Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan (RPT) Sains Tahun 4, 201 2: Theme: Investigating Living Things
Transféré par
Chris TeoDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan (RPT) Sains Tahun 4, 201 2: Theme: Investigating Living Things
Transféré par
Chris TeoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
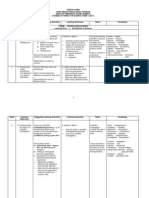
RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN TAHUNAN (RPT) SAINS TAHUN 4, 2012
THEME : INVESTIGATING LIVING THINGS
SC/Y4/ - 12 -
WEEK
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1.1 Understanding that humans have a basic needs 1.2 Understanding that animals have a basic needs
1 (6/1) 2 (13/1)
1.Living things have a basic needs
3 (20/1) 4 (27/1)
1.3 Understanding that plants have basic needs 2.1 Analyzing life processes that humans undergo
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils identify the basic needs of humans Pupils give reasons why humans need food, water, air and shelter Pupils identify the basic needs of animals Pupils give reasons why animals need food, water, air and shelter. Pupils describe types of shelters for animals. Pupils identify the basic needs of plants
NOTE
SPS : - Predicting - Observing - Communicating - Making Inferences CTS - Group and Classifying - Analyzing -Evaluating SPS : - Predicting - Observing - Communicating - Making Inferences -Making Hypotheses CTS - Group and Classifying - Analyzing -Evaluating - Making conclusions
5 (3/2) 6 (10/2)
7 17/2
2.2 Being aware that certain behaviors can disturb life processes.
Pupils Explain that humans breathe. Describe what inhale is Describe what exhale is. Differentiate the air that we inhale and the air that we exhale State that humans use lungs to breathe. Identify the passage of air during breathing. Conclude that not all individuals have the same rate of breathing State that human excrete and defecate. State the product of human excretion. State the product of human defecation. Give reasons why humans need to excrete and defecate. State humans respond to stimuli. Give reasons why humans responds to stimuli State that humans reproduce Predict what will happen if humans do not reproduce. Pupils Give example of habits that bring harm to humans life processes. State the effect of smoking on lungs. Explain that taking drugs and alcohol can delay a persons response to stimuli. Participate in a campaign to discourage smoking, drugs taking and alcohol drinking among their peers. SC/Y4/ - 12 -
SPS : - Predicting - Observing - Communicating - Making Inferences -Making Hypotheses CTS - Group and Classifying - Analysing -Evaluating - Making conclusions
2. Living things undergo life processes
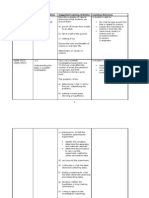
THEME : INVESTIGATING FORCE AND ENERGY.
SC/Y4/ - 12 -
WEEK 13 (6/4)
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1.1Understanding the measurement of length.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils State the different ways to measurement length. State the standard unit for length in the metric system. Choose the appropriate measurement tools to measure length. Measure length using the correct technique. Record lengths in standard units. Pupils Compare a square and a rectangle and guess which object has a bigger area. Carry out a test to confirm their guesses. State that area= length X width. State the standard unit for area in the metric system. Calculate the area of a given shape in metrics system. Pupils Compare a cube and cuboids and guess which one bigger volume. Carry out a test to confirm their guesses. State that volume = length X width X height. State the standard unit for volume of solids in the metric system. Calculate the volumes of cubes and cuboids based on the measurements taken in standard unit. Pupils State the different ways to measure the volume of a liquid. State the standard units for volume of liquid in the metric system. Choose the appropriate measuring tools to measure the volume of a liquid. Measure the volume of a liquid using the correct technique. Record the volume measured in a metric system. Pupils State tools for measuring mass State the standard unit for mass in the metric system. Measure the mass of an object using the correct SC/Y4/ - 12 technique. Record the measurement using standard unit. Pupils
NOTES SPS : - Predicting - Observing Communicating - Making Inferences -Making Hypotheses CTS - Group and Classifying - Analysing -Evaluating - Making conclusions
1.2 Understanding how to calculate area. 14 (13/4)
1.3 Understanding how to measure the volume of solid 15 (20/4)
16 (27/4)
