Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
KJ
Transféré par
Menalyn SilvestreDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
KJ
Transféré par
Menalyn SilvestreDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CHAPTER 4 : FINANCIAL MARKETS
WHAT ARE FINANCIAL MARKETS? These markets provide a permanent venue for savers and borrowers, and which render financial services whenever required by their customers.
BENEFITS OF FINANCIAL MARKETS 1. Funds are directed to DSUs which can use them most efficiently 2. Liquidity is provided to savers WHY FIRMS INVEST AND BORROW? Firms, at one time or another are confronted by capital deficiency. This happens when opportunities for investment come by. Additional investment may bring additional income or economies in operation. When the owners of the firm cannot provide additional capital, they will resort to borrowing. This situation happens not only to small firms but to big firms as well. A system must be able to address that particular economic need. The answer lies in the operation and maintenance of a financial system which includes financial markets.
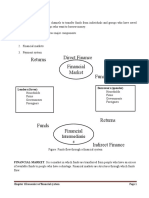
METHOD BY WHICH FINANCIAL MARKETS TRANSFER FUNDS DIRECT FINANCE Refers to lending by ultimate borrowers with no intermediary. Under this method the SSUs gives money to the DSU in exchange for financial claims on the DSU. The claims issued by the DSU are called direct claims and are typically sold in direct credit markets such as the money or capital markets. Direct financing provides SSUs with a venue for savings with expected returns. The DSUs as a result are provided with a source of funds for consumption or investment. This arrangement increases the efficiency of the financial market. ADVANTAGES OF DIRECT FINANCING: 1. These are few DSUs which can transact in the direct market because the denominations of securities sold are very large (usually millions of pesos). 2. It is difficult to match the requirements of SSUs and DSUs in terms of denomination, maturity, and other factors.
METHODS OF DIRECT FINANCING: Private placements Brokers and dealers Investment brokers
Private placement refers to the selling of securities by private negotiation directly to insurance companies, commercial banks, pension funds, large-scale corporate investors, and wealthy individual investors. Brokers is one who acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers but does not take title to the securities traded. Dealer is one who is in the security business acting as a principal rather than an agent. The dealer buys for his account and sells to customers from inventory. He makes profits by selling his inventory of securities at a price higher than the acquisition cost. Investment broker is a person who provides financial advice and who underwrites and distributes new investment securities.
INDIRECT FINANCE (also called financial intermediary) Refers to lending by an ultimate lender to a financial intermediary that then relends to ultimate borrowers. Financial intermediaries include commercial; banks, mutual savings bank, credit unions, life insurance companies and pension funds.
CLASSIFICATION OF FINANCIAL MARKETS Financial markets may be classified as follows : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Primary market Secondary market Money market Capital market Bond market Stock market Mortgage market Consumer credit market Auction market Negotiation market Organized market Over the counter market Spot market Futures market
15. Options market 16. Foreign exchange market
PRIMARY MARKET a financial market in which newly issued primary and securities are traded for the first time. Investors who buy these new issues are supplying funds to DSUs which issue the securities. Large corporations needing large amount of funds usually tap the primary market through bond issuance. SECONDARY MARKET- is that financial market through which existing financial securities are traded. SSUs which bought new securities from the primary market may sell the same to the secondary market anytime they wish to change their portfolios before maturity dates. The secondary market provides liquidity to the SSUs with securities held. MONEY MARKET- is that financial market on which debt securities with an original maturity of one year or less are traded. Long term securities are traded in the money market if they have six months or less left to maturity. CAPITAL MARKET- is that portion of the financial market where trading is under taken for securities with maturity of more than one year. The capital market is subdivided into three parts; 1. The bond market; 2. The stock market and; 3. The mortgage market. BOND MARKET- the market for debt instruments of any kind. It operates through a system of dealers using a telecommunications network, rather than in a single physical location for trading. Dealers include giant banking firms located around the world. STOCK MARKET- is that financial market where the common and preferred stocks issued by corporations are traded. It has two components: (1) the organized exchanges: and (2) the less formal overthe-counter markets. The Philippine Stock Exchange is classified into the ff categories; 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Banks Financial services Communication Power and energy Transportation services Construction and other related products Food, beverages, and tobacco Holding firms Manufacturing, distribution, and trading Hotel, recreation, and other services
11. Bonds, preferred stocks, and warrants 12. Others MORTGAGE MARKET- is that portion of the financial market which deals with loans on residential, commercial, and industrial real estate and on farmland. Various financial institutions comprise the mortgage market. CONSUMER CREDIT MARKET- the market involved in loans on autos, appliances, education, travel is referred to as the consumer credit market. As there are millions of consumers tapping the credit market, it is expected that there will be a number of financing institutions extending auto, salary, and various personal loans to consumers. AUCTION MARKET- is one where trading is conducted by an independent third party according to a matching of prices on orders received to buy and sell a particular security. Stocks are sold to the highest bidder on the trading floor. NEGOTIATION MARKET- when buyers and sellers of securities negotiate with each other regarding price and volume, either directly or through a broker or dealer, they are engage in the financial market called negotiation market. ORGANIZED MARKET- is that financial market with fixed trading rules. It is situated at a central location in the financial district in which trading is generally conducted by auction. Another name for organized markets are exchanges like the Philippine Stock Exchange, and the Australian Stock Exchange. OVER-THE-COUNTER MARKET- is that market consisting of large collection of brokers and dealers, connected electronically by telephones and computers that provide for trading in unlisted securities. All securities not traded in the stock exchange for one reason or another are traded over the counter. The over-the-counter market consists of facilities namely: 1. Relatively few dealers who hold inventories or over the-counter securities and act as a securities market; 2. The many brokers who act as agents in bringing these dealers together with investors and 3. The computers, terminals, and electronic networks that provide a communications link between dealers and brokers.
