Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SR
Transféré par
MartharidiIbnuKhairuddinDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SR
Transféré par
MartharidiIbnuKhairuddinDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Skills Review
Chapter 2
Forces And Motion
1 Which of the following quantities are scalar quantities?
Deceleration
Velocity
Distance
Speed
Answer: ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2 Define
(a) displacement:
(b) velocity:
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(c) acceleration:
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3 Write down the equations of motion. State the meaning of each symbol used.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4 A stone is thrown vertically upwards from the ground with velocity 20 m s1. What is the maximum height achieved
by the stone?
5 An object experiences deceleration of 6 m s2 and is stopped in 4 s. What is the initial velocity of the object?
6 An object moves with an initial velocity 20 m s1 and experiences a retardation of 4 m s2. What is the distance
travelled between the second second and the fifth second?
7 A car moves with an initial velocity of 15 m s1 and accelerates with constant acceleration 4 m s2 for 50 seconds.
What is the total distance travelled?
8 When a driver stops his car from a velocity of 64 m s1 in 8 s, calculate the
(a) deceleration, and
(b) total displacement of the car.
9 A van moves from rest with an acceleration of 2 m s2. If the total displacement of the van is 120 m, calculate the
(a) final velocity of the van, and
(b) total time taken to come to a stop.
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Skills Review
Chapter 2
Forces And Motion
1 Calculate the average velocity shown on the ticker tape in the diagram below.
10 ticks
15 cm
The average velocity =
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2 In a ticker-timer experiment to study the motion of an object,
a graph of 10 ticks tapes is plotted side-by-side against time.
Determine the
(a) initial velocity,
(b) final velocity, and
(c) acceleration of the object.
Direction of motion of trolley
12 cm
The figure above shows a ticker tape acquired when it is attached to a moving trolley. The frequency of the supplied
a.c. current to the ticker timer is 50 Hz.
(a) Describe the motion of the trolley.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) What is the total time to obtain a stretch of 12 cm length of the ticker tape?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(c) Calculate the average velocity of the trolley.
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Chapter 2
Skills Review
Forces And Motion
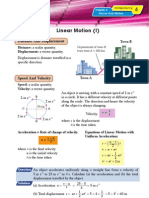
1 From the four displacement-time graphs shown
below, comment on the velocity of each graph.
The figure shows a displacement-time graph of an
object. Calculate
(a) the total displacement of the object,
Graph A:
______________________________________________________________
Graph B:
______________________________________________________________
Graph C:
______________________________________________________________
Graph D:
______________________________________________________________
(b) the velocity of the object.
2
4
Comment the velocity of each of the displacementtime graph given above.
Graph P:
______________________________________________________________
Graph Q:
______________________________________________________________
The figure shows a graph of displacement s against t
for an object.
(a) Calculate the gradient of the graph m.
(b) Write an equation which relates s and t.
_______________________________________________________________________
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Chapter 2
Skills Review
Forces And Motion
1 The graphs on the right show tape cuttings, each of 10 ticks,
arranged side-by-side and consecutively. Comment on the
acceleration of each graph.
Graph P:
________________________________________________________________________
Graph Q:
________________________________________________________________________
Graph R:
________________________________________________________________________
Graph S:
________________________________________________________________________
2 The figure shows a graph of velocity v against time t.
(a) State the physical quantity represented by the
gradient of the graph.
___________________________________________________________________________
(b) Calculate the gradient of the graph.
(c) Write down an equation which relates v and t.
___________________________________________________________________________
(d) Calculate the total distance travelled by the object.
3 The figure shows a velocity-time graph for a student
who rode bicycle from his house to school.
(a) Explain whether the student stopped along the
journey.
___________________________________________________________________________
(b) What is the time taken, in minutes, for the student
to reach the school?
___________________________________________________________________________
(c) State which
experiences
(i)
part
uniform velocity:
of
the
students
journey
______________________________________________
(ii) acceleration:
_____________________________________________________
(iii) deceleration:
_____________________________________________________
(d) Calculate the distance travelled in the first 10 seconds.
(e) What is the distance of the school from the students house?
