Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 3 Questions Heuristic Search and Game Playing
Transféré par
hoangduc007Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 3 Questions Heuristic Search and Game Playing
Transféré par
hoangduc007Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
TRNG I HC BCH KHOA TP.
HCM Khoa Khoa hc & K thut My tnh
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Tutorial 3 Questions HEURISTIC SEARCH AND GAME PLAYING
Question 1. The heuristic path algorithm is a best-first search in which the objective function is f(n) = (2 - w).g(n) + w.h(n) For what values of w is this algorithm guaranteed to be optimal? (You may assume that h is admissible) What kind of search does this perform when w = 0? When w = l? When w = 2? Question 2. Prove each of the following statements: a. Breadth-first search is a special case of uniform-cost search. b. Breadth-first search, depth-first search, and uniform-cost search are special cases of best-first search. c. Uniform-cost search is a special case of A* search. Question 3.
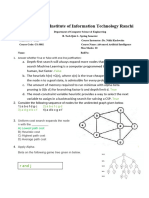
Figure 1 A road map of Romania 1
TRNG I HC BCH KHOA TP.HCM Khoa Khoa hc & K thut My tnh Figure 1 gives a simplified road map of Romania, in which the road distances between cities are indicated. Meanwhile, Table 1 presents the straight-line distance from the cities to Bucharest. Table 1 The straight-line distances to Bucharest
a. Find a path from Arad to Bucharest using the greedy algorithm, in which the h function is defined as the straight-line distance given in Table 1. Present the total cost and the nodes (cities) to be expanded, in the corresponding order. b. Find a path from Arad to Bucharest using the uniform-cost search algorithm, in which the g function is defined as the road distance given in Figure 1. Present the total cost and the nodes (cities) to be expanded, in the corresponding order. c. Find a path from Arad to Bucharest using A* algorithm, whose g and f functions are as presented in Question 1a and 1b. Present the actual total cost and the nodes (cities) to be expanded, in the corresponding order. d. Find a case that the greedy function will suffer infinitive loop when finding path between cities in Romania?
TRNG I HC BCH KHOA TP.HCM Khoa Khoa hc & K thut My tnh Question 4. Given a tree of a game state as presented in Figure 2 (assume that node A is corresponding to the MAXs player). If directly applied in the nodes, the static function will yield the results as given in Table 2.
Figure 2 A game-state tree Table 2 The results returned by the static function when directly applied Node A B C D E F G H I J Score 0.95 0.25 0.1 0.05 1.0 -1.0 -0.2 -0.7 0.75 -1.0
State the next move that the game playing program will choose if using a Minimax algorithm. Redraw the subtree with nodes associated with the corresponding evaluated scores. Suppose that the Minimax algorithm will be set to cover: a. Up to level 1 b. Up to level 2 c. Unlimited depth.
TRNG I HC BCH KHOA TP.HCM Khoa Khoa hc & K thut My tnh Question 5. Figure 3 presents a resultant tree when the Minimax algorithm is fully applied on the tree. In the best case of applying alpha-beta prunes (i.e. best nodes will be incidentally visited first), which nodes (and branches) will be cut-off?
