Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SA Maths
Transféré par
SURESHKUMAR BANDARUDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SA Maths
Transféré par
SURESHKUMAR BANDARUDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
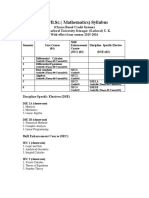
TRT 2012 Category of Post: School Assistant - Mathematics Syllabus Part I GENERAL KNOWLEDGE AND CURRENT AFFAIRS (Marks:
s: 10) Part - II PERSPECTIVES IN EDUCATION (Marks: 10) 1. History of Education : Pre-Vedic and Post-Vedic period, Medieval Education, Recommendations of various committees during British period with special reference to Woods Despatch (1854), Hunter Commission (1882), Hartog Committee (1929), Sargent Committee (1944), Recommendations of various committees during post independent period with special reference to Mudaliar Commission (1952-53), Kothari Commission(1964-66), Ishwarbhai Patel committee (1977), NPE-1986, POA-1992 2. Teacher Empowerment: Meaning, interventions for empowerment, Professional code of conduct for teachers, Teacher motivation, Professional development of Teachers and Teacher organizations, National / State Level Organizations for Teacher Education, Maintenance of Records and Registers in Schools. 3. Educational Concerns in Contemporary India: Environmental Education, Meaning and scope of Environmental Education, Concept of sustainable development, Role of Teacher, School and NGOs in development and protection of environment, Democracy and Education, Equality, Equity, Quality in Education, Equality of Educational opportunities, Economics of Education, Meaning and scope, Education as Human Capital, Education and Human Resource Development, Literacy Saakshar Bharat Mission, Population Education, Significance of Population Education, Population situation, policies and programmes in India, Approaches to Population Education and role of school and teacher, Themes of population Education, Family life Education, Sustainable development, Adolescence Education, Health Education, Gender Equality, Equity and Empowerment of Women, Urbanization and migration, Life skills, Inclusive Education, Conceptual Clarification and Definition, Prevalence, Myths & Facts, Characteristics, Classification & Types, Importance of Early Identification and assessment, Planning Inclusive Education, Classroom Management in Inclusive Education, Evaluation, Documentation and Record Maintenance, Psycho-Social management, Awareness & Sensitization Strategies, Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization, Value Education, Sarva Siksha Abhiyan, National Programme for Education of Girls at Elementary Level (NPEGEL), Mid-day-meals, Rashtriya Madhyamika Siksha Abhiyan(RMSA), KGBVs and SUCCESS Schools. 4. Acts / Rights: Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009, Right to Information Act, 2005, Child Rights, Human Rights 5. National Curriculum Framework, 2005: Perspective, Learning and Knowledge, Curricular Areas, School Stages and Assessment, School and Classroom Environment, Systemic Reforms Part - III CONTENT(Marks: 44) 1. NUMBER OF SYSTEM: Number system (N,W,Z,Q,R,)and their properties, diff. types of surds, Rationalization of mono, Binomial surds, extraction of square roots of real numbers. Complex number as an order pair of real numbers and their fundamental operations, representation in the form of SA - Mathematics Page 1
a+ib conjugate complex numbers , Modules and amplitude of complex numbers-illustrations, geometrical representations of complex numbers in Argand plane- Argand diagram. Prime and composite numbers, types of primes (co, twin, relative etc.) prime factors, multiple factors, GCF,LCM, relation bet. GCD & LCM. Modulus of a real number, Absolute value 2. SETS AND RELATIONS: Statements: Consecutiveness, Negation, Disjunction, Conjunction, Conditional, Bi-conditions (Bi-Implications), algebra of statements, Quantifies ,Converse, Inverse and contra positive of a conditional, proofs Direct and indirect proofs methods of disproof, an application of truths tables to switching networks, sets proofs of some laws of set operations, principle of duality, a comparison between the algebra of sets and statements, Tautologies and contradictions, Concept of a set: Definition ,Null set, equality of set, cardinal number, subset, super set, Universal set, union, intersection, venn diagrams, compliment, Relations: Ordered pairs, image, pre-image, range, injection, surjection, Bijection, finite set Cartesian products, Domain and range of a relations, Inverse relation, Types of relations, Relations and functions. Functions: Types of functions- definitions, Theorems on function, Domain, Range, inverse and real valued functions. Identity function, Constant function, Equal function, even and odd function, polynomial functions, Rational functions, Algebraic functions, Exponential functions, Logarithmic functions, Exponential and Logarithmic Series, Greatest Integer functions. Composite function, and its property, graphs of functions, Compound functions. equations of functions Limits: Concept, and limits of a function. Continuity, Neighbourhoods. 