Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Preparation
Transféré par
ToTa KatkotaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Preparation
Transféré par
ToTa KatkotaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Preparation
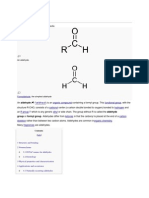
Sulfonic acid is produced by the process of sulfonation. Usually the sulfonating agent is sulfur trioxide. A particularly large scale application of this method is the production of alkylbenzenesulfonic acids: RC6H5 + SO3 RC6H4SO3H In this reaction, sulfur trioxide is an electrophile and the arene undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution.[1] Thiols can be oxidized to sulfonic acids: RSH + 3/2 O2 RSO3H Certain sulfonic acids, such as perfluorooctanesulfonic acid are prepared by electrophilic fluorination of preformed sulfonic acids. The net conversion can be represented simplistically: C8H17SO3H + 17 F2 C8F17SO3H + 17 HF
Reactions
[edit]Esterification Sulfonic acids can be converted to esters. This class of organic compounds has the general formula R-SO2-OR. Sulfonic esters such as methyl triflate are considered good alkylating agents inorganic synthesis. Such sulfonate esters are often prepared by alcoholysis of the sulfonyl chlorides: RSO2Cl + R'OH RSO2OR' + HCl
Methyl triflate
Chlorination
Sulfonyl halide groups occur when a sulfonyl functional group is singly bonded to a halogen atom. They have the general formula R-SO2-X where X is a halide, almost invariably chloride. They are produced by chlorination of sulfonic acids using thionyl chloride and related reagents. [edit]Displacement Although the C-SO3H bond is strong, the (aryl)C-SO3 bond can be cleaved by certain nucleophiles. Of historic and continuing significance is the -sulfonation of
anthroquinone followed by displacement of the sulfonate group by other nucleophiles, which cannot be installed directly.[3] An early method for producing phenolinvolved the base hydrolysis of sodium benzenesulfonate, which can be generated readily from benzene.[5] C6H5SO3Na + 2 NaOH C6H5ONa + Na2SO3 + H2O
Applications
Although both alkyl and aryl sulfonic acids are known, most of the applications are associated with the aromatic derivatives. [edit]Detergents
and surfactants
Detergents and surfactants are molecules that combine highly nonpolar and highly polar groups. Traditionally, soaps are the popular surfactants, being derived from fatty acids. Since the mid-20th century, the usage of sulfonic acids has surpassed soap in advanced societies. For example, an estimated 2 billion kilograms of alkylbenzenesulfonates are produced annually for diverse purposes. Lignin sulfonates, produced by sulfonation of lignin are components of drilling fluids and additives in certain kinds of concrete.[2] [edit]Dyes Many if not most of the anthroquinone dyes are produced or processed via sulfonation.[3] Sulfonic acids tend to bind tightly to proteins and carbohydrates. Most "washable" dyes are sulfonic acids (or have the functional sulfonyl group in them) for this reason. p-Cresidinesulfonic acid is used to make food dyes. [edit]Acid
catalysts
Being strong acids, sulfonic acids are also used as catalysts. The simplest examples are methanesulfonic acid, CH3SO2OH and p-toluenesulfonic acid, which are regularly used in organic chemistry as acids that are lipophilic (soluble in organic solvents). Polymeric sulfonic acids are also useful. Dowex resin are sulfonic acid derivatives of polystyrene and is used as catalysts and for ion exchange (water softening).Nafion, a fluorinated polymeric sulfonic acid is a component of proton exchange membranes in fuel cells.[4] [edit]Drugs Antibacterial drugs sulfa drugs are produced from sulfonic acids.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Sulfonation (Report)Document2 pagesSulfonation (Report)Alma LaylayPas encore d'évaluation
- H 2 So 4Document8 pagesH 2 So 4Satyam Sharma100% (1)
- SULPHONATIONDocument8 pagesSULPHONATIONsairaPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument10 pagesIntroductionAmith Singh J100% (1)
- Carboxylic AcidDocument6 pagesCarboxylic AcidVishu AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic 2Document8 pagesCarboxylic 2johnsmithprayPas encore d'évaluation
- Concentrated sulfuric acid properties and usesDocument13 pagesConcentrated sulfuric acid properties and usesSilviaJimenez03Pas encore d'évaluation
- History of Sulfuric AcidDocument2 pagesHistory of Sulfuric Acidravie setyawanPas encore d'évaluation
