Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Questions ETE 482
Transféré par
Dipen K. DasDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Questions ETE 482
Transféré par
Dipen K. DasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
North South University
Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science
ETE 482: Advanced Electronics & Communications Lab-II
Fall 2010 ___________________________________________________________
Questions for the experiments
Experiment no. 1: FSK - Signal Generation
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is frequency shift keying (FSK)? Write an example of FSK. What is the difference between bit rate and baud rate? Draw the FSK signal for 0111001 binary number. What is the bandwidth required for FSK signal? What is line coding? Why it is required? Describe Nonreturn to Zero (NRZ) level and invert line coding scheme, briefly. What is the problem of NRZ level and invert encoding scheme? Draw the signal for 0111001 binary number that is encoded using NRZ-invert scheme.
Please read the operating manual. You need to understand each step properly. Book: Data Communications and Networking by Behrouz Forouzan (Chapter 4 and 5) Answer question no. 2, 5, 7 and 8 in the lab report.
Experiment no. 2: Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (SCR)
1. What is SCR? Draw an SCR two-transistor equivalent circuit and briefly describe how it works. 2. After SCR is turned on, do we need to supply positive gate current? Explain briefly. 3. What is holding current I H ? 4. Draw the SCR characteristics curve for different levels of gate current I G , starting from zero. 5. What is the relationship between I G and I H ? 6. How SCR can be stopped conducting? 7. Consider the circuit diagram for this experiment. When SCR 2 is turned on due to the conducting zener diode at 19 V, why the SCR 1 stops conducting? 1
8. Consider the circuit diagram for this experiment. Why a 1 k resistor is used before the diode for SCR 1? 9. Consider the circuit diagram for this experiment. Why the diode is used? 10. Consider the circuit diagram for this experiment. Why the 10 F capacitor is used? Book: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory by Boylestad and Nashelsky (Chapter 17) Answer question no. 2, 5, 6 and 7 in the lab report.
Experiment no. 3: Stepper Motor Controller
1. What is stepper motor? How it works? What are the applications of stepper motor? 2. What is the difference between general motor and stepper motor? 3. Consider the circuit diagram for this experiment. What role the transistors are playing? How they are operating? In other words, explain how does a transistor (BJT) function as an electronic switch? [Read Boylestad, chapter 4: 4.9] 4. Consider the circuit diagram with coils (not the one with LEDs) for this experiment. Why the diodes have been used? What happens if we take out the diodes? [Note: diodes have no impact on LED-based circuit.] Answer question no. 2, 3 and 4 in the lab report.
Experiment no. 4: FM generation by VCO
1. What is Schmitt trigger? Explain the function of Schmitt trigger briefly with an appropriate figure. 2. In the block diagram of the 566 VCO, what is the role of the Schmitt trigger? 3. What is free-running or center-operating frequency f 0 of voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO)? State the formula of f 0 . 4. Describe the operation of a VCO circuit briefly using the block diagram. 5. Why two buffer amplifiers are used in the design of 566 VCO unit? 6. What are the components of 566 VCO unit through which you can control f 0 ? 7. Consider the circuit diagram of 566 VCO unit (Boylestad, page 716, Fig. 13.22). Determine f 0 for the given values. 8. Consider the circuit diagram of 566 VCO unit (Boylestad, page 716, Fig. 13.23). Determine f 0 by varying the potentiometer wiper to its two opposite ends. 9. Consider the circuit diagram of 566 VCO unit (Boylestad, page 717, Fig. 13.24). Determine V C set by the voltage-divider network. If ac input signal has 1.4 V peak, then determine the two modulated frequencies. 10. What is frequency modulation (FM)? Briefly explain how frequency modulation is operating in the modulator that you designed.
Book: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory by Boylestad and Nashelsky (Chapter 13) Answer question no. 2, 3, 5 and 6 in the lab report.
Experiment no. 5: Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Circuit Operation and FM detection with a PLL
Read the manual for this experiment. Review questions at the end of section 7.1 and 7.2 are relevant.
Answer the following review questions (Lab-Volt manual) in the lab report: Section 7.1 - 2, 3, 4 and 5 Section 7.2 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Experiment no. 6: FM Demodulation using 565 IC
1. What is the function of resistor R 1 and capacitor C 1 which are connected with the VCO? 2. Write down the formula for the free-running frequency. 3. In the design of FM Demodulator, why it is important to control the freerunning frequency? 4. What is the function of the C 2 capacitor? 5. What is the function of the phase detector? Why do we need to feed the output of the phase detector into the low-pass filter? 6. Why do we observe square wave at pin 4 and triangular wave at pin 9? 7. Using the formulas for the free-running frequency, lock range and capture range practice problems. 8. For a 565 FM demodulator the free-running frequency is 136.36 kHz, capture range is +/- 156.1 kHz and lock range is +/- 181.82 kHz. If the input frequency range is 300 kHz ~ 481 kHz, how the output voltage should vary? Increasing, decreasing or unchanging? Explain your answer. Answer question no. 1, 3, 5 and 8 in the lab report.