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Skills Review
Chapter 2
10
Forces And Motion
1 Suggest two ways to reduce the negative effect of inertia on the driver of a car during an accident.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2 For an object moving with a uniform velocity, the object will continue to move with that velocity unless acted upon
by an ______________________________.
3 A ball rolling on a horizontal surface will eventually stop. Does this contradict Newtons first law of motion?
Give the reason for your answer.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4 What happens to a passenger standing in a moving bus when the bus suddenly stops? Why?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5 A ball rolls down an inclined plane to a smooth horizontal
surface. What will happen to the ball on the horizontal
surface?
Smooth surface
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
6 An astronaut throws a stone away from him as shown in the figure on the right.
What will happen to the stone?
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
7 What is the purpose of headrests placed in cars?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Skills Review
Chapter 2
11
Forces And Motion
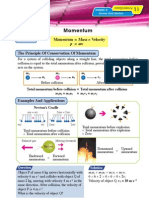
1 A homemade cannon is placed on an inertia cart as
shown. A little fuel is pumped into the cannon
chamber. When the fuel is ignited, the tennis ball is
propelled through the muzzle of the cannon.
(a) What is the total momentum before explosion?
(b) What is the total momentum after explosion?
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
(c) State the directions of motion of the inertia cart
and the tennis ball after explosion.
(d) Compare the velocities of the inertia cart and the
tennis ball after explosion. Give reason.
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
2 Two boys are each standing on a trolley as shown in the figure. If the boy of 80 kg
pushes another boy of 30 kg so that the 80 kg boy moves with initial velocity of 10 m
s1, what will be the initial velocity of the 30 kg boy?
3 Trolley A of mass m1 and trolley B of mass m2 are stationary and are
attached to a spring as shown in the figure. If the spring is released, each
trolley moves with velocity v1 and v2 respectively. Write down an
equation, which relates the quantities stated.
4 A bullet of mass 0.05 kg moves with horizontal
velocity 120 m s1 after it is shot from a pistol of
mass 0.5 kg. What is the velocity of recoil of the
pistol?
5 Object A of mass m, moving with velocity u,
collides with stationary object B of mass 2m on a
smooth floor. What is the ratio of total momentum
before collision to total momentum after collision?
6 A small vehicle of mass 400 kg is moving with
horizontal velocity 20 m s1. Suddenly, a boy of mass
80 kg falls from a tree onto the vehicle. What is the
new velocity of the vehicle?
7 A force of 4 N acts horizontally on a block of
wood, which is stationary and of mass 0.4 kg on a
smooth horizontal surface. What is the velocity of
the block of wood after 2 seconds?
8 A ball of mass 0.4 kg is thrown horizontally with
velocity 4 m s1 towards a vertical wall. The ball
rebounds from the wall with horizontal velocity
3 m s1. What is the change of momentum of the
ball?
9 A bullet of mass 10 g strikes horizontally at a
target of mass 2 kg and is embedded in it. These
two objects then move together with velocity
4 m s1. What is the velocity of the bullet just
before collision?
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Chapter 2
Skills Review
12
Forces And Motion
1 A load of 5 kg is placed on a weighing machine. A man at the
end A of the string then pulls up the load.
(a) (i) What is the reading of the weighing machine
when the load is not pulled up?
________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) What is the tension of the string if the load is pulled up
so that the weighing machine shows zero reading?
________________________________________________________________________________
(b) What is the tension of the string if the load is pulled up with
acceleration 4 m s2?
______________________________________________________________________________________
(c) Explain the difference in readings for (a)(ii) and (b).
______________________________________________________________________________________
2 A vehicle of mass 1 800 kg moves with uniform velocity of 5 m s1 on a smooth horizontal surface. The engine of
the vehicle stops suddenly and the vehicle comes to a stop after moving a distance of 250 m. Calculate the frictional
force which opposes the motion of the vehicle.
3 The figure shows forces 6 N, 4 N and 12 N acting on a point O.
What is the magnitude of the resultant force acting on point O?
4 The figure shows a load of mass 3 kg pulled by a horizontal
force 52 N and tension T. When the system is in equilibrium,
what is the value of T?
