Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ROMVOLT
Transféré par
alexiuteodorCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ROMVOLT
Transféré par
alexiuteodorDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
AC Voltage Drop Calculation Notes and Instructions
*
*
*
*
1. Enter
2. Enter
3. Enter
4. Enter
5. Enter
6. Enter
7. Enter
8. Enter
9. Enter
10. Enter
11. Enter
12. Enter
13. Enter
Project Data
Conduit Number
From: (Location)
To: (Location)
Voltage (220,380 or 400) Volts.
Phase (1 or 3)
Current (Amperes)
Power Factor
(decimal form)
Distance (meter)
Conduit Type (S=Steel, A=Aluminum, P=PVC)
Wire Type (C=Copper, A=Aluminum)
Wire Size (1.5, 2.5,400) mm
the Number of Wires per Phase.
Note: * = Optional Entries
No.
1
REVISION HISTORY
Date
Description
15/11/2001
ORIGINAL RELEASE
By
OST
Checked
TGA
ROMANIAN - AC VOLTAGE-DROP CALCULATION WORKSHEET
W.O. #
PROJECT
NAME
DATE
Washington Group Romania S.R.L.
N0138
S.C. ROMPETROL RAFINARE - COMPLEX PETROMIDIA S.A.
15-Nov-01
Circuit Description
CONDUIT # 0019F34
TO: Heat Tracing Panel 200kW
FROM: TD 403/1
Electrical Characteristics
Voltage:
Phase
Current
Power Factor
415 Volts (L-L for 3 , L-N for 1)
3 ( 1 or 3)
12 Amps
0.85 (Enter in decimal form 0.7, 0.8.1.0)
Physical Characteristics
Distance
Conduit Type:
Wire Type:
Wire Size:
No. Wires/Phase:
60 Meter (Distance to load, NOT footage of conductor)
s (S=Steel, A=Aluminum, P=PVC)
c (C=Copper, A=Aluminum)
4 (1.5, 2.5,,400) mm
1
Calculated Voltage Drop
Voltage Drop:
% Voltage Drop:
5.72 Volts (L-L for 3 , L-N for 1)
1.38% Voltage drop is below 3%
NOTE: Calculations are based upon 70 C temperature and Tab. 8.42, 8.49 of 1971 Mem. Ing. Ele. - Siemens .
REVISION HISTORY
No.
Date
Prepared by OST 02/20/2012
Description
RomVolt_Drop.xls
By
Checked
Page 2 of 4
Prepared by OST 02/20/2012
RomVolt_Drop.xls
Page 3 of 4
Table 9. AC Resistance and Reactance for 600Vac Cables, 3 Phase 60 Hz, 75C (167 F) - Three Single Conductors in Conduit
Size
AWG/
MCM
1
1/0
10
1000
12
14
2
2/0
250
3
3/0
300
350
4
4/0
400
500
6
600
750
8
X (Inductance)
for All Wires
PVC, Al.
Steel
Conduit
Conduit
0.046
0.057
0.044
0.055
0.050
0.063
0.037
0.046
0.054
0.068
0.058
0.073
0.045
0.057
0.043
0.054
0.041
0.052
0.047
0.059
0.042
0.052
0.041
0.051
0.040
0.050
0.048
0.060
0.041
0.051
0.040
0.049
0.039
0.048
0.051
0.064
0.039
0.048
0.038
0.048
0.052
0.065
AC Resistance for
Uncoated Copper Wires
PVC
Aluminum
Steel
Conduit
Conduit
Conduit
0.150
0.160
0.160
0.120
0.130
0.120
1.200
1.200
1.200
0.015
0.019
0.018
2.000
2.000
2.000
3.100
3.100
3.100
0.190
0.200
0.200
0.100
0.100
0.100
0.052
0.057
0.054
0.250
0.250
0.250
0.077
0.082
0.079
0.044
0.049
0.045
0.038
0.043
0.039
0.310
0.310
0.310
0.062
0.067
0.063
0.033
0.038
0.035
0.027
0.032
0.029
0.490
0.490
0.490
0.023
0.028
0.025
0.019
0.024
0.021
0.780
0.780
0.780
Ohms to Neutral per 1000 Feet
AC Resistance for
Aluminum Wires
PVC
Aluminum
Steel
Conduit
Conduit
Conduit
0.250
0.260
0.250
0.200
0.210
0.200
2.000
2.000
2.000
0.023
0.027
0.025
3.200
3.200
3.200
99.000
99.000
99.000
0.320
0.320
0.320
0.160
0.160
0.160
0.085
0.090
0.086
0.400
0.410
0.400
0.130
0.130
0.130
0.071
0.076
0.072
0.061
0.066
0.063
0.510
0.510
0.510
0.100
0.110
0.100
0.054
0.059
0.055
0.043
0.048
0.045
0.810
0.810
0.810
0.036
0.041
0.038
0.029
0.034
0.031
1.300
1.300
1.300
Effective Z at 0.85 PF for
Uncoated Copper Wires
PVC
Aluminum
Steel
Conduit
Conduit
Conduit
0.160
0.160
0.160
0.130
0.130
0.130
1.100
1.100
1.100
0.032
0.036
0.040
1.700
1.700
1.700
2.700
2.700
2.700
0.190
0.190
0.200
0.110
0.110
0.110
0.066
0.070
0.073
0.230
0.240
0.240
0.088
0.092
0.094
0.059
0.063
0.065
0.053
0.058
0.060
0.290
0.290
0.300
0.074
0.078
0.080
0.049
0.053
0.056
0.043
0.048
0.050
0.440
0.450
0.450
0.040
0.044
0.047
0.036
0.040
0.043
0.690
0.690
0.700
Effective Z at 0.85 PF for
Aluminum Wires
PVC
Aluminum
Steel
Conduit
Conduit
Conduit
0.240
0.240
0.250
0.190
0.200
0.200
1.800
1.800
1.800
0.039
0.042
0.046
2.800
2.800
2.800
99.000
99.000
99.000
0.300
0.300
0.300
0.160
0.160
0.160
0.094
0.098
0.100
0.370
0.370
0.370
0.130
0.130
0.140
0.082
0.860
0.088
0.073
0.077
0.080
0.460
0.460
0.460
0.110
0.110
0.110
0.066
0.071
0.073
0.057
0.061
0.064
0.710
0.720
0.720
0.051
0.055
0.058
0.045
0.049
0.052
1.100
1.100
1.100
Size
AWG/