1.4 Understanding how to measure volume of liquid.
1. Measurement
17 (4/5)
1.5 Understanding how to measure mass.
1.6 Understanding how to
PENGGAL KEDUA (2) 2011 THEME: INVESTIGATING MATERIALS
SC/Y4/ - 12 -
WEEK 21 (15/6) 22 (22/6)
LEARNING AREA 1. Properties of materials
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils Classify objects into groups according to the materials they are made of. Identify materials that conduct electricity. Identify materials that conduct heat. Identify materials that float on water. Identify materials that absorb water. Identify materials that can be stretched. Identify materials that allow light to pass through. State what a conductor is. State what an insulator is. Conclude that a good conductor of heat is also good conductor of electricity. Classify materials based on their abilities to allow light pass through. State what a transparent material is. State what a translucent material is. State what an opaque material is. List uses of transparent, translucent and opaque marerials.
NOTE
23 (29/6)
1.1 Understanding the properties of materials.
SPS : - Predicting - Observing - Communicating - Making Inferences -Making Hypotheses CTS - Group and Classifying - Analysing -Evaluating - Making conclusions
24 (6/7)
25 (13/7)
26 (20/7)
27 ( 27/7) 28
1.2 Applying the knowledge of Pupils properties of materials in Suggest ways to keep things cold. everyday life. Suggest ways to keep things hot. Design an effective way to keep things hot or to keep things cold. 1.3 Synhesising the knowledge Pupils about uses of materials based List objects and the materials that they are made. on their properties. Give reasons why particular materials are used to make an object. State that materials are chosen to make an object based on their properties. Design an object for a specific purpose and give reasons why certain materials are used to make it. 1.4 Knowing the importance Pupils of reuse, reduce and recycle of Give example of natural materials. materials. Give example of man-made materials. SC/Y4/ - 12 State that man-made materials come from natural materials. Give reasons why materials need to be conserved.
SPS : - Predicting - Observing - Communicating - Making Inferences -Making Hypotheses CTS - Group and Classifying - Analysing -Evaluating - Making conclusions
THEME : INVESTIGATING THE EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE WEEK 33 (14/9) LEARNING AREA LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1.1 Understanding the Solar System LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils List the constituents of the Solar System List the planets in the Solar System in a sequence. State that planets move around the Sun Pupils State the size of the Sun relative to the size of the Earth State the size of the Earth relative to the size of the Moon. State the relative distance from the Earth to the Sun compared to the Relative distance from the Moon to the Earth. Pupils State why certain planets are not conducive for living things. Predict what will happen if the Earth is placed much nearer or farther from the Sun. Conclude that the Earth is the only planet in the Solar System that has living things. NOTE SPS : - Predicting - Observing Communicating - Making Inferences -Making Hypotheses CTS - Group and Classifying - Analysing -Evaluating - Making conclusions
34 (21/9) 1. The solar system
1.2 Understanding the relative size and distance between the Earth , the Moon and the Sun.
35 (28/9) 36 (5/10)
1.3 Appreciating the perfect of the planet Earth in the Solar System.
SC/Y4/ - 12 -
THEME : INVESTIGATING TECHNOLOGY WEEK LEARNING AREA LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1.1 understanding the importance of technology in everyday life. LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils State that there are limitations to humans abilities to do things Identify devices used to overcome humans limitations. Explain how certain devices are used to overcome humans limitation. Pupils Give example of development of technology Recognise the needs to innovate or invent devices for the betterment of mankind. Pupils Identify problems they encounter in their daily life. Generate ideas to solve the problems identified. Design a device to solve the problem identified. Demonstrate how the device invented can be used to solve the problem identified. Pupils State that technology has advantages and disadvantages. Conclude that technology can benefit mankind if used wisely. NOTE
37 (12/10)
38 (19/10) 1. Technology 39 (2/11)
