Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pa Tho Physiology
Transféré par
nhiqueDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pa Tho Physiology
Transféré par
nhiqueDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
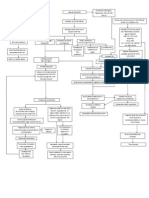
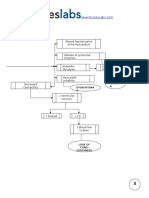
a. Pathophysiology a.
2 Patient-centered
Non-modifiable: Modifiable factors: High sodium diet Post Streptococcal Infection
Age: 6 years old Sex: MALE
Invasion of antigen Group A beta hemolytic streptococcus
Antigen-antibody reaction stimulating plasma
Deposition of antigenantibody complexes in glomerulus
Increase in production of epithelial cells lining the glomerulus
Chemotactic attraction
Infiltration of WBC to the glomerulus Swelling of the cells Phagocytosis + release of proteases and free radicals
Release of endogenous pyrogens
Inflamed tissue containing varying portion of necrotic tissue, dead neutrophils and macrophages
Damage to the glomeruli Basement membrane of glomerulus is exposed Platelet aggregation
Stimulates release of prostaglandins
Reset the hypothalamic thermostat to higher temperature
Increase passage of pus in the urine (Pus cells of 25hpf, 01-24-12; 10-15hpf 1-2512;on the urinalysis)
Thickening of glomerular filtration membrane Some loss of glomerular filtration membrane Acute Glomerulonephritis
Absence of disruption of excretory function
Altered kidney function
Increase permeability of glomerular membrane
Decrease excreation of nitrogenous waste
Altered glomerular function
Retention of nitrogenous waste in the body
Passage/release of red blood cells (Hematuria: 10-15hpf 01-24-12; 15-20 01-25-12 in the urinalysis) Decrease red blood cell count (Hemoglobin of 100g/l in the urinalysis, 01-24-12)
increase protein loss ( +2 01-24-12; +3 01-25-12 in the urinalysis )
Increase BUN and Creatinine
Loss of plasma albumin, Hypoalbuminemia
Decrease colloid oncotic pressure
Fluid diffuse into the interstitial space
Decrease intravascular volume (Hypovolemia)
Accumulation of fluid in the face and extremities
Reduced glomerular filtration rate
Stimulation of renninangiotensin aldosterone system
Facial, both hands and feet edema Release of rennin from juxtamedullary of kidneys onto the bloodstream feet edema during the admission and only at the lower extremeties at 01/24-25/12
Rennin reacts with angiotensin from the liver
Angiotensin I
Angiotensin will interact with angiotensin converting enzyme from the lungs
Release of Angiotensin II (potent vasoconstrictor)
Stimulation of adrenal cortex, excretion of aldosterone Sodium and water retention
Generalized vasoconstriction
Hypertension (BP of 130/90 mmHg, 01/24-26/12)
Adding to the accumulation of extracellular fluid
edema during admission and only lower extremities 01/24-25/12)
Boost blood pressure
Hypertension (BP of 130/90 mmHg, 01/24-26/12)
Sodium dilution
Extracellular fluid hypoosmolality
Potassium shifts from intracellular fluids compartment to extracellular fluids
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)D'EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Acute GlomerulonephritismatahfakahPas encore d'évaluation
- Schemdi NcaDocument8 pagesSchemdi NcaEiram Esoj SalcedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Alert Medical Series: Internal Medicine Alert I, II, IIID'EverandAlert Medical Series: Internal Medicine Alert I, II, IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology: PolydipsiaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology: PolydipsiaMichael Erick Valera VirtucioPas encore d'évaluation
- UWorld Cards July 14Document7 pagesUWorld Cards July 14smian08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sindroma NefrotikDocument57 pagesSindroma NefrotikAstria Puspita SariPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrotic Syndrome (NS)Document16 pagesNephrotic Syndrome (NS)Nur Suci AmanahPas encore d'évaluation
- GlomerulonephritisDocument59 pagesGlomerulonephritistressPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Electrolyte Interactive DiscussionDocument64 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Interactive DiscussionGloria Shiela CoyocaPas encore d'évaluation
- HyperkalemiaDocument86 pagesHyperkalemiaSuresh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Glo Me Rulo NephritisDocument74 pagesGlo Me Rulo NephritisnewtypePas encore d'évaluation
- Patient Evaluation ChartsDocument63 pagesPatient Evaluation Chartsulka07100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Clients With Urinary Tract DisordersDocument70 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Urinary Tract DisordersYuu Ayu'k LifestarPas encore d'évaluation
- Screenshot 2022-12-05 at 15.41.06Document122 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-05 at 15.41.06Senuri ManthripalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Steroid Responsif Nephrotic Syndrome (SRNS)Document16 pagesSteroid Responsif Nephrotic Syndrome (SRNS)Ikrar AbdillahPas encore d'évaluation