MCM
1
1/0
10
1000
12
14
2
2/0
250
3
3/0
300
350
4
4/0
400
500
6
600
750
8
Notes:
1. These values are based on the following constants: UL-type RHH wires withClass B stranding, in cradled configuration. Wire conductivities are 100% IACS
copper and 61% IACS aluminum, and aluminum conduit is 45% IACS. Capacitive reactance is ignored, since it is negligible at these voltages.
These resistance values are valid only at 75C (167F) and for the parameters as given, but not representative for 600-volt wire types operating at 60 Hz.
2. "Effective Z" is defined as R cos(theta)+X sin(theta), where "theta" is the power factor angle of the circuit. Multiplying current by effective impedance gives
a good approximation for line to neutral voltage drop. Effective impedance values shown in this table are valid only at .85 power factor.
For another circuit power factor (PF), effective impedance (Ze) can be calculated from R and X values given in this table as follows:
Ze = R x PF + Xsin[arccos(PF)].
NEC Tables
07:49:22
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mustang Engineering, Inc.: Lighting CalculationDocument1 pageMustang Engineering, Inc.: Lighting CalculationalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto Transfer SchemeDocument10 pagesAuto Transfer SchemenitinpePas encore d'évaluation
- Considerations and Methods For An Effective Fast Bus Transfer SystemDocument12 pagesConsiderations and Methods For An Effective Fast Bus Transfer SystemThameemul BuhariPas encore d'évaluation
- Hubbel ATS PDFDocument16 pagesHubbel ATS PDFalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation and Maintenance Manual Automatic Transfer Switch ZTSH Series 30 - 4000 AMPSDocument37 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual Automatic Transfer Switch ZTSH Series 30 - 4000 AMPSYassin AlkadyPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Pump Sample CalculationDocument4 pagesMotor Pump Sample CalculationalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Hubbel ATS PDFDocument16 pagesHubbel ATS PDFalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation and Maintenance Manual Automatic Transfer Switch ZTSH Series 30 - 4000 AMPSDocument37 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual Automatic Transfer Switch ZTSH Series 30 - 4000 AMPSYassin AlkadyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cable Gland - DistancesDocument1 pageCable Gland - DistancesalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chromalox Technical OverviewDocument78 pagesChromalox Technical Overviewalexiuteodor100% (1)
- Analysis of Networks Using Symmetrical ComponentsDocument33 pagesAnalysis of Networks Using Symmetrical ComponentsashawishPas encore d'évaluation
- 3RB30261QB0 Datasheet enDocument8 pages3RB30261QB0 Datasheet enalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Pagina Pietei de Capital Din Romania - WWW - Kmarket.Ro Sumar Fonduri Deschise de InvestitiiDocument6 pagesPagina Pietei de Capital Din Romania - WWW - Kmarket.Ro Sumar Fonduri Deschise de InvestitiialexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Funding Your Studies in 2015 PDFDocument2 pagesFunding Your Studies in 2015 PDFalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Funding Your Studies in 2015 PDFDocument2 pagesFunding Your Studies in 2015 PDFalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformer Sizing Using ETAP PDFDocument24 pagesTransformer Sizing Using ETAP PDFalexiuteodor100% (2)
- Funding Your Studies in 2015 PDFDocument2 pagesFunding Your Studies in 2015 PDFalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- ANSI Functions RelayDocument1 pageANSI Functions RelayalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
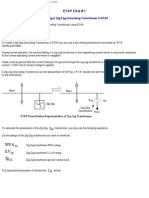
- ETAP Zig-Zag TransformerDocument2 pagesETAP Zig-Zag Transformervlady33Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cable Sizing Calculation - Appendix E Cables Selection ChartDocument80 pagesCable Sizing Calculation - Appendix E Cables Selection ChartalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Pump Sample CalculationDocument2 pagesMotor Pump Sample CalculationalexiuteodorPas encore d'évaluation
