Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
HW 1
Transféré par
Kyto_oDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
HW 1
Transféré par
Kyto_oDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
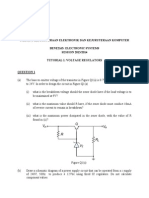
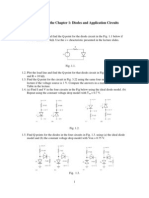
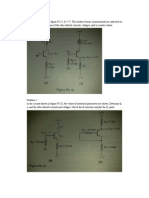
Problem 1 a) Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.39.
The value of R1 is reduced to R1= 10K and the cut- in voltage of the diode is V=0.7V. Determine ID and VD. b) Repeat part (a) if R1=50K
Problem 2 The cut- in voltage of the diode shown in the circuit in Figure P1.43 is V=0.7V. The diode is remain biased On for a power supply voltage in the range 5<=Vps<=10 V. The minimum diode current is to be ID(min)=2 mA. The maximum power dissipated in the diode is to be no more than 10 mW. Determine appropriate values of R1 and R2.
Problem 3 The diode cut- in voltage is V=0.7V in the four circuits shown in Figure P1.44. Find I and V0 in each of the circuits.
Problem 4 a) In the circuit shown in Figure P1.46, find the diode voltage VD and the supply voltage V such that the current is ID= 0.4mA. Assume the diode cut- in voltage is V=0.7V. b) Using the results of part(a), determine the power dissipated in the diode.
Problem 5 Assume each diode in the circuit shown in Figure P1.47 has a cut- in voltage of V=0.65V. a) The input voltage is VI=5V. Determine the value of R1 required such that ID1 is one-half the value of ID2. What are the values of ID1 and ID2? b) If V1=8 V and R1 = 2K, determine ID1 and ID2.
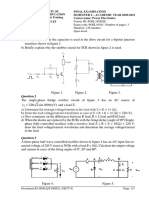
Problem 6 The circuit in Figure P2.9 is a complementary output rectifier. If Vs 26 sin[ 2 (60)t ]V , sketch the output waveforms v0+ and v0- versus time, assuming V=0.6 V for each diode.
Problem 7 a) Sketch v0 versus time for the circuit in Figure P2.13. The input is a sine wave given by
vi 10 sin t V. Assume V=0 V.
b) Determine the rms value of the output voltage.
Problem 8 Consider the circuit in Figure P2.24. Let V=0 V. a) Plot v0 versus v1 over the range -10<=v1<=+10V. b) Plot i1 over the same input voltage range as part (a).
Problem 9 For the circuit in Figure P2.25, a) plot v0 versus v1 for 0<=v1<=15V. Assume V=0.7 V. Indicate all breakpoints. b) Plot iD over the same range of input voltage. c) Compare the results of parts (a) and (b) with a computer simulation.
Problem 10 The diodes in the circuit in Figure P2.37 have piecewise linear parameters of V=0.6 V and
f 0 . Determine the output voltage V0 and the diode currents ID1 and ID2 for the following input
conditions. a) V1 =10V, V2 = 0V. b) V1 =5V, V2 = 0V. c) V1 =10V, V2 = 5V. d) V1 =10V, V2 = 10V. e) Compare the results of parts (a) through (d) with a computer simulation analysis.
Problem 11 Consider the circuit in Figure P2.49. The output of a diode OR logic gate is connected to the input of a second diode OR logic gate. Assume V=0.6 V for each diode. Determine the outputs VO1 and VO2 for: a) V1 = V2 =0; b) V1 = 5V, V2 = 0V; c) V1 = V2 =5V. What can be said about the relative values of VO1 and VO2 in their 'high' state?
Problem 12 Consider the circuit in Figure P2.50. The output of a diode AND logic gate is connected to the input of a second diode AND logic gate. Assume V=0.6 V for each diode. Determine the outputs V01 and VO2 for a) V1 = V2 =5V. b) V1 = 0V, V2 = 5 V; c) V1 = V2 =0; What can be said about the relative values of VO1 and VO2 in their 'low' state?