SPOT MARKET- when securities are traded for immediate delivery and payment, the market type referred to is the spot market. The spot price is the feature of the spot market and which is actually the price paid for a security that will be delivered on the spot immediately. The term immediately may actually mean one or two days to one week depending on the facilities used or the tradition in the area. The spot market is an alternative to the future market. FUTURE MARKET- is that market where contracts are originated and traded that gives the holder the right to buy something in the future at a price specified by the contract.
OPTION MARKET- is one where stock options are traded. A stock option is a contract giving the owner the right to either buy or sell a fixed number of shares of a stock (usually 100) at any time before the expiration date at a price specified in the option. Option contracts may cover items like gold and Treasury bonds. Option are traded in organized securities exchanges like the Philippine Stock Exchange. One purpose of the options market is to make possible for investors who wish to reduce the risk of losing money due to price changes in the future. FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET - is the market where people buy and sell currencies. This market is composed of the ff: 1. Banks located throughout the world buying and selling foreign moneys, in the form of foreign currencies in foreign banks 2. Foreign exchange dealers and 3. Currency exchanges catering mostly to tourist and are found in the downtown areas, airports, and railroad stations in major tourist center.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- MALALUAN Kathleen ALDABA Dave BUERRA Irhil Module 1 FM101 Financial Management 1Document9 pagesMALALUAN Kathleen ALDABA Dave BUERRA Irhil Module 1 FM101 Financial Management 1Ma. Eden SombilonPas encore d'évaluation
- 117549-Article Text-325788-1-10-20150527 PDFDocument16 pages117549-Article Text-325788-1-10-20150527 PDFBizu AtnafuPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1 Overview of Financial Management and Financial EnvironmentDocument68 pagesTopic 1 Overview of Financial Management and Financial EnvironmentMicaella Fevey BandejasPas encore d'évaluation
- BCom (H) Indian Financial System Second Year Sem 3Document24 pagesBCom (H) Indian Financial System Second Year Sem 3Santosh ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital MarketDocument21 pagesCapital MarketKaran Kumar100% (3)
- Introduction To Secondary MarketDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Secondary MarketSandeep K BiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- NISM XB Invt Advisor 2 Short NotesDocument32 pagesNISM XB Invt Advisor 2 Short NotesAnchal100% (1)
- Nism Series Ix Merchant Banking WorkbookDocument127 pagesNism Series Ix Merchant Banking Workbookalpha012550% (2)
- Rangkuman KLMPK 8 PPT Chapter 16Document17 pagesRangkuman KLMPK 8 PPT Chapter 16Safitri Eka LestariPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Return Anaysis of Telecom CompaniesDocument79 pagesRisk Return Anaysis of Telecom CompaniesAkash Venugopal0% (1)
- Project Report On Analysis of Depository Participant With Reference To SHCILDocument94 pagesProject Report On Analysis of Depository Participant With Reference To SHCILAtulesh Singh79% (19)
- Finman7.Module Sir RhomarkDocument69 pagesFinman7.Module Sir RhomarkLeynard ColladoPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Market Chapter 2 TestDocument5 pagesFinancial Market Chapter 2 TestAbd El-Rahman El-syeoufyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ianuali 2000 enDocument339 pagesIanuali 2000 ensolajeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1shraddha amatyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital MarketDocument102 pagesCapital MarketChandan SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Combine Slide JFP463EDocument333 pagesCombine Slide JFP463EZuhairy ZakariaPas encore d'évaluation
- NISM XA - Investment Adviser 1 Short NotesDocument35 pagesNISM XA - Investment Adviser 1 Short Notesmasafr100% (1)
- My FileDocument56 pagesMy FileVinod AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Approved CAE - BSA BSMA BSAIS BSIA - ACC 212 - Tenedero - Enriquez 1Document144 pagesApproved CAE - BSA BSMA BSAIS BSIA - ACC 212 - Tenedero - Enriquez 1hdejnPas encore d'évaluation
- MAEC - Project Report - Group PDocument21 pagesMAEC - Project Report - Group PSudip KarPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition of 'Shares'Document8 pagesDefinition of 'Shares'c_vijaykumaryadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Environment Chapter 1 SummaryDocument57 pagesFinancial Environment Chapter 1 Summaryn nPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Management 1 Internal Assessment By: Nivas Niranjan Division: CDocument5 pagesFinancial Management 1 Internal Assessment By: Nivas Niranjan Division: CShretha lakshmi rPas encore d'évaluation
- FIAM PaperDocument62 pagesFIAM Papereyob yohannesPas encore d'évaluation
- CF 2023 Module IDocument272 pagesCF 2023 Module IFabio MotaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sources of FundsDocument13 pagesSources of FundsSenelwa Anaya0% (1)
- Internship Report BBADocument101 pagesInternship Report BBAKamal Uddin Suman57% (7)
- Dissertation On Debt Securities Market in IndiaDocument103 pagesDissertation On Debt Securities Market in Indiaumesh kumar sahu0% (2)
- FINANCIAL-MARKETS Prelims RevDocument13 pagesFINANCIAL-MARKETS Prelims RevJasmine TamayoPas encore d'évaluation