5 The figure shows two weights attached to a string which passes
through a smooth pulley. What is the resultant force acting on
the system of weights? [Acceleration due to gravity = 10 m s2.]
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Chapter 2
Skills Review
13
Forces And Motion
1 A car of mass 1 200 kg moves with velocity 5 m s1 towards a
wall and rebounds with velocity 4 m s1 in the opposite direction.
(a) Calculate
(i) the initial momentum,
5 m s1
4 m s1
(ii) the final momentum,
(iii) the impulse,
(iv) the impulsive force if the time of collision is 0.02 s.
(b) If the car does not rebound after collision, calculate
(i) the impulse,
5 m s1
0 m s1
(ii) the impulsive force if the time of collision is 0.2 s.
2 A man of mass 80 kg jumps from a vertical height of 5 m to the ground.
(a) What is the velocity of the man just before reaching the ground?
(b) (i)
If the man bends his knees, the time taken for him to stop is 0.5 s. What is the impulsive force acting on
him?
(ii) If the man does not bend his knees, the time taken for him to stop is 0.05 s, what is the impulsive force
acting on him? [g = 10 m s2.]
3 A force of 500 N is applied to an object for 0.08 s.
(a) What is the impulse applied to the object?
(b) What is the change of momentum experienced by the object?
4 A trolley of mass 60 kg is moving with velocity 20 m s1. An impulse of 2 000 N s is applied to the trolley in the
direction of motion of the trolley. Calculate
(a) the change in momentum, and
(b) the final momentum of the trolley.
5 Explain why a nylon rope, and but not a steel rope, is attached to a mountain climber?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Skills Review
Chapter 2
14
Forces And Motion
1 The picture below shows a crash test of a vehicle conducted by a car manufacturer.
Q
(a) State the labelled parts in the picture.
P
Q
R
S
(b) Describe the safety features of the following parts.
P
Q
S
2 The major consideration to design safety features of a car is to reduce the _______________ during an accident.
The longer the ______________, the smaller will be the impulsive force acting on the car.
3 The 2002 model of a car from Ford Motor Company is designed in such a way that the bonnet will spring up
automatically during an accident as shown in the figure. Explain how this feature might save the life of a pedestrian.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Skills Review
Chapter 2
15
Forces And Motion
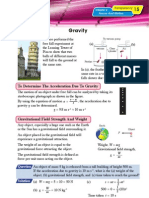
1 The unit for gravitational field strength is _____________________________ or
_____________________________
2 Explain why an object released from a building falls to the ground.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3 An object under free fall experiences an acceleration ____________________________________________________________________________________________.
4 A boy holds a ball in a lift, which is under free fall due to the gravitational force. What will happen if the ball is
released from the hand of the boy?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5 A loaded spring balance is hung from the ceiling of a lift. When the lift is stationary, the spring balance shows a
reading of 40 N. When the cable of the lift snaps suddenly, what will be the reading of the spring balance?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6 An object is released from rest to the base of a dry well. If the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m s2, what is the
(a) velocity of the object after 1 s?
(b) depth of the well if the object takes 2 s to reach its base?
7 (a) An object has a mass of 36 kg. If the acceleration due to gravity of the Earth is 10 m s2, what is the weight of
the object?
(b) If the same object is placed on the surface of the Moon where its acceleration due to gravity is 1 that of the
6
Earth, what is the new weight of the object?
(c) What is the
(i) change of weight, and
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) change of mass when the object is placed on the Moons surface?
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
8 (a) If you are given a beam balance and a spring balance, which instrument would you use to measure weight of
an object?
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(b) If an object is measured by using both instruments in a lift, which is accelerating downwards, explain what will
happen to the reading of each instrument.
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Chapter 2
Skills Review
16
Forces And Motion
1 Given that the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m s2 and the
balance in the figure on the right is in equilibrium. What is the
force of reaction acting on the fulcrum?
2 The figure shows three weights hung from inelastic strings
through two smooth pulleys. If the three weights are in a state of
equilibrium, what is the value of F3?