Experiment no. 7: FSK Decoder using Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) 565 IC
1. Describe the operation of a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) circuit briefly using the block diagram. 2. Why the low-pass filter is used in the design of PLL? 3. What is capture range?
4. What is PLL lock range and hold range? 5. State the formula for the free-running frequency f 0 of PLL. 6. Consider the circuit diagram of PLL FM unit (Boylestad, page 719, Fig. 13.26c). Determine f 0 , lock range and capture range for the given values. 7. In the FSK decoder circuit, why do we use the RC ladder filter? Book: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory by Boylestad and Nashelsky (Chapter 13) Answer question no. 2, 6 and 7 in the lab report.
Experiment no. 8: Frequency Synthesizer using 565 IC
1. What is frequency synthesis? 2. What is the limitation of the VCO output signal? [Hint: compare it with the output of crystal oscillator.] 3. What advantage do we get in the output of a PLL device compared to the output of VCO? 4. How PLL and Frequency Synthesizer differ? [Hint: compare the nature of the output signals for both devices.] 5. Draw the basic block diagram of the frequency synthesizer and briefly explain its operation. 6. What are the limitations of frequency synthesizers? [Hint: consider the range of capacitance of the varactor of the VCO.] 7. Why frequency synthesizers are useful for radio communication devices? Answer question no. 1, 3, 4 and 7 in the lab report.
Experiment no. 9: Assembly language programming
1. If a processor uses 20 bits for an address, how many memory bytes can be accessed? 2. What are the advantages of assembly language over high-level languages? 3. What are the differences between machine language and assembly language? 4. Intel 8086 is a 16-bit microprocessor. What is the significance of 16-bit processor? 5. How many types of registers 8086 microprocessor has? 6. In total 8086 contains how many registers? Each register is of how many bits? 7. Describe briefly four types of data registers. 8. What is memory segment? Why 8086 microprocessor needs to segment its memory locations? 9. Solve example 3.1 and 3.2 from the handout (Maruts book).
10. What is the function of segment registers? 11. What is the function of pointer and index registers? 12. What is the function of flags registers? 13. What is the difference between pseudo-op DB and DW? 14. What is the elaboration of MASM? What does it do? 15. Using a block diagram show how to create an .exe file for an assembly language code. 16. What is the function of the flags registers? 17. How many types of flags registers are used? 18. Describe different types of status flags registers briefly. 19. Why .asm extension is used to create a source program file? 20. What is the function of MASM? 21. Why a machine language object file (.obj) can not be executed directly with out using the LINK program? What function does the LINK program perform on the object file? Explain briefly. 22. Why the Interrupt 21h command is used? Book: Assembly Language Programming and Organization of the IBM PC by ytha Yu and Charles Marut (Chapter 3 and 4) Answer question no. 3, 8, 10, 13, 16, 21 and 22 in the lab report.
Experiment no. 10: 8255 Microcontroller
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What is the difference between simple I/O and interrupt I/O? What is the difference between Bit Set/Reset (BSR) mode and I/O mode? Describe the function of BSR mode briefly. What are three types of I/O mode? Describe each type briefly. What is the difference between A-B ports and C ports? In other words, what special role C ports perform? How many I/O pins the microcontroller has? In how many groups they are arranged? What are the six lines of control logic section? What is the function of CS , A 0 and A 1 ? What is the function of control register? If you want to access this register to write a control word, what condition must be satisfied for A 0 and A 1 ?
10. What is the function of D 7 register? 11. What should be the bit of D 7 for I/O functions? 12. What is the function Mode 0? 13. Solve example 15.1 from the handout. 14. What is the function of Mode 1 and 2?
