Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Kingdom
Transféré par
Flore-ed AlvarezDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Animal Kingdom
Transféré par
Flore-ed AlvarezDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Animal Kingdom Vertebrates animals with backbone Invertebrates animals without backbone
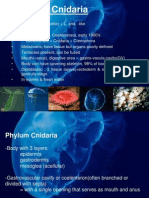
Phylum Porifera Most of the organisms are marine and some are freshwater organisms they vary in color from white, gray, brown to red, yellow, purple and black. They may live singly or colonies , the body of sponges consists of tiny pores, the small incurrent pores and excurrent pores Oxygen and food in the form of diatoms, small protozoans, bacteria and organic particles, are carried to the sponge in water. Carbon dioxide and wastes leaves sponge body through the excurrent pore called oscullum. Adult sponges are sessile while their larvae are ciliated and free swimming. A simple sponge consists of a hollow body whose wall contains many tubes. Reproduction of sponges sexually and asexually most freshwater species reproduce asexually through the formation of buds or gemmules BUDS are group of cells that enlarge and attached to the parents for sometime while GEMMULES- are group of cell masses which are surrounded by a heavy coats of organic matter and produce by the parent sponge. Sexually these animals develop eggs and sperms that shed into the water to fertilize the egg. Examples: grantia and venus flower basket Porifera comes from latin word porus which means pores and ferre meaning to bear. Phylum Coelenterata Coenleterates have more specialization that poriferans these are hollow cuplike animals which have a central digestive cavity and a nervous system of a primitive kind. They often vase shaped occurring singly or in colonies. Like sponges , coelenterates are aquatic and mostly marine. Members in this group vary in size from microscopic t o the largest jellyfish with diameter of 3.6 metre. Includes animals like hydra, coral, jellyfish, sea anemone , and Portuguese man of war Hydra is one of well known freshwater coelenterate they are tiny animals about centimeters long quite flexible and may be five times as long when they stretched out. Hydra exists as single individual and exhibits only one body form . Polyp which is vase shaped exists as single individual body. Produce second body type the medusa or bell shaped form that floats or swims freely in water. There are white,green and brown species of hydra which live in quiet ponds ,lakesand streams.
The body of Hydra consists of two cell layers the ectoderm and endoderm which are separated by a jellyfish material called mesoglea. It has single opening that is surrounded by tentacles with stinging cells . These cells bear nematocysts which contain a poison that paralyzes and sometimes kills the animals that they hit. Nematocyst are found only in coelenterate . They perform asexual reproduction it form buds which develop knobs that grow into tentacles from which individual hydras develop. Sexually hydra undergo egg fertilization during rainy season and cooler months . the eggs fertilized in the ovary and resulting zygote grows into a spherical many celled structure with a hard protective covered . Jellyfish stings and brings pain to anyone swimming in the ocean a common jellyfish that is found in Manila Bay is Acrometoides purpureus Filipino call it dikya. Coelenterata comes from the greek term koilos which means hollow and enteron which means intestine
Phylum Platyhelminthes The flatworms the name of the phylum comes from the greek word platys which means flat and helmis meaning worm Flat bodied worms are small inconspicuous animal with digestive , nervous, excretory and reproductive system Some of them are free living while others are parasitic living in bodies of various animals including humans. Planaria are free living flatworm s that thrives in freshwater habitats most especially in ponds and streams. They range from 8 to 16 millimeters in length and vary in color from black brown and white. They are bilaterally symmetrical with a blunt anterior end and a pointed posterior end. Two eyespots which are photosensitive are found in the anterior end of animals body
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Types of InvertebratesDocument7 pagesTypes of InvertebratesRay Lorenz OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Is Awesome!: 101 Incredible Things Every Kid Should KnowD'EverandScience Is Awesome!: 101 Incredible Things Every Kid Should KnowPas encore d'évaluation