3 The figure shows a load of mass 3 kg pulled by a horizontal force
52 N and tension T. When the system is in equilibrium, what is
the value of T?
A framed picture is suspended by strings as shown in the figure.
What is the weight of the framed picture?
5 The figure shows two forces 12 N and 5 N acting perpendicularly
to each other at a point. Find the resultant force F and its direction
.
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Chapter 2
Skills Review
17
Forces And Motion
1 Work done is a form of _____________________________
2 Work done is defined as a product of force and _____________________________.
3 Greater work done is needed if the
moved is longer.
_____________________________
of the object is greater and the displacement of the object
4 A stone of mass 8 kg is lifted to a vertical height of 3 m. What is the work done to the stone? [g = 10 m s2.]
5 Figure (a) shows block A of mass 1 kg being lifted through a
vertical height of 60 cm whereas figure (b) shows block B of the
same mass moving through a displacement of 60 cm along an
inclined plane. The angle of the inclined plane to the horizontal is
30. Calculate the difference in work done to move the block. [The
acceleration due to gravity = 10 m s2.]
6 The figure shows a metal sphere of mass 150 kg being pulled by a
force of 400 N at angle 60o to the floor surface. It is found that the
metal sphere moves with uniform speed along the floor.
[Acceleration due to gravity = 10 m s2.] Calculate
(a) the normal reaction of the metal sphere,
(b) the frictional force,
(c) the work done in moving the metal sphere through a distance of 50 m.
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Skills Review
Chapter 2
18
Forces And Motion
1 (a) State the change of energy for the dolphins in the
figure below.
(b) State the principle of conservation of energy for
the roller coaster in figure below.
Answer : __________________________________________________________
Answer: __________________________________________________________
2 A lorry of mass 5 000 kg moves with a constant velocity of 4 m s1 along a horizontal road. What is the kinetic
energy of the lorry in kJ?
3 A load of mass 4 kg is lifted from a height of 5 m through a height of another 10 m. What is the increase in
gravitational potential energy of the load? [g = 10 m s2.]
4 A ball of mass 120 kg is situated at a height of 3.6 m from the surface of the
floor as shown in the figure. When the ball rolls down a smooth rail, what is
the speed of the ball just before it reaches the floor? [g = 10 m s2.]
5 A ball of mass 0.2 kg is thrown vertically upwards from the surface of the Earth with an initial velocity 20 m s1.
What is the maximum gravitational potential energy acquired?
6 When the speed of an object increases by 3 times, its kinetic energy will be increased by _____________________________ times.
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Chapter 2
Skills Review
19
Forces And Motion
1 The rate of energy transfer is equivalent to _____________________________.
2 Another unit for J s1 is _____________________________.
3 The figure on the right shows a conveyor belt system carrying a
load of mass 30 kg from position X to position Y in 15 seconds.
What is the output power of the conveyor system?
4 A boat of mass 800 kg moves on the surface of the sea with a uniform velocity of 2 m s1. If the thrust required to
overcome frictional force is 3 200 N, what is the average power of the boat?
5 If the power of a vehicle moving with a uniform velocity of 30 m s1 is 60 kW, what is the force due to air resistance
and friction?
6 A wooden block of mass 4 kg is moved by a force of 10 N along a straight road at a uniform velocity of 5 m s1.
What is the work done to overcome the friction in 2 seconds?
7 A boy of mass 50 kg can climb a coconut tree of height 15 m in 30 seconds. What is the power generated by the
boy? [Acceleration due to gravity = 10 m s2.]
8 A car of mass 500 kg can move from rest to 20 m s1 in 10 seconds. What is the power of the car in kW?
9 A motor can produce a power of 1 200 kW. If the efficiency of the motor is 60%, what is the output power of the
motor?
10 A cranes efficiency to lift a load of 4 500 kg through a vertical height of 20 m in 5 seconds is 90%. What is the
input power of the crane? [Acceleration due to gravity = 10 m s2.]
11 A hoist raises an elevator with a total weight of 5 000 N through a height of 30 m in 20 seconds. What is the average
power generated by the motor?
