth has gear B? b) What is the transmission ratio of the system? c) And the speed ratio? d) If shaft A rotates at 60 rpm, at what speed does shaft B rotate? e) If shaft A rotates anti-clockwise, in which direction does shaft B rotate?
MISCELLANEOUS 1. In the transmission system of the figure:
a) What is the name of the system formed by elements 1 and 2? b) What is the name of the system formed by elements 3 and 4? c) If 1 rotates clockwise, draw arrows to indicate the rotation of the rest of elements d) If 3 rotates at 90 rpm and its diameter is 10 cm, what is the speed of 4 if its diameter is 2 cm? e) Calculate the transmission ratio between 3 and 4. 2. Indicate the direction of the motion for the following mechanisms.
Colegio Ntra. Seora del Prado (Ciudad Real)
3 ESO Tecnologa
3. The following systems are a mix of belt drives and gears. a) Use arrows to indicate the direction of the motion for all the elements. b) Circle the right answer.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesD'EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023 Octubr Cadena CinematicaDocument6 pages2023 Octubr Cadena CinematicaANGELA ARACELY PAZ ARROYOPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Aptitude & Spatial Relations Practice QuestionsD'EverandMechanical Aptitude & Spatial Relations Practice QuestionsPas encore d'évaluation
- TEE Model Question Paper (For)Document2 pagesTEE Model Question Paper (For)yashvantPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationD'EverandDesign Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Classical and Modern Approaches in the Theory of MechanismsD'EverandClassical and Modern Approaches in the Theory of MechanismsPas encore d'évaluation
- Module3 TutorialDocument7 pagesModule3 TutorialAayush KPas encore d'évaluation
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 2 Questionss-1Document3 pagesPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 2 Questionss-1AlbertPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ Tom Chap. 2Document11 pagesMCQ Tom Chap. 2AdityaPas encore d'évaluation
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachD'EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 010 504 Kinematics of MachineryDocument4 pagesMe 010 504 Kinematics of MachinerysithananthansithuPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanism Final ProjectDocument14 pagesMechanism Final Projectsundari_murali100% (2)
- 2010 - May - June-06ME44Document2 pages2010 - May - June-06ME44nitte5768Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 3Document10 pagesSheet 3Mahmoud salahPas encore d'évaluation
- 615301Document4 pages615301rahulmnm007Pas encore d'évaluation
- EMG 2208 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment - MMU Sept 2012Document4 pagesEMG 2208 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment - MMU Sept 2012Charles OndiekiPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A14402 Theory of MachinesDocument8 pages9A14402 Theory of MachinessivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 503 DomDocument9 pagesME 503 Domsuneel kumar rathorePas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics of Machinery Question BankDocument5 pagesKinematics of Machinery Question BankSree MurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityKrinal AdakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 5 Spur GearDocument2 pagesSheet 5 Spur GearMustafa FayezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter One and Chapter 2 WorksheetDocument9 pagesChapter One and Chapter 2 WorksheetSena MekoninPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 1 5 A GearspulleydrivessprocketspracticeproblemsDocument4 pages1 1 5 A Gearspulleydrivessprocketspracticeproblemsapi-308395650100% (1)
- Theory of Machines and MechanismsDocument17 pagesTheory of Machines and MechanismsmagnifcoPas encore d'évaluation
- 06me44 Dec 13 VTUDocument2 pages06me44 Dec 13 VTUArun DixitPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Tech I SEM (Set-C) : End Term Examination January-2013 Time: 1:30 Hrs. Maximum Marks: 30Document3 pagesB. Tech I SEM (Set-C) : End Term Examination January-2013 Time: 1:30 Hrs. Maximum Marks: 30Sanjay GomastaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear - Problems 2 FogDocument2 pagesGear - Problems 2 FogLamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Circular Motion and Rotational DynamicsDocument2 pagesCircular Motion and Rotational DynamicsChasel Jane LaygoPas encore d'évaluation
- Module-5 Toothed GearingDocument4 pagesModule-5 Toothed Gearingonkarlamkane4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-1: Introduction: Question BankDocument12 pagesUnit-1: Introduction: Question BankAmit BharadwajPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Engineering & Built Environment Subject: Ege 3411 Laboratory Investigations 2 Experiment 1: Gear TrainDocument7 pagesFaculty of Engineering & Built Environment Subject: Ege 3411 Laboratory Investigations 2 Experiment 1: Gear TrainJameel MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 323 Lab 4 Mohammed Ahmed Tahhan 392027113Document10 pagesME 323 Lab 4 Mohammed Ahmed Tahhan 392027113engineer.mohammedtahhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Me6401 Kinematics of Machinery UNIT-I (Basics of Mechanism)Document8 pagesMe6401 Kinematics of Machinery UNIT-I (Basics of Mechanism)Ãraviñdhañ RändýPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Question Paper Kinematics of MachinesDocument3 pagesSample Question Paper Kinematics of MachinesAnonymous utfuIcnPas encore d'évaluation
- rr310304 Kinematics of MachineryDocument11 pagesrr310304 Kinematics of MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTAPas encore d'évaluation