- AnimalsDocument43 pagesAnimalsGina ZannePas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Diversity 1 PDFDocument20 pagesAnimal Diversity 1 PDFRica Jane Delan MapaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument27 pagesKingdom AnimaliaBlanche Mascarinas LabortePas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical Botany With Taxonomy: "Kingdom Protista and Algae"Document10 pagesPharmaceutical Botany With Taxonomy: "Kingdom Protista and Algae"TheQueen SnobberPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Practical Specimen StudyDocument6 pagesBio Practical Specimen StudyShailjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tunicates and Sponges For ESSAY 2Document18 pagesTunicates and Sponges For ESSAY 2ottermanerttwbPas encore d'évaluation
- The Phylum Coelenterates: A. General CharacteristicDocument12 pagesThe Phylum Coelenterates: A. General CharacteristicCindy RahmahPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Animals-2Document23 pagesCharacteristics of Animals-2api-297087367Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Kingdom ClasfificationDocument14 pages5 Kingdom ClasfificationDarsh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Annelida Written ReportDocument11 pagesAnnelida Written ReportIrish MaireignPas encore d'évaluation
- ObeliaDocument7 pagesObeliaPralex PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Vertebrates and Invertebrate Phylum.: Prepared By: Arifa AsadDocument18 pagesVertebrates and Invertebrate Phylum.: Prepared By: Arifa Asadarifaasad100% (1)
- Alternation of Generation in InvertebratesDocument22 pagesAlternation of Generation in InvertebratesBrza RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Algae JupebDocument6 pagesAlgae JupebDavid AsuquoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument6 pagesPhylum Platyhelminthesjuancho de mesa100% (2)
- Handouts VertebratesDocument5 pagesHandouts VertebratesDiane PamanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationDocument9 pagesThe Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationliugirmayPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Kingdom ClassificationDocument20 pagesAnimal Kingdom Classificationsarvesh672Pas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Animal KingdomDocument8 pagesActivity Animal KingdomGerald Agacid BangeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Multicellular and Tissue Level OrganizationDocument88 pagesChapter 3 Multicellular and Tissue Level OrganizationfatimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum CnidariaDocument3 pagesPhylum CnidariaMA. LYN CASIPEPas encore d'évaluation
- Invertebrate Animals (6TH Grade Science)Document47 pagesInvertebrate Animals (6TH Grade Science)anonymousPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom Animalia - Ernesto MarinDocument26 pagesKingdom Animalia - Ernesto MarinsanazhPas encore d'évaluation
- InvertebratesDocument13 pagesInvertebratesLazurdyPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of AnimalsDocument47 pagesClassification of AnimalsReylen MaderazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Amphibian 2022&23ADocument9 pagesAmphibian 2022&23AqueendaxxyPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Kingdom BiologyDocument8 pagesAnimal Kingdom BiologyMary Ann SalvatierraPas encore d'évaluation
- General ZoologyDocument22 pagesGeneral Zoologytonie rose abePas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum AnimaliaDocument28 pagesPhylum Animaliaapi-310714826Pas encore d'évaluation
- Animal DiversityDocument3 pagesAnimal DiversityChristian Dave Sanchez0% (1)
- Plant KingdomDocument83 pagesPlant KingdomBhargavi PriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yellow Retro Brainstorm PresentationDocument20 pagesYellow Retro Brainstorm Presentationbalingit09jayePas encore d'évaluation
- Plant KingdomDocument11 pagesPlant KingdomSuresh SPas encore d'évaluation
- Fungus KingdomDocument24 pagesFungus KingdomKayla-may MollisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom ProtistaDocument27 pagesKingdom ProtistaHELMA B. JABELLOPas encore d'évaluation
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument33 pagesDiversity in Living OrganismsNilaksh BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Protista Written ReportDocument8 pagesProtista Written ReportLance RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant KingdomDocument9 pagesPlant KingdomsanaullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Classifying Animals into Vertebrates and Invertebrates - Animal Book for 8 Year Olds | Children's Animal BooksD'EverandClassifying Animals into Vertebrates and Invertebrates - Animal Book for 8 Year Olds | Children's Animal BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom Animalia (Jeidre Pamorca)Document62 pagesKingdom Animalia (Jeidre Pamorca)jeidre pamorcaPas encore d'évaluation
- PoriferaDocument25 pagesPoriferaAmelia MeiriskaPas encore d'évaluation
- ZoologyDocument9 pagesZoologymiarriePas encore d'évaluation
- (Biol 12) Grade 9 - Unit 5 Notes and MCQ (2016)Document18 pages(Biol 12) Grade 9 - Unit 5 Notes and MCQ (2016)Bekele GonfaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.2. Kingdom ProtistaDocument21 pages4.2. Kingdom ProtistaJacePas encore d'évaluation
