Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Class Chart
Transféré par
DaisyDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Class Chart
Transféré par
DaisyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
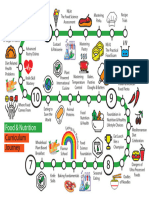
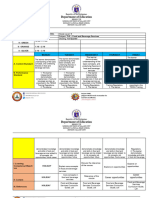
PROMOTING LIFELONG
HEALTHY EATING HABITS
Classroom Curriculum Chart
Learning objectives for nutrition education in primary schools in developing countries
GRADES
AGE GROUP A B C D E F G H
TOPICS FOOD AND EMOTIONAL DEVELOPMENT
1. Sensory perception of foods
EATING HABITS AND CULTURAL AND SOCIAL
INFLUENCES
FOOD, NUTRITION AND PERSONAL HEALTH
1. Food classifications
FOOD SUPPLY, PRODUCTION, PROCESSING AND
DISTRIBUTION
CONSUMER ASPECTS OF FOODS
1. Food quality
FOOD PRESERVATION AND
STORAGE
FOOD PREPARATION
1. Preparation techniques and skills
HYGIENE AND SANITATION
1. Water
n development of sensory awareness 1. Eating habits and values n food composition; nutritional value 1. Food supply 1. Food spoilage n sources of water
2. Food shopping
and n children’s feelings about eating, drinking and well-
being
n children’s own food and eating habits and values
n those of others/different cultural groups
n degree of processing and preparation
n social values, cultural values
n food sources (plants, animals)
n food production; techniques (farming, fishing, hunting, factory);
n points of food acquisition (shop, market,
supermarket, etc.)
n lifecycle of foods
n signs of food spoilage
2. Cooking techniques and skills
3. Planning
n properties of water
n making water safe
factors influencing food production; importance of land (access, n use of water
2. Food preferences 2. Social significance of food and eating 2. Functions of food for health (physical, mental) n skills in handling budget and food selection 2. Food preservation 4. Serving food
SUBTOPICS n trying new foods
3. Meals and meal patterns
n health (basic concepts and characteristics)
n nutrients
quality)
n food chain/path
n interests of buyer and seller
n planned vs. impulse buying
3. Food storage in the home 5. Safety
n storing water
2. Personal hygiene
3. Body image, self-esteem n variation in food habits (regional, cultural, religious) n prices and costs
n digestion
4. Responsibility n history of food and eating 3. Advertising and marketing 3. Food safety and hygiene
3. Dietary needs of different groups 2. Food gardens n principles; basic action skills
n children’s own responsibility n traditional foods
n production techniques (farming, fishing, hunting, factory) 4. Functions of packaging
n in particular, breastfeeding and weaning n food poisoning – causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
n social responsibility
4. Factors influencing own food choice (individual, n other groups of life cycle/activity level 5. Food labels
3. Food manufacturing and processing 4. Diarrhoea
psychological, environmental, socio-cultural factors) n reading labels
4. Principles of healthy eating and diets n basic techniques and their advantages/disadvantages
n food availability and supply n prevention and treatment (ORS)
n novel foods and product design n regulations
n norms for eating behaviour, etiquette n variety, balance, meeting nutritional needs
n effects of manufacturing and processing on nutritional quality 5. Waste disposal
n peer pressure n food selection models 6. Consumption patterns and environment
n media, advertising n “extra foods” (snacks, sweets) 4. Food security (at global, national, regional and household level) 7. Consumer rights
5. Diet-related health risks and diseases n determinants and state of food security (at all levels)
5. Settings for food consumption
n types (malnutrition; diarrhoea; worms; “diseases of lifestyle” such as cardio-vascular disease, cancer, n changes of food supply in time/history
n eating times
diabetes mellitus, obesity; dental caries; physical activity n food politics; food policies
n special occasions
n prevention; growth monitoring 5. Environmental aspects
n importance of maintaining a healthy weight n impact of food production and trade on physical environment,
6. Dietary guidelines and food guides and vice versa
KEY QUESTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVES
1. What do I eat and drink? 1. Sensory perception of foods 1. Eating habits and values 1. Food classifications 1. Food supply 2. Food shopping 1. Food spoilage 1. Preparation techniques and skills 1. Water
2. How and when do I eat? n to identify the taste, look, touch, sound and smell of n to know their own eating habits and to be aware of those n to recognize different types of foods and drinks available in the community n to know basic food plants and non-food plants n to identify places where food is sold in the n to realize that foods have a natural life n to be able to name the fuel and n to understand that water is essential for all living things
3. What do other people eat and drink? a variety of foods and recognize them on this basis of others n to identify foods important for growth and health (basic foods) n to understand that all food originates from plants and animals and community cycle which ends in decay unless they utensils needed to prepare food n to identify water sources in the community and how water is used
n to describe which foods and drinks they consume water n to be able to assist in simple food shopping tasks are preserved or stored correctly n to enjoy simple tasks in food n to recognize the importance of clean, safe water for drinking or
4. How do I feel about eating and drinking? 2. Food preferences 2. Functions of food for health
Grade 1 and 2
n to explain the importance of traditional foods n to identify locally-available foods n to feel, smell and touch fresh vegetables and fruits n to understand that decayed food, if preparation preparing food
n to know their own food preferences and to be n to describe (by drawing) what food and health means to me
5. Can I feed myself? n to identify what other family-members at home, or n to realize that food is produced and transported to places where it eaten, will lead to illness n to know the basics of safe storage of water for food and drinking
aware of those of others n to be aware of the need of food for growth, health and activity 3. Advertising and marketing 4. Serving food
6. Why do I need food? friends, are eating and drinking is sold (basic stages of the food path) n to know that food and water should be covered when stored
n to be aware that food is eaten for enjoyment n to understand the concept of growth and its relation to food n to identify different food advertisements n to be able to help with the serving