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Skills Review
Chapter 2
20
Forces And Motion
1 Why do we have to maximise the efficiency of electrical appliances?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2 Why is it not advisable to install a spotlight in a storeroom?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3 To boil enough water for a cup of coffee, an electric kettle is used. Discuss the suitability of the appliance.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4 Other than fossil fuel energy, state three other alternative sources of energy that can be harnessed to supplement
world consumption of energy.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5 Fill in the appropriate data in the following table for the various power consumption.
Task
Power rating
Time taken
Boiling enough water
to make two cups of
tea in a kettle
2.5 kW
10 s
Watching TV in the
evening
200 W
1 hour
Heating up an
evening meal for one
in a microwave oven
1.2 kW
Energy
(a)
(b)
(c)
36 kJ
(d)
Playing a computer
game
20 s
10 kJ
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Chapter 2
Skills Review
21
Forces And Motion
1 A spring is stretched from a length of 12 cm to 16 cm by a force of 40 N. What is the work done to stretch the
spring?
2 A wire obeys Hookes law has length of l1 when it is stretched by a tensile force of F1 and its length is increased
to l2 when the tensile force is increased to F2. What is the energy stored in the wire when it is stretched to l2?
3 A wire is stretched by a force F so that it experiences an extension of x. The energy stored in the wire is F only
2
if the extension has not exceeded the _____________________________.
4 The figure shows a graph of force F against extension x for an elastic
string. What is the elastic potential energy of the string, which experiences
an extension of 5 cm?
5 A spring, pulled by a force of 10 N, produces an extension of 40 mm. Two identical springs are arranged in series
to produce a total extension of 40 mm. What is the energy stored in the two springs?
6 A wire, under an increasing tension, elongates as shown in the graph.
What is the work done to the wire when it extends by 9 mm?
Marshall Cavendish (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CRDocument8 pagesCRMartharidiIbnuKhairuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 15Document1 pagePdfa2 15aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 16Document1 pagePdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 11Document1 pagePdfa2 11aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 12Document1 pagePdfa2 12aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 14Document1 pagePdfa2 14aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 13Document1 pagePdfa2 13aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 9Document1 pagePdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 3Document1 pagePdfa2 3aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 7Document1 pagePdfa2 7aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 10Document1 pagePdfa2 10aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 2Document1 pagePdfa2 2aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 6Document1 pagePdfa2 6aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 8Document1 pagePdfa2 8aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 5Document1 pagePdfa2 5aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- SchemeDocument15 pagesSchemeMartharidiIbnuKhairuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 4Document1 pagePdfa2 4aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa2 1Document1 pagePdfa2 1aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa1 2Document1 pagePdfa1 2aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer:: Introduction To PhysicsDocument5 pagesAnswer:: Introduction To PhysicsharieswaarPas encore d'évaluation
- Travel With NASA From The Biggest To The Smallest Distance of The UniverseDocument45 pagesTravel With NASA From The Biggest To The Smallest Distance of The Universegvphuonga100% (4)
- Pdfa1 1Document1 pagePdfa1 1aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.4 MeasurementsDocument20 pages1.4 MeasurementsMohdHaniPas encore d'évaluation