- Research No. 2Document46 pagesResearch No. 2Bai Putri Rohaina S. MalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Cnidaria and Porifera Group 1Document32 pagesPhylum Cnidaria and Porifera Group 1JulesPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom Plantae & Kingdom Animalia Prepared By: Ms. Jonna Karla C. Bien, RNDocument66 pagesKingdom Plantae & Kingdom Animalia Prepared By: Ms. Jonna Karla C. Bien, RNvhebhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Isopoda Biological NotesDocument1 pageIsopoda Biological NotesJasonPas encore d'évaluation
- InvertebratesDocument21 pagesInvertebratesJohann FaustPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4: ProtistaDocument8 pagesChapter 4: ProtistaNawal Che IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum: PoriferaDocument6 pagesPhylum: PoriferaNurul JannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 08Document17 pagesChapter 08Wajeeh Ahmed ZakaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 33: An Introduction To InvertebratesDocument6 pagesChapter 33: An Introduction To InvertebratesPatricia SioPas encore d'évaluation
- ProstistaDocument43 pagesProstistaNovelynLozano-EdrosoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument24 pagesThe Phylum PlatyhelminthesFlora NeriPas encore d'évaluation
- Nature for Kids | Plants, Animals and Nature Quiz Book for Kids | Children's Questions & Answer Game BooksD'EverandNature for Kids | Plants, Animals and Nature Quiz Book for Kids | Children's Questions & Answer Game BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 - Intro. To MetazoaDocument30 pagesLecture 3 - Intro. To MetazoaSambili TonnyPas encore d'évaluation
- ScribdDocument28 pagesScribdGuelan LuarcaPas encore d'évaluation
- EndocnidozoaDocument6 pagesEndocnidozoaKevin Rucci100% (1)
- Chapter6-Phylum Porifera NotesDocument4 pagesChapter6-Phylum Porifera Notesapi-195601294Pas encore d'évaluation
- CnidariaDocument48 pagesCnidariaMafe CabilesPas encore d'évaluation
- Stephen Pikesley 2015 JellyfishDocument49 pagesStephen Pikesley 2015 JellyfishCoastal FuturesPas encore d'évaluation
- Jellyfish Blooms in The Mediterranean and Black SeaDocument63 pagesJellyfish Blooms in The Mediterranean and Black SeaangryhamsterPas encore d'évaluation
- Repaso Examen Laboratorio ZOOLOGIADocument12 pagesRepaso Examen Laboratorio ZOOLOGIAcaripukisPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Porifera ClassificationDocument3 pagesPhylum Porifera ClassificationSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Wiki JellyfishDocument1 pageWiki Jellyfishwdm00Pas encore d'évaluation
- Invertebrate ZoologyDocument233 pagesInvertebrate ZoologyCHRehanMaqsood100% (3)
- Animal Kingdom (Phylum 1-7)Document4 pagesAnimal Kingdom (Phylum 1-7)AllenPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 09 Sum MT PoriferaDocument17 pages02 09 Sum MT PoriferaMudasir AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiate AnimalsDocument58 pagesRadiate AnimalsBudi AfriyansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Box Jellyfish: Tarlac Christian CollegeDocument7 pagesBox Jellyfish: Tarlac Christian CollegeNaddie DeorePas encore d'évaluation
- Occ Pub 15Document356 pagesOcc Pub 15Nabiela Sharif0% (1)
- Hard Coral Identification GuideDocument7 pagesHard Coral Identification GuideramontranquiloPas encore d'évaluation
- Cnidaria QuestionsDocument2 pagesCnidaria QuestionsJosiah CrepowPas encore d'évaluation
- AnimalphylaparagraphsDocument3 pagesAnimalphylaparagraphsapi-272770403Pas encore d'évaluation
- ZoologyDocument3 pagesZoologyAljane Mae Flores ManaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum PoriferaDocument2 pagesPhylum PoriferayashsodhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Klas AnthozoaDocument6 pagesKlas AnthozoaPranowo Ibnu KhakimPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Cnidaria Mirani NotesDocument17 pagesPhylum Cnidaria Mirani NotesBudi Afriyansyah100% (1)
- Jellyfish: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageJellyfish: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediawdm00Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lion's Mane Jellyfish - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesLion's Mane Jellyfish - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaLuis Javier del PozoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Phylum CtenophoraDocument3 pagesThe Phylum CtenophoraTI Journals PublishingPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab-Porifera Cnidaria 2015Document8 pagesLab-Porifera Cnidaria 2015api-283045497100% (1)
- Some Characteristics of The Phylum CnidariaDocument5 pagesSome Characteristics of The Phylum CnidariaTI Journals PublishingPas encore d'évaluation
- Cnidarians OverviewDocument46 pagesCnidarians OverviewTiff VoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dichotomous KeyDocument4 pagesDichotomous KeyJojee ErraPas encore d'évaluation