Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cisco Discovery Protocol: Understanding CDP
Transféré par
weiipennaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cisco Discovery Protocol: Understanding CDP
Transféré par
weiipennaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cisco Discovery Protocol
This document describes how to configure Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP). It contains these sections:
Understanding CDP, page 1 Configuring CDP, page 1 Monitoring and Maintaining CDP, page 4
Understanding CDP
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a device-discovery protocol that runs on all Cisco network equipment. Each device sends identifying messages to a multicast address, and each device monitors the messages sent by other devices. Information in CDP packets is used in network management software such as CiscoWorks2000. CDP is enabled on the WMICs Ethernet and radio ports by default.
Note
For best performance on your wireless LAN, disable CDP on all radio interfaces and on subinterfaces if VLANs are enabled.
Configuring CDP
This section contains CDP configuration information and procedures:
Default CDP Configuration, page 2 Configuring the CDP Characteristics, page 2 Disabling and Enabling CDP, page 2 Disabling and Enabling CDP on an Interface, page 3
Americas Headquarters: Cisco Systems, Inc., 170 West Tasman Drive, San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA
2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Discovery Protocol Configuring CDP
Default CDP Configuration
Table 1 lists the default CDP settings.
Table 1 Default CDP Configuration
Feature CDP global state CDP interface state CDP holdtime (packet holdtime in seconds) CDP timer (packets sent every x seconds)
Default Setting Enabled Enabled 180 60
Configuring the CDP Characteristics
You can configure the CDP holdtime (the number of seconds before the WMIC discards CDP packets) and the CDP timer (the number of seconds between each CDP packets the WMIC sends). To configure the CDP holdtime and CDP timer, follow these steps, beginning in privileged EXEC mode: Command
Step 1 Step 2
Purpose Enters global configuration mode. (Optional) Specifies the amount of time a receiving device should hold the information sent by your device before discarding it. The range is from 10 to 255 seconds; the default is 180 seconds. (Optional) Sets the transmission frequency of CDP updates in seconds. The range is from 5 to 254; the default is 60 seconds. Returns to Privileged EXEC mode.
configure terminal cdp holdtime seconds
Step 3
cdp timer seconds
Step 4
end
Use the no form of the CDP commands to return to the default settings. This example shows how to configure and verify CDP characteristics:
bridge# configure terminal bridge(config)# cdp holdtime 120 bridge(config)# cdp timer 50 bridge(config)# end bridge# show cdp Global CDP information: Sending a holdtime value of 120 seconds Sending CDP packets every 50 seconds
For additional CDP show commands, see the Monitoring and Maintaining CDP section on page 4.
Disabling and Enabling CDP
To disable the CDP device discovery capability, follow these steps, beginning in privileged EXEC mode:
Cisco 3200 Series Wireless MIC Software Configuration Guide
Cisco Discovery Protocol Configuring CDP
Command
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Purpose Enters global configuration mode. Disables CDP. Returns to Privileged Exec mode.
configure terminal no cdp run end
To enable CDP, follow these steps, beginning in privileged EXEC mode: Command
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Purpose Enters global configuration mode. Enables CDP after disabling it. Returns to privileged EXEC mode.
configure terminal cdp run end
This example shows how to enable CDP.
bridge# configure terminal bridge(config)# cdp run bridge(config)# end
Disabling and Enabling CDP on an Interface
CDP is enabled by default on all supported interfaces to send and receive CDP information. To disable CDP on an interface, follow these steps, beginning in privileged EXEC mode: Command
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 5
Purpose Enters global configuration mode. Enters interface configuration mode, and enter the interface on which you are disabling CDP. Disables CDP on an interface. Returns to privileged EXEC mode. (Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file.
configure terminal interface interface-id no cdp enable end copy running-config startup-config
To enable CDP on an interface, follow these steps, beginning in privileged EXEC mode: Command
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 5
Purpose Enters global configuration mode. Enters interface configuration mode, and enter the interface on which you are enabling CDP. Enables CDP on an interface after disabling it. Returns to privileged EXEC mode. (Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file.