- ObjectiveDocument4 pagesObjectiveMartharidiIbnuKhairuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa1 5Document1 pagePdfa1 5aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa1 4Document1 pagePdfa1 4aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa1 3Document1 pagePdfa1 3aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfa1 1Document1 pagePdfa1 1aizatPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- GIS BasedLandSuitabilityAnalysistoSupportTransit OrientedDevelopmentTODMasterPlanACaseStudyoftheCampusStationofThammasatUniversityandItsSurroundingCommunitiesDocument13 pagesGIS BasedLandSuitabilityAnalysistoSupportTransit OrientedDevelopmentTODMasterPlanACaseStudyoftheCampusStationofThammasatUniversityandItsSurroundingCommunitiesAzka RamadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Igt - Boot Os List Rev B 10-28-2015Document5 pagesIgt - Boot Os List Rev B 10-28-2015Hector VillarrealPas encore d'évaluation
- Public Relations Proposal Template: Executive SummaryDocument3 pagesPublic Relations Proposal Template: Executive SummaryErmi SusilowatiPas encore d'évaluation
- NURKSE's Balanced GrowthDocument7 pagesNURKSE's Balanced GrowthArnab MutsuddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tagum Doctors Hospital Inc.,: Republic of The Philippines Department of Health National Highway 54, Tagum CityDocument8 pagesTagum Doctors Hospital Inc.,: Republic of The Philippines Department of Health National Highway 54, Tagum CityRoel John Atamosa CasilacPas encore d'évaluation
- Edgevpldt Legazpi - Ee As-Built 121922Document10 pagesEdgevpldt Legazpi - Ee As-Built 121922Debussy PanganibanPas encore d'évaluation
- Motorola l6Document54 pagesMotorola l6Marcelo AriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Prospectus 2020 WebDocument89 pagesTraining Prospectus 2020 Webamila_vithanagePas encore d'évaluation
- Yale Smart Door Locks GuideDocument50 pagesYale Smart Door Locks GuidejaganrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Dau Terminal AnalysisDocument49 pagesDau Terminal AnalysisMila Zulueta100% (2)
- COA Full Syllabus-CSEDocument3 pagesCOA Full Syllabus-CSEAMARTYA KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 2 - Assignment 2 - A Case Study of Telecom SectorDocument13 pagesGroup 2 - Assignment 2 - A Case Study of Telecom Sectorfajarina ambarasariPas encore d'évaluation
- SSTMCV Retail PowerDocument5 pagesSSTMCV Retail Powervipin.yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- GA 7 Parts ManualDocument565 pagesGA 7 Parts ManualDave SchallPas encore d'évaluation
- OFW Dependent Scholarship AssessmentDocument3 pagesOFW Dependent Scholarship AssessmentJosebeth CairoPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 04 06 SCDocument30 pages15 04 06 SCSugarPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Weblogic Server 12c Administration II - Activity Guide PDFDocument188 pagesOracle Weblogic Server 12c Administration II - Activity Guide PDFNestor Torres Pacheco100% (1)
- Dep 32.32.00.11-Custody Transfer Measurement Systems For LiquidDocument69 pagesDep 32.32.00.11-Custody Transfer Measurement Systems For LiquidDAYOPas encore d'évaluation
- AirtelDocument2 pagesAirtelShraddha RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Research career paths in Spain: funding opportunities overviewDocument7 pagesResearch career paths in Spain: funding opportunities overviewfidalgocastroPas encore d'évaluation
- SUTI Report - Metro ManilaDocument87 pagesSUTI Report - Metro ManilaIvan Harris TanyagPas encore d'évaluation
- Xu10j4 PDFDocument80 pagesXu10j4 PDFPaulo Luiz França100% (1)
- Url Profile Results 200128191050Document25 pagesUrl Profile Results 200128191050Wafiboi O. EtanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Asset-V1 RICE+46 6 4010+2021 Q1+type@asset+block@MCQs For HO SDH New WBCS 2nd SM 2nd Class Constitution QDocument5 pagesAsset-V1 RICE+46 6 4010+2021 Q1+type@asset+block@MCQs For HO SDH New WBCS 2nd SM 2nd Class Constitution QSourin bisalPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Aids For TeachingDocument19 pagesDifferent Aids For TeachingPrecious CabarsePas encore d'évaluation
- Office of The Protected Area Superintendent: Mt. Matutum Protected LandscapeDocument3 pagesOffice of The Protected Area Superintendent: Mt. Matutum Protected LandscapeNurah LaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project 863 EvidenceDocument5 pagesProject 863 EvidenceMilan TolhuisenPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructions Manual Skatey 150/250/400/600Document19 pagesInstructions Manual Skatey 150/250/400/600Denys GavrylovPas encore d'évaluation
- Index: Title Page Acknowledgement Chapter 1: ProfilesDocument43 pagesIndex: Title Page Acknowledgement Chapter 1: ProfilesRaushan singhPas encore d'évaluation
- D882 - Pruebas A Películas.Document11 pagesD882 - Pruebas A Películas.CamiloSilvaPas encore d'évaluation