- A 1Document29 pagesA 1Christopher WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- K01587 - 20200217130414 - Chapter 9 - Industrial ChemicalsDocument54 pagesK01587 - 20200217130414 - Chapter 9 - Industrial ChemicalsAbdulRahim059Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sulfonation Processes and ReactionsDocument54 pagesSulfonation Processes and ReactionsZain Ul AbideenPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulfonamidas PDFDocument58 pagesSulfonamidas PDFPablo AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulphuric Acids: Group Members: Samoi Oladipo Alliyah LindsayDocument11 pagesSulphuric Acids: Group Members: Samoi Oladipo Alliyah Lindsaysamoi oladipoPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument15 pagesCarboxylic Acidsmadhu bonamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ester: For Other Uses, SeeDocument15 pagesEster: For Other Uses, SeemeritnasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufactured Substances in IndustryDocument68 pagesManufactured Substances in IndustryAmirul AzzamPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulphonation Plant ChemithonDocument36 pagesSulphonation Plant ChemithonKantilal Malwania100% (1)
- Carboxylic AcidDocument13 pagesCarboxylic AcidJeremy NayagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry SulferDocument4 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry SulferAmna ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- INSUDTRIAL CHEMISTRY ASSIGNMENT BY GROUP OneDocument19 pagesINSUDTRIAL CHEMISTRY ASSIGNMENT BY GROUP OneMamoona kareemPas encore d'évaluation
- Rings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie PeckDocument14 pagesRings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie Peckrobbiepeck100% (1)
- Production of Sulfuric AcidDocument29 pagesProduction of Sulfuric Aciddeshaka11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Process TechnologyDocument17 pagesChemical Process TechnologyNaik LarkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcohols LabDocument7 pagesAlcohols Lab7sky7harveyPas encore d'évaluation
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument25 pagesAldehydes and Ketonesabigail_acostaPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemistryDocument80 pagesChemistryÖzgür DalPas encore d'évaluation
- Bab I Pendahuluan 1.1 Latar Belakang MaslahDocument13 pagesBab I Pendahuluan 1.1 Latar Belakang MaslahDwiki RamadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21 - Sulfuric AcidDocument12 pagesChapter 21 - Sulfuric AcidargoniodidePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 Properties of MonosaccharidesDocument9 pagesLesson 3 Properties of MonosaccharidesMAN'S BEST FRIENDPas encore d'évaluation
- Sul Fo NationDocument48 pagesSul Fo NationAleem ChoudhryPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcohols, Diols, TriolsDocument32 pagesAlcohols, Diols, TriolsShivam GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of A Carboxylic AcidDocument7 pagesStructure of A Carboxylic AcidKajal SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulphonation and LABS Formulation Using SO3-AIR MethodDocument3 pagesSulphonation and LABS Formulation Using SO3-AIR Methodaneece786Pas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic AcidDocument9 pagesCarboxylic AcidjohnsmithprayPas encore d'évaluation
- Contact ProcessDocument16 pagesContact ProcessOmar Almonte100% (1)
- Alcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsDocument12 pagesAlcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsAmihanPas encore d'évaluation
- Aromatic Sulfonation - WikipediaDocument6 pagesAromatic Sulfonation - WikipediaAhmed ranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulfuric Acid As It Is Called The King of ReagentsDocument3 pagesSulfuric Acid As It Is Called The King of ReagentsAnubhav SwaroopPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulphur - Element, Allotropes, Uses, Sulphuric Acid ProductionDocument28 pagesSulphur - Element, Allotropes, Uses, Sulphuric Acid ProductionHyung Sholahuddin AlayPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of Related LiteratureBobbie BernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Their ReactionsDocument8 pagesCarboxylic Acid Derivatives and Their ReactionsBoobalan Maria SusaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulfur and Sulfuric Acid: Key Uses and Production MethodsDocument24 pagesSulfur and Sulfuric Acid: Key Uses and Production MethodsdhavalPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic Acid Structure and PropertiesDocument11 pagesCarboxylic Acid Structure and PropertiesDipti BagdePas encore d'évaluation
- Sulphur: Sulphur: Sources and UsesDocument4 pagesSulphur: Sulphur: Sources and UsesDavies MasumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- P-Block Elements Group 15Document9 pagesP-Block Elements Group 15AlokPas encore d'évaluation
- Go 5 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid, Nitric AcidDocument21 pagesGo 5 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid, Nitric AcidcikaifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microsoft Word - Sulfo and Sulfa 1.doc - Sulfo and Sulfa 1Document36 pagesMicrosoft Word - Sulfo and Sulfa 1.doc - Sulfo and Sulfa 1Donna ameliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 13, Helping MaterialDocument40 pagesLecture 13, Helping MaterialHuraira AbidPas encore d'évaluation
- Enamines and YlidesDocument18 pagesEnamines and YlidesVijay Pradhan100% (1)
- Aldehyde group reactionsDocument9 pagesAldehyde group reactionssenkatuukaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Anaerobic Respiration: As Compared With FermentationDocument3 pagesTopic: Anaerobic Respiration: As Compared With FermentationVINDHYA SHANKERPas encore d'évaluation