3. COMMERCIAL MATHEMATICS: Ratio and proportion, Rate, Unitary method, Percentages, Trade Discount, Average, Simple interest, Compound interest, Partnership, Time and distance, Time and work, clocks and calendar problems. 4. ALGEBRA: Laws of exponents: Laws of rational indices, Multiplication and division of polynomials, Some special products, Factorization of Quadratic Expressions. Logarithms: Definition, simple laws of logarithms, some additional laws, characteristic, Mantissa Exponents. Algebra of expressions: Square roots, Homogeneous, Symmetric cyclic expression and Factorization, symmetric expressions, cyclic expressions, quadratic equations, reciprocal equation, relation between roots and coefficients, nature of roots, to find the quadratic equation whose roots are given. Remainder theorem, Horners method, trial and error method, finding multiple roots, graphical solutions. Binomial Theorem: Standard binomial expansion, theorem, integral part, fractional part, numerically greater terms, largest problems, approximation using Binomial theorem. Mathematical induction: principles of mathematical induction and theorems and its applications, problems on divisibility. 5. LINEAR EQUATIONS: Linear equations in two variables: System of linear equations ,Simultaneous equation in two variables, Dependant equations,Linear equations and their graphs, Linear functions , System of equations, linear programming-problems (LPP). The fundamental theorem, graphical method of solving an LPP, a closed converse polygon, general graphical methods application of LPP. SA - Mathematics Page 2
In-equations: Linear in-equations and their graphs, System of in-equations. Linear equations in two variables, System of linear equations, simultaneous equation in two variables Dependant equations, linear equations and their graphs, linear functions, system of equations, System of two points, which is not parallel to X-axis, Midpoint of the segment following A(x1,y1), B(x2,y2) equation of a line passing through the origin having slope m, The slope intercept form of a line, the point slope form of a line, the intercept form of a line, the two point form of a line, linear in-equations, their graphs, system of linear in-equations. Rational integral of x, remainder theorem, Horners method of synthetic division, problems leading to quadratic equations, graphical solutions of quadratic, Quadratic inequalities in one variable, solution of quadratic in-equations the principle of mathematical induction , The binomial theorem, Pascal triangle. Quadratic expressions, equations in one variable, sign of quadratic expressions, changes in signs and maximum and minimum values, quadratic in-equations, relation between the roots and the coefficient in an equation, remainder theorem, connecting problems, solving an equation when two or more of its roots are connected by Cartesian relations, Horners method of synthetic division, trial and error method, Procedure to find multiple roots. 6. GEOMETRY Structure of geometry, axioms, Historical background, Basic axioms, Parallel line, theorems, triangles and polygons, angles of a polygons, theorems based on, Polygon congruence of triangle SAS, ASA, SSA, axioms, Parallelogram and its properties, Triangles, Particular types, geometric inequalities in a triangles some theorem, circles and concurrent lines in triangles, Theorems based on circles, Concurrent lines in a triangle, Median, Altitudes of a triangle, line of symmetry, axis of symmetry, point symmetry, image of an angle. Quadrilaterals, example of different Quadrilaterals, Parallel lines and triangles, theorems, intercept, Theorems, locus, points equidistant from two given points. Theorems, an concurrency, attitude, circum centre, ortho centre, centroid, Areas, polygonal region, Area axiom, congruent axiom, area monotonic axiom, area of parallelogram theorem, Area of Triangle, Theorem based quit, circles are of a circle, semi circle, segment of a circle, Congruence of a circle, Theorems based on circle. Similar polygons, similar triangle and their properties, Basic proportionality theorem, vertical angle bisection theorem, Similar Triangle, AAA similarity, SSA, SAS similarities Pythagoras theorem, Tangents to a circle, different properties of a tangent to a circle, segments of a chord, Common tangents to two circles. GEOMETRICAL CONSTRUCTIONS Construction of triangles, constructions involving concurrence lines, triangles and circles, harder cases, Geometrical constructions involving circles and tangents and triangles and quadrilaterals. 7. MENSURATION Square, rectangle, triangle, Quadrilateral, Circle, Ring (Annulus), Sector. Prism, total surface area of right prism, volume of a prism, Volume of a cube, Cuboids, The right pyramid, Cylinder, Hollow cylinder, Cylindrical shell, ratios of cylinders, cone, Hollow cone, solid cone, Curved surface area, total surface area, volume of a right circular cone, Sphere: Surface area of a