7. Where does my food and water come from? n to know that foods start from raw material, e.g. flour-bread n to know that it is dangerous to play in contaminated water
n to be prepared to try different foods 2. Social significance of food and eating of food
3. Dietary needs of different groups
(6-7)
8. How do we grow plants for food? Can I do it? n to recognize how food relates to our culture and relates 2. Food gardens 2. Personal hygiene
3. Body image, self-esteem n to recognize (basics) that different age groups and lifestyles need different foods and different amounts of 5. Safety
9. How can I keep food and water clean and fresh? to social habits n to practise simple skills in growing food
n to understand that caution is n to understand that hands should be washed before eating or touching
n to know that you are unique and special food
10. Can I help with shopping and preparing food? n to enjoy a meal with others foods
n to appreciate that different persons have different 3. Food manufacturing and processing needed in the kitchen because
n to participate in the work involved in preparing food 4. Principles of healthy eating and diets
11. Can I keep myself clean? body-shapes and sizes n to understand that some foods need to be prepared in order to eat of sharp instruments and hot 3. Food safety and hygiene
n to know that food needs to be chewed well
12. When must I wash my hands? 3. Meals and meal patterns them surfaces, boiling water, fire, etc. n to understand that fresh fruit and vegetables should be washed before
4. Responsibility n to drink sufficient water each day
n to recognize the difference between meals and snacks n to understand that some foods are made or changed in the factory eating
n to be able to make decisions when offered simple n to know that breakfast is a good starter meal for the day, and therefore important
n to compare and know the difference between everyday
choices n to know the importance of regular meals 5. Waste disposal
n to be able to feed yourself
foods and special foods (foods for festive occasions/
n to throw away organic rubbish and food wrappers in appropriate
celebrations/cultural ceremonies) 5. Diet-related health risks and diseases
n to take care of your own body places
n to relate frequency of food consumption during the day to dental caries
5. Settings for food consumption
n to realize the importance of dental hygiene for oral health
n to identify when food is eaten during the day
1. How do foods taste? 1. Sensory perception of foods 1. Eating habits and values 1. Food classifications 1. Food supply 1. Food quality 1. Food spoilage 1. Preparation techniques and skills 1. Water
2. What do I choose to eat and why? What do others n to correctly identify the four basic tastes (salty, n to be aware of differences in the eating habits of others n to identify local food that gives energy n to know where food comes from (basics of food chain/path) n to recognize rotten or spoiled vegetables, fruits and n to understand the ways in which food n to be able to prepare simple foods n to know about water-borne diseases
choose? sweet, sour, bitter) compared to their own n to identify local food for vitality (particularly vegetables, green leaves, fruits) n to identify the origin of certain plant and animal foods other foods can become spoiled n to be able to follow simple recipes n to be able to differentiate between clean and dirty water
n to be able to discuss their own feelings when eating n to identify what food is eaten by different members of the n to identify “extra” foods (snacks and sweets), their nutritional and social function n to describe which foods are obtained through farming, fishing, n to describe what to do with left-over n to know the main locally practised n to be aware of safe water sources
3. What does it mean to be healthy? 2. Food shopping
and drinking family n to identify different types of drinks hunting or produced in factories foods preparation and cooking methods n to be able to make water safe by purifying (chlorination) or boiling
4. What is a healthy lifestyle? Do I have one? n to identify the different foods which are sold in
2. Food preferences 3. Meals and meal patterns n to classify local foods by: origin (plant/animal); cooked, processed, raw n to know the tools used in growing, hunting, and fishing foods
different places (street, market, shop) 2. Food preservation for (various) staple foods and other n to understand the role of water in the body
5. What does our community normally eat, when and how? n to understand the importance of soil locally important food groups
n to be prepared to broaden the range of acceptable n to be aware that different regions have different eating 2. Functions of food for health n to be able to do simple food shopping tasks n to know how to preserve different types 2. Personal hygiene
6. What do different foods give us? foods habits n to describe how food was produced in the past n to be familiar with the reasons for
n to understand why certain foods are important to health of food (e.g. via packaging) n to know that common parasites, bacteria and viruses can be
7. What is a good diet? Do I have one? 3. Advertising and marketing those practices
Grade 3, 4, 5
3. Body image, self-esteem n to be aware of different traditional foods, and the values 2. Food gardening n to know the main locally practised transmitted by dirty hands
n to be able to describe the relationship between being healthy and eating enough appropriate foods n to be able to recognize an advertisement as a sales
8. How can we have a good diet all the year round? n to recognize different rates of physical development
attached to them n to know that foods contain nutrients and provide energy, needed for growth and activity n to start a food garden where feasible (with parent’s or teacher’s food preservation methods 2. Cooking techniques and skills n to understand the link between not washing hands after toilet use and
method
9. Where do our foods come from? How are they grown/ n to be able to describe the local diet (in terms of staple help) n to be familiar with the reasons for those n to know the reasons for cooking food contamination
n to respect different body shapes and sizes
food, additions and variations) 3. Dietary needs of different groups 4. Function of packaging practices food
(8-10)
caught/processed? n to identify signs of good health and ill health 3. Food manufacturing and processing n to understand the causes of diarrhoea and its consequences