Figure 3 - A game-state tree with Minimax applied Question 6. Figure 4 presents a resultant Minimax-applied tree. What are the corresponding resultant trees when the alpha-beta prunes are applied in the following cases: a. Normal case: nodes will be visited from left to right when in the same levels b. Best case c. Worst case
TRNG I HC BCH KHOA TP.HCM Khoa Khoa hc & K thut My tnh
Figure 4 - A resultant Minimax-applied tree -- End --
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Tut 3 - SolDocument9 pagesTut 3 - Soltuphong_90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 3 - Using The AStar Algorithm PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment 3 - Using The AStar Algorithm PDFAnonymous kFHpVUPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Level: Easy: Part A (20 1 20)Document9 pagesQuestion Level: Easy: Part A (20 1 20)axar kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Coursehero 34726625 PDFDocument11 pagesCoursehero 34726625 PDFScarletPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Summative AssessmentDocument4 pagesUnit 3 Summative AssessmentLindsey100% (1)
- AI Quiz 1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesAI Quiz 1 Solutionsfunnyclups413Pas encore d'évaluation
- AI Exercises Chapter 1-3 Search and HeuristicDocument24 pagesAI Exercises Chapter 1-3 Search and Heuristicbach khongPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Neural Networks Exam ReviewDocument11 pagesArtificial Neural Networks Exam ReviewahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ans: DDocument10 pagesAns: DVishal FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Neural networks and fuzzy logic question paperDocument2 pagesNeural networks and fuzzy logic question paperJhumur SantraPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Paradigms - C++ FS 2017: Universit at BaselDocument4 pagesProgramming Paradigms - C++ FS 2017: Universit at BaselBookDownPas encore d'évaluation
- Sec 33 BDocument1 pageSec 33 BroufixPas encore d'évaluation
- A Robust and Efficient Scheme For Image Encryption-DecryptionDocument5 pagesA Robust and Efficient Scheme For Image Encryption-DecryptionInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementPas encore d'évaluation
- Suppose There Are Two Singly Linked Lists Which Intersect Each Other at Some Point. The Start Pointers of BothDocument11 pagesSuppose There Are Two Singly Linked Lists Which Intersect Each Other at Some Point. The Start Pointers of Bothmir zainPas encore d'évaluation
- Two Dimensionalanalysisofshotput KrishDocument3 pagesTwo Dimensionalanalysisofshotput Krishapi-267928498Pas encore d'évaluation
- AI Worksheets - CT2Document7 pagesAI Worksheets - CT2Aditya DeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Image Sampling & QuantizationDocument70 pagesBasics of Image Sampling & QuantizationYomif NigusePas encore d'évaluation
- AI Sheet 1 2 3 V1.0Document9 pagesAI Sheet 1 2 3 V1.0mohammed ameerPas encore d'évaluation
- DIP-question PaperDocument3 pagesDIP-question PaperJohn JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 11 Test 2Document14 pagesYear 11 Test 2Maya Ammar100% (1)
- CG LAB: Implement Boundary and Flood Fill AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesCG LAB: Implement Boundary and Flood Fill AlgorithmsPrathmesh GaikwadPas encore d'évaluation
- AI Notes Unit IIDocument29 pagesAI Notes Unit IIKrithika SKPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 A TestDocument6 pagesUnit 5 A Testengineerdude5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Answer Key Asst Professor ItDocument20 pagesFinal Answer Key Asst Professor ItA SrikrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- School of Computer Science & Engineering Digital Assignment - I Fall 2021-22 Slot: C2Document2 pagesSchool of Computer Science & Engineering Digital Assignment - I Fall 2021-22 Slot: C2Majety S LskshmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Old Quesition Papers (III Sem) Dec-13Document52 pagesOld Quesition Papers (III Sem) Dec-139966197483Pas encore d'évaluation
- INT354 Question BankDocument11 pagesINT354 Question Bankbharad wajPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Mid Term ACIDocument3 pagesSample Mid Term ACIshipra.luckyPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Linear Equations in Two Variables inDocument10 pagesGrade 9 Linear Equations in Two Variables inKamatchi RajeshPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQs on basic CS conceptsDocument18 pagesMCQs on basic CS conceptsJayant TanwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Zero Gravity - Math 1010Document8 pagesZero Gravity - Math 1010api-533983196Pas encore d'évaluation
