Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Human Skin - The Sense of Touch: Receptors - Special Sensory Structures in Your Skin Ends (Terminal Branches of
Transféré par
dindi1818Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Human Skin - The Sense of Touch: Receptors - Special Sensory Structures in Your Skin Ends (Terminal Branches of
Transféré par
dindi1818Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Human Skin The Sense of Touch
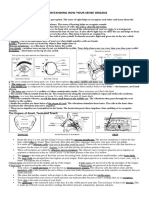
While your other four senses (sight, hearing, smell, and taste) are located in specific parts of the body, your sense of touch is found all over. This is because your sense of touch originates in the bottom layer of your skin called the dermis. The dermis is filled with many tiny nerve endings which give you information about the things with which your body comes in contact. They do this by carrying the information to the spinal cord, which sends messages to the brain where the feeling is registered.
Receptors special sensory structures in your skin ends (terminal branches of dendrites of sensory neurons)
each receptor is suited to receive only one type of stimulus and to start
impulses to the central nervous system
there are receptors for touch, pain, pressure, heat and cold
There are many pain receptors distributed throughout your skin. However, receptors that respond to pressure and touch lie deeper. If one presses something against your skin, you feel both pressure and touch.
The Tongue - The Sense of Taste
Taste buds probably play the most important part in helping you enjoy the many flavors of food. Your taste buds can recognize four basic kinds of tastes: sweet, salty, sour, and bitter. The salty/sweet taste buds are located near the front of your tongue; the sour taste buds line the sides of your tongue; and the bitter taste buds are found at the very back of your tongue.
Everyone's tastes are different. In fact, your tastes will change as you get older. When you were a baby, you had taste buds, not only on your tongue, but on the sides and roof of your mouth. This means you were very sensitive to different foods. As you grew, the taste buds began to disappear from the sides and roof of your mouth, leaving taste buds mostly on your tongue. As you get older, your taste buds will become even less sensitive, so you will be more likely to eat foods that you thought were too strong as a child.
Taste results from the chemical stimulation of certain nerve endings Your sense of taste is centered in the taste buds distributed unevenly over the surface of your tongue. They contain taste receptors. You are able to taste food as it mixes with your saliva and enters the pores of the taste buds. The nerve endings are then stimulated by the presence of food.
The Nose The Sense of Smell
Smell results from the chemical stimulation of the nerves, except the odors are in the form of gases. Turbinates the nasal passages found in three layers of cavities separated by bony layers
The upper turbinate contains branched endings of the olfactory nerve, a
sensory cranial nerve. The stimulation of these endings by odors results in the sensation of smell Smell receptors neurons embedded in the lining of your nose The axons of the neurons compose the nerves in your nose.
Seven Primary Odors Odor Camp horic Musky Roses Pepper minty Ethera l Punge nt Putrid Example Mothballs Perfume/Afte rshave Floral Mint Gum Dry Cleaning Fluid Vinegar Rotten Eggs
The Ear The Sense of Hearing and Balance How You Hear
When an object makes a noise, it sends vibrations (better known as sound waves) speeding through the air. These vibrations are then funneled into your ear canal by your outer ear. As the vibrations move into your middle ear, they hit your eardrum and cause it to vibrate as well. This sets off a chain reaction of vibrations. Your eardrum, which is smaller and thinner than the nail on your pinky finger, vibrates the three smallest bones in your body: first, the hammer, then the anvil, and finally, the stirrup. The stirrup passes the vibrations into a coiled tube in the inner ear called the cochlea.
The fluid-filled cochlea contains thousands of hair-like nerve endings called cilia. When the stirrup causes the fluid in the cochlea to vibrate, the cilia move. The cilia change the vibrations into messages that are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve carries messages from 25,000 receptors in your ear to your brain. Your brain then makes sense of the messages and tells you what sounds you are hearing.
How You Keep Your Balance
Near the top of the cochlea are three loops called the semi-circular canals. The canals are full of liquid also. When you move your head, the liquid moves. It pushes against hairlike nerve endings, which send messages to your brain. From these messages, your brain can tell whether or how your body is moving.
If you have ever felt dizzy after having spun around on a carnival ride, it was probably because the liquid inside the semicircular canals swirled around inside your ears. This makes the hairs of the sensory cells bend in all different directions, so the cells' signals confuse your brain.
