Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Practice Quiz Diffraction 1
Transféré par
pauljkt1Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Practice Quiz Diffraction 1
Transféré par
pauljkt1Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Practice Quiz Diffraction Name_________________________
1) In a single-slit diffraction experiment, the width of the slit through which light passes is reduced. What happens to the central bright fringe? A) It stays the same. B) It becomes narrower. C) It becomes wider. D) None of the other answers is correct. Answer: C 2) In a single-slit diffraction experiment, a beam of monochromatic light passes through a slit of width 11.0 mm. If the first order dark fringe of the resulting diffraction pattern is at an angle of 4.31, what is the wavelength of light? A) 827 nm B) 301 nm C) 602 nm D) 402 nm Answer: A 3) In a single-slit diffraction experiment, the central maximum is broadened if the wavelength of light increased. A) True B) False Answer: TRUE 4) In a single-slit diffraction experiment, the width of the slit is 1.90 m. If a beam of light of wavelength 610 nm forms a diffraction pattern, what is the angle associated with the first minimum above the central bright fringe? A) 11.4 B) 12.2 C) 39.9 D) 18.7 Answer: D 5) In a single-slit diffraction experiment, the width of the slit is 1.90 m. If a beam of light of wavelength 610 nm forms a diffraction pattern, what is the angle associated with the second dark fringe above the central bright fringe? A) 11.4 B) 12.2 C) 39.9 D) 18.7 Answer: C 6) In a single slit diffraction experiment, the width of the slit is 3.1 10-5 m and the distance from the slit to the screen is 2.2 m. If the beam of light of wavelength 600 nm passes through the slit and forms a diffraction pattern on the screen, what is the linear distance on the screen from the center of the diffraction pattern to the second dark fringe? A) 3.9 cm B) 4.2 cm C) 2.1 cm D) 8.5 cm Answer: D
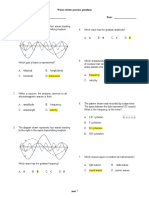
7) A planar cross section through two spherical waves emanating from the sources S1 and S2 in the plane is shown in the figure. S1 and S2 are in phase. The black circles are one and two wavelengths from their respective sources. The lighter circles are one half and one and a half wavelengths distant from their respective sources. If the waves shown arriving at P1 both arrive with amplitude A, the resultant amplitude at point P1 is
P1 P2 S1 S2
a. b. c. d. e.
0.
1 A. 2
A.
3 A. 2
2A.
8) In an interference pattern, the wavelength and frequency are a. b. c. d. e. a 9) The figure shows two point sources of light, A and B. B emits light waves that are + radians out of phase with the waves from A. A is 3 from P. B is 5 from P. ( is the wavelength.) The phase difference between waves arriving at P from A and B is
A B
the same in both the regions of constructive interference and the regions of destructive interference. greater in regions of constructive interference than in regions of destructive interference. smaller in regions of constructive interference than in regions of destructive interference. unchanged in regions of destructive interference but greater in regions of constructive interference. unchanged in regions of destructive interference but smaller in regions of constructive interference.