- (Supplies (: IndexDocument22 pages(Supplies (: Indexalexandra_rusu_39Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Fault Analysis Using PSCAD EMTDC For 150 KV South Sulawesi Transmission SystemDocument6 pagesFault Analysis Using PSCAD EMTDC For 150 KV South Sulawesi Transmission SystemMAKMUR SAINIPas encore d'évaluation
- CA3KN40BD3: Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesCA3KN40BD3: Product Data Sheetsherub wangdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Service ManualDocument265 pagesAdvanced Service ManualManuel Vivero Diéguez100% (2)
- An17808a PDFDocument8 pagesAn17808a PDFtatingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Buy Clamp Meter Online - GeM PDFDocument7 pagesBuy Clamp Meter Online - GeM PDFsunilkumarmeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21 AviDocument13 pagesChapter 21 Avianton_deocampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Beol - CL 636 (2) (10759)Document37 pagesBeol - CL 636 (2) (10759)shubhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Maxwell's Correction To Ampère's Law - Displacement CurrentDocument3 pagesMaxwell's Correction To Ampère's Law - Displacement CurrentmusamausmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Temperature Switch: Easy Multi-Unit Programming, 16A SPDT Relay OutputDocument1 pageDigital Temperature Switch: Easy Multi-Unit Programming, 16A SPDT Relay OutputIvan Hernandez VelazquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes 5th Week Ac BridgesDocument34 pagesLecture Notes 5th Week Ac BridgesPavan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- RFQ - TransformersDocument6 pagesRFQ - Transformersasim469Pas encore d'évaluation
- Encoder TbifDocument1 pageEncoder TbifHanns JorgPas encore d'évaluation
- 0349 300 543 Spare PartsDocument14 pages0349 300 543 Spare PartsJaime ArreolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure FDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure FRaju SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Bảng thông số sản phẩm: Micrologic 5.0 A - for Masterpact NT - drawoutDocument2 pagesBảng thông số sản phẩm: Micrologic 5.0 A - for Masterpact NT - drawoutair VPas encore d'évaluation
- An Integrated 6 MV Linear Accelerator Model From Electron Gun To Dose in A Water TankDocument11 pagesAn Integrated 6 MV Linear Accelerator Model From Electron Gun To Dose in A Water TankFrançois IdjiwolePas encore d'évaluation
- Final Research SHSDocument30 pagesFinal Research SHSEuniceCareLanaja91% (76)
- Symptom Procedures: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mfi)Document167 pagesSymptom Procedures: Multiport Fuel Injection (Mfi)1342231Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arihant, Ncert ExemplarDocument269 pagesArihant, Ncert Exemplarhghhbg100% (7)
- TransformersDocument43 pagesTransformersDavid LeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic LevitationDocument7 pagesMagnetic LevitationCofetaria FragutaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cathodic Protection of Reinforced Concrete Distance LearningDocument4 pagesCathodic Protection of Reinforced Concrete Distance LearningRohit RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis and Design Considerations of A Buck Converter With A Hysteresis PWM ControllerDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design Considerations of A Buck Converter With A Hysteresis PWM ControllerRGinanjar Nur RahmatPas encore d'évaluation
- Client - Consultant - Contractor - Project: Package-Ii: Doc. Name: Design Calculation Sheet For HT Power Cable Document No.Document2 pagesClient - Consultant - Contractor - Project: Package-Ii: Doc. Name: Design Calculation Sheet For HT Power Cable Document No.Pramod B.WankhadePas encore d'évaluation
- Purdue ECE 433 - Lecture 1Document25 pagesPurdue ECE 433 - Lecture 1John DoePas encore d'évaluation
- Wca-21 Rolls Royce - Umas V PDFDocument365 pagesWca-21 Rolls Royce - Umas V PDFAPas encore d'évaluation
- The Seven Stages of ConsciousnessDocument10 pagesThe Seven Stages of ConsciousnessSon of Rizq100% (1)
- ESD DetectorDocument8 pagesESD DetectorNurul AqilahPas encore d'évaluation
- Cold Juction - 01Document6 pagesCold Juction - 01camila65Pas encore d'évaluation
- PCS100 UPS-I BrochureDocument4 pagesPCS100 UPS-I BrochureJosephine Wong Sian CheePas encore d'évaluation