The Eye The Sense of Sight
When light rays pass through your pupil, the muscle called the iris (colored ring) makes the size of the pupil change depending on the amount of light that's available. If there is too much light, your pupil will shrink to limit the number of light rays that enter. Likewise, if there is very little light available, the pupil will enlarge to let in as many light rays as it can. Just behind the pupil is the lens and it focuses the image through a jelly-like substance called the vitreous humor onto the back surface of the eyeball, called the retina. The retina, which is the size of your thumbnail, is filled with approximately 150 million light-sensitive cells called rods and cones. Rods identify shapes and work best in dim light. Cones on the other hand, identify color and work best in bright light. Both of these types of cells then send the information to the brain by way of the optic nerve. The amazing thing is, when they send the image to the brain, the image is upside down! It is the brain's job to turn the image rightside up
and then tell you what you are looking at. The brain does this in a specific place called the visual cortex.
Protection
The eyebrows are the strips of hair above your eyes which prevent sweat from running into them. Eyelashes help keep the eye clean by collecting small dirt and dust particles floating through the air. The eyelashes also protect the eye from the sun's and other light's glare. The eyelids sweep dirt from the surface of the eye. The eyelid also protects the eye from injury. Tears are sterile drops of clean water which constantly bathe the front of the eye, keeping it clean and moist.
Imperfect Eyesight
People who can see things up close, but not far away are considered to be nearsighted. This happens when the light entering the eye focuses on a point in front of the retina. On the other hand, people who can see far away objects but not those that are up close are farsighted. Farsightedness occurs when the light that enters the eye focuses on a point behind the retina. Whether a person is nearsighted or farsighted, glasses or contacts help that person to see things much more clearly.
TRIVIAS
You have more pain nerve endings than any other type. The least sensitive part of your body is the middle of your back.
The most sensitive areas of your body are your hands, lips, face, neck, tongue, fingertips and feet. Shivering is a way your body has of trying to get warmer. There are about 100 touch receptors in each of your fingertips. Rattlesnakes use their skin to feel the body heat of other animals. We have almost 10,000 taste buds inside our mouths; even on the roofs of our mouths. Insects have the most highly developed sense of taste. They have taste organs on their feet, antennae, and mouthparts. Fish can taste with their fins and tail as well as their mouth.
In general, girls have more tastebuds than boys.
Taste is the weakest of the five senses. Dogs have 1 million smell cells per nostril and their smell cells are 100 times larger than humans! Humans use insect warning chemicals, called pheromones, to keep away pesky insects! People who cannot smell have a condition called Anosmia. If your nose is at its best, you can tell the difference between 4000-10,000 smells! As you get older, your sense of smell gets worse. Children are more likely to have better senses of smell than their parents or grandparents. Babies can get earaches because of milk backing up in the Eustachian tube, which causes bacteria to grow and may cause hearing problems later in life. When you go up to high elevations, the change in pressure causes your ears to pop. Children have more sensitive ears than adults. They can recognize a wider variety of noises. Dolphins have the best sense of hearing among animals. They are able to hear 14 times better than humans. Animals hear more sounds than humans. An earache is caused by too much fluid putting pressure on your eardrum. Earaches are often the result of an infection, allergies or a virus. Most people blink every 2-10 seconds. Each time you blink, you shut your eyes for 0.3 seconds, which means your eyes are closed at least 30 minutes a day just from blinking. If you only had one eye, everything would appear twodimensional. (This does not work just by closing one eye.) Owls can see a mouse moving over 150 feet away with light no brighter than a candle. The reason cat's and dog's eyes glow at night is because of silver mirrors in the back of their eyes called the tapetum. This makes it easier for them to see at night.