n to realize that people of different ages have different food needs (lifecycle – in particular, babies and n to know some environmental impacts of packaging
n to be aware of the eating habits of grandparents, n to know simple techniques for
10. Why are foods labelled, packaged and advertised? 4. Responsibility toddlers, schoolchildren, grown-ups) n to explain the stages of processing: e.g. cereal grain – flour 3. Food storage in the home 3. Food safety and hygiene
compared with their own – product made of flour 5. Food labels preparing food: cutting, peeling,
11. How do I help with buying, producing, gathering and n to be aware of how they and other children spend n to experience the need for energy intake related to physical activity n to describe inappropriate methods of n to understand that before starting food preparation, hands, utensils
4. Factors influencing food choice n to realize that certain products are not easy to link with their n to recognize basic information on food labels such
washing
preparing food at home? money on food n to experience the need for more liquids in hot weather home storage that causes foods to spoil and workplace need to be clean
n to become aware of some of the personal factors of their original raw materials as the “best before” date n to understand the basic rules of 5. Safety
12. How do we preserve food and keep it fresh? n to recognize their own role in the food and water n to relate eating and drinking to individual needs (height, weight, age and activity) n to understand that germs can cause illness
process and in the family (food production, own food choices hygiene for food storage (e.g. via clean n to know how to behave safely n to know that germs are found in many places and can be prevented
13. How and why should water be collected, stored, n to recognize that breastmilk is the best for babies 4. Food security 6. Consumption patterns and the environment
purified? How can I help? preparation, helping with feeding younger children, 5. Settings for food consumption n to know the main factors influencing family food supply n to identify the costs of locally produced food and
containers) when preparing food (e.g. with from spreading
4. Principles of healthy eating and diets n to know how to store different types of fire, hot water, knives)
14. When and why must we wash our hands? fetching water, etc.) n to identify the different social settings for food n to understand that everyone needs to have sufficient food food that has to be transported to shops
n to recognize that eating regularly is important food 4. Diarrhoea
consumption in their own surroundings throughout the year to be healthy
n to recognize that sufficient water/liquid needs to be drunk each day n to know how to prepare and use oral rehydration solutions (ORS)
n to recognize how many times a day they eat, and n to recognize that differences of food availability exist in different
whether these are meals or snacks n to recognize that a variety of food is needed for health 5. Waste disposal
regions
n to know the uses of organic waste (e.g. as food for livestock,
5. Diet-related health risks and diseases
5. Environmental aspects compost)
n to explain the consequences to health of eating too much or too little
n to be able to identify the basic environmental impacts of food n to know safe ways to dispose of waste water
n to recognize the importance of growth monitoring
production
n to recognize the importance of physical activity for health
1. What influences my eating habits? Emotional, social, 1. Sensory perception of foods 1. Eating habits and values 1. Food classifications 1. Food supply 1. Food quality 1. Food spoilage 1. Preparation techniques and skills 1. Water
cultural, economic, mental and physical factors. n to realize that perceptions of flavour differ and n to compare their own choices with those of others in the n to be able to classify foods into groups according to their sources as well as nutrient content n to understand that plants are the basis of the food chain n to know some criteria of food quality: taste, smell, n to recognize when food is spoiled n to experiment with different food n to identify ways in which water may be contaminated
2. How and why do eating patterns change with time, influence food choice group 2. Functions of food for health n to identify food production systems and techniques in their own freshness and so on n to understand the role of bacteria in preparation techniques: cutting, n to identify ways of protecting water and its sources
place and culture? n to be aware of the manner in which food is eaten 2. Social significance of food and eating n to realize the importance of nutrition for good health
country (dairy farming, meat farming, vegetable growing, grains food poisoning peeling, cooking, frying, stirring, n to identify local problems with safe water, sanitation and hygiene
2. Food shopping
3. What are the nutrients in food? and its relationship to the enjoyment of food n to appreciate and respect others’ food choices and eating
and cereals, subsistence farming) etc. n to know how rain water can be conserved
n to recognize that nutrition is only one factor which influences health n to be able to handle a shopping assignment (money, 2. Food preservation
n to understand the influence of climate on food production in their n to prepare a simple meal for the
4. What happens to food in the body? 2. Food preferences habits n to be able to describe the links between eating enough appropriate food and health (physical, mental) buying the right products) n to recognize the different methods of 3. Food safety and hygiene
n to understand that it is possible to modify or adapt
own country home situation, taking others’
5. How does diet affect health? 3. Meals and meal patterns n to name and relate nutrients, water and fibre to their functions in the body n to identify different packages and wrappings of the preserving nutritional value and of n to practise (WHO) guidelines for food hygiene
their own sense of taste and thereby change n to understand ecological principles of food production (including wishes into account
n to be aware of the change in food choices and methods n to understand that proteins, fat and carbohydrates provide energy for the body which is needed for same food item reducing spoiling n to understand that food can be contaminated through poor handling
6. Why do different people need different diets? preferences crop rotation)
of preparation as compared to previous generations development n to describe traditional methods of 2. Cooking techniques and skills and unhygienic practices