- 10ME/AU44: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 pages10ME/AU44: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartsatheeshPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.kinematics of MachineryDocument14 pages2.kinematics of MachineryJegan ParamasivamPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision 4Document39 pagesRevision 4YUVARAJAN DPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice RotationDocument20 pagesMultiple Choice RotationJohnathan BrownPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A14402 Theory of MachinesDocument8 pages9A14402 Theory of MachinessivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- TOM Question BankDocument10 pagesTOM Question BankMadhan Kumar GovindarajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculate SpeedDocument4 pagesCalculate SpeedAbhishek NaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesPage 1 of 3Shyloo GsaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1424R05310304 Kinematics of MacDocument10 pages1424R05310304 Kinematics of Macأحمد جمالPas encore d'évaluation
- Additional ProblemsDocument10 pagesAdditional ProblemsManda Ramesh BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- MODEL EXAM QUESTION PAPER Kom Final PDFDocument2 pagesMODEL EXAM QUESTION PAPER Kom Final PDFCarlos ContrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Midsem Question Paper 2015Document1 pageMidsem Question Paper 2015shashankmay18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KomRajueswarPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Ratio and RPM CalculationsDocument7 pagesGear Ratio and RPM CalculationsRaul Real GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 323 Lab 4-Omar AlfahadDocument9 pagesME 323 Lab 4-Omar Alfahadengineer.mohammedtahhanPas encore d'évaluation
- MET301 Dec 2021Document3 pagesMET301 Dec 2021Sudeesh SudevanPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A03401 Kinematics of MachineryDocument8 pages9A03401 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument3 pagesKinematics of Machinessameer_m_daniPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Machines - Final Exams2015Document2 pagesTheory of Machines - Final Exams2015Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice RotationDocument21 pagesMultiple Choice RotationJanina OrmitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gearbox Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesGearbox Questions and Answersamdan srl100% (2)
- Gear Trains: 8.1. Angular Velocity RatioDocument16 pagesGear Trains: 8.1. Angular Velocity RatioaddisudagnePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7 - Theory and Word Problems (Metric and Imperial Systems)Document13 pagesUnit 7 - Theory and Word Problems (Metric and Imperial Systems)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 14 - Word Scramble (2D+3D Geometry)Document1 pageUnit 14 - Word Scramble (2D+3D Geometry)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 13 - Length and Area (Word Problems)Document11 pagesUnit 13 - Length and Area (Word Problems)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 14 - Volume (Word Problems) PDFDocument9 pagesUnit 14 - Volume (Word Problems) PDFbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7 - Word Scramble (Units of Measurement)Document1 pageUnit 7 - Word Scramble (Units of Measurement)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 14 - Volume (Theory)Document12 pagesUnit 14 - Volume (Theory)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 8 - Key Ideas (Proportionality)Document6 pagesUnit 8 - Key Ideas (Proportionality)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 10 - Key Ideas (Statistics + Probability)Document10 pagesUnit 10 - Key Ideas (Statistics + Probability)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Units 11+12 - Theory and Word Problems (Basic Geometry 2D)Document20 pagesUnits 11+12 - Theory and Word Problems (Basic Geometry 2D)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 8 - Word Scramble (Proportionality) PDFDocument1 pageUnit 8 - Word Scramble (Proportionality) PDFbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 8 - Increase Decrease PDFDocument2 pagesUnit 8 - Increase Decrease PDFbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 - Exercises and Problems (Integers)Document9 pagesUnit 2 - Exercises and Problems (Integers)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 10 - Mean ActivityDocument1 pageUnit 10 - Mean ActivitybemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 - Word Scramble (Algebra + Linear Equations)Document1 pageUnit 6 - Word Scramble (Algebra + Linear Equations)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 - Word Scramble (Integers)Document1 pageUnit 2 - Word Scramble (Integers)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 - Exercises and Problems (Fractions) - Inicial Con ErroresDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Exercises and Problems (Fractions) - Inicial Con ErroresbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 - Word Scramble (Decimals)Document1 pageUnit 5 - Word Scramble (Decimals)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 - Word Scramble (Powers)Document1 pageUnit 3 - Word Scramble (Powers)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 - Exercises and Problems (Fractions) - Inicial Con ErroresDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Exercises and Problems (Fractions) - Inicial Con ErroresbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 - Exercises and Word Problems (Decimals)Document6 pagesUnit 5 - Exercises and Word Problems (Decimals)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 - Exercises and Problems (Powers) - Inicial Con ErroresDocument8 pagesUnit 3 - Exercises and Problems (Powers) - Inicial Con ErroresbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocabulario Ingles Ud06Document2 pagesVocabulario Ingles Ud06Eva MPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 - Roman NumeralsDocument1 pageUnit 1 - Roman NumeralsbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 - Exercises and Problems (Powers) - Inicial Con ErroresDocument8 pagesUnit 3 - Exercises and Problems (Powers) - Inicial Con ErroresbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 - Key Ideas (Fractions)Document5 pagesUnit 4 - Key Ideas (Fractions)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 - Puzzle Factors and MultiplesDocument2 pagesUnit 1 - Puzzle Factors and MultiplesbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 - Number SequencesDocument1 pageUnit 1 - Number SequencesbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 - Exercises and Problems (Divisibility) PDFDocument6 pagesUnit 1 - Exercises and Problems (Divisibility) PDFbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 - Key Ideas (Divisibility)Document3 pagesUnit 1 - Key Ideas (Divisibility)bemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 - Exercises and Problems (Divisibility) PDFDocument6 pagesUnit 1 - Exercises and Problems (Divisibility) PDFbemdasPas encore d'évaluation