configure terminal interface interface-id cdp enable end copy running-config startup-config
Cisco 3200 Series Wireless MIC Software Configuration Guide
Cisco Discovery Protocol Monitoring and Maintaining CDP
This example shows how to enable CDP on an interface:
bridge# configure terminal bridge(config)# interface x bridge(config-if)# cdp enable bridge(config-if)# end
Monitoring and Maintaining CDP
To monitor and maintain CDP on your device, perform one or more of these tasks, beginning in privileged EXEC mode. Command clear cdp counters clear cdp table show cdp show cdp entry entry-name [protocol | version] Description Resets the traffic counters to zero. Deletes the CDP table of information about neighbors. Displays global information, such as frequency of transmissions and the holdtime for packets being sent. Displays information about a specific neighbor. You can enter an asterisk (*) to display all CDP neighbors, or you can enter the name of the neighbor about which you want information. You can also limit the display to information about the protocols enabled on the specified neighbor or information about the version of software running on the device. show cdp interface [type number] Displays information about interfaces where CDP is enabled. You can limit the display to the type of interface or the number of the interface about which you want information (for example, entering gigabitethernet 0/1 displays information only about Gigabit Ethernet port 1). show cdp neighbors [type number] [detail] Displays information about neighbors, including device type, interface type and number, holdtime settings, capabilities, platform, and port ID. You can limit the display to neighbors on a specific type or number of interface or expand the display to provide more detailed information. show cdp traffic Displays CDP counters, including the number of packets sent and received and checksum errors. Below are six examples of output from the CDP show privileged EXEC commands:
bridge# show cdp Global CDP information: Sending CDP packets every 50 seconds Sending a holdtime value of 120 seconds bridge# show cdp entry * ------------------------Device ID: bridge Entry address(es): IP address: 10.1.1.66 Platform: cisco WS-C3550-12T, Capabilities: Switch IGMP Interface: GigabitEthernet0/2, Port ID (outgoing port): GigabitEthernet0/2 Holdtime : 129 sec
Cisco 3200 Series Wireless MIC Software Configuration Guide
Cisco Discovery Protocol Monitoring and Maintaining CDP
Version : Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) C3550 Software (C3550-I5Q3L2-M), Experimental Version 12.1(20010612:021 316) [jang-flamingo 120] Copyright (c) 1986-2001 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Fri 06-Jul-01 18:18 by jang advertisement version: 2 Protocol Hello: OUI=0x00000C, Protocol ID=0x0112; payload len=27, value=0000000 0FFFFFFFF010221FF00000000000000024B293A00FF0000 VTP Management Domain: '' Duplex: full ------------------------Device ID: idf2-1-lab-l3.cisco.com Entry address(es): IP address: 10.1.1.10 Platform: cisco WS-C3524-XL, Capabilities: Trans-Bridge Switch Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1, Port ID (outgoing port): FastEthernet0/10 Holdtime : 141 sec Version : Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) C3500XL Software (C3500XL-C3H2S-M), Version 12.0(5.1)XP, MAINTENANCE IN TERIM SOFTWARE Copyright (c) 1986-1999 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Fri 10-Dec-99 11:16 by cchang advertisement version: 2 Protocol Hello: OUI=0x00000C, Protocol ID=0x0112; payload len=25, value=0000000 0FFFFFFFF010101FF000000000000000142EFA400FF VTP Management Domain: '' bridge# show cdp entry * protocol Protocol information for talSwitch14 : IP address: 172.20.135.194 Protocol information for tstswitch2 : IP address: 172.20.135.204 IP address: 172.20.135.202 Protocol information for tstswitch2 : IP address: 172.20.135.204 IP address: 172.20.135.202 bridge# show cdp interface GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/2 is up, line protocol is down Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/3 is administratively down, line protocol is down Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/4 is up, line protocol is down Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/5 is up, line protocol is up Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds
Cisco 3200 Series Wireless MIC Software Configuration Guide
Cisco Discovery Protocol Monitoring and Maintaining CDP