1.2 Understanding the development of technology
1.3 Synthesising how technology can be used to solve problems.
SPS : - Predicting - Observing Communicating - Making Inferences -Making Hypotheses CTS - Group and Classifying - Analysing -Evaluating - Making conclusions
40 (9/11)
1.4 Analysing that technology can benefit mankind if used wisely.
SC/Y4/ - 12 -
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ubd Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesUbd Lesson PlanLove BorjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8 - Science in Action - Topics ABC - Lesson PlansDocument446 pagesScience 8 - Science in Action - Topics ABC - Lesson PlansLizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Secondary 1 Science Curriculum FrameworkDocument14 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 Science Curriculum Frameworkapi-217350410100% (3)
- Science 9-Chemistry Unit PlanDocument8 pagesScience 9-Chemistry Unit PlanLauren NovakPas encore d'évaluation
- Science and the Global Environment: Case Studies for Integrating Science and the Global EnvironmentD'EverandScience and the Global Environment: Case Studies for Integrating Science and the Global EnvironmentPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT SCIENCE YEAR 4 EXAMINES LIVING THINGS AND FORCESDocument14 pagesRPT SCIENCE YEAR 4 EXAMINES LIVING THINGS AND FORCESMohammad FadzliPas encore d'évaluation
- Orientation Programme For Form 1 StudentsDocument24 pagesOrientation Programme For Form 1 StudentsVictor ManivelPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Form 1 EditedDocument15 pagesYearly Plan Form 1 EditedDianasalmie AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Planning Science1 EditedDocument24 pagesYearly Planning Science1 Editedalena67Pas encore d'évaluation
- RPT SC Form 1Document22 pagesRPT SC Form 1Norhidayah Binti PazilPas encore d'évaluation
- Weeks: Science Form 1 Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyDocument23 pagesWeeks: Science Form 1 Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyAsmanura YahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Minggu 12 (2 April - 6 April)Document7 pagesMinggu 12 (2 April - 6 April)Nor HayatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introducing Science WeekDocument26 pagesIntroducing Science WeekSahrulRashidPas encore d'évaluation
- Constructscoreandcriteria Peka - 2Document99 pagesConstructscoreandcriteria Peka - 2Che Sharifuddin IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- Observation and Questioning: Summary: Students Will Explore The Nature and Process of ScienceDocument19 pagesObservation and Questioning: Summary: Students Will Explore The Nature and Process of ScienceKenneth AtokPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th Science Scheme of Work Semester IDocument9 pages4th Science Scheme of Work Semester IEzhilita EzhillPas encore d'évaluation
- Hs Science StandardsDocument16 pagesHs Science Standardsapi-271737972Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Supplement eDocument52 pagesBio Supplement eTom ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Area Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesLearning Area Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomesnor shafiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 1 Yearly Plan Theme Learning Area and Learning Objectives Vol/Page WeekDocument22 pagesScience Form 1 Yearly Plan Theme Learning Area and Learning Objectives Vol/Page WeekSaya DiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Map (1) From OtherDocument20 pagesCurriculum Map (1) From Otherapi-281972267Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Science Year 1Document45 pagesIntegrated Science Year 1Andre Swaggerific PickettPas encore d'évaluation
- Jhs Integrated Science Jan 2012 - FinalDocument50 pagesJhs Integrated Science Jan 2012 - FinalNanaleo0% (2)
- Science Yearly Plan Year 6 2013Document12 pagesScience Yearly Plan Year 6 2013Su ReshPas encore d'évaluation
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bukit Guntong Subject: Science Form: 1Document9 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bukit Guntong Subject: Science Form: 1Santhiya MadhavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan For Science Form 1Document9 pagesYearly Plan For Science Form 1untatahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Lesson in The BoxDocument6 pagesScience Lesson in The Boxapi-340404014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Science Curriculum FrameworkDocument18 pagesPrimary Science Curriculum Frameworkstraf238100% (1)
