Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mosfet
Transféré par
Shaina ArifDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Mosfet
Transféré par
Shaina ArifDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Introduction:
MOSFET
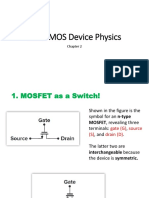
MOSFET stands for metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor.it is transistor that is used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. MOSFET is four (4) terminal device which are source (S),gate (G), drain (D) and body (B) terminals. Body of MOSFET is also called as Substrate that is often connected to the source terminal that make it a three terminal device like other field-effect transistor (FET). Only three-terminals appear in electrical diagrams, when two terminals are connected to each other (short-circuited).it is most common transistor in both digital and analog circuits, though the bipolar junction transistor was at one time much more common. In enhancement mode MOSFET's, between the contacts of source and drain via the field effect a conducting channel induces when a voltage drop across the oxide.The term "enhancement mode" refers to the increase of conductivity with increase in oxide field that adds carriers to the channel, also referred to as the inversion layer. The channel can contains electrons or holes. The channel that has excess amount of electrons than holes called an nMOSFET or nMOS and the channel that has excess amount of holes than electrones called a pMOSFET or pMOS.It is opposite in type to the substrate, so nMOS is made with a p-type sustrate and pMOS with an ntype substrate. In the less common depletion mode MOSFET, the channel consists of carriers in a surface impurity layer of opposite type to the substrate, and conductivity is decreased by application of a field that depletes carriers from this surface layer.
Composition
Usually the semiconductor of choice is silicon, but some chip manufacturers, most notably IBM and Intel, recently started using a chemical compound of silicon and germanium (SiGe) in MOSFET channels. Unfortunately, many semiconductors with better electrical properties than silicon, such as gallium arsenide, do not form good semiconductor-to-insulator interfaces, thus are not suitable for MOSFETs. Research continues on creating insulators with acceptable electrical characteristics on other semiconductor material. In order to overcome the increase in power consumption due to gate current leakage, a high- dielectric is used instead of silicon dioxide for the gate insulator, while polysilicon is replaced by metal gates.a The gate is separated from the channel by a thin insulating layer, traditionally of silicon dioxide and later of silicon oxynitride. Some companies have started to introduce a high- dielectric + metal gate combination in the 45 nanometer node. When a voltage is applied between the gate and body terminals, the electric field generated penetrates
through the oxide and creates an "inversion layer" or "channel" at the semiconductor-insulator interface. The inversion channel is of the same type, p-type or n-type, as the source and drain, thus it provides a channel through which current can pass. Varying the voltage between the gate and body modulates the conductivity of this layer and thereby controls the current flow between drain and source.
Circuit symbols
A variety of symbols are used for the MOSFET. The basic design is generally a line for the channel with the source and drain leaving it at right angles and then bending back at right angles into the same direction as the channel. Sometimes three line segments are used for enhancement mode and a solid line for depletion mode. Another line is drawn parallel to the channel for the gate. The bulk connection, if shown, is shown connected to the back of the channel with an arrow indicating PMOS or NMOS. Arrows always point from P to N, so an NMOS (N-channel in P-well or P-substrate) has the arrow pointing in (from the bulk to the channel). If the bulk is connected to the source (as is generally the case with discrete devices) it is sometimes angled to meet up with the source leaving the transistor. If the bulk is not shown (as is often the case in IC design as they are generally common bulk) an inversion symbol is sometimes used to indicate PMOS, alternatively an arrow on the source may be used in the same way as for bipolar transistors (out for nMOS, in for pMOS). Comparison of enhancement-mode and depletion-mode MOSFET symbols, along with JFET symbols (drawn with source and drain ordered such that higher voltages appear higher on the page than lower voltages):