GigabitEthernet0/6 is up, line Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/7 is up, line Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/8 is up, line Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 Holdtime is 180 seconds
protocol is up seconds protocol is down seconds protocol is down seconds
bridge# show cdp neighbor Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater Device IDLocal InterfaceHoldtmeCapabilityPlatformPort ID Perdido2Gig 0/6125R S IWS-C3550-1Gig0/6 Perdido2Gig 0/5125R S IWS-C3550-1Gig 0/5 bridge# show cdp traffic CDP counters : Total packets output: 50882, Input: 52510 Hdr syntax: 0, Chksum error: 0, Encaps failed: 0 No memory: 0, Invalid packet: 0, Fragmented: 0 CDP version 1 advertisements output: 0, Input: 0 CDP version 2 advertisements output: 50882, Input: 52510
Cisco 3200 Series Wireless MIC Software Configuration Guide
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)Document3 pagesCisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)CCNAResourcesPas encore d'évaluation
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkD'EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Discovery Protocol: Understanding How CDP WorksDocument5 pagesCisco Discovery Protocol: Understanding How CDP Worksabhia16Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - Configure CDP and LLDP: (Instructor Version)Document20 pagesLab - Configure CDP and LLDP: (Instructor Version)de veronPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.2.2.6 Lab - Configure CDP and LLDPDocument10 pages2.2.2.6 Lab - Configure CDP and LLDPAnonymous XQC6Rw0% (2)
- Configuring Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)Document4 pagesConfiguring Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)spirit9009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationD'EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2. CDP - LLDP - Telnet - SDMDocument15 pages3.2. CDP - LLDP - Telnet - SDMQuân Lâm MinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 4 1 6Document6 pagesLab 4 1 6HamzaSpahijaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.8.2 Lab Configure CDP, LLDP, and NTP - PDF AnswerDocument15 pages10.8.2 Lab Configure CDP, LLDP, and NTP - PDF AnswerVinicio MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 8 Switching Features and Technologies For Campus NetworksDocument74 pagesCh. 8 Switching Features and Technologies For Campus NetworksJe RelPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning About Other Devices - JPDocument10 pagesLearning About Other Devices - JPCehPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Network Lab - 1 (Cisco Packet Tracer) 1. Build A Peer To Peer Network Between Two PcsDocument11 pagesComputer Network Lab - 1 (Cisco Packet Tracer) 1. Build A Peer To Peer Network Between Two PcsmunshinawPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-9 Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) : Free CCNA Study GuidesDocument7 pages3-9 Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) : Free CCNA Study GuidesJose A Aparicio FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna2 4p2Document41 pagesCcna2 4p2Alok SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- C05 (En) (Learning About Other Devices CDP)Document22 pagesC05 (En) (Learning About Other Devices CDP)NisrinePas encore d'évaluation
- 14 - Configuring A RouterDocument25 pages14 - Configuring A RouterQuan PhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Router Behind CM 19268Document5 pagesRouter Behind CM 19268Pablo Guerrero GuzmánPas encore d'évaluation
- Close Window: T o P o F F o R M B o TT o M o F F o R M 2094090Document8 pagesClose Window: T o P o F F o R M B o TT o M o F F o R M 2094090Chioma Iheanacho CynthiaPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Sample QuestionsDocument12 pagesCCNA Sample Questionssujit mohanPas encore d'évaluation
- ENSA Module 10Document69 pagesENSA Module 10Hanifi ElabidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer:A & EDocument15 pagesAnswer:A & ELvenkatesh VenkateshPas encore d'évaluation
- © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument19 pages© 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedVo Ngoc HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Quiz + AdditivesDocument57 pagesCCNA Quiz + AdditivesAfiz Kam100% (3)
- Module 10: Network Management: Instructor MaterialsDocument81 pagesModule 10: Network Management: Instructor Materialspatrick gucakePas encore d'évaluation