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Noralizah IsmadiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 3 and 2 3Document8 pages2 3 and 2 3api-366807311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science 9-Chemistry Unit PlanDocument8 pagesScience 9-Chemistry Unit PlanLauren NovakPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 Chemistry Unit Planner 1 2015 16Document14 pagesGrade 8 Chemistry Unit Planner 1 2015 16Anupa Medhekar100% (9)
- Title of Unit: Evolution Grade Level: 10th Grade Subject: Biology Time Frame: Five WeeksDocument8 pagesTitle of Unit: Evolution Grade Level: 10th Grade Subject: Biology Time Frame: Five Weeksapi-281582336Pas encore d'évaluation
- RPT: Understanding Science Form 1Document9 pagesRPT: Understanding Science Form 1Choo Li MingPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade Four Science: Aligned To Alberta CurriculumDocument18 pagesGrade Four Science: Aligned To Alberta CurriculummurondarabbiePas encore d'évaluation
- Year Planner (f1) LatestDocument13 pagesYear Planner (f1) LatestNor ShakeelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Research Designs (Calcmorin) : When To Use Historical Research?Document4 pagesMajor Research Designs (Calcmorin) : When To Use Historical Research?Habin PermantanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Plan CDocument6 pagesUnit Plan Capi-535301706Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Document9 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1adleenshazPas encore d'évaluation
- Sciences 7Document4 pagesSciences 7api-235829794Pas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Sains Ting. 1Document10 pagesRPT Sains Ting. 1Norzaliatun RamliPas encore d'évaluation
- Yr 1 CurriculumdocsDocument54 pagesYr 1 CurriculumdocsShiela Dela Rosa PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Plan Part BDocument6 pagesUnit Plan Part Bapi-535301706Pas encore d'évaluation
- snc1p SyllabusDocument3 pagessnc1p Syllabusapi-100040718Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science Course OutlineDocument4 pagesScience Course OutlineJack LovinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit PhysicsDocument5 pagesUnit Physicsapi-222512017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science 7 Unit Plan Interactions and EcosystemsDocument20 pagesScience 7 Unit Plan Interactions and Ecosystemsapi-266874931Pas encore d'évaluation
- Framework Science1 VirginiaDocument26 pagesFramework Science1 Virginiagamjaam7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tia - Science PracDocument4 pagesTia - Science Pracapi-460354727Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kontrak SC Yr 6Document9 pagesKontrak SC Yr 6Shafinaz SaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual For Chemistry A Molecular Approach With Masteringchemistry 2Nd Edition by Tro Isbn 0321706153 9780321706157 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry A Molecular Approach With Masteringchemistry 2Nd Edition by Tro Isbn 0321706153 9780321706157 Full Chapter PDFthomas.chatman911100% (9)
- Science Programmes of Study: Key Stage 4: National Curriculum in EnglandDocument18 pagesScience Programmes of Study: Key Stage 4: National Curriculum in EnglandRoger HoodPas encore d'évaluation
- snc2p SyllabusDocument3 pagessnc2p Syllabusapi-100040718Pas encore d'évaluation
- STS PrelimDocument8 pagesSTS PrelimCrestinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan 1 Water CycleDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 1 Water Cycleapi-624400995Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Science Year 6Document15 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 6Diana LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1: What Is Environmental ScienceDocument3 pagesModule 1: What Is Environmental ScienceShaneilPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantitative Ecology: Measurement, Models and ScalingD'EverandQuantitative Ecology: Measurement, Models and ScalingPas encore d'évaluation