SA - Mathematics
Page 3
sphere, total surface area of a hemisphere, Volume of a sphere, Hollow hemisphere. 8. MATRICES Matrix Definition, Order of a matrix, Types of matrices, Equality of two matrices, Addition, Subtraction, multiplication of matrix, Product of two matrices, properties of products of matrices, transpose of matrix, properties, skew symmetric matrix, Adjoint and inverse of a matrix, simultaneous linear equations, types of system of simultaneous linear equations, consistency and inconsistency of Simultaneous equation. . Multiplicative inverse of a square matrix, singular and non singular matrix, solution of a system of linear equations in two variable using matrices determinants, properties of determinants, Matrix inverse method and Cramers , Inversion and Gauss Jordan method and Solving Equations Triangle matrices, properties of addition of matrices, sector multiple of a matrix 9. STATISTICS Cumulative frequency distribution, LCFD, GCFD, Frequency graphs, lesser then frequency distribution, Greater than frequency distribution. Central Tendency: means of the ungrouped data, Weighted AM, means grouped data, Merit and demerits of AM, Medians from ungrouped and grouped data, mode of ungrouped and grouped data, Empirical relation among mean, Median and mode. Probability: Random Experiments and Events, Definition, Axiomatic Approach, Independent and Dependent Events, Conditional Probability, Bayes Theorem, random variables , theoretical distributions. 10. COMPUTING Introduction to computers, Historic development of computers, Structure of a computer, working characteristics of Computers, Problem solving, flow charts and their representation, Operations box, Data box, Decision box, loops, Algorithm, Flow diagram using boxes for mechanics. 11. PROGRESSIONS Progressions: Common difference, nth term, sum of the first nth terms Arithmetic, Geometric and Harmonic Progressions and problems. AM, GM, HM and its Problems. 12. TRIGONOMETRY Unit of measurement of angles: Radian measure, relation between radian and degrees, 6 Trigonometric ratios and transformations, behavior of trigonometric functions, Trigonometric functions of complementary angles, trigonometrically tables. Inverse trigonometric functions, Hyperbolic Functions, Properties of Triangles, graphs and periodicity, Trigonometric ratios of compound angles, Trigonometric ratios of multiple and sub multiple angles, Angle of elevation and angle of depression, heights and distance. Trigonometric Expansions. 13. ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Distance between two points, Division of a segment internally and externally in a given ratio, slope, Area of triangle, The Straight Line; Pairs of St Lines. LOCUS, Transformation of Axes. Three Dimensional Geometry: Co-ordinates; Direction Cosines and Ratios; Cartesian equation of a plane. Circles and System of Circles, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola and polar coordinates.
SA - Mathematics
Page 4
Part IV Teaching Methodology (Marks: 16) 1. Meaning and nature of Mathematics, History of mathematics, How does History of Mathematics helps Teacher 2. History of Mathematics Aryabhatta, Bhaskaracharya, Srinivasa Ramanajain, Euclid, Pythagoras, George cantor. 3. Aims and values of teaching Mathematics, Instructional objective (Blooms taxonomy) 4. Curriculum of mathematics Principals of cumulus construction, organization of curriculum (Logical and psychological, topical and concentric Spiral approaches), Qualities of a good Mathematics, text book. 5. Methods of teaching mathematics- Heuristic method, laboratory method, Inductive and deductive methods, Analytic and synthetic methods project method and problem solving method. 6. Unit plan, year plan, lesson planning in mathematics. 7. Constructional materials is teaching mathematics, Edgar dales cone of experience. 8. Backwardness in the subject slow learners gifted learner identification, characteristics and remedial measures. 9. Mathematics teacher techniques of teaching mathematics like oral work, writer work, drilling, Asymmetry, project, speed and Accuracy. 10. Mathematics club, mathematics structure of mathematics order, pattern sequence. 11. Evaluation Types Tools and Teaching of Evaluation Preparation of SAT Analysis, Characteristics of a good test.