- Physio B 1.2 Renal Physiology Pt. 4 (Dr. Vila) : Because of Increase Water ReabsorptionDocument5 pagesPhysio B 1.2 Renal Physiology Pt. 4 (Dr. Vila) : Because of Increase Water ReabsorptionAnny AlvrzPas encore d'évaluation
- Isotope Cases NucsDocument68 pagesIsotope Cases NucsMahmoud HussienPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation (1) NephroticDocument13 pagesPresentation (1) Nephrotictsmajumder96Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument44 pagesAcute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney DiseaseIda Bagus Putu Swabawa100% (1)
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument11 pagesPa Tho PhysiologyJonathan CuaPas encore d'évaluation
- ShockDocument53 pagesShockYazn Amjad Mahmoud ElayanPas encore d'évaluation
- RX - RenalDocument4 pagesRX - RenalZahraa RahalPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute & Chronic Pancraetitis 11Document10 pagesAcute & Chronic Pancraetitis 11rebellefleurmePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Conference 1 Renal PhysiologyDocument24 pagesCase Conference 1 Renal PhysiologyFrances GrefalPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Pancreatitis CPCDocument38 pagesAcute Pancreatitis CPCSariu Ali DidiPas encore d'évaluation
- CKD - For Concept MappingDocument7 pagesCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- ICS - 1st LeDocument4 pagesICS - 1st LeAbigail Mayled LausPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 2 STUDY GUIDEDocument121 pagesExam 2 STUDY GUIDEJulie BrandtPas encore d'évaluation
- Anaesthesia For Renal TransplantationDocument46 pagesAnaesthesia For Renal TransplantationShehan WijayasiriwardanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacillary HemoglobinuriaDocument14 pagesBacillary HemoglobinuriaM R AhmmedPas encore d'évaluation
- LaboratoryDocument9 pagesLaboratorymonique_maniquisPas encore d'évaluation
- Sepsis: Recognition, Diagnosis and Early Management: DR Muhammad Burhan PashaDocument38 pagesSepsis: Recognition, Diagnosis and Early Management: DR Muhammad Burhan PashapashaPas encore d'évaluation
- RenalDocument8 pagesRenalLoislane RullPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Pediatrics Head of Pediatric Department RMC RawalpindiDocument34 pagesDr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Pediatrics Head of Pediatric Department RMC RawalpindiHassan AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- NSG IV Test 3Document4 pagesNSG IV Test 3Maria Phebe SinsayPas encore d'évaluation
- GlomerulonephritisDocument8 pagesGlomerulonephritisMatthew Ryan100% (1)
- ACute Kidney Injure Dogs and CatsDocument14 pagesACute Kidney Injure Dogs and CatsBrvo CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 Curs Nefrologie-De Prezentat 4-Ian 2014Document291 pages2014 Curs Nefrologie-De Prezentat 4-Ian 2014Violeta Malina Bîrsan Hodivoianu100% (1)
- Chapter 13 Plasma ProteinsDocument40 pagesChapter 13 Plasma ProteinsHisham AlhirerePas encore d'évaluation
- t2 Kidney DiseaseDocument52 pagest2 Kidney Diseasewany.fyza54Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: By: Jhaziel E. BermejoDocument20 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis: By: Jhaziel E. BermejoJhaziel BermejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument16 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosisjoyshe111100% (2)
- Routine Examination of Urine AND It'S InterpretationDocument64 pagesRoutine Examination of Urine AND It'S InterpretationmeherulafmcPas encore d'évaluation
- Glomerulnephrities, Nephrotic SyndromDocument28 pagesGlomerulnephrities, Nephrotic SyndromJils SureshPas encore d'évaluation
- Glomerulonephritis-1 (Dr. Soffa)Document58 pagesGlomerulonephritis-1 (Dr. Soffa)Rahmailla Khanza Diana FebriliantriPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Kidney Injury - Chronic Kidney DeseaseDocument71 pagesAcute Kidney Injury - Chronic Kidney DeseaseFina Ahmad Fitriana100% (1)
- Fluids Concept MappingDocument1 pageFluids Concept Mappingmariagarcia415100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of DM IIDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of DM IIJulie SimaurioPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolism Study NotesDocument24 pagesMetabolism Study Notesxxx xPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 3 Path o PhysiologyDocument8 pagesExam 3 Path o PhysiologyJennifer JaworskyPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS) : Inayatur Rosyidah., S.Kep - NsDocument62 pagesMultiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS) : Inayatur Rosyidah., S.Kep - Nsmahendra-kurniahPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument23 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesNanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 A PresentationDocument79 pagesModule 3 A PresentationMelinda FiskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Pancreatitis: Sudden Severe Abdominal Pain Systemic UpsetDocument40 pagesAcute Pancreatitis: Sudden Severe Abdominal Pain Systemic UpsetcoolcaesarPas encore d'évaluation