- F334 - What's in A Medicine?Document11 pagesF334 - What's in A Medicine?Becky Tenney100% (1)
- Saponification-The Process of Making Soap: What Are Fatty Acids?Document5 pagesSaponification-The Process of Making Soap: What Are Fatty Acids?Anonymous UoRu4sPas encore d'évaluation
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidD'EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidPas encore d'évaluation
- Organosilicon Reagents Synthesis and ApplicationsD'EverandOrganosilicon Reagents Synthesis and ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Silicon in Organic Synthesis: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringD'EverandSilicon in Organic Synthesis: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingD'EverandBiochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Notes Socialism in Europe and RussianDocument11 pagesNotes Socialism in Europe and RussianAyaan ImamPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Packaging, Labelling and Shipping Plans: What's NextDocument17 pagesProduct Packaging, Labelling and Shipping Plans: What's NextShameer ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Science PDFDocument118 pagesEnvironmental Science PDFJieyan OliverosPas encore d'évaluation
- Kids' Web 1 S&s PDFDocument1 pageKids' Web 1 S&s PDFkkpereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Marlissa - After School SpecialDocument28 pagesMarlissa - After School SpecialDeepak Ratha50% (2)
- Revolutionizing Via RoboticsDocument7 pagesRevolutionizing Via RoboticsSiddhi DoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 11 Economics Introduction NotesDocument9 pagesYear 11 Economics Introduction Notesanon_3154664060% (1)
- The Future of Indian Economy Past Reforms and Challenges AheadDocument281 pagesThe Future of Indian Economy Past Reforms and Challenges AheadANJALIPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Drill FlightsDocument2 pagesEarth Drill FlightsMMM-MMMPas encore d'évaluation
- Education: Address: Mansoura, EL Dakhelia, Egypt EmailDocument3 pagesEducation: Address: Mansoura, EL Dakhelia, Egypt Emailmohammed sallemPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Effectiveness ISO 9001Document50 pagesTraining Effectiveness ISO 9001jaiswalsk1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Virtue Ethics: Aristotle and St. Thomas Aquinas: DiscussionDocument16 pagesVirtue Ethics: Aristotle and St. Thomas Aquinas: DiscussionCarlisle ParkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Bread and Pastry Production NC IiDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Bread and Pastry Production NC IiMark John Bechayda CasilagPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternity and Newborn MedicationsDocument38 pagesMaternity and Newborn MedicationsJaypee Fabros EdraPas encore d'évaluation
- DINDIGULDocument10 pagesDINDIGULAnonymous BqLSSexOPas encore d'évaluation
- Golin Grammar-Texts-Dictionary (New Guinean Language)Document225 pagesGolin Grammar-Texts-Dictionary (New Guinean Language)amoyil422Pas encore d'évaluation
- Strategies To Promote ConcordanceDocument4 pagesStrategies To Promote ConcordanceDem BertoPas encore d'évaluation
- My PDSDocument16 pagesMy PDSRosielyn Fano CatubigPas encore d'évaluation
- Nazi UFOs - Another View On The MatterDocument4 pagesNazi UFOs - Another View On The Mattermoderatemammal100% (3)
- Obtaining Workplace InformationDocument4 pagesObtaining Workplace InformationJessica CarismaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultramat 2 instructions for useDocument2 pagesUltramat 2 instructions for useBalaji BalasubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Parts For Diy Dremel CNC by Nikodem Bartnik: Part Name Quantity BanggoodDocument6 pagesList of Parts For Diy Dremel CNC by Nikodem Bartnik: Part Name Quantity Banggoodyogesh parmarPas encore d'évaluation
- B2 WBLFFDocument10 pagesB2 WBLFFflickrbonePas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced VLSI Architecture Design For Emerging Digital SystemsDocument78 pagesAdvanced VLSI Architecture Design For Emerging Digital Systemsgangavinodc123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesDatabase Interview QuestionsshivaPas encore d'évaluation
- CP ON PUD (1) ADocument20 pagesCP ON PUD (1) ADeekshitha DanthuluriPas encore d'évaluation
- McLeod Architecture or RevolutionDocument17 pagesMcLeod Architecture or RevolutionBen Tucker100% (1)
- An Analysis of Students Pronounciation Errors Made by Ninth Grade of Junior High School 1 TengaranDocument22 pagesAn Analysis of Students Pronounciation Errors Made by Ninth Grade of Junior High School 1 TengaranOcta WibawaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effects of Cabergoline Compared To Dienogest in Women With Symptomatic EndometriomaDocument6 pagesThe Effects of Cabergoline Compared To Dienogest in Women With Symptomatic EndometriomaAnna ReznorPas encore d'évaluation
- Episode 8Document11 pagesEpisode 8annieguillermaPas encore d'évaluation