An ostrich has eyes that are two inches across. Each eye weighs more than the brain. A chameleon's eyes can look in opposite directions at the same time. A newborn baby sees the world upside down because it takes some time for the baby's brain to learn to turn the picture rightside up. One in every twelve males is color blind.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Look, Listen, Taste, Touch, and Smell: Learning About Your Five SensesD'EverandLook, Listen, Taste, Touch, and Smell: Learning About Your Five SensesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (9)
- Key Nursing SkillsDocument359 pagesKey Nursing Skillsmordanga100% (6)
- User Manual: Samsung Medison Diagnostic Ultrasound SystemDocument686 pagesUser Manual: Samsung Medison Diagnostic Ultrasound SystemHuế Trần100% (1)
- The Five SensesDocument15 pagesThe Five SensesMy name is傻逼Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Five SensesDocument15 pagesThe Five SensesHyper IonPas encore d'évaluation
- Soc AssignmentDocument3 pagesSoc AssignmentIsraq AhmmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory OrganDocument20 pagesSensory OrganJanePas encore d'évaluation
- Human Body HandbookDocument27 pagesHuman Body Handbookgksamy100% (1)
- The Five Human SensesDocument17 pagesThe Five Human SensesAntonio Gonzalez100% (1)
- Sense of Hearing: How You HearDocument8 pagesSense of Hearing: How You HearZuLianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansMelanie GialogoPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan SenseDocument16 pagesLaporan SenseladylomoPas encore d'évaluation
- World Through Our Senses (All Sensory Organs)Document48 pagesWorld Through Our Senses (All Sensory Organs)Chin Kok Soon100% (3)
- Is Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesDocument11 pagesIs Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesHafizah Ghany HayudinnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Your Sense of SmellDocument2 pagesYour Sense of SmellMarxlen Apostol BedolidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Sense: DR - Rr. Sri Ratna Rahayu M.Kes, PHDDocument37 pagesFive Sense: DR - Rr. Sri Ratna Rahayu M.Kes, PHDDewi Rahma PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 104 Module "G": Sensory Organ FactsDocument12 pagesNCM 104 Module "G": Sensory Organ FactsIsaiah RabangPas encore d'évaluation
- I Can Hear, See, Taste, Smell and Feel! Senses Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksD'EverandI Can Hear, See, Taste, Smell and Feel! Senses Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Document5 pagesPsychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Lyanna MormontPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Fun Facts About Ears: A 15-Minute BookD'Everand14 Fun Facts About Ears: A 15-Minute BookÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Let's Remember: Understanding How Your Sense OrgansDocument1 pageLet's Remember: Understanding How Your Sense OrgansJohn LimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Human BodyDocument12 pagesThe Human BodyGuruKPOPas encore d'évaluation
- The Senses: Working of Human EarDocument4 pagesThe Senses: Working of Human EarskymannearthPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Senses ReadingDocument4 pages5 Senses ReadingAdrian Trincado FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture in GEd 202 - Module 08Document12 pagesLecture in GEd 202 - Module 08Anne BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Fun Facts About Noses: A 15-Minute BookD'Everand14 Fun Facts About Noses: A 15-Minute BookÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- The Nervous System - Human SensesDocument23 pagesThe Nervous System - Human Sensesapi-240330821Pas encore d'évaluation
- Five Senses of A Human BodyDocument6 pagesFive Senses of A Human BodyJennie TanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sense Organs and It'S PartsDocument38 pagesThe Sense Organs and It'S PartsSk Laila AyeshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory OrgnasDocument8 pagesSensory OrgnasNisha ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hearing: The SensesDocument7 pagesHearing: The SensesSourav DasPas encore d'évaluation
- General Psychology AssignmentDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology AssignmentSaaB PanaraagPas encore d'évaluation
- Hearing: The SensesDocument20 pagesHearing: The SensesSourav DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Let's Know More Things AboutDocument10 pagesLet's Know More Things Aboutmar_gd_8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sensation BBA 1st LectureDocument37 pagesSensation BBA 1st Lecture52wtq8v288Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sense OrgansDocument9 pagesSense OrgansЕкатерина КовальPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Senses ProjectDocument15 pagesSpecial Senses Projectapi-268957635Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument5 pagesSensation and PerceptionCamille Nathalie JuloyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensation and Perception CHP 8Document53 pagesSensation and Perception CHP 8api-293070066Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sensation & PerceptionDocument55 pagesSensation & PerceptionMary James100% (1)
- Human Sense Organs PrelimDocument50 pagesHuman Sense Organs PrelimJersen Mae MaglabePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Proper For Week 8Document8 pagesLesson Proper For Week 8Merlyn NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory OrgnasDocument8 pagesSensory OrgnasNisha ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 11-16Document121 pagesModule 11-16djbechtelnlPas encore d'évaluation