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- MOSFET Seminar Report on Vaish College of EngineeringDocument11 pagesMOSFET Seminar Report on Vaish College of EngineeringbambernitinPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET Basics ExplainedDocument22 pagesMOSFET Basics ExplaineddadadabababaPas encore d'évaluation
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignD'EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendalePas encore d'évaluation
- Mosfet: Surface-Mount D2Pak Volts Amperes Watts MatchstickDocument7 pagesMosfet: Surface-Mount D2Pak Volts Amperes Watts MatchstickJudel AnovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mosfet PDFDocument19 pagesMosfet PDFAditya MadhusudhanPas encore d'évaluation
- MosfetDocument7 pagesMosfetwahyunuryantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mosfet, Ic Cd4047, Lm358 Comparator Mini Ups SystemDocument28 pagesMosfet, Ic Cd4047, Lm358 Comparator Mini Ups SystemSruthi ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Phase AC Motor ControlDocument42 pagesThree Phase AC Motor ControlParayatham ManasaPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET: A Guide to the Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorDocument21 pagesMOSFET: A Guide to the Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorthesumitsinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Mosfet: Navigation SearchDocument24 pagesMosfet: Navigation SearchAjay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mosfet: MOS-FET, or MOS FET) Is A Transistor Used For Amplifying orDocument22 pagesMosfet: MOS-FET, or MOS FET) Is A Transistor Used For Amplifying orVinay SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mosfet: Computer Engineering Department Adamson UniversityDocument44 pagesThe Mosfet: Computer Engineering Department Adamson Universityroxy8marie8chanPas encore d'évaluation
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractVivek SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Igfet'S Insulated Gate Field Effect TransistorsDocument4 pagesIgfet'S Insulated Gate Field Effect TransistorsAnonymous xzi9LiTPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT II (Part 2) PDFDocument7 pagesUNIT II (Part 2) PDFZulkifl KhairoowalaPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFETDocument28 pagesMOSFETBck SreedharPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mosfet: The Operating Process of A Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorDocument4 pagesThe Mosfet: The Operating Process of A Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistormjd5600Pas encore d'évaluation
- The MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: Unit-I (Mos Transistor Theory)Document232 pagesThe MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: Unit-I (Mos Transistor Theory)Manish AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Transistor MOSFETDocument18 pages04 Transistor MOSFETNatalie mirelesPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFETDocument18 pagesMOSFETAditya PriyadarshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mosfets WorstDocument3 pagesMosfets WorstMuhammad Umar AslamPas encore d'évaluation
- FetDocument17 pagesFetSagar SabharwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Hawkins CH 3Document35 pagesHawkins CH 3Rinat EzerPas encore d'évaluation
- MosfetDocument22 pagesMosfetNilakash100% (1)
- Design and Analysis of D Flip Flop Based Shift RegisterDocument49 pagesDesign and Analysis of D Flip Flop Based Shift RegistermaniroopPas encore d'évaluation
- Microelectronic CircuitDocument696 pagesMicroelectronic CircuitImtiaz AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Debre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)Document10 pagesDebre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)enidegPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A MOSFET - Basics, Working Principle & ApplicationsDocument3 pagesWhat Is A MOSFET - Basics, Working Principle & ApplicationsKimberly Camacho CatubigPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec8095-Vlsi Design-607796847-Ec 8095 NotesDocument163 pagesEc8095-Vlsi Design-607796847-Ec 8095 Noteshmpudur1968Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)Document47 pagesChapter 4 Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)redhataPas encore d'évaluation
- Mosfet: Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorsDocument47 pagesMosfet: Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistorschandanayadav8490Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 NotesDocument9 pagesUnit 5 NotesShashikant PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 3Document8 pagesUnit - 3AgnathavasiPas encore d'évaluation