7. Can I make some balanced meals for the family? n to know which crops are suitable for growing in their region 3. Advertising and marketing
3. Body image, self-esteem n to describe the functions of the different parts of the digestive system processing and preserving foods n to be able to prepare (simple) n to be aware of hygiene problems associated with foods sold by
n to identify what is nutritionally correct in traditional n to understand why and how advertisers influence
n to know the basics of preventing and treating common plant pests
Grade 6 and 7
8. How is our food produced and processed, and why? n to consciously identify the links between body- foods and what is not 3. Food storage in the home meals or dishes for themselves vendors on the streets
3. Dietary needs for different groups people’s food choices
9. How can we produce a good diet all year round? image, self-confidence, self-esteem, well-being and 3. Food manufacturing and processing n to understand the principles of food n to be able to measure ingredients
n to recognize the significance of food for celebration n to identify personal need for foods, based on nutritional needs according to age, weight and activity 4. Diarrhoea
eating patterns n to relate processing of certain foods in their own country to 5. Food labels storage at home (e.g. temperature, for cooking
10. Can I do the shopping well? (e.g. choosing, reading n to identify the food habits of different cultural, religious, pattern n to know different ways of preventing diarrhoea
n to understand the information regarding appropriate
(11-13)
labels and ads, complaining) ethnic and regional groups n to adapt the daily intake of food according to the changing requirements of the body as it goes through
products in the shops: milk, cheese, meat, bread, etc. protection against insects/animals) 3. Planning
4. Responsibility storage of a food, as printed on its label 5. Waste disposal
n to be aware of eating habits and food styles in other parts n to recognize some of the stages that original raw materials n to understand the use of cold storage n to know how to plan the process
11. Why does food go bad? How can we keep it fresh and n to be aware of their own responsibility in choosing various stages of development n to know how to create and use a compost heap
or products undergo in factories, and the difference between n to understand the concept of a product’s shelf life
clean? food and their personal limitations of the country and the world n to know the nutritional needs of pregnant and lactating women in particular (i.e. a cool place, a of cooking and preparing food
ingredients and end product n to be able to read ingredient lists on labels refrigerator, a freezer)
12. How can we preserve food and its nutrients? n to identify community action for health 4. Factors influencing food choice 4. Principles of healthy eating and diets 4. Serving food
n to understand that foods are processed to: make them edible or 7. Consumer rights n to understand that cooked foods need
13. How is water contaminated? How can we have safe n to take responsibility for food related tasks in the n to identify what influences their own personal food n to realize the relationship between energy intake (food eaten) and energy expenditure (activities n to describe different ways of
more palatable; improve their storage qualities; for convenience; n to increase self-efficacy skills in making complaints special storage
clean water? household choices undertaken) serving food
for making profit to food sellers concerning poor quality
n to explain the importance of breastfeeding to others n to recognize the influence of peer-pressure on their n to realize the importance of vegetables and fruits as sources of vitamins and micronutrients
14. How do we prevent diarrhoea? 5. Safety
n to be able to help feed younger children and teach eating habits n to be able to compose mixed and balanced meals
4. Food security
n to know about the inequality of global food supplies n to learn how to use sharp utensils
them simple food, water and hygiene tasks n to recognize the influence of advertising on their food
5. Diet-related health risks and diseases n to know the advantages and disadvantages of commercial versus
safely in food preparation
choices
n to know the main causes of nutrient deficiencies and their prevention
n to be aware of the influence of the availability of subsistence farming
n to be familiar with the links between malnutrition and disease
products n to know how to compensate for seasonal variations in food supply
n to be able to recognize important symptoms of nutrition-related diseases
n to be aware of economic considerations in food choices n to know the disadvantages of having large and small families
n to know that an imbalance in energy intake and energy expenditure has an effect on weight
n to know how to minimize post-harvest food losses
n to understand the dangers of drinking alcohol
n growth monitoring: to know why it should be done and to be able to do it (basics)
5. Environmental aspects
n to be able to identify important environmental impacts of food
6. Dietary guidelines and food guides production: shifting culture; use of pesticides or natural means;
n to know (national) guidelines for healthy eating and drinking transport; climate
1. What is the food situation in my country and in the 1. Sensory perception of foods 2. Social significance of food and eating 2. Functions of food for health 1. Food supply 1. Food quality 1. Food spoilage 1. Preparation techniques and skills 1. Water
world? How are food habits changing? n to be aware of their own changing perceptions of n to recognize that food preparation and eating is a social n to make connections between food and their present and future health n to understand the food path and ways in which it can be blocked n to understand quality issues in food, for example n to explain how food spoilage can n to prepare a meal for the home, n to identify local problems with safe water, sanitation and hygiene
2. What are my key values regarding food, eating and flavour event n to understand how the body processes food, making nutrients and energy available n to understand that food production methods often differ between freshness, colour, smell, bruising be slowed down by the addition of taking others’ wishes into account n to identify ways water is contaminated
health? 3. Body image, self-esteem 3. Meals and meal patterns 3. Dietary needs of different groups countries 2. Food shopping substances such as vinegar, sugar, etc. n to identify ways to protect water and water sources
2. Cooking techniques and skills