- Zero ProejctDocument5 pagesZero Proejctapi-509904273Pas encore d'évaluation
- MTH601-11 KalDocument74 pagesMTH601-11 Kalzaheer asghar83% (6)
- Fuzzy Membership Functions for Age and Vehicle PricesDocument9 pagesFuzzy Membership Functions for Age and Vehicle PricesAavesh DagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Complex Boolean Functions: Algorithms and ApplicationsDocument8 pagesLearning Complex Boolean Functions: Algorithms and ApplicationsMario Betanzos UnamPas encore d'évaluation
- Fin Draft KhoziumDocument9 pagesFin Draft KhoziumbassemPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2Mohsin ArifPas encore d'évaluation
- Final - Assessment CIE 227Document4 pagesFinal - Assessment CIE 227Ihab RagabPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving systems of linear equationsDocument25 pagesSolving systems of linear equationsmvdurgadeviPas encore d'évaluation
- ps2 Report PDFDocument8 pagesps2 Report PDFTalha YILMAZPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE422 Midterm Fall 2022Document2 pagesCSE422 Midterm Fall 2022Ali HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile CommunicationDocument3 pagesMobile Communicationistiaque_hmdPas encore d'évaluation
- Zero GravityDocument9 pagesZero Gravityapi-534521342Pas encore d'évaluation
- Image Processing QuestionsDocument4 pagesImage Processing QuestionsabhinavPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Assignment (Beng 1113)Document15 pagesGroup Assignment (Beng 1113)Faris AzminPas encore d'évaluation
- Study - Material - 1st Year 1 Sem All Paper (2020-21) 1619326582759Document33 pagesStudy - Material - 1st Year 1 Sem All Paper (2020-21) 1619326582759khuship200102Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bài tập về xử lý ảnhDocument5 pagesBài tập về xử lý ảnhlephuckt100% (1)
- University of Bologna: Masters in Civil Engineering Sustainable Transportation Engineering (Time Allowed: TWO Hours)Document14 pagesUniversity of Bologna: Masters in Civil Engineering Sustainable Transportation Engineering (Time Allowed: TWO Hours)Sufian AbusninaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Computer Graphics?Document14 pagesWhat Is Computer Graphics?Abdur RahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam1 s15 SolDocument10 pagesExam1 s15 SolVũ Quốc NgọcPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structure QPDocument8 pagesData Structure QPTinku The BloggerPas encore d'évaluation
- EportzerogravityDocument5 pagesEportzerogravityapi-534221212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Learning Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument20 pagesMachine Learning Multiple Choice QuestionsSatyanarayan Gupta100% (1)
- MidSQ Image ProcessingDocument29 pagesMidSQ Image Processingsimgeuckun1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Answer:c: Loop Loo PDocument37 pagesAnswer:c: Loop Loo PVivek CHOWDARYPas encore d'évaluation
- Project 2 Zero GravityDocument6 pagesProject 2 Zero Gravityapi-344664513Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Sheet 1 - SIT 433Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 1 - SIT 433Nzelle BidePas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Vision in Vehicle Technology: Land, Sea, and AirD'EverandComputer Vision in Vehicle Technology: Land, Sea, and AirPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 6 Predicate Logic and Structured Knowledge: Artificial Intelligence Exercises Page 1/5Document5 pagesTutorial 6 Predicate Logic and Structured Knowledge: Artificial Intelligence Exercises Page 1/5hoangduc007100% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 7 Questions Uncertainty and ImprecisionDocument6 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 7 Questions Uncertainty and Imprecisionhoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 7 Questions Uncertainty and ImprecisionDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 7 Questions Uncertainty and Imprecisionhoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 5 Solutions Predicate LogicDocument5 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 5 Solutions Predicate Logichoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 6 Questions Predicate Logic and Structured KnowledgeDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 6 Questions Predicate Logic and Structured Knowledgehoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 5 Questions Predicate LogicDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 5 Questions Predicate Logichoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 4 Solutions Propositional LogicDocument5 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 4 Solutions Propositional Logichoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 4 Questions