Problem 13 Sketch the steady- state output voltage v0 versus time for each circuit with the input voltage shown in Figure P2.32. Assume V=0 V and assume the RC time constant is large.
Problem 14 Design a diode clamper to generate a steady- state output voltage v0 from the input voltage v1 shown in Figure P2.33 if a) V=0 V b) V=0.7 V
Problem 15 For the circuit in Figure P 2.32(a) in Problem 13, let V=0 V and v1 10 sin t . Plot v0 versus time over 3 cycles of input voltage for a) VB= +3 V b) VB= -3 V Problem 16 a) Consider a pn juction diode biased at IDQ = 1mA. A sinusoidal voltage is superimposed on VDQ such that the peak- to- peak sinusoidal current is 0.05IDQ . The diode ideality factor n=1. Find the value of the applied peak- to- peak sinusoidal voltage. b) Repeat part (a) if IDQ = 0.1 mA. Problem 17 The diode in the circuit shown in Figure P1.49 is biased with a constant current source I. The diode ideality factor n=1. A sinusoidal signal vs is coupled through Rs and C. Assume that C is large so that it acts as a short circuit to the signal. a) Show that the sinusoidal component of the diode voltage is given by v0 vs ( b) If RS = 260 , find v0 / vs , for I = 1mA, I = 0.1 mA, and I = 0.01 mA.
VT ) VT IRS
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Recurdyn Solver - Theoretical ManualDocument325 pagesRecurdyn Solver - Theoretical ManualsawamurPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisD'EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics ProblemsDocument6 pagesElectronics ProblemsOsama AlviPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics Assignment #2 Chapter 2 Diode ApplicationsDocument11 pagesElectronics Assignment #2 Chapter 2 Diode ApplicationsKhairi SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog and Digital Electronics PDFDocument34 pagesAnalog and Digital Electronics PDFJatinPas encore d'évaluation
- Air PurgingDocument14 pagesAir PurgingjgdberizoPas encore d'évaluation
- Manage bank account statementDocument6 pagesManage bank account statementYATINDER DAHIYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct Conversion ReceiversDocument6 pagesDirect Conversion ReceiversAmir ChishtiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cronbach Reliability AnalysisDocument6 pagesCronbach Reliability AnalysisLesli Perez GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Camb Igcse Co Sci 001-013-So PDFDocument16 pagesSample Camb Igcse Co Sci 001-013-So PDFali002200Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 4 Electronics - AnswerDocument7 pagesSheet 4 Electronics - AnswerOla SamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Semiconductor diode and transistor tutorialDocument19 pagesSemiconductor diode and transistor tutorialmntykrPas encore d'évaluation
- Diode circuit analysis and characteristicsDocument9 pagesDiode circuit analysis and characteristicsArturo MontealegrePas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocument19 pagesAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 2: Semiconductor Diodes and Diode Circuits A. BackgroundDocument12 pagesExperiment 2: Semiconductor Diodes and Diode Circuits A. BackgroundShivankur KapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage Regulators Tutorial: Designing Regulator Circuits for Variable Input VoltagesDocument9 pagesVoltage Regulators Tutorial: Designing Regulator Circuits for Variable Input Voltages马铃淑Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diode Applications Tutorial Sheet Rectifier CircuitsDocument3 pagesDiode Applications Tutorial Sheet Rectifier CircuitsDaniel EkassiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Dr. Balraj SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 15:: and IDocument19 pagesProblem 15:: and IANER MOHAMEDPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Circuit Analysis Problem SetDocument2 pagesElectronic Circuit Analysis Problem Sethakkı_aPas encore d'évaluation
- DOC-20240327-WA0002.Document1 pageDOC-20240327-WA0002.GauravPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic 1st 7 8Document22 pagesElectronic 1st 7 8mohsindalvi87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bai Tap Ve BJT3Document23 pagesBai Tap Ve BJT3nguyenphuonghuy1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Part1 ElectronicsDocument48 pagesPart1 ElectronicsRalph NakadPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios de MOSFETDocument5 pagesEjercicios de MOSFETLuis Enrique GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- BEC - ASSIGNMENT I and IIDocument6 pagesBEC - ASSIGNMENT I and IIMansi BhatiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayDocument3 pagesPower Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayTấn Long Đoàn NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1Pasindu PramodPas encore d'évaluation