3. Can I make food choices that are right for me? Can I n to feel comfortable with their own body-image and n to relate their own food habits to food in history n to be aware of sustainable methods of food production n to be able to prepare a shopping list
n to know and understand the nutritional needs of family members at different times: in normal health; in 2. Food preservation n to apply different cooking 2. Personal hygiene
recognize and handle all the influences and pressures? to respect the body-image of others n to recognize food trends sickness; in pregnant and lactating women; in babies; in toddlers; in primary schoolchildren and older 2. Food gardens n to be able to establish a food budget for a given n to know different methods of food techniques, use appropriate n to understand the life cycle of worms, their effects on the body and
Can I help others to make good food choices? n to become aware of the processes of physical, n to identify the links between eating habits and the global schoolchildren; in adolescents; in adult men and women; in elderly adults n to develop and sustain their own food garden (with help) period of time preservation (cooking, sterilization, equipment and develop other how to prevent them
4. How does the body use the nutrients in food? emotional and social change food system n to be able to buy according to their actual needs freezing, canning, drying, etc.) skills of food preparation
4. Principles of healthy eating and diets 3. Food manufacturing and processing 3. Food safety and hygiene
n to identify the emotional cues for eating n to compare prices and quality n to know that certain preservation
Grades 8, 9, 10
5. What is a good diet, and why? 4. Factors influencing food choice n to identify the constituents of a varied diet: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fibre, vitamins, minerals and n to realize that processing foods may affect nutritional value 3. Planning n to know the most important forms of food poisoning, their symptoms
n to identify the need for change (self-evaluation of n to enhance their ability to make their own food choices water 3. Advertising and marketing techniques have an effect on
6. How can we have a good diet all through the year? n to know how to plan the process and treatment
eating pattern) n to identify the links between eating habits and role n to understand the need for a varied diet (because no single food contains all the essential nutrients)
4. Food security n to be able to understand the advertising techniques
nutritional value
7. When do people have special food needs, and why? of cooking and preparing food n to apply principles of food hygiene to real-life situations
n to feel confident in managing change (what, why, n to explain ways in which families try to ensure that there is n to understand why the food industry
(14 – 16)
patterns n to apply the principles of variety in diet used in supermarkets, markets and other stores, and n to be aware that each individual can make a difference to their own
8. Can I take care of my own diet? how, when) sufficient food all year round uses additives 4. Serving food
n to understand and constructively manage peer-pressure n to recognize the importance of a balanced diet in the media survival
9. Can I grow food? n to identify incentives and reinforcements for their n to explain how governments ensure that there is sufficient food for n to know about new and community- n to arrange food in an appealing
n to develop skills for overcoming barriers in the n to assess diets at a food and nutrient level n to be able to think critically about the messages n to know the (WHO) guidelines for food hygiene
current eating behaviour all to eat throughout the year based technologies for food way when serving it
10. Can I budget and shop wisely for food for the environment n to be able to take care of their own meals and snacks given by advertising
household? 4. Responsibility n to be aware of unequal food distribution in the world preservation (sun-drying, etc.) 5. Safety 4. Diarrhoea
n to be aware of media and social pressure n to make informed choices concerning their own nutrition 5. Food labels
n to understand how personal food choices may affect the global n to be able to use a range of n to know the effects of diarrhoea
11. How do I respond to food advertising? n to develop self-management skills (decision- n to be able to apply principles of balance and moderation to their own daily food intake 3. Food storage in the home
food system n to know how to read the information on food labels
making; combating social pressure) kitchen equipment safely, n to know how to prevent diarrhoea
12. Do I know how to get information on food (e.g. national n to be able to choose food and balanced meals for a family – considering quality, cost and nutrition n to know how to store different foods
(nutrient value, use of additives, expiration date, n to know why replacement of fluid lost by diarrhoea is important
rules and guidelines)? n to take responsibility for their own food choices n to identify what is nutritionally correct in lay beliefs about food and eating 5. Environmental aspects and for how long confidently and independently
etc.)
n to take others into consideration n to be able to read labels to get n to be able to respond appropriately n to be able to prepare and correctly administer oral rehydration
n to recognize the ecological impact of food production practices
13. Do I know how to prevent food spoilage? 5. Diet-related health risks and diseases 7. Consumer rights therapy
n to share knowledge of food with others such as the use of pesticides, fertilizer and biotechnology information on storage, additives used in emergency situations
14. Can I preserve food? n to look critically at their own habits of alcohol intake and its effects n to be aware of food regulations in their country
n to take responsibility for explaining the advantages n to recognize the environmental aspects of food production and production techniques used
15. Can I plan and prepare meals for all the family? n to be able to assist in the growth monitoring of children n to be able to look up national rules, regulations
of breastfeeding, and correct weaning practices, to practices: climate, transport, packaging and waste
n to focus on the relationship between eating habits, diet-related diseases and disease prevention and guidelines on food declarations (regarding
16. What are our local water problems? How can I make others
sure we have clean safe water? (specifically fat, sugar, fibre and energy) ingredients, additives, shelf life, etc.)
