Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
IB Chemistry BioChem WS 1
Transféré par
whalerfishDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
IB Chemistry BioChem WS 1
Transféré par
whalerfishDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
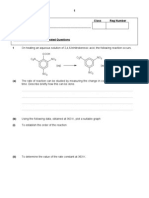
IB Chemistry BioChem WS 1 Carbon Compounds
1. What is an organic compound? 2. Besides carbon, name 3 other elements that make up most organic compounds. 3. Carbon dioxide, CO2, is NOT an organic compound. Explain why.
4. How many electrons are in the outermost energy level of carbon? How many does it need to have this energy level filled?
5. How many covalent bonds can carbon form?
6. Draw these 3 molecules and circle a single bond, double bond, and a triple bond in your drawings --- benzene, acetylene, and ethanol.
7. Explain what is meant by a functional group, & tell what effect they have on the molecules they are attached to.
8. Write the formula for these functional groups --- hydroxyl, carboxyl, phosphate group, amino group, and methyl group.
9. Hydroxyl groups attached to carbon atoms forms an _____________. 10. Name an alcohol used in humans to assemble molecules needed for life.
11. Large carbon molecules are built from smaller, simpler molecules called ____________. 12. Large carbon molecules made of monomers are called _______________. 13. What are large polymers called? 14. What type of reaction links monomers to make polymers? 15. Sketch a molecule of sucrose (table sugar) formed from condensation. Name the 2 sugars that were combined to form sucrose
16. Condensation reactions involve the removal of a molecule of ____________. 17. What reaction is used to breakdown polymers? Is water added or removed? How does this compare to condensation?
Macromolecules
18. Name the 4 main classes of macromolecules (organic molecules) & tell what 3 elements all of these contain.
Carbohydrates store energy for organisms!
19. In what ratio are hydrogen & oxygen atoms in carbohydrates? 20. In what 3 forms do carbohydrates exist?
21. What are the monomers of carbohydrates called? What is their common name? Give the ratio of carbons, hydrogens, & oxygens.
22. Name the 3 common monosaccharides.
23. Sketch & label a molecule of each of these monosaccharides. How do they compare? Write the chemical formula for all three.
24. Because all 3 simple sugars have the same chemical, but different structural formulas, they are called _______________. 25. What are double sugars called? Name & describe the process that forms them.
26. Name 3 common disaccharides and draw and label each part. How do they compare? Write the chemical formula for all three. Why are they important to the human body?
27. What forms a polysaccharide? Name a polysaccharide found in animals. Name 2 found in plants? What are their functions?
28. What chemical reaction formed these large molecule? What reaction would be needed to break these molecules? What human disorders might be caused by these?
Proteins are used to build cells, & they act as enzymes!
29. What are the 4 main elements making up proteins? How many covalent bonds does each of these elements form?
30. Sketch these two amino acids --- glycine & alanine. Circle the center carbon, place a triangle around the amino group, and put a box around the carboxyl group.
31. What are the monomers of proteins called? How many are there? Name the 4 things bonded to the center carbon of this monomer.
32. The main difference among amino acids is their ___________ group. What is the R-group on glycine? on alanine? Why is this important?
33. How does a dipeptide form? Sketch and label the dipeptide formed from glycine and alanine. What molecule had to be removed to join these 2 amino acids?
34. What do you call the covalent bonds that hold amino acids together? Put a box around these bonds and label them in the sketch you did on question 33. 35. Long chains of amino acids are called ___________________ and these join together to make a ________________.
36. Hydrogen bonding among individual amino acids in a chain cause what effect on the protein's shape?
37, What is the effect of temperature on protein shape? Give an example of this.
Lipids include fats that are used for long-term energy storage!
38. Are lipids polar or nonpolar? What happens to lipids when they are placed in water? 39. Compared to carbohydrates, what is true about the ratio of carbon & hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms? If a compound has more bonds, what can it store more of in those bonds?
40. Most lipids are made of ______________ acids. Describe their shape. What functional group is found on the head end of the molecule?