- DelphiDocument2 pagesDelphirahairiPas encore d'évaluation
- PB99127 2 Full Power Brake CatalogDocument20 pagesPB99127 2 Full Power Brake CatalogMAHMOUDPas encore d'évaluation
- AGC ManualDocument183 pagesAGC ManualmiansaruPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulsar 220 - FIDocument46 pagesPulsar 220 - FIsupercool_sidd86% (7)
- 94 Supra Wiring DiagramsDocument59 pages94 Supra Wiring DiagramsGaston MerinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Marketing Strategy of Rahimafrooz Bangladesh LimitedDocument28 pagesReport On Marketing Strategy of Rahimafrooz Bangladesh LimitedMuntasirPas encore d'évaluation
- HistoryDocument54 pagesHistoryDaniel Raj RichardPas encore d'évaluation
- Geely Case Study - Set 2Document13 pagesGeely Case Study - Set 2Qasim Ali100% (1)
- Scenario Study: Tyre IndustryDocument25 pagesScenario Study: Tyre IndustrySarath SPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving The Powertrain PuzzleDocument517 pagesSolving The Powertrain PuzzleIgor MândruPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Concepts and ClassificationsDocument19 pagesCost Concepts and ClassificationssarahbeePas encore d'évaluation
- Air Filter For TurbineDocument8 pagesAir Filter For TurbineAnonymous Q9i062VPas encore d'évaluation
- Swot Analysis of Indian Automobile Industry - RiteshDocument3 pagesSwot Analysis of Indian Automobile Industry - Riteshpunya.trivedi200360% (5)
- Power Gear Owners ManualDocument8 pagesPower Gear Owners ManualSonnyPas encore d'évaluation
- BMW Group Anteilslisten enDocument12 pagesBMW Group Anteilslisten enMara AlexandruPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study On Automotive Textile SupplyDocument19 pagesCase Study On Automotive Textile SupplyDipanjan RoychoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Effects of Partnership Between Manufacturers and Suppliers For New Product Development The Supplier's StandpointDocument17 pagesPerformance Effects of Partnership Between Manufacturers and Suppliers For New Product Development The Supplier's Standpointapi-3851548Pas encore d'évaluation
- Training Activity Matrix AutomotiveDocument3 pagesTraining Activity Matrix AutomotiveMarx Engel Monreal JuntadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sumit RanaDocument4 pagesSumit RanasumitranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Title of The Study: "A Study On Analysis of Financial Performance of Maruti Suzuki India LTD Using Ratio Analysis"Document3 pagesTitle of The Study: "A Study On Analysis of Financial Performance of Maruti Suzuki India LTD Using Ratio Analysis"Mohan RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiat Bravo 1.4 Tjet EngineDocument165 pagesFiat Bravo 1.4 Tjet EngineRajivChandran100% (4)
- Cat Motor USA WebDocument52 pagesCat Motor USA WebVamshi Kumar Reddy MPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Analysis of Ford and ToyotaDocument26 pagesComparative Analysis of Ford and ToyotaShadman Tauheed100% (3)
- Vibratory Bowl Feeder Selection CriteriaDocument4 pagesVibratory Bowl Feeder Selection CriteriaimrancenakkPas encore d'évaluation
- Job Shop LeanDocument29 pagesJob Shop LeanSyuhadah Khusaini100% (1)
- Indian Auto Industry . The Way: Presentation By-Sunil Kakkar General Manager (Supplychain) Maruti Suzuki India LTDDocument35 pagesIndian Auto Industry . The Way: Presentation By-Sunil Kakkar General Manager (Supplychain) Maruti Suzuki India LTDViral JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Labour LawDocument93 pagesLabour LawPrashant PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- 54 - Fuller FSO 6109A Transmission Service Manual PDFDocument134 pages54 - Fuller FSO 6109A Transmission Service Manual PDFJulio OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jebel Ali Free Zone Data File .Document714 pagesJebel Ali Free Zone Data File .umairbaber8778% (9)
- Justin Otten Architect CVDocument6 pagesJustin Otten Architect CVapi-264021545Pas encore d'évaluation
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonD'EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Electronics All-in-One For Dummies, 3rd EditionD'EverandElectronics All-in-One For Dummies, 3rd EditionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeD'EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (9)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)D'EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesD'EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosD'EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesD'EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceD'EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpicePas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialD'EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesD'EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionD'EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (543)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsD'EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Heat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesD'EverandHeat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationD'EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersD'EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Practical Power Distribution for IndustryD'EverandPractical Power Distribution for IndustryÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (2)
- Wearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsD'EverandWearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsEdward SazonovPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsD'EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tD'EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (27)