n to participate in the family and community tasks of
food provision, preparation and hygiene 6. Dietary guidelines and food guides n to be aware of, and to be able to exercise, consumer
© FAO 2005
17. What are the main rules of food hygiene? Do I apply
them? n to set an example to others of improved hygiene n to understand the implications of recommended daily food intakes rights, such as getting good quality for money and
and eating practices n to reflect on the use of such recommendations for personal needs making complaints
18. What are the symptoms and the causes of diarrhoea?
How can we prevent it and how should we treat it?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Regenerating Japan: Organicism, Modernism and National Destiny in Oka Asajirō's Evolution and Human LifeD'EverandRegenerating Japan: Organicism, Modernism and National Destiny in Oka Asajirō's Evolution and Human LifePas encore d'évaluation
- Alexa Brand Resume 1 21 22Document2 pagesAlexa Brand Resume 1 21 22api-592261976Pas encore d'évaluation
- M1 Lesson 1Document4 pagesM1 Lesson 1Catherine Sinen ObinquePas encore d'évaluation
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Food Nutrition and Health 2nd Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Food Nutrition and Health 2nd Edition PDF Scribdmichael.cahill319100% (39)
- Australian Dietary Guidelines - Product CatalogueDocument1 pageAustralian Dietary Guidelines - Product CatalogueutilitarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Real Food in The Tube: DisclosuresDocument11 pagesReal Food in The Tube: DisclosuresTisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition and Food Sciences OAJDocument4 pagesNutrition and Food Sciences OAJrienaPas encore d'évaluation
- Homescience TrackerDocument61 pagesHomescience TrackerSidharth BhoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Detroit Food Metrics ReportDocument42 pagesDetroit Food Metrics ReportWDET 101.9 FM100% (6)
- 2018-3-24 Uand Poster CF InterventionDocument1 page2018-3-24 Uand Poster CF Interventionapi-275031698Pas encore d'évaluation
- English Pedagogical Module 2: What Are Your Favorite Foods?Document24 pagesEnglish Pedagogical Module 2: What Are Your Favorite Foods?Lady SuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- ICN2Glossary Nov2014 Updated2016 - 01Document6 pagesICN2Glossary Nov2014 Updated2016 - 01Equipo CuatroPas encore d'évaluation
- Secrets of Indian Gastronomy - EiDocument8 pagesSecrets of Indian Gastronomy - EiSwathi PriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- HMPE3 Culinary Nutrition SyllabusDocument8 pagesHMPE3 Culinary Nutrition SyllabusJaja Dondon67% (3)
- Hmpe3 Culinary NutritionDocument8 pagesHmpe3 Culinary NutritionSheena HarrienPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Food in Eastern Part of The WorldDocument34 pagesFunctional Food in Eastern Part of The Worldrenu.j.bhicoo100% (1)
- NutritionDocument2 pagesNutritionashish kuntewarPas encore d'évaluation
- MensahDocument2 pagesMensahapi-604656125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrición Humana y Dietética: para Ti, Información PrácticaDocument4 pagesNutrición Humana y Dietética: para Ti, Información PrácticaEsPas encore d'évaluation
- State Indicator Report Fruits Vegetables 2013Document16 pagesState Indicator Report Fruits Vegetables 2013Daniel CiolacuPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive System MindmapDocument11 pagesDigestive System MindmapPakeerathy Sreesparalingam SutharshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bauan Technical High SchoolDocument5 pagesBauan Technical High SchoolJhon Leon MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Afb 19M Food Production TheoryDocument5 pagesAfb 19M Food Production TheoryIts JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Vegetarian Food FactsDocument2 pagesVegetarian Food FactsRoisinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Document63 pages2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Taif SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Attendace MonitoringDocument2 pagesAttendace MonitoringMaria Manoa GantalaPas encore d'évaluation
- CUP Strong Evidence MatrixDocument1 pageCUP Strong Evidence Matrixmajetan212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Food Composition Table PDFDocument13 pagesFood Composition Table PDFChris Ordz0% (1)
- Gastroenterology Services Operational Policy 2016Document335 pagesGastroenterology Services Operational Policy 2016alibaalbake1997Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hartleyetal 2022Document11 pagesHartleyetal 2022brillyyudoPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work Home Economics Year 9Document9 pagesScheme of Work Home Economics Year 9Bridget OmonikePas encore d'évaluation
- ENGLISH Week 7jun IIQ IIP (1) PUMALPA JUAN 10 MDocument4 pagesENGLISH Week 7jun IIQ IIP (1) PUMALPA JUAN 10 MJessi JesPas encore d'évaluation
- Adpcn NCM 105Document5 pagesAdpcn NCM 105leih jsPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrient: MIR DNA AnalysisDocument2 pagesNutrient: MIR DNA AnalysisAnonymous q92uZM4EymPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrient: MIR DNA AnalysisDocument2 pagesNutrient: MIR DNA AnalysisJose Luis RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- ELC197-Mark Lester Jacosalem Tanguan (Daily Lesson Log)Document11 pagesELC197-Mark Lester Jacosalem Tanguan (Daily Lesson Log)Mark Lester TanguanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Learners Book 8 - Cambridge GO 2Document1 pageCambridge Lower Secondary Science Learners Book 8 - Cambridge GO 27dwg75s8mgPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Learners Book 8 - Cambridge GO 2Document1 pageCambridge Lower Secondary Science Learners Book 8 - Cambridge GO 27dwg75s8mgPas encore d'évaluation