SA - Mathematics
Page 5
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Orthogonal Sets and Polar Methods in Linear Algebra: Applications to Matrix Calculations, Systems of Equations, Inequalities, and Linear ProgrammingD'EverandOrthogonal Sets and Polar Methods in Linear Algebra: Applications to Matrix Calculations, Systems of Equations, Inequalities, and Linear ProgrammingPas encore d'évaluation
- TRT - School Assistant Mathematics SyllabusDocument5 pagesTRT - School Assistant Mathematics Syllabusratna2k5Pas encore d'évaluation
- TGT - Mathematics Syllabus and Teaching MethodologyDocument3 pagesTGT - Mathematics Syllabus and Teaching MethodologyMadhusudan Reddy PinintiPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Matrix Algebra in the Statistical SciencesD'EverandApplied Matrix Algebra in the Statistical SciencesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Higher Secondary School Teacher (Junior) (Mathematics) Kerala Higher Secondary EducationDocument6 pagesHigher Secondary School Teacher (Junior) (Mathematics) Kerala Higher Secondary EducationIbrahim MeharoofPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Techniques for Transportation EngineeringD'EverandStatistical Techniques for Transportation EngineeringÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- UPSC SCRA Mathematics SyllabusDocument33 pagesUPSC SCRA Mathematics SyllabusAditya Pratap Singh SengarPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE (Advanced) 2024: Syllabus: MathematicsDocument3 pagesJEE (Advanced) 2024: Syllabus: Mathematicsrbqjm9jv4zPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument8 pagesDepartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology PatnaGargi SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus-PGT - Math FDocument5 pagesSyllabus-PGT - Math Fsahudebashis2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Detailes Syllabus Lecturer in MathsDocument5 pagesDetailes Syllabus Lecturer in MathsmiscPas encore d'évaluation
- RPSC Lecturer Exam Syllabus for MathematicsDocument6 pagesRPSC Lecturer Exam Syllabus for MathematicsGajen BishnoiPas encore d'évaluation
- RPSSC SR Teacher Exam Math SyllabusDocument6 pagesRPSSC SR Teacher Exam Math Syllabussanju kumari meenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus PGTsDocument54 pagesSyllabus PGTspriyambada biswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Prilims: Syllabus of Paper I (General Studies - I)Document3 pagesPrilims: Syllabus of Paper I (General Studies - I)Akella Surya Prakasa DeekshithPas encore d'évaluation
- M-SET Mathematical Sciences SyllabusDocument5 pagesM-SET Mathematical Sciences SyllabusTeertha SomanPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths SyllabusDocument2 pagesMaths SyllabusNeerajPrabhakaranPas encore d'évaluation
- HNB Garhwal University B.A./B.Sc. SyllabusDocument11 pagesHNB Garhwal University B.A./B.Sc. SyllabusMandar Priya PhatakPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Topics Part IVDocument3 pagesMaths Topics Part IVDeepika PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusSECRET ButterflyPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus For The Course of M.Phil/Ph.D Session 2010-11: R Z Q Dy P DXDocument2 pagesSyllabus For The Course of M.Phil/Ph.D Session 2010-11: R Z Q Dy P DXRehaan FayazPas encore d'évaluation
- Upsc Syllabus Converted 2509042eDocument8 pagesUpsc Syllabus Converted 2509042eShivan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- VITEEE2018 Mathematics PDFDocument2 pagesVITEEE2018 Mathematics PDFmn m,n m, bmPas encore d'évaluation
- Viteee - 2020-MathematicsDocument2 pagesViteee - 2020-MathematicsSwaroop BijuPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Syllabus PDFDocument5 pagesMathematics Syllabus PDFLETCHUMY A/P MARIPAN MoePas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra - Inder Sir - DemoDocument45 pagesLinear Algebra - Inder Sir - DemoGnanam SekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- B.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Document10 pagesB.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Najeeb FatimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Syllabus 2021: Unit-1: Algebra, Number Theory and Linear AlgebraDocument3 pagesMathematics Syllabus 2021: Unit-1: Algebra, Number Theory and Linear AlgebraPriyadrshani nayakPas encore d'évaluation
- std12 Maths em 1Document297 pagesstd12 Maths em 1api-320105488Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics 7lKqzNJDocument2 pagesMathematics 7lKqzNJAgony busterPas encore d'évaluation