Propositional LogicDocument3 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 4 Questions Propositional Logichoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 2 Questions State Space Search and StrategiesDocument3 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 2 Questions State Space Search and Strategieshoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 2 Solutions State Space Search and StrategiesDocument6 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 2 Solutions State Space Search and Strategieshoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 1 Questions PrologDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 1 Questions Prologhoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence: Tutorial 1 Solutions PrologDocument3 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Tutorial 1 Solutions Prologhoangduc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Printable Sudoku High-Five, July 23Document1 pagePrintable Sudoku High-Five, July 23News-PressPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures (Binary Trees)Document21 pagesData Structures (Binary Trees)Mohammad ZawarPas encore d'évaluation
- GREEDY ALGORITHM OPTIMIZATIONDocument78 pagesGREEDY ALGORITHM OPTIMIZATIONknoxxPas encore d'évaluation
- BFS, DFS, Best First SearchDocument15 pagesBFS, DFS, Best First Searchelsa annaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises Block1Document3 pagesExercises Block1asdf1212Pas encore d'évaluation
- IntroIA TP1 enDocument2 pagesIntroIA TP1 enNistor GrozavuPas encore d'évaluation
- Celta Upper-Intermediate: Student ADocument2 pagesCelta Upper-Intermediate: Student AAna PadillaPas encore d'évaluation
- BrainBashers - Daily Kakuro - CombinationsDocument4 pagesBrainBashers - Daily Kakuro - Combinationszero_cool_oooPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual For Algorithm Design 1st Edition Jon Kleinberg Eva TardosDocument8 pagesSolution Manual For Algorithm Design 1st Edition Jon Kleinberg Eva TardosJerome Devore100% (36)
- Printable Sudoku High-Five, April 9Document1 pagePrintable Sudoku High-Five, April 9News-PressPas encore d'évaluation
- 5x5 03Document2 pages5x5 03api-3843571Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sudoku BlocDocument13 pagesSudoku BlocPery G S SenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Moderate Sudoku 1Document10 pagesModerate Sudoku 1recie lamboPas encore d'évaluation
- NP CompleteDocument32 pagesNP CompleteSabaniPas encore d'évaluation
- DAA Worksheet-3.2 20BCS7611Document4 pagesDAA Worksheet-3.2 20BCS7611AYUSH TIWARIPas encore d'évaluation
- Sudoku #1: Easy Sudoku Puzzles by Krazydad, Volume 10, Book 6Document10 pagesSudoku #1: Easy Sudoku Puzzles by Krazydad, Volume 10, Book 6pro madridPas encore d'évaluation
- Hard SudoRETERTkuDocument125 pagesHard SudoRETERTkuJohn BaguioPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2B - Greedy - FinalDocument40 pagesModule 2B - Greedy - FinalSIDDHARTH CHATTERJEEPas encore d'évaluation
- KD Kakuro 5x5 v7 s2 b029Document3 pagesKD Kakuro 5x5 v7 s2 b029RADU GABIPas encore d'évaluation
- Algorithms For VLSI Design Automation: Chapter-4 Tractable and Intractable ProblemsDocument6 pagesAlgorithms For VLSI Design Automation: Chapter-4 Tractable and Intractable ProblemskiranpaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Uninformed SearchDocument45 pagesUninformed Searchyusifovyadigar1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kakuro #1-4: 6X6 Kakuro Puzzles by Krazydad, Volume 1, Book 1Document3 pagesKakuro #1-4: 6X6 Kakuro Puzzles by Krazydad, Volume 1, Book 1Aashirtha SPas encore d'évaluation
- NP-Completeness and ReducibilityDocument100 pagesNP-Completeness and Reducibilitydipanjali chavarePas encore d'évaluation
- Network Flow UNIT - 14: Chandan Sinha RoyDocument18 pagesNetwork Flow UNIT - 14: Chandan Sinha RoyRISHIRAJ CHANDAPas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse Delete Algorithm for Minimum Spanning TreeDocument3 pagesReverse Delete Algorithm for Minimum Spanning TreeHasibul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide and Intervention Solving Compound InequalitiesDocument2 pagesStudy Guide and Intervention Solving Compound InequalitiesMohamedYehiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - Network ModelsDocument53 pagesChapter 5 - Network ModelsNam PhạmPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Source Shortest PathsDocument17 pagesSingle Source Shortest PathsAnukul GangwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Occupations Crossword Puzzle Crosswords Fun Activities Games Icebreakers Oneono 52063Document2 pagesOccupations Crossword Puzzle Crosswords Fun Activities Games Icebreakers Oneono 52063Nathalie Rojas100% (1)