- Special ExamDocument4 pagesSpecial ExamPerol YuuzouPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller2 FullDocument5 pagesTaller2 FullAlexander DitestaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic - 1st 7 8 PDFDocument22 pagesElectronic - 1st 7 8 PDFtazeb AbebePas encore d'évaluation
- SolutionDocument8 pagesSolutionPallavi SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3 EEE1016 2022-2023 2Document5 pagesTutorial 3 EEE1016 2022-2023 2j2yshjzzsxPas encore d'évaluation
- TITLEElectronic Circuits Tutorial SolutionsDocument9 pagesTITLEElectronic Circuits Tutorial SolutionsKemproof100% (3)
- Tutorial #1Document3 pagesTutorial #1Greenhearthazel Varma PdgPas encore d'évaluation
- 2004 IE Theory PaperDocument26 pages2004 IE Theory PaperRafael Mario da SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE590 - Tutorial 3 (UiTM)Document5 pagesECE590 - Tutorial 3 (UiTM)NazhammerheartPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercicios 8Document3 pagesExercicios 8douglas.julianiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan BhagatDocument32 pages1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan Bhagatabhishek kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- NIT Rourkela ECE Dept B.Tech 1st Sem Basic Electronics Mid-Term Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesNIT Rourkela ECE Dept B.Tech 1st Sem Basic Electronics Mid-Term Exam QuestionsYASHPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Questions For Electronic DevicesDocument54 pagesPractice Questions For Electronic Devicesblessedgeraldie78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diode - ProblemsDocument6 pagesDiode - ProblemsTiệp VũPas encore d'évaluation
- Rectifier Probelems and SolutionsDocument11 pagesRectifier Probelems and SolutionsMichael Jerlit J EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- power electronics questions answersDocument59 pagespower electronics questions answersPascal UZABAKIRIHOPas encore d'évaluation
- Microelectronic Circuit Design ProblemsDocument17 pagesMicroelectronic Circuit Design ProblemsLê Hoàng ChínhPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Sheet 2 Electronic CircuitsDocument15 pagesSolution Sheet 2 Electronic CircuitsWajdi BELLILPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial-03 (Rectifiers and Clipper-Clamper) .Document1 pageTutorial-03 (Rectifiers and Clipper-Clamper) .Subodh SinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- DiodeDocument3 pagesDiodeprasanthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Question - ECE1312 - Sem1 - 14-15Document9 pagesFinal Question - ECE1312 - Sem1 - 14-15FARAZ ABDUL BASITPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)Document23 pagesTutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)vineetha nagahagePas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Electronic Circuits Assignment QuestionsDocument6 pagesAnalog Electronic Circuits Assignment QuestionschaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 01Document6 pagesAssignment 01Z S PlaysPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 2Document10 pagesHW 2Kyto_oPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Exam Review: Electronics FundamentalsDocument10 pagesMidterm Exam Review: Electronics FundamentalsOppa Sollehudin SapariPas encore d'évaluation
- UNSW Sydney Australia: Question DA1Document18 pagesUNSW Sydney Australia: Question DA1Marquee BrandPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Document9 pagesFinal Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Fatihah AinaPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 2: Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument14 pagesUNIT 2: Bipolar Junction TransistorWaleed HåšhįmPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Questions in Electronics/F 6, Gths K'Bo Paper Two: January 2010Document6 pagesTraining Questions in Electronics/F 6, Gths K'Bo Paper Two: January 2010NGOUNEPas encore d'évaluation