- CSIR NET Mathematical Sciences SyllabusDocument4 pagesCSIR NET Mathematical Sciences Syllabuskumar HarshPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Syllabus - 01 MainDocument16 pagesJEE Syllabus - 01 MainVijay PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Syllabus SAEEE 2024Document7 pagesMaths Syllabus SAEEE 2024Pavithra JPas encore d'évaluation
- B.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Document10 pagesB.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Upperwala RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ojee Btech 2023Document4 pagesOjee Btech 2023Jerry MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- CSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test (NET) For Junior Research Fellowship and Lecturer-Ship Mathematical Sciences Unit 1Document4 pagesCSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test (NET) For Junior Research Fellowship and Lecturer-Ship Mathematical Sciences Unit 1Faiz ImamPas encore d'évaluation
- MTE-01 Calculus 4 Credits:, Cos SinDocument14 pagesMTE-01 Calculus 4 Credits:, Cos SinNepsonPas encore d'évaluation
- C Math-1001Document1 pageC Math-1001Muhammad UmerPas encore d'évaluation
- mathmeticascience_syllbusDocument4 pagesmathmeticascience_syllbusjayasankari kumariPas encore d'évaluation
- Kumaun University, Nainital Department of Mathematics: B.A./B. Sc. Mathematics Course Structure (Semester System)Document7 pagesKumaun University, Nainital Department of Mathematics: B.A./B. Sc. Mathematics Course Structure (Semester System)Ashutosh NegiPas encore d'évaluation
- Joint Entrance Examination (Advanced) - 2014 Indian Institutes of TechnologyDocument3 pagesJoint Entrance Examination (Advanced) - 2014 Indian Institutes of TechnologyAvinash TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- VIT Maths SyllabusDocument2 pagesVIT Maths SyllabusAnudeex ShettyPas encore d'évaluation
- RBI Syllabus (Phase-II) Paper DetailsDocument7 pagesRBI Syllabus (Phase-II) Paper DetailsGaurav GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE (Main) - Mathematics Syllabus: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsDocument5 pagesJEE (Main) - Mathematics Syllabus: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsSahithReddyRegattePas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics FinalDocument731 pagesMathematics FinalChanduPas encore d'évaluation
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabussourav gangulyPas encore d'évaluation
- Master Syllabus (Iit-Jam, M-Stats and Some PG Diploma in Isi)Document18 pagesMaster Syllabus (Iit-Jam, M-Stats and Some PG Diploma in Isi)Sakshi ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- MYP_Gr 9_Topic Sheet_2023-24Document2 pagesMYP_Gr 9_Topic Sheet_2023-24shikhaPas encore d'évaluation
- GATE-Mathematics-K Manikantta Reddy (Gate2016.info) PDFDocument231 pagesGATE-Mathematics-K Manikantta Reddy (Gate2016.info) PDFvishalkhorwalPas encore d'évaluation
- M.a.M.sc. Part I Mathematics (Ext - Reg I) 09Document25 pagesM.a.M.sc. Part I Mathematics (Ext - Reg I) 09Hitesh RathorePas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main 2023 Maths SyllabusDocument4 pagesJEE Main 2023 Maths SyllabusTieaglePas encore d'évaluation
- Jee Main Mathematics SyllabusDocument3 pagesJee Main Mathematics SyllabusexamfarraPas encore d'évaluation
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusQader KarimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Real Analysis: (Review: Elementary Set Theory, Finite, CountableDocument3 pagesReal Analysis: (Review: Elementary Set Theory, Finite, CountablelukasPas encore d'évaluation
- Sust Math SyllabusDocument12 pagesSust Math SyllabusMohanned KhairyPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Mains Advanced Latest SyllabusDocument24 pagesJEE Mains Advanced Latest SyllabusViki HPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Science M.Sc. / M.A. (Statistics)Document3 pagesFaculty of Science M.Sc. / M.A. (Statistics)Gaurav VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Mathematics: Topicwise Previous GATE Solved Questions of CE, ME, EE, EC, IN & CS/IT: 2003-2015Document8 pagesEngineering Mathematics: Topicwise Previous GATE Solved Questions of CE, ME, EE, EC, IN & CS/IT: 2003-2015Divyanshu SemwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate Aerospace Notes PDFDocument231 pagesGate Aerospace Notes PDFபிரகதீஸ்வரன் தமிழன்100% (3)
- The Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation BillDocument63 pagesThe Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Billnavn76Pas encore d'évaluation