41. Sketch these 2 fatty acids --- palmitic & linoleic. Circle the carboxyl group on the "head" of the molecule. Is this end polar or nonpolar? Will this end be attracted to or repelled by water?
42. Are both ends of a fatty acid polar? Explain.
43. Hydophilic means water ___________. Which end of a fatty acid is hydrophilic. The nonpolar end of a fatty acid is said to be _______________ or "water fearing". 44. Which end of a fatty acid chain WOULD dissolve in water? Which WOULDN'T?
45. In what type of fatty acid are there only single bonds in the carbon chain? Name one such fatty acid. 46. What type of bond appears in an unsaturated fatty acid? Give an example of an unsaturated fatty acid. Go back to your fatty acid drawings in question 41 and put a box around the double bond in the unsaturated fatty acid.
47. Name the 3 groups of complex lipids. 48. What makes up a triglyceride? What is the difference between a saturated & unsaturated triglyceride?
49. What type of triglycerides tend to be solids at room temperature & why? Which are liquids & why?
50. What type of triglyceride would these substances be --- vegetable oil? butter & shortening?
51. What makes up a phospholipid? How are they different from triglycerides? What main part of a cell is made of phospholipids?
52. What is meant by a lipid bilayer? What makes this such an effective barrier between the inside & the outside of the cell? Draw and label a phospholipid bilayer.
53. What makes up steroids? To what group of organic compounds do steroids belong? How are they used in animals?
54. Name a steroid made by the body & used by nerve cells.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Organic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristicDocument8 pagesOrganic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristictasneemPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.1 Calculation Sheet Shapes of MoleculesDocument2 pages6.1 Calculation Sheet Shapes of MoleculesRoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Kerboodle StuffDocument4 pagesKerboodle StuffRoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter: 1 Stoichiometric Relationships: SubtopicsDocument108 pagesChapter: 1 Stoichiometric Relationships: SubtopicsBPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Chemistry Objectives - KineticsDocument1 pageIB Chemistry Objectives - KineticslizarrdoPas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel IAS Bonding 1Document14 pagesEdexcel IAS Bonding 1mostafa barakatPas encore d'évaluation
- Mini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationDocument15 pagesMini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationSahanNivanthaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 Molecules To Metabolism WorksheetDocument3 pages2.1 Molecules To Metabolism WorksheetSayedMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- BondingDocument52 pagesBondingArian CoenPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 10 HLQDocument23 pagesTopic 10 HLQVũ Đức DuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib Chemistry SL SyllabusDocument3 pagesIb Chemistry SL Syllabusapi-235378008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spectroscopy WorksheetDocument24 pagesSpectroscopy Worksheetpokemon goPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Sample TestDocument31 pagesIB Sample TeststonedinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rates Review Questions (HL)Document8 pagesRates Review Questions (HL)nadia sykesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Topic 4 QuestionsDocument19 pagesChem Topic 4 QuestionsOscarHigson-SpencePas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Document3 pagesGas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Nikhil Singh100% (1)
- Ib PPT 3 SL PDFDocument24 pagesIb PPT 3 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4 TestDocument10 pagesTopic 4 TestRitik YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFDocument78 pagesH2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFBobPas encore d'évaluation
- Rings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie PeckDocument14 pagesRings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie Peckrobbiepeck100% (1)
- H2 Inorganic ChemistryDocument7 pagesH2 Inorganic ChemistrykitoniumPas encore d'évaluation
- SNR Chemistry 19 Formula Data BookDocument17 pagesSNR Chemistry 19 Formula Data Bookapi-125934329Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acids and BasesDocument49 pagesAcids and BasesapagtemainPas encore d'évaluation