a. b. c. d. e. d
0 rad. rad. 2 rad. 3 rad. 4 rad.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Musical Instrument Design Practical Information For Instrument Making Hopkin BartDocument116 pagesMusical Instrument Design Practical Information For Instrument Making Hopkin BartLuiz Roberto100% (4)
- Problem Set Waves and Wave PropertiesDocument2 pagesProblem Set Waves and Wave PropertiesYohana Glorya TobingPas encore d'évaluation
- PSI AP Physics 1: Sound Waves Practice ProblemsDocument16 pagesPSI AP Physics 1: Sound Waves Practice ProblemsAlexa AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Optics and Modern Physics DC PandeyDocument559 pagesOptics and Modern Physics DC PandeyLalith Kumar Reddy Vedium100% (1)
- The Nature of Light WaveDocument25 pagesThe Nature of Light WavepankajharitashPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometric Physical OpticsDocument122 pagesGeometric Physical OpticsĐạt VũPas encore d'évaluation
- Coulomb's Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesCoulomb's Law Worksheetpauljkt1100% (1)
- Sindrom Gradenigo Pada OMSK Tipe Bahaya - YurniDocument15 pagesSindrom Gradenigo Pada OMSK Tipe Bahaya - YurniIKM MayorPas encore d'évaluation
- Lorentz TransformationDocument11 pagesLorentz Transformationpauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Honors Physics Midterm Review: Exam DayDocument8 pagesHonors Physics Midterm Review: Exam DayEarl averzosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diffraction Grating Equation With Example ProblemsDocument8 pagesDiffraction Grating Equation With Example Problemspauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 32 - Electromagnetic WavesDocument19 pagesChapter 32 - Electromagnetic WavesKarla PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Details of Courses January 2019: PHY320 Physics Lab VDocument13 pagesPhysics Details of Courses January 2019: PHY320 Physics Lab VAdwinPittPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves Review Practice Questions Name: DateDocument15 pagesWaves Review Practice Questions Name: DateShammany AlsuwaidiiPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 1 Test Bank Physics 1Document28 pagesCH 1 Test Bank Physics 1nour100% (1)
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument14 pagesRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêPas encore d'évaluation
- Refraction Physics SATDocument3 pagesRefraction Physics SATAyman ElAshmawyPas encore d'évaluation
- Snells Law ProblemsDocument1 pageSnells Law Problemsmayank98108Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wave HandoutDocument2 pagesWave HandoutBridget CumlatPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report Phy098 - E33 - Group 4Document9 pagesLab Report Phy098 - E33 - Group 4Danial Sharil OthmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound - ICSE Solutions For Physics: Short AnswersDocument34 pagesSound - ICSE Solutions For Physics: Short AnswersPooja SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- A. Wave Introduction: Waves InterferenceDocument13 pagesA. Wave Introduction: Waves InterferenceJeromeDelCastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Waves MCQDocument6 pagesPhysics Waves MCQAnubhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Harmonic Motion-278Document33 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion-278Hashim Khan50% (4)
- Lecture - 4 - Wave MotionDocument46 pagesLecture - 4 - Wave MotionAlkgema Stores100% (1)
- Chapter III: Population EcologyDocument10 pagesChapter III: Population EcologyKyla Capis BascoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document9 pages1MCHPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Chapter 26 AnswersDocument7 pagesPhysics Chapter 26 AnswersKarissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 03Document15 pagesChapter 03nourPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics HW 8 CH 22 Wave Optics PDFDocument25 pagesMastering Physics HW 8 CH 22 Wave Optics PDFJasdeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 04 Humidity Condensation and CloudsDocument13 pagesChapter 04 Humidity Condensation and CloudsnaveedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch12 Giancoli7e TestBankDocument24 pagesCh12 Giancoli7e TestBankHarishChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves - 3 Sound WavesDocument3 pagesWaves - 3 Sound WavesullasagwPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Solving Questions (Part I) PDFDocument6 pagesProblem Solving Questions (Part I) PDFclainPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Final ExamDocument3 pagesPhysics Final ExamJoey Aguilar VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Que InterferenceDocument3 pagesShort Que InterferenceKamran Ali100% (1)