- Appsc Typist PaperDocument6 pagesAppsc Typist PaperRaghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Nalgonda Vro NotifiactionDocument3 pagesNalgonda Vro NotifiactionSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- Tgbill TeluguDocument57 pagesTgbill TeluguSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- APPSC Junior MarketingDocument6 pagesAPPSC Junior MarketingSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- DSC2012 Community Female NALGONDADocument265 pagesDSC2012 Community Female NALGONDASURESHKUMAR BANDARU100% (1)
- DSC 2012 General Merit List RangareddyDocument501 pagesDSC 2012 General Merit List RangareddySURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- APTETDocument2 pagesAPTETSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- Kama Sutra TeluguDocument792 pagesKama Sutra TeluguSURESHKUMAR BANDARU72% (242)
- APCET 2012 ResultsDocument54 pagesAPCET 2012 Resultsaleem_shaik7308Pas encore d'évaluation
- DSC2012 General NalgondaDocument645 pagesDSC2012 General NalgondaSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- Appsc Draughtsman PaperDocument7 pagesAppsc Draughtsman PaperSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- DSC2012 Community NalgondaDocument630 pagesDSC2012 Community NalgondaSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- Dy SurveyorDocument11 pagesDy SurveyorRaghu100% (2)
- Computer Draughtsman GS KEYDocument7 pagesComputer Draughtsman GS KEYSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- Appsc Group 1 2012 KeyDocument7 pagesAppsc Group 1 2012 KeySURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- Sa SSDocument7 pagesSa SSSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- APPSC ASO General Studies Model PaperDocument7 pagesAPPSC ASO General Studies Model PaperRavi LorventPas encore d'évaluation
- SGT TeluguDocument9 pagesSGT TeluguSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- Sa PSDocument8 pagesSa PSSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- Appsc Fro Solved PaperDocument11 pagesAppsc Fro Solved PaperSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- SA MathsDocument5 pagesSA MathsSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- TRT – 2012 Category of Post: School Assistant - Bio-Sciences SyllabusDocument3 pagesTRT – 2012 Category of Post: School Assistant - Bio-Sciences Syllabusmadhujo123Pas encore d'évaluation
- SA TeluguDocument2 pagesSA TeluguSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- SA EnglishDocument3 pagesSA EnglishSURESHKUMAR BANDARUPas encore d'évaluation
- DSC PetDocument3 pagesDSC PetraghavendrapavuluriPas encore d'évaluation
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (8)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormD'EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsD'EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeD'EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenD'EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingD'EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusD'EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Psychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideD'EverandPsychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathD'EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormD'EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (20)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)D'EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Pas encore d'évaluation
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsD'EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (9)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.D'EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldD'EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (79)
- Math Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsD'EverandMath Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (15)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorD'EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceD'EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidencePas encore d'évaluation
- Classroom-Ready Number Talks for Kindergarten, First and Second Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Activities and Strategies that Teach Number Sense and Math FactsD'EverandClassroom-Ready Number Talks for Kindergarten, First and Second Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Activities and Strategies that Teach Number Sense and Math FactsPas encore d'évaluation
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersD'EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)