- Cristian EBBS 2015 LHDocument1 pageCristian EBBS 2015 LHcristian olartePas encore d'évaluation
- AG SCI 205 - Advance Methods in Animal Breedind SyllabusDocument4 pagesAG SCI 205 - Advance Methods in Animal Breedind SyllabusKRIZZAPEARL VERPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 classVI ch-2 - Components of FoodDocument2 pages2 classVI ch-2 - Components of FoodAnil AnilPas encore d'évaluation
- Food and Nutrition MapDocument1 pageFood and Nutrition MappehPas encore d'évaluation
- NTC The Pulse TestDocument2 pagesNTC The Pulse TestEvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Culinary NutritionDocument12 pagesCulinary NutritionJian Miee Rama LequironPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Grading g9 Eating Habits July 30 Aug3Document6 pages1st Grading g9 Eating Habits July 30 Aug3Gene Edrick CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Mast Cells and Its Relation To Collagen and VEGF in Oral Inflammatory LesionsDocument8 pagesMast Cells and Its Relation To Collagen and VEGF in Oral Inflammatory LesionsFlávia Godinho C. W. RochaPas encore d'évaluation
- LhZpfkZzSauFBq9lkKdV BLANCOAllergyChart2022MayDocument1 pageLhZpfkZzSauFBq9lkKdV BLANCOAllergyChart2022MaySkyler Gosselin-SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014, Fisioterapia Na EscolioseDocument11 pages2014, Fisioterapia Na EscolioseLuana ScuveroPas encore d'évaluation
- Stephanie Janecek Current Resume For WeeblyDocument1 pageStephanie Janecek Current Resume For Weeblyapi-351572858Pas encore d'évaluation
- Competency Music: Mapeh 10 Teacher: Ma. Bernadette A. Ablao Date Submitted: October 3, 2019Document2 pagesCompetency Music: Mapeh 10 Teacher: Ma. Bernadette A. Ablao Date Submitted: October 3, 2019Badeth AblaoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Quarter TOP 11-ABMDocument3 pages1st Quarter TOP 11-ABMMonica Pendel CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- En Us PolycDocument1 pageEn Us Polycfusuke9Pas encore d'évaluation
- IredemoIMs docxQUESTIONAIREDocument2 pagesIredemoIMs docxQUESTIONAIREGerros RemoladoPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL - FBS 1st Week WordDocument6 pagesDLL - FBS 1st Week WordAires IchonPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Modules: "I Am What I Eat."Document2 pagesCourse Modules: "I Am What I Eat."Christian C. MendizabelPas encore d'évaluation
- Light Up 2 SB WB CeleDocument115 pagesLight Up 2 SB WB CeleEL CUMPLE DE BENJA EMPRESA100% (1)
- DLL Mapeh-4 Q1 W2Document12 pagesDLL Mapeh-4 Q1 W2Jan Jan HazePas encore d'évaluation
- More Complications : Food Shortage Hunger DeathDocument2 pagesMore Complications : Food Shortage Hunger DeathVaishnavi KVGPas encore d'évaluation
- Stage 5 Food Technology - Food Trends: - NSW Department of EducationDocument14 pagesStage 5 Food Technology - Food Trends: - NSW Department of EducationRaquel WhitePas encore d'évaluation
- Lectura Control 5 Designing Food Structures For Nutrition and Health BenefitsDocument21 pagesLectura Control 5 Designing Food Structures For Nutrition and Health BenefitsfggoycooleaPas encore d'évaluation
- The New Sharing EconomyDocument13 pagesThe New Sharing EconomyDaisy100% (4)
- Forty Rules of LoveDocument41 pagesForty Rules of LoveDaisy100% (8)
- Companion To Philosophy of ScienceDocument465 pagesCompanion To Philosophy of ScienceMario de Turey93% (15)
- Jessican Conrad Sharing RevolutionDocument81 pagesJessican Conrad Sharing RevolutionZaq MosherPas encore d'évaluation
- Systems Intelligence 2004Document320 pagesSystems Intelligence 2004Daisy100% (1)
- How To Design Our World For HappinessDocument69 pagesHow To Design Our World For HappinessDaisy100% (1)
- Building Sustainability in An Urbanizing World - WB 2013Document216 pagesBuilding Sustainability in An Urbanizing World - WB 2013DaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- Paving The Way For Climate Resilient InfrastructureDocument148 pagesPaving The Way For Climate Resilient InfrastructureDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sustainable Everyday ENGDocument276 pagesSustainable Everyday ENGDaisy100% (4)
- Social Dimensions Climate ChangeDocument16 pagesSocial Dimensions Climate ChangeSamrerng KriengprathanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Investing in Resilience: Ensuring A Disaster-Resistant FutureDocument188 pagesInvesting in Resilience: Ensuring A Disaster-Resistant FutureAsian Development BankPas encore d'évaluation
- ADB Flood Risk ManagementDocument206 pagesADB Flood Risk ManagementDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- ADB Climate Change Assessment CooDocument28 pagesADB Climate Change Assessment CooDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- ADB Building Climate Resilience Agriculture SectorDocument322 pagesADB Building Climate Resilience Agriculture SectorDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- ADB Climate Change Assessment CooDocument28 pagesADB Climate Change Assessment CooDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelty - ProfToolkit - Healthy Living Healthy MindDocument149 pagesKelty - ProfToolkit - Healthy Living Healthy MindDaisy100% (2)