- CDP CommandsDocument24 pagesCDP CommandsAaron Reyes SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco DSL Router Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide Step by Step Configuration of Pppoe With A Static Ip AddressDocument8 pagesCisco DSL Router Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide Step by Step Configuration of Pppoe With A Static Ip AddresschatwirojPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Router ConfigDocument8 pagesBasic Router ConfigKaka MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Tejas Node ConfigDocument20 pagesTejas Node ConfigAnuj Kumar100% (1)
- Show - CDP - Neighbors - HTML - CiscoDocument3 pagesShow - CDP - Neighbors - HTML - Ciscomobio jeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Day3 Ch2 Manag IOSDocument27 pagesDay3 Ch2 Manag IOSManoj BorahPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna 2 Module 5Document8 pagesCcna 2 Module 5Jerry CherPas encore d'évaluation
- ICND20S01L04Document37 pagesICND20S01L04api-3706840Pas encore d'évaluation
- Day 10 CDPDocument10 pagesDay 10 CDPPranavPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 3.0 Network ManagementDocument70 pagesTopic 3.0 Network Managementabinissri rajamuniswaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Acl 4.2.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1Document3 pagesAcl 4.2.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1Emerson Emerson AemersonPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA2 Lab Inst 3 1 5 enDocument18 pagesCCNA2 Lab Inst 3 1 5 enblahblah2331Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Command SummaryDocument3 pagesCisco Command SummaryLeelavathi BakthavathchalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Spanning Tree Lab: Step 1: Getting Familiar With Switch IOSDocument21 pagesSpanning Tree Lab: Step 1: Getting Familiar With Switch IOSNPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring Devices For Use With Cisco Configuration Professional (CCP) 2.5Document8 pagesConfiguring Devices For Use With Cisco Configuration Professional (CCP) 2.5Irfee100% (1)
- Configuring Ipsec With Eigrp and Ipx Using Gre Tunneling: Document Id: 14136Document12 pagesConfiguring Ipsec With Eigrp and Ipx Using Gre Tunneling: Document Id: 14136cybersh3657Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Security Packet Tracer Skill Based Assessment PracticeDocument9 pagesCCNA Security Packet Tracer Skill Based Assessment PracticeFrija011Pas encore d'évaluation
- Radio Setup Procedures - Remote - ACMDocument10 pagesRadio Setup Procedures - Remote - ACMEdwin RincónPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Implement SNMP and SyslogDocument11 pagesLab Implement SNMP and SyslogJuan PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Mod5 TestDocument6 pagesMod5 TestGavin Spartan WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.9.2 Lab - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - ILMDocument12 pages2.9.2 Lab - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - ILMMariano PereyraPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced IOS Functions - : The Configuration RegisterDocument5 pagesAdvanced IOS Functions - : The Configuration RegisterMkPas encore d'évaluation
- QCI-AN028 ModbusTCPDocument9 pagesQCI-AN028 ModbusTCPSergio RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- NP301 NP312 ManualDocument14 pagesNP301 NP312 ManualĐiều Ước Giản ĐơnPas encore d'évaluation
- It010 707 (Reference) Internetworking LabDocument109 pagesIt010 707 (Reference) Internetworking LabDivya K.SPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route PropagationDocument4 pagesLab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route Propagationmohammad_shahzad_iiuiPas encore d'évaluation
- CNE Tutorial 06 - General Router Conf and Static Routing Conf UpdatedDocument7 pagesCNE Tutorial 06 - General Router Conf and Static Routing Conf UpdatedThơm VũPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.2.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1Document9 pages4.2.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1fabian rodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna2 Mod4 GWDocument21 pagesCcna2 Mod4 GWbaraynavab100% (1)
- 24.1.3 Lab - Implement SNMP and SyslogDocument11 pages24.1.3 Lab - Implement SNMP and SyslogAhmet OZERENPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna HCL Exam QuestionsDocument25 pagesCcna HCL Exam Questionsshyam80Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Routing Protocols OSPF Skills AssessmentDocument10 pagesCCNA Routing Protocols OSPF Skills AssessmentAntonio Adkins75% (4)
- 4.2.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1Document4 pages4.2.2.10 Packet Tracer - Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1Elizabeth BarreraPas encore d'évaluation