- projest pptDocument2 pagesprojest pptdevilsking578Pas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET Seminar: An Introduction to the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorDocument23 pagesMOSFET Seminar: An Introduction to the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorRahulKushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- SECA1503Document149 pagesSECA1503Thabasum Aara SPas encore d'évaluation
- Mosfet, TeorijaDocument2 pagesMosfet, Teorijazelko kovacevicPas encore d'évaluation
- BE Finals 10Document2 pagesBE Finals 10Somebody NobodyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mos FetDocument45 pagesMos FetbhawnaPas encore d'évaluation
- MosfetDocument5 pagesMosfetKancharana SarathchandraPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET Basics and OperationDocument4 pagesMOSFET Basics and OperationenigmangoPas encore d'évaluation
- J3b PDFDocument13 pagesJ3b PDFSrikrishna JanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 510.22E - Lecture - 7Document12 pages510.22E - Lecture - 7SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document46 pagesChapter 3Mayank KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- DC-DC MOSFET Chopper Design and TestingDocument25 pagesDC-DC MOSFET Chopper Design and Testingcharan524Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Micro Electronics Circuit NotesDocument59 pagesChapter 1 Micro Electronics Circuit NotesswamySLR100% (1)
- Unit I Cmos Technology An MOS (Metal-Oxide-Silicon) Structure Is Created by Superimposing Several Layers of ConductingDocument2 pagesUnit I Cmos Technology An MOS (Metal-Oxide-Silicon) Structure Is Created by Superimposing Several Layers of ConductingIshita AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET GuideDocument5 pagesMOSFET GuideKIT EEPas encore d'évaluation
- ETI 2203 Lesson 7Document10 pagesETI 2203 Lesson 7amash.emillyPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic MOSFET Characteristics: Understanding Threshold VoltageDocument4 pagesBasic MOSFET Characteristics: Understanding Threshold VoltagerashiborgohainPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET Basics: Working Principles and ApplicationsDocument19 pagesMOSFET Basics: Working Principles and ApplicationsSanyam BajpaiPas encore d'évaluation
- EI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFDocument21 pagesEI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFsartpgitPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To MOSFET.Document4 pagesIntroduction To MOSFET.Akib Hasan NiloyPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET Device Physics and OperationDocument13 pagesMOSFET Device Physics and OperationKarl Steven BaylonPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To CMOS Logic CircuitsDocument176 pagesIntroduction To CMOS Logic CircuitsrdanwaraPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationDocument4 pages7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationManoj VatsPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Security ChecklistDocument4 pagesAudit Security ChecklistPeter George100% (1)
- Blockchain Technology For Secure Supply Chain Management A Comprehensive ReviewDocument27 pagesBlockchain Technology For Secure Supply Chain Management A Comprehensive Reviewseley94024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Delta Ltl2000sDocument45 pagesDelta Ltl2000sDritta Anies CahayaPas encore d'évaluation
- COBIT 2019 Executive Summary - v1.1Document19 pagesCOBIT 2019 Executive Summary - v1.1Stephanie Gumapac100% (1)
- Computer Network MCQsDocument55 pagesComputer Network MCQsTarandeep singh100% (2)
- Cdi 109 Introduction To Cybercrime and Environmental Laws and Protection Powerpoint PresentationDocument17 pagesCdi 109 Introduction To Cybercrime and Environmental Laws and Protection Powerpoint PresentationJoebell Villanueva100% (19)
- Micro ServicesDocument2 pagesMicro ServicesNitesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- MP Lab ManualDocument36 pagesMP Lab Manualapi-19951707Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study of Building A Data Warehouse With Analysis ServicesDocument10 pagesCase Study of Building A Data Warehouse With Analysis ServicesbabussnmcaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Bootcampers Guide To Web AccessibilityDocument137 pagesThe Bootcampers Guide To Web AccessibilityNguyen Duy HaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 10067-Material-ConstantsDocument10 pages10067-Material-ConstantsSrinivas SherpallyPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP WEB IDE For SAP HANA Installation Troubleshooting Guide: Public 2021-09-29Document52 pagesSAP WEB IDE For SAP HANA Installation Troubleshooting Guide: Public 2021-09-29Tariq AliPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 Alexandr - Dubovikov Sipcapture Introducing Homer 5 Captagent 6Document40 pages07 Alexandr - Dubovikov Sipcapture Introducing Homer 5 Captagent 6Đăng Đào Hải100% (1)