- The NSTA Quick-Reference Guide to the NGSS, Middle SchoolD'EverandThe NSTA Quick-Reference Guide to the NGSS, Middle SchoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Strategy of Air-Conditioning Companies: Project SynopsisDocument13 pagesMarketing Strategy of Air-Conditioning Companies: Project SynopsisSrikanta ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Plug & Socket TypesDocument49 pagesPlug & Socket TypeskerissaktiemasPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolis User ManualDocument28 pagesEvolis User ManualIonmadalin1000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Exchanger Design and Drawing FundamentalsDocument11 pagesHeat Exchanger Design and Drawing Fundamentalsjeevanantham 5846Pas encore d'évaluation
- Traffic Sign Detection and Recognition Using Image ProcessingDocument7 pagesTraffic Sign Detection and Recognition Using Image ProcessingIJRASETPublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Uv Spectrophotometric Estimation of Carvedilol Hydrochloride by First Order Derivative and Area Under Curve Methods in Bulk and PH PDFDocument7 pagesUv Spectrophotometric Estimation of Carvedilol Hydrochloride by First Order Derivative and Area Under Curve Methods in Bulk and PH PDFMeilia SuhermanPas encore d'évaluation
- PENERAPAN ARSITEKTUR TROPIS PADA HOTEL RESORT DI PANTAI KRAKALDocument12 pagesPENERAPAN ARSITEKTUR TROPIS PADA HOTEL RESORT DI PANTAI KRAKALleo adoPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Introduction To Ecology and The BiosphereDocument38 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Ecology and The BiosphereFrancis Rey Bactol PilapilPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloning of CELLDocument43 pagesCloning of CELLsashaikh1213Pas encore d'évaluation
- Boutique Olive Oil Machines Catalogue ENG5Document33 pagesBoutique Olive Oil Machines Catalogue ENG5Younesse EL BraiPas encore d'évaluation
- El DoradoDocument12 pagesEl Doradoandrewwilliampalileo@yahoocomPas encore d'évaluation
- 19174the Rise of Industrial Big Data WP Gft834Document6 pages19174the Rise of Industrial Big Data WP Gft834em01803257Pas encore d'évaluation
- Christmas Around the WorldDocument16 pagesChristmas Around the WorldVioleta Veljanovska100% (1)
- 692pu 6 6Document1 page692pu 6 6Diego GodoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unchained MelodeeDocument93 pagesUnchained MelodeeRafael Cornholio RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Plan of Easy Meal ServiceDocument41 pagesBusiness Plan of Easy Meal ServiceCeddie UnggayPas encore d'évaluation
- Orpheus' Tragic Love and Quest to Save EurydiceDocument3 pagesOrpheus' Tragic Love and Quest to Save EurydiceShiedrose Allaina ArangorinPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 Project ManagementDocument19 pagesUnit 5 Project ManagementYashu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Rooftop Solar PV Opportunity in Tempe, Arizona: A Consultancy PlanDocument4 pagesRooftop Solar PV Opportunity in Tempe, Arizona: A Consultancy PlanAli KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Anhydrous Ammonia Unloading Station & Storage/Vaporizer SystemDocument2 pagesAnhydrous Ammonia Unloading Station & Storage/Vaporizer SystemWalter Rigamonti100% (1)
- User ManualDocument14 pagesUser ManualKhaled BellegdyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ichroma™ COVID-19 Ab (With Ichroma™ II Reader) Test SystemDocument6 pagesIchroma™ COVID-19 Ab (With Ichroma™ II Reader) Test SystemGopinath AgnihotramPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise 2 Mole-Mole Mass-Mass: Sorsogon State CollegeDocument2 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise 2 Mole-Mole Mass-Mass: Sorsogon State CollegeJhon dave SurbanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Operational Transconductance Amplifier ThesisDocument6 pagesOperational Transconductance Amplifier ThesislaurahallportlandPas encore d'évaluation
- Prometheus BoundDocument10 pagesPrometheus BoundPhillip HosfeldtPas encore d'évaluation
- ASSIGNMENTDocument10 pagesASSIGNMENTKoleen Lopez ÜPas encore d'évaluation
- 03-Mechanical Seal &seal System Basics-REV01Document39 pages03-Mechanical Seal &seal System Basics-REV01Fayez Al-ahmadiPas encore d'évaluation
- ABS Fire Extinguisher CatalogueDocument56 pagesABS Fire Extinguisher CatalogueqwertyPas encore d'évaluation
- On The Problem of The External World in The Ch'Eng Wei Shih LunDocument64 pagesOn The Problem of The External World in The Ch'Eng Wei Shih LunGuhyaprajñāmitra3100% (1)
- Research PaperDocument13 pagesResearch PaperHamid ElmyPas encore d'évaluation