- RGUKT EE1201 Remedial Exam KeyDocument16 pagesRGUKT EE1201 Remedial Exam KeySrikanth AllamsettyPas encore d'évaluation
- PN Junction Diode - ExamplesDocument8 pagesPN Junction Diode - ExamplesNehemiah LemombianPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework SolutionsDocument46 pagesHomework SolutionsKashif AmjadPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied One Tutorial ExcerciseDocument18 pagesApplied One Tutorial ExcerciseABENEZER EPHREMPas encore d'évaluation
- Ideal Diode CharacteristicsDocument24 pagesIdeal Diode CharacteristicssPas encore d'évaluation
- On TapDocument7 pagesOn TapLê Minh ThắngPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesD'EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy 3101.0001Document4 pagesPhy 3101.0001Kyto_oPas encore d'évaluation
- Relative Resource ManagerDocument1 pageRelative Resource ManagerKyto_oPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 2Document10 pagesHW 2Kyto_oPas encore d'évaluation
- StatisticsDocument5 pagesStatisticsKyto_oPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Routing Security ConsiderationsDocument19 pagesDynamic Routing Security ConsiderationsNickhil RevuPas encore d'évaluation
- Top Deals on OnePlus MobilesDocument8 pagesTop Deals on OnePlus MobilesParinita PariharPas encore d'évaluation
- April SHETA Newsletter PDFDocument2 pagesApril SHETA Newsletter PDFtong_jPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Mining MCQ FINALDocument32 pagesData Mining MCQ FINALAmit Kumar SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Columbia 1987-02-25 0001Document11 pagesColumbia 1987-02-25 0001Becket AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Somove Lite V1.5: ReadmeDocument15 pagesSomove Lite V1.5: ReadmeNilton Manrique CossioPas encore d'évaluation
- Tactical Buyer - SpanishDocument4 pagesTactical Buyer - SpanishCata VarticPas encore d'évaluation
- SSRN Id635803Document90 pagesSSRN Id635803jorgeorsomoPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadmeDocument2 pagesReadmeridhoahluPas encore d'évaluation
- Sandra Coates Skating Club: Creating Tables, Queries, Forms, and Reports in A DatabaseDocument9 pagesSandra Coates Skating Club: Creating Tables, Queries, Forms, and Reports in A DatabaseKalama KitsaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Estimation of Timber Volume in A Coniferous Plantation Forest Using Landsat TMDocument5 pagesEstimation of Timber Volume in A Coniferous Plantation Forest Using Landsat TMMagno JuniorPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerogen Solo Parts ListingDocument2 pagesAerogen Solo Parts ListingBo ScoobmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Create Geo Model from Live HANA Calculation ViewDocument10 pagesCreate Geo Model from Live HANA Calculation Viewpurnima100Pas encore d'évaluation
- FZ502E ManualDocument16 pagesFZ502E ManualArdelean GrigorePas encore d'évaluation
- Fortiap SeriesDocument41 pagesFortiap SeriesKamel BoumazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Creating EPortfolio As A Technology ToolDocument56 pagesCreating EPortfolio As A Technology ToolTrisha CenitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesCs Lesson Planapi-426721162Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heavy OilDocument6 pagesHeavy Oilsnikraftar1406Pas encore d'évaluation
- Daa Lab Term Work - Pcs 409Document13 pagesDaa Lab Term Work - Pcs 409Tem PPas encore d'évaluation
- Price List 16 Okt 2010-1Document16 pagesPrice List 16 Okt 2010-1Muhammad Jamil HadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Trisha Paola Lagura - Activity No. 4 How Globalized Is Your HomeDocument2 pagesTrisha Paola Lagura - Activity No. 4 How Globalized Is Your HomeTrisha Paola LaguraPas encore d'évaluation
- Komatsu Engine 155 4 Shop Manual Sebe6120a05Document20 pagesKomatsu Engine 155 4 Shop Manual Sebe6120a05charles100% (27)
- Access Network Optical Network Data Com Core Network Wireless Terminal Storage and Network Security Application & Software Product & Solution Public Icons Cloud IconsDocument98 pagesAccess Network Optical Network Data Com Core Network Wireless Terminal Storage and Network Security Application & Software Product & Solution Public Icons Cloud IconsRaul QuinterosPas encore d'évaluation
- FPGA Xilin XcellDocument68 pagesFPGA Xilin XcellJustin JenningsPas encore d'évaluation