- YOUNG'S DOUBLE SLIT EXPERIMENT (30-08-2016) (To Be Submitted by 5/6 September 2016) (To Be Submitted in The Tutorial Notebook)Document5 pagesYOUNG'S DOUBLE SLIT EXPERIMENT (30-08-2016) (To Be Submitted by 5/6 September 2016) (To Be Submitted in The Tutorial Notebook)Uday GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set - Sound IntensityDocument1 pageProblem Set - Sound IntensityStef BacalangcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Science MODULE 1 PDFDocument10 pagesEarth Science MODULE 1 PDFyhajj jamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Range MCQs On Introductory StatisticsDocument26 pagesMultiple Range MCQs On Introductory StatisticsKennyPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Map Grade 7Document7 pagesCurriculum Map Grade 7Khim Stephannie VillarinPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ Electrical Engg. Unit 1.Document69 pagesMCQ Electrical Engg. Unit 1.Trupti NandikolmathPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3-Wave Properties of ParticleDocument29 pagesChapter 3-Wave Properties of ParticleI Gowtham ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- UCE Physics 2015 Paper 1 GuideDocument11 pagesUCE Physics 2015 Paper 1 GuideChristinePas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument2 pagesNuclear PhysicsOrbit MBBS PreparationPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 35 Interference PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 35 Interference PDFAttabik AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Test For XIDocument5 pagesTest For XIKamran AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS) : Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument28 pagesExercise Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS) : Light-Reflection and RefractionWesPas encore d'évaluation
- Formal Report (Speed of Sound)Document2 pagesFormal Report (Speed of Sound)Gly LagasonPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Answer KeyDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Answer KeySeedy B Fofana100% (1)
- Spatial & Temporal Coherence: Optical EngineeringDocument15 pagesSpatial & Temporal Coherence: Optical EngineeringDinesh Katoch100% (1)
- Cercado MidtermExam AdvancedPhySciDocument6 pagesCercado MidtermExam AdvancedPhySciJudy Ann CercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 71 1st Long ExamDocument12 pagesPhysics 71 1st Long ExamAb YZPas encore d'évaluation
- SED 3269 Module 1 - History of AstronomyDocument24 pagesSED 3269 Module 1 - History of AstronomySuiee GenrieePas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection and RefractionDocument11 pagesReflection and RefractionNikki GuisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bushong: Radiologic Science For Technologists, 11th EditionDocument2 pagesBushong: Radiologic Science For Technologists, 11th Editiongasai gasai100% (1)
- UNIT 13-PHY 131-Chapter 23-Reflection and RefractionDocument26 pagesUNIT 13-PHY 131-Chapter 23-Reflection and RefractioncharliePas encore d'évaluation
- One Way ANOVA PDFDocument21 pagesOne Way ANOVA PDFSarah SeunarinePas encore d'évaluation
- Hapter: Conceptual QuestionsDocument16 pagesHapter: Conceptual QuestionsadelPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces & Motion, IGCSEDocument4 pagesForces & Motion, IGCSEsapiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Formal Report (Resonance and Speed of Sound)Document2 pagesFormal Report (Resonance and Speed of Sound)felice_belmontePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson10 Universal Wave Equation WorksheetDocument2 pagesLesson10 Universal Wave Equation WorksheetJep Val0% (1)
- Uclm Cesafi QuestionsDocument1 pageUclm Cesafi QuestionsBeverly Ann GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- GEASDocument71 pagesGEASEugene Embalzado Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsBacillus SubtilisPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ From Sound & WaveDocument3 pagesMCQ From Sound & WaveRaktimPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rdLESample PDFDocument10 pages3rdLESample PDFMarco ConopioPas encore d'évaluation
- 9936858-Class 12 - Physics - Wave Optics - Ws With Ans - AnuDocument14 pages9936858-Class 12 - Physics - Wave Optics - Ws With Ans - AnuJoyce CarilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Bio For You T2 FQ Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesAdvanced Bio For You T2 FQ Mark Schemepauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oxford University Press Advanced Biology For You, Second Edition © Williams Services Limited 2015Document18 pagesOxford University Press Advanced Biology For You, Second Edition © Williams Services Limited 2015pauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism: ConceptsDocument21 pagesLesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism: Conceptspauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blackbody Radiation Derivation of Planck S Radiation LawDocument20 pagesBlackbody Radiation Derivation of Planck S Radiation Lawpauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Useful Tips On How To Properly Study Chapter 32Document8 pagesUseful Tips On How To Properly Study Chapter 32pauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paper - 1: Physics, Mathematics & Chemistry 1:: 40 Test Booklet CodeDocument40 pagesPaper - 1: Physics, Mathematics & Chemistry 1:: 40 Test Booklet Codepauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- WEP Self Test 2Document7 pagesWEP Self Test 2pauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Uniform Circular Motion Self Test 2Document7 pagesUniform Circular Motion Self Test 2pauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics: Higher 2 (2017) (Syllabus 9749)Document37 pagesPhysics: Higher 2 (2017) (Syllabus 9749)pauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bishnu ShresthaDocument1 pageBishnu Shresthapauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Example1 - Flexural ModulusDocument3 pagesExample1 - Flexural Moduluspauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Single and Double-Slit InterferenceDocument13 pagesSingle and Double-Slit Interferencepauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Error Analysis and PropagationDocument7 pagesError Analysis and Propagationpauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Food Preparations and Their BenefitsDocument4 pagesFood Preparations and Their Benefitspauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- TAP 118-1: Potential DividersDocument4 pagesTAP 118-1: Potential Dividerspauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- UFC 3-340-02 Structures To Resist The Effects of Accidental ExplosionsDocument5 pagesUFC 3-340-02 Structures To Resist The Effects of Accidental ExplosionsAnkit KhuranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Examples of Oscillations.: Time Equations Displacement EquationsDocument4 pagesExamples of Oscillations.: Time Equations Displacement Equationsstephanus abednegoPas encore d'évaluation
- Neets Module 10 SummaryDocument11 pagesNeets Module 10 SummarySigmund VesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Phase Noise Fundamentals: White Paper - Version 01.01 - Paul DenisowskiDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Phase Noise Fundamentals: White Paper - Version 01.01 - Paul DenisowskiVo_Danh26Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Polarization? 1Document7 pagesWhat Is Polarization? 1Shaswath SasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Observation of Zenneck-Like Waves Over A Metasurfa PDFDocument6 pagesObservation of Zenneck-Like Waves Over A Metasurfa PDFgospodarmunjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz On ScienceDocument26 pagesQuiz On SciencennnPas encore d'évaluation
- WaveguidesDocument40 pagesWaveguidesChristian Razel CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- Lennard Jones1931Document24 pagesLennard Jones1931Enkh-Amar ShPas encore d'évaluation
- IP21 HW6 SOL RDocument3 pagesIP21 HW6 SOL R吳昭亮Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure: Follow-Up ProblemsDocument32 pagesChapter 7 Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure: Follow-Up Problems원철이Pas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Tutorial EM WavesDocument2 pages06 Tutorial EM WavesmukeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 33 - Electromagnetic WavesDocument43 pagesChapter 33 - Electromagnetic WavesDiễn Trần PhướcPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Simulation of Microstrip Patch Antenna Array For X-Band ApplicationsDocument6 pagesDesign and Simulation of Microstrip Patch Antenna Array For X-Band ApplicationsMạnh HiệpPas encore d'évaluation
- chp16 Part1Document68 pageschp16 Part1api-255402590Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 11-08 Interference, Huygenss Principle, Youngs Double Slit ExperimentDocument2 pagesPhysics 11-08 Interference, Huygenss Principle, Youngs Double Slit Experimentmechanical_lecturerPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Impedance Matching - Chapter 5 - Microwave EngineeringDocument2 pagesProblem Impedance Matching - Chapter 5 - Microwave EngineeringTuấn LêPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Foundation Design: Lawrence O. GalvezDocument43 pagesMachine Foundation Design: Lawrence O. GalvezJaher Wasim100% (1)
- SAW& ComsolDocument5 pagesSAW& Comsollabirint10Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1993 Hydrodynamics of Oscillating Cylinder and Disks at Low Keulegan-Carpenter NumberDocument156 pages1993 Hydrodynamics of Oscillating Cylinder and Disks at Low Keulegan-Carpenter Numbershubham khodiyarPas encore d'évaluation
- DopplerEffect PDFDocument5 pagesDopplerEffect PDFNeelam KapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGGPHYS Codes: 2671, 2857, 3002, and 3592 Engr. B.R. P. MallareDocument10 pagesENGGPHYS Codes: 2671, 2857, 3002, and 3592 Engr. B.R. P. MallareUploader101Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Frequency Selective Surfaces and Its ApplicationsDocument7 pagesA Review On Frequency Selective Surfaces and Its ApplicationsVijeta Diwan.21DR0213Pas encore d'évaluation
- For You to Do 1. In an area free of obstacles, stretch out a Slinky® so the turns are a few Centimeters apart. Mark the positions of the end of the Slinky by sticking pieces of Tape on the floor. Measure the distance between the pieces of tape. a) Record the distance between the pieces of tape in your log. 2. With the Slinky stretched out to the tape, grab the spring near one end, as Shown in the drawing, and pull sideways 20 cm and back. To move it correctly,Document4 pagesFor You to Do 1. In an area free of obstacles, stretch out a Slinky® so the turns are a few Centimeters apart. Mark the positions of the end of the Slinky by sticking pieces of Tape on the floor. Measure the distance between the pieces of tape. a) Record the distance between the pieces of tape in your log. 2. With the Slinky stretched out to the tape, grab the spring near one end, as Shown in the drawing, and pull sideways 20 cm and back. To move it correctly,api-26084273Pas encore d'évaluation
- Test Paper Oscillation & WavesDocument3 pagesTest Paper Oscillation & Wavesumved singh yadav100% (1)