- U3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT WatermarkDocument45 pagesU3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT Watermarkapi-125934329Pas encore d'évaluation
- NMR Booklet QuestionsDocument21 pagesNMR Booklet QuestionsSumaira AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Redox WKSHTDocument4 pagesRedox WKSHTMarco ConopioPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxidation Numbers: Chemistry For The Gifted and Talented 61Document14 pagesOxidation Numbers: Chemistry For The Gifted and Talented 61EricPas encore d'évaluation
- Module As Level ChemistryDocument407 pagesModule As Level ChemistryBank Yossy WoluslawePas encore d'évaluation
- Rates and EquilibriaDocument15 pagesRates and EquilibriaThaarvena RetinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Foundation Organic Q in A LevelDocument21 pagesCommon Foundation Organic Q in A Level黄维燕Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Stoichiometric RelationshipsDocument77 pages7 Stoichiometric RelationshipsLuka MaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 10 Organic Chemistry 10.1 To 10.2 20.1 To 20.3Document120 pagesTopic 10 Organic Chemistry 10.1 To 10.2 20.1 To 20.3Supriyaa ChordiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 YJC Prelim H2 Chem P1 W AnsDocument18 pages2014 YJC Prelim H2 Chem P1 W AnswaimoePas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 7 - Chemistry - IBDocument22 pagesTopic 7 - Chemistry - IBAN NGUYENPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-IB Chemistry Mid-Term Review List (Nagel)Document3 pagesPre-IB Chemistry Mid-Term Review List (Nagel)Helie100% (1)
- H432-01-Periodic Table, Elements and Physical Chemistry/a Level Chemistry A H432 - H432-01 - QS13Document5 pagesH432-01-Periodic Table, Elements and Physical Chemistry/a Level Chemistry A H432 - H432-01 - QS13Altay ShawPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ Madness 1 PDFDocument15 pagesMCQ Madness 1 PDFnotabc gamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 Organic QuestionsDocument65 pagesUnit 4 Organic Questionsareyouthere92100% (1)
- A2 Acid and Base NotesDocument33 pagesA2 Acid and Base NotesZim Ahmed ZavianPas encore d'évaluation
- Ques202 295bon2mcDocument13 pagesQues202 295bon2mcMuhammad HaneefPas encore d'évaluation
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 18 Answer SchemeDocument17 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 18 Answer SchemeNicholas OwPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Chemical EquilibriumDocument43 pagesCharacteristics of Chemical Equilibriumpimpin1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fill in The Table Below:: Empirical Formula WorksheetDocument2 pagesFill in The Table Below:: Empirical Formula WorksheetSherida GibbsPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 10 HLQDocument21 pagesTopic 10 HLQPipen 5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Practice Test 4u1Document4 pagesChapter 4 Practice Test 4u1helloblargPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Quantitative Chemistry Home Learning SheetsDocument30 pagesGCSE Quantitative Chemistry Home Learning SheetsShaheer HashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1.1 Arenes Notes OCR A2 ChemistryDocument3 pages1.1.1 Arenes Notes OCR A2 ChemistryCharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry II EM Basic Learning MaterialDocument40 pagesChemistry II EM Basic Learning MaterialMAHINDRA BALLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 MCQsDocument22 pagesUnit 6 MCQsFiras AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5Document386 pagesEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5AbdulRahman Mustafa100% (1)
- H2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)Document12 pagesH2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)iuhihzPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Notes PT 1Document55 pagesChemistry Notes PT 1EdcademiaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Determination of Carboxylic Functional Groups: Monographs in Organic Functional Group AnalysisD'EverandThe Determination of Carboxylic Functional Groups: Monographs in Organic Functional Group AnalysisPas encore d'évaluation
- A New Fatigue Damage Accumulation Rating Life Model of Ball Bearings Under Vibration LoadDocument11 pagesA New Fatigue Damage Accumulation Rating Life Model of Ball Bearings Under Vibration LoadAlbertoPas encore d'évaluation