- Joy of Learning - Lesson Plans On Hygiene, Sanitation, Water, Health and EnvironmentDocument98 pagesJoy of Learning - Lesson Plans On Hygiene, Sanitation, Water, Health and EnvironmentDaisy80% (5)
- Mekong Environmental Symposium 2013 - Abstract VolumeDocument282 pagesMekong Environmental Symposium 2013 - Abstract VolumeDaisy100% (1)
- Mangroves - Soldiers of Our CoastsDocument17 pagesMangroves - Soldiers of Our CoastsDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Toolkit Healthy LivingDocument73 pagesFamily Toolkit Healthy LivingDaisy100% (1)
- Transcript of Interview With Ignacio On Montevideo's Territorial Approach To Climate ChangeDocument4 pagesTranscript of Interview With Ignacio On Montevideo's Territorial Approach To Climate ChangeDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- Interview With MarthaDocument2 pagesInterview With MarthaDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- Interview With DR Alberto MaturanaDocument3 pagesInterview With DR Alberto MaturanaDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ecosystem Approach - 5 Steps To ImplementationDocument39 pagesThe Ecosystem Approach - 5 Steps To ImplementationDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Worldwide Adventure of DroppyDocument48 pagesThe Worldwide Adventure of DroppyDaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Guidelines For Healthy EatingDocument13 pages9 Guidelines For Healthy EatingJeann ManlangitPas encore d'évaluation
- TruEarth Healthy Foods - Case SolutionDocument29 pagesTruEarth Healthy Foods - Case SolutionYogendra RathorePas encore d'évaluation
- Ankita's Diet Plan - Married, IT ProfessionalDocument10 pagesAnkita's Diet Plan - Married, IT Professionalpavani21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Health and WellnessDocument8 pagesHealth and WellnessAbdul Rahim JaafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Secrets of Living LongerDocument108 pagesTime Secrets of Living Longeraramisbirsan2132Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Kill CancerDocument88 pagesHow To Kill Cancerkalpesh deora100% (2)
- Your Weight Your HealthDocument36 pagesYour Weight Your Healthkarina2227Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition in Old AgeDocument16 pagesNutrition in Old Agekarunamoorthi_p100% (1)
- Cover Page MergedDocument98 pagesCover Page MergedAmos OngPas encore d'évaluation
- Asl - Class 9 - TeacherDocument11 pagesAsl - Class 9 - TeacherMeenakshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Healthy Food in Pregnancy and Mediterain Type of Food PyramidDocument14 pagesHealthy Food in Pregnancy and Mediterain Type of Food Pyramidfawzia rashediPas encore d'évaluation
- Healthy Active Living and Balance: Dr. Annick Buchholz, C.Psych. Dr. Laurie Clark, C.Psych. Kelly Heffernan, RDDocument46 pagesHealthy Active Living and Balance: Dr. Annick Buchholz, C.Psych. Dr. Laurie Clark, C.Psych. Kelly Heffernan, RDbalajiboss005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Junior 2 - Unit #8: Staying HealthyDocument18 pagesJunior 2 - Unit #8: Staying HealthyANDRES LOZANOPas encore d'évaluation
- De On Thi Vao Lop 10 Chuyen Ngoai Ngu Co Dap AnDocument15 pagesDe On Thi Vao Lop 10 Chuyen Ngoai Ngu Co Dap AnThuỳ VyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sicem2016 P 062 Jundrian DoringoDocument3 pagesSicem2016 P 062 Jundrian DoringoSharnelle Valdez NotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Education Course. Lesson Plans For EducatorsDocument111 pagesSafety Education Course. Lesson Plans For EducatorsSAFIGI Outreach Foundation100% (1)
- YÊN BÁI - ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT DUYÊN HẢI BẮC BỘDocument8 pagesYÊN BÁI - ĐỀ THI ĐỀ XUẤT DUYÊN HẢI BẮC BỘLương Hiền VyPas encore d'évaluation
- Roth 10e Nclex Chapter 15Document3 pagesRoth 10e Nclex Chapter 15jennaaahhhPas encore d'évaluation
- Course: Ivsem. Bba Team: 4 D A T E: 1 0 / 0 6 / 2 2 TOPIC:Impact of Fast FoodsDocument10 pagesCourse: Ivsem. Bba Team: 4 D A T E: 1 0 / 0 6 / 2 2 TOPIC:Impact of Fast FoodsRishit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre TestDocument8 pagesPre TestChesca charmaine MEsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Practice Unit 6 2GDocument2 pagesExtra Practice Unit 6 2GLilo MorPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Food Addiction: A Major Public Health Issue: Archives in Biomedical Engineering & BiotechnologyDocument8 pagesFast Food Addiction: A Major Public Health Issue: Archives in Biomedical Engineering & Biotechnologyabdullah khalidPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Essay 2017Document44 pagesSPM Essay 2017Sharon Siow Chen50% (2)
- "Mag HL Tayo": RationaleDocument2 pages"Mag HL Tayo": Rationalemale nurse75% (4)
- Question 2 Terengganu Trial 2019Document6 pagesQuestion 2 Terengganu Trial 2019YunernPas encore d'évaluation
- How To End Stomach Pain Forever EvenDocument22 pagesHow To End Stomach Pain Forever EvenYaquifox0% (1)
- BBL NutritionGuide BootyliciousMealPlan Bvl2ueDocument64 pagesBBL NutritionGuide BootyliciousMealPlan Bvl2ueLanna Elizabeth Cozzens100% (1)
- Cholesterol Lab ReportDocument9 pagesCholesterol Lab Reportapi-313510960Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathfit EssayDocument8 pagesPathfit Essayjeffmyself901Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pep Science Curriculum WorkupDocument18 pagesPep Science Curriculum WorkupAnrewPas encore d'évaluation