15. In the program that you wrote during the experiment with the 8255 microcontroller, the control word register was initialized by two values 90H and 0FH respectively. Explain why? Answer question no. 1, 2, 5, 9, 14 and 15 in the lab report.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 002 5956Document62 pages002 5956Dipen K. DasPas encore d'évaluation
- CST DipoleDocument3 pagesCST DipoleDipen K. DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenna Assignment: Antenna GT D Rrad Prad 3Db BW Eff. AreaDocument2 pagesAntenna Assignment: Antenna GT D Rrad Prad 3Db BW Eff. AreaDipen K. DasPas encore d'évaluation
- ITA - Pitch Movement & Tone CHoiceDocument14 pagesITA - Pitch Movement & Tone CHoiceDipen K. DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecen Introduction To Telecommunication EngineeringDocument10 pagesEcen Introduction To Telecommunication EngineeringDipen K. DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 06Document1 pageHomework 06Dipen K. DasPas encore d'évaluation
- C Chap01Document17 pagesC Chap01Dipen K. DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Hewlett Packard 8722ES Vector Network Analyzer Programming GuideDocument546 pagesHewlett Packard 8722ES Vector Network Analyzer Programming Guideprofnick_253685716Pas encore d'évaluation
- New Doc 1Document11 pagesNew Doc 1Dipen K. DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Basic Electronics LabDocument3 pagesBasic Electronics LabMushtansir AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Kasturba Institute of Technology: Minor ProjectDocument15 pagesKasturba Institute of Technology: Minor ProjectRiya KumariPas encore d'évaluation
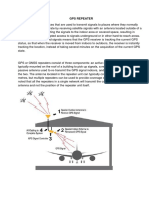
- Gps Signal AmplifierDocument5 pagesGps Signal AmplifierAadal ArasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Signal Conditioning For Resistive, Rectance Varian and Self Generating SensorsDocument74 pagesSignal Conditioning For Resistive, Rectance Varian and Self Generating SensorsYash BhattPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A04501 Analog CommunicationsDocument4 pages9A04501 Analog CommunicationssubbuPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Sheet: 83C145 83C845 83C055 87C055Document41 pagesData Sheet: 83C145 83C845 83C055 87C055VictorManuelBernalBlancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Wide Band (And Narrow Band) Band - Pass Microwave Filters On The Insertion Loss BasisDocument14 pagesDesign of Wide Band (And Narrow Band) Band - Pass Microwave Filters On The Insertion Loss BasisG P AnkushPas encore d'évaluation
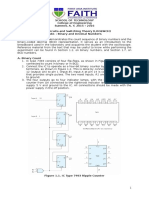
- State Reduction and AssignmentDocument49 pagesState Reduction and AssignmentJames Francis100% (4)
- Class A'B'ab Amplifier PDFDocument8 pagesClass A'B'ab Amplifier PDFShehzadtajPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE 310 Circuits and ElectronicsDocument19 pagesCSE 310 Circuits and ElectronicsHemmy m.SambokoPas encore d'évaluation
- PLTW: Digital Electronics Syllabus For Mrs. Yusufi: Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and DigitalDocument5 pagesPLTW: Digital Electronics Syllabus For Mrs. Yusufi: Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and DigitalTriston DurbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Combination of Basic Logic GatesDocument21 pagesCombination of Basic Logic GatesJrom EcleoPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Phase Load CalculatorDocument1 pageThree Phase Load Calculatorbadri0% (1)
- EPM240 DatasheetDocument102 pagesEPM240 DatasheetLong VũPas encore d'évaluation
- VLSI Lab Manual Aug 2016Document35 pagesVLSI Lab Manual Aug 2016Shubham borawakePas encore d'évaluation
- Single Phase Firing Board Manual FCRO2100 - EnERPRODocument14 pagesSingle Phase Firing Board Manual FCRO2100 - EnERPROmanuel99a2k100% (1)
- Rizzoni5eSM CH11 LsDocument22 pagesRizzoni5eSM CH11 Ls이민서Pas encore d'évaluation
- EE221 Lecture 39 42Document41 pagesEE221 Lecture 39 42sayed Tamir janPas encore d'évaluation
- LOGSWCH Lab1Document3 pagesLOGSWCH Lab1topherskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Book - DRAM Circuit Design A Tutorial by Brent Keeth R Jacob Baker (Z-LibDocument213 pagesBook - DRAM Circuit Design A Tutorial by Brent Keeth R Jacob Baker (Z-LibVăn CôngPas encore d'évaluation
- VLSI Lab Assignment Final AjithDocument44 pagesVLSI Lab Assignment Final Ajithsndpkv4999Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 04: Peripherals Interfacing With 8086 and ApplicationsDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 04: Peripherals Interfacing With 8086 and ApplicationsAnikhet MulkyPas encore d'évaluation
- PCM 1718Document14 pagesPCM 1718isaiasvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bss Fds360 Service ManualDocument8 pagesBss Fds360 Service Manualokan uysalPas encore d'évaluation
- IE1204 Digital Design F11: Programmable Logic, VHDL For Sequential CircuitsDocument68 pagesIE1204 Digital Design F11: Programmable Logic, VHDL For Sequential CircuitsAhmad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Eval Ad76xxcb 8 10 PinDocument18 pagesEval Ad76xxcb 8 10 PincsclzPas encore d'évaluation
- 4A, 21V 500Khz Synchronous Step-Down Converter: General Description FeaturesDocument14 pages4A, 21V 500Khz Synchronous Step-Down Converter: General Description FeaturesRakesh SutharPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Boolean AlgebraDocument52 pagesChapter 3 Boolean AlgebraChetan DongarsanePas encore d'évaluation
- S98 Lecture13Document12 pagesS98 Lecture13manohar487Pas encore d'évaluation
- Common Transistors and CharacteristicsDocument1 pageCommon Transistors and CharacteristicsjunkPas encore d'évaluation