- IC-FR3000 FR4000 Series BrochureDocument2 pagesIC-FR3000 FR4000 Series BrochureMikePas encore d'évaluation
- Audio Quality White Paper (YAMAHA)Document76 pagesAudio Quality White Paper (YAMAHA)KennyChoePas encore d'évaluation
- Valentin Yuhimenko CV Sept 2020Document1 pageValentin Yuhimenko CV Sept 2020Валентин ЮхименкоPas encore d'évaluation
- India's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future TrendsDocument5 pagesIndia's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future Trendspriyaa2688Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simplified server configuration stepsDocument3 pagesSimplified server configuration stepsJonathan PalerPas encore d'évaluation
- SpeedXmac Portal - Geniptv.123tv - To 8080@? BRAWN?Document113 pagesSpeedXmac Portal - Geniptv.123tv - To 8080@? BRAWN?Hristo SlawowPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Chain Management For enDocument14 pagesSupply Chain Management For enMario EnriquePas encore d'évaluation
- HT12D Ht12d-20soplf HT12FDocument13 pagesHT12D Ht12d-20soplf HT12FAnonymous t9tLb3WgPas encore d'évaluation
- Landmark Technology v. Bridgestone AmericasDocument18 pagesLandmark Technology v. Bridgestone AmericasPriorSmartPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Media Gatekeeping: An Analysis of The Gatekeeping Influence of Newspapers' Public Facebook PagesDocument20 pagesSocial Media Gatekeeping: An Analysis of The Gatekeeping Influence of Newspapers' Public Facebook PagescharlessPas encore d'évaluation
- Windows 10 Installation Manual UPGRADEDocument32 pagesWindows 10 Installation Manual UPGRADEConrad RobertsPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading in English Week 3 Day 2 Theme: Conditional IfDocument3 pagesReading in English Week 3 Day 2 Theme: Conditional IfFelipe Cabeza ParejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Getting Maximum Value When Evaluating ProductsDocument18 pagesGetting Maximum Value When Evaluating ProductsLiliannePas encore d'évaluation
- 3D Printing For The Jewellery IndustryDocument4 pages3D Printing For The Jewellery Industryru4angelPas encore d'évaluation
- Make in India: ESurvey CADD ModulesDocument10 pagesMake in India: ESurvey CADD ModulesNagarajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Guia Modem ZTE F670LDocument5 pagesGuia Modem ZTE F670LCarlos PalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing ProceudeDocument2 pagesTesting ProceudeThilak PonnusamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8D'EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityD'EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenD'EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenPas encore d'évaluation
- On Teaching Science: Principles and Strategies That Every Educator Should KnowD'EverandOn Teaching Science: Principles and Strategies That Every Educator Should KnowÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionD'EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Creative Investigations in Early Engineering and TechnologyD'EverandCreative Investigations in Early Engineering and TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- How to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasD'EverandHow to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Stay Curious and Keep Exploring: 50 Amazing, Bubbly, and Creative Science Experiments to Do with the Whole FamilyD'EverandStay Curious and Keep Exploring: 50 Amazing, Bubbly, and Creative Science Experiments to Do with the Whole FamilyPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Big Book of Nature Activities: A Year-Round Guide to Outdoor LearningD'EverandThe Big Book of Nature Activities: A Year-Round Guide to Outdoor LearningÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Nature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetD'EverandNature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Simple STEAM: 50+ Science Technology Engineering Art and Math Activities for Ages 3 to 6D'EverandSimple STEAM: 50+ Science Technology Engineering Art and Math Activities for Ages 3 to 6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cool Science Experiments for Kids | Science and Nature for KidsD'EverandCool Science Experiments for Kids | Science and Nature for KidsPas encore d'évaluation