- The SensesDocument41 pagesThe Sensesfemfen1225Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansPaula QuinteroPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 3 SCI-100 LESSON PLAN FERNANDEZ MICHAEL SodapdfDocument8 pagesWEEK 3 SCI-100 LESSON PLAN FERNANDEZ MICHAEL Sodapdfmichaelfernandez38060Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hearing: How Your Ears WorkDocument3 pagesHearing: How Your Ears WorkKelsey HillPas encore d'évaluation
- April 29Document7 pagesApril 29api-292905822Pas encore d'évaluation
- Five SensesDocument41 pagesFive SensesJobel Sibal CapunfuerzaPas encore d'évaluation
- SCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Document49 pagesSCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Nurul NasaruddinPas encore d'évaluation
- A Tour of the Senses: How Your Brain Interprets the WorldD'EverandA Tour of the Senses: How Your Brain Interprets the WorldÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter OneDocument10 pagesThe World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter Onegan tong hock a.k.a ganosPas encore d'évaluation
- My Five SensesDocument29 pagesMy Five SensesOMAR VARAPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansBonjovi VerdejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-Science (Form 2)Document128 pagesChapter 1-Science (Form 2)Yeoh Hui KoonPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 SensesDocument5 pages5 SensesRandm SouvenirPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: The World Through Our SensesDocument38 pagesChapter 1: The World Through Our SensesJamel GriffinPas encore d'évaluation
- Brown Aesthetic Group Project PresentationDocument18 pagesBrown Aesthetic Group Project Presentationdapanasgaya07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IX The Anatomy and Physiology of The Sensory SystemDocument54 pagesUnit IX The Anatomy and Physiology of The Sensory SystemEldona HilarioPas encore d'évaluation
- DexaDocument36 pagesDexaVioleta Naghiu100% (1)
- TNEB Thermal Power PlantDocument107 pagesTNEB Thermal Power Plantvicky_hyd_130% (1)
- Fpubh 10 1079779Document10 pagesFpubh 10 1079779Dona WirdaningsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rec Site Visit Report 1Document6 pagesRec Site Visit Report 1api-474887597Pas encore d'évaluation
- Treeleaf Basic Zazen InstructionsDocument16 pagesTreeleaf Basic Zazen InstructionsFaisal sarhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibacterial Effects of Essential OilsDocument5 pagesAntibacterial Effects of Essential Oilsnightshade.lorna100% (1)
- Tips To Diagnose & Address Common Horse AilmentsDocument6 pagesTips To Diagnose & Address Common Horse AilmentsMark GebhardPas encore d'évaluation
- Report of Initial / Annual / Intermediate / Renewal / General Examination SurveyDocument9 pagesReport of Initial / Annual / Intermediate / Renewal / General Examination SurveyJagjit SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Prednisolone Versus Dexamethasone For Croup: A Randomized Controlled TrialDocument11 pagesPrednisolone Versus Dexamethasone For Croup: A Randomized Controlled TrialA Joel ZjPas encore d'évaluation
- Nato Code Numbers: Scope of ListDocument6 pagesNato Code Numbers: Scope of ListRain HeinPas encore d'évaluation
- The Necessity of Using Neurophysiological Methods For Diagnosing Communication Disorders. by Akhsaful To Tawhida Jahan MamDocument11 pagesThe Necessity of Using Neurophysiological Methods For Diagnosing Communication Disorders. by Akhsaful To Tawhida Jahan MamAkhsaful ImamPas encore d'évaluation
- PsychodramaDocument5 pagesPsychodramaAkhila R KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- BMP (Class 14 - Class-17) WeldingDocument24 pagesBMP (Class 14 - Class-17) WeldingAsesh PramanikPas encore d'évaluation
- Fischer General-CatalogueDocument108 pagesFischer General-Cataloguebo cephusPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Slides - Internal Forced Convection & Natural ConvectionDocument31 pagesTutorial Slides - Internal Forced Convection & Natural ConvectionVivaan Sharma75% (4)
- Imperial SpeechDocument2 pagesImperial SpeechROJE DANNELL GALVANPas encore d'évaluation
- FACSDocument8 pagesFACSKarthick ThiyagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Victron Orion-Tr - Smart - DC-DC - Charger-Manual Non IsolatedDocument19 pagesVictron Orion-Tr - Smart - DC-DC - Charger-Manual Non IsolatedThomist AquinasPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles in Biochemistry (SBK3013)Document3 pagesPrinciples in Biochemistry (SBK3013)Leena MuniandyPas encore d'évaluation
- Eliasmith2012-Large-scale Model of The BrainDocument5 pagesEliasmith2012-Large-scale Model of The Brainiulia andreeaPas encore d'évaluation
- To Be or Not To Be Healthy 4144Document3 pagesTo Be or Not To Be Healthy 4144Vesna Milosavljevic100% (1)
- 3 Day WorkoutDocument3 pages3 Day Workoutsonu091276Pas encore d'évaluation
- UWSAs 2008-09 Projects Report (Final)Document48 pagesUWSAs 2008-09 Projects Report (Final)David SabaflyPas encore d'évaluation
- A-Level: Psychology 7182/1Document20 pagesA-Level: Psychology 7182/1Queen Bee (Tt)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Peritoneal Dialysis Unit Renal Department SGH PD WPI 097 Workplace InstructionDocument10 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis Unit Renal Department SGH PD WPI 097 Workplace InstructionAjeng SuparwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 23Document5 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 23sarasjunkPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet Lm311Document10 pagesDatasheet Lm311Ed FreemanPas encore d'évaluation
- ISBB CompilationDocument6 pagesISBB CompilationElla SalesPas encore d'évaluation