- Narrative Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 pageNarrative Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeNicaMariannePañaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jawaban PertanyaanDocument13 pagesJawaban PertanyaantsruliantyPas encore d'évaluation
- Uworld NotesDocument7 pagesUworld NotesJorge L CastelarPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 5886227480594875398Document7 pages4 5886227480594875398Yousef Al-AmeenPas encore d'évaluation
- AtropineDocument2 pagesAtropineKhalid MatterPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review KEYDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review KEYbipin jainPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem LEC-Activity 1Document2 pagesBiochem LEC-Activity 1PATRICIA DIANNE EHONGPas encore d'évaluation
- Life Processes 2Document30 pagesLife Processes 2Generic namePas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Failure in Dogs: 6 Practical Tips From CardiologistsDocument6 pagesHeart Failure in Dogs: 6 Practical Tips From CardiologistsJessareth Atilano CapacioPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 10 Biology - Transportation in Human BeingsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 10 Biology - Transportation in Human BeingsmrneetgamerPas encore d'évaluation
- (Electroconvulsive Therapy in Practice) David Semple - Pragmatic Guidance For EEG Interpretation-Independently Published (2016)Document81 pages(Electroconvulsive Therapy in Practice) David Semple - Pragmatic Guidance For EEG Interpretation-Independently Published (2016)Josue LeivaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Spleen Meridian, Sweet Flavors and Balanced BioRhythmsDocument5 pagesThe Spleen Meridian, Sweet Flavors and Balanced BioRhythmsلوليتا وردةPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 1 Philippine Medical Technology LawsDocument4 pagesPart 1 Philippine Medical Technology LawsEdgie CaburalPas encore d'évaluation
- CVC RemovalDocument5 pagesCVC RemovalRiza ZaharaPas encore d'évaluation
- EE3BB3 Homework2 SolnsDocument6 pagesEE3BB3 Homework2 SolnsKashif AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Plant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions Part 2 PDFDocument57 pagesModule 1 Plant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions Part 2 PDFMoto FlashPas encore d'évaluation
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- F4D 24Document2 pagesF4D 24Ivan WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12: Heart: Functions of The HeartDocument12 pagesChapter 12: Heart: Functions of The Heartchristian anchetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation STO: (Goal Met)Document2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation STO: (Goal Met)Arian May MarcosPas encore d'évaluation
- Braza, Reynold o Hencm109Document43 pagesBraza, Reynold o Hencm109Glen DalePas encore d'évaluation
- Shock in Children TutorialDocument37 pagesShock in Children TutorialSsenyonga DominicPas encore d'évaluation
- Syok HipovolemikDocument21 pagesSyok HipovolemikIrfandy Chairi Sulaiman LubisPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemical Pharmacology - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocument17 pagesBiochemical Pharmacology - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVPas encore d'évaluation
- SAS For Biochemistry (BIO 024) Module #9Document35 pagesSAS For Biochemistry (BIO 024) Module #9jeannikkavPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg or TmegDocument23 pagesEcg or TmegdikstfivePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan #1 Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goal/Objective Intervention Rational EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan #1 Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goal/Objective Intervention Rational EvaluationmalindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Nursing Mnemonics & Tips - NurseslabsDocument19 pagesPharmacology Nursing Mnemonics & Tips - Nurseslabsmaniz442100% (2)
- Solved Problems in ErgonomicsDocument31 pagesSolved Problems in Ergonomicsrianna rose dela cruz100% (2)
- First Semester 2020-2021 ECG Course Study Guide: University of The CordillerasDocument27 pagesFirst Semester 2020-2021 ECG Course Study Guide: University of The CordillerasGlory Anne Joy WillyPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEx PDFDocument79 pagesPhysioEx PDFSanchai RabinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nodes of RanvierDocument25 pagesNodes of RanvierHariharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Araling Panlipunan 2Document64 pagesAraling Panlipunan 2Alyce Ajtha100% (1)