- SaciDocument55 pagesSaciMohammad Arif ImronPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Mukesh Kumar Department of Earthquake Engineering, NED University, KarachiDocument37 pagesDr. Mukesh Kumar Department of Earthquake Engineering, NED University, KarachiMukesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Antena Tipo LazoDocument2 pagesAntena Tipo LazoMarllory CobosPas encore d'évaluation
- Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, HisarDocument42 pagesGuru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, HisarSwati SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- WHCP BasicsDocument21 pagesWHCP BasicsbalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Internship Report Sample 5Document35 pagesInternship Report Sample 5SUMIT KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements of Feedback Control SystemsDocument53 pagesElements of Feedback Control SystemschanonPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic of Tangential VortexDocument14 pagesHydraulic of Tangential VortexKhanh ChiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Separation of Oil and WaterDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Separation of Oil and Waterodracir091865100% (1)
- As 1012.11-2000 Methods of Testing Concrete - DeterminationDocument9 pagesAs 1012.11-2000 Methods of Testing Concrete - Determinationmm100% (1)
- The Comparative Study For Scale Inhibition On Surface of RO Membranes in Wastewater Reclamation: CO2 Purging Versus Three Different AntiscalantsDocument9 pagesThe Comparative Study For Scale Inhibition On Surface of RO Membranes in Wastewater Reclamation: CO2 Purging Versus Three Different AntiscalantsKashif ButtPas encore d'évaluation
- NEXAFS Tutorial Review ArticleDocument12 pagesNEXAFS Tutorial Review ArticleAngelique LusuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces Balanced and UnbalancedDocument24 pagesForces Balanced and UnbalancedInah Cunanan-BaletePas encore d'évaluation
- Nonlinear Systems: Lyapunov Stability Theory - Part 2Document36 pagesNonlinear Systems: Lyapunov Stability Theory - Part 2giacomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gazetas 2015 Soil - Footing - Interaction PDFDocument17 pagesGazetas 2015 Soil - Footing - Interaction PDFMatías MoragaPas encore d'évaluation
- THE FIFTH HORSEMAN OF THE APOCALYPSE. July - December 1962 UFOS - A HISTORY. Copyright Fremont CADocument86 pagesTHE FIFTH HORSEMAN OF THE APOCALYPSE. July - December 1962 UFOS - A HISTORY. Copyright Fremont CAOvnis FormosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Test: Grade: 3 Time: 30 Minutes Your Name: .. ScoreDocument8 pagesFinal Test: Grade: 3 Time: 30 Minutes Your Name: .. ScoreThu NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Cat Apem Ermec Nuevo Catalogo General de Pulsadores Interruptores Apem Big Blue 2011 12Document589 pagesCat Apem Ermec Nuevo Catalogo General de Pulsadores Interruptores Apem Big Blue 2011 12Josue BerzunzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Life in Zero-G: Physiological EffectsDocument2 pagesLife in Zero-G: Physiological Effectsansweringthecal100% (1)
- Leaded Receptacle Switch BrochureDocument18 pagesLeaded Receptacle Switch BrochureArturo De Asis SplushPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurements and Instrumentation Unit 1Document62 pagesMeasurements and Instrumentation Unit 1R. Jhansirani83% (6)
- Test SyllabusDocument4 pagesTest SyllabusAjinkya Aniruddha DangePas encore d'évaluation
- BC 107Document3 pagesBC 107Sreerag Kunnathu SugathanPas encore d'évaluation
- W Stephens Resume 2013Document3 pagesW Stephens Resume 2013Marcus HumphreyPas encore d'évaluation
- GEC 17 Lesson 1 Introduction To STSDocument15 pagesGEC 17 Lesson 1 Introduction To STSJhupit Ganihay100% (1)
- First-Order Linear Fuzzy Differential Equations On The Space of Linearly Correlated Fuzzy NumbersDocument33 pagesFirst-Order Linear Fuzzy Differential Equations On The Space of Linearly Correlated Fuzzy NumbersHo Nhat NamPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and Life Science Copy (Repaired)Document39 pagesEarth and Life Science Copy (Repaired)Aaron Manuel MunarPas encore d'évaluation
- B Sc-MathsDocument24 pagesB Sc-MathsVijayakumar KopPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008 PJC CH H2 P3 PrelimDocument12 pages2008 PJC CH H2 P3 PrelimdeadbeanPas encore d'évaluation