- ITCE 416 Lab 1Document8 pagesITCE 416 Lab 1Amna AzmatPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3D'EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Magic Mirror American English Teacher Ver2Document7 pagesMagic Mirror American English Teacher Ver2COORDENAÇÃO FISK CAXIASPas encore d'évaluation
- English 8: First Monthly ExaminationDocument2 pagesEnglish 8: First Monthly ExaminationFloramie MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Friedman and Laurison - Excerpt From The Class CeilingDocument23 pagesFriedman and Laurison - Excerpt From The Class CeilingRyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Herzberg's Model: Motivating and Leading Self-InstructionalDocument2 pagesHerzberg's Model: Motivating and Leading Self-Instructionalp.sankaranarayananPas encore d'évaluation
- COT 1 Plate Boundaries Science 10Document6 pagesCOT 1 Plate Boundaries Science 10Christy Rose VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Attendance Monitoring System and Information Dissemination With Sms Dissemination"Document4 pagesAttendance Monitoring System and Information Dissemination With Sms Dissemination"Emmanuel Baccaray100% (1)
- POEMS Syndrome - A Report of 14 Cases and Review of The LiteratureDocument6 pagesPOEMS Syndrome - A Report of 14 Cases and Review of The LiteratureHabib G. Moutran BarrosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Plan - ME 639Document2 pagesCourse Plan - ME 639Satya SuryaPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-III (Gropu Discussion) (MBA-4 (HR)Document6 pagesUNIT-III (Gropu Discussion) (MBA-4 (HR)harpominderPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: I - ObjectiveDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: I - ObjectiveYanny Manggugubat50% (2)
- Shak-Kushan Abhilekhon Me Varnit Kshatrapa Avam MahaKshatrapaDocument7 pagesShak-Kushan Abhilekhon Me Varnit Kshatrapa Avam MahaKshatrapaAvinash PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Arrival of Guest: Script For Emcee in The Opening CeremonyDocument3 pagesArrival of Guest: Script For Emcee in The Opening Ceremonyamelia golda100% (1)
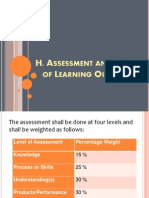
- Assessment and Rating of Learning OutcomesDocument28 pagesAssessment and Rating of Learning OutcomesElisa Siatres Marcelino100% (1)
- IITH Staff Recruitment NF 9 Detailed Advertisement 11-09-2021Document14 pagesIITH Staff Recruitment NF 9 Detailed Advertisement 11-09-2021junglee fellowPas encore d'évaluation
- 5e Lesson-AmharveyDocument3 pages5e Lesson-Amharveyapi-352123670100% (1)
- Lesson1-Foundations of Management and OrganizationsDocument21 pagesLesson1-Foundations of Management and OrganizationsDonnalyn VillamorPas encore d'évaluation
- FE Final ExamDocument2 pagesFE Final Examabraham kassahunPas encore d'évaluation
- Panjab University BA SyllabusDocument245 pagesPanjab University BA SyllabusAditya SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Use of Mind Mapping in The Teaching of Reading A Procedure TextDocument12 pagesThe Use of Mind Mapping in The Teaching of Reading A Procedure TextMuhammad Hidayatul Rifqi100% (1)
- Development CLASSDocument33 pagesDevelopment CLASSJulie JančíPas encore d'évaluation
- CST 47 TeacherDocument56 pagesCST 47 TeacherElena DavalosPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Political EconomyDocument10 pagesWhat Is Political EconomyayulatifahPas encore d'évaluation
- FA3 - Contemporary WorldDocument15 pagesFA3 - Contemporary WorldGill GregorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbs PrepositionsDocument4 pagesVerbs PrepositionsKarina RossiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment TASK 3 AnswerDocument4 pagesAssessment TASK 3 AnswerRajkumar TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Manual For Power System Analysis and Design 5th Edition by Glover PDFDocument15 pagesSolutions Manual For Power System Analysis and Design 5th Edition by Glover PDFFrederick Cas50% (2)
- Resume Final Apr 2019Document2 pagesResume Final Apr 2019Matthew LorenzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Propaganda and Utopianism: The F Amil y and Visual Culture in Earl y Third Republic France (1871-1905)Document642 pagesPropaganda and Utopianism: The F Amil y and Visual Culture in Earl y Third Republic France (1871-1905)Julian Santa RitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wandering Minds Mobile ExhibitDocument3 pagesWandering Minds Mobile ExhibitMichelleTurla-MacarayoPas encore d'évaluation
- MPCE 15 InternshipDocument56 pagesMPCE 15 InternshipRaghavPas encore d'évaluation