Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Principles of Money and Time Relationships
Transféré par
Chris AlunanDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Principles of Money and Time Relationships
Transféré par
Chris AlunanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PRINCIPLES OF MONEY AND TIME RELATIONSHIPS INTEREST the amount of the money paid for the use of borrowed
d capital. Simple Interest the interest paid that is directly proportional to the length of time the amount or principal is borrowed. Principal the amount of money borrowed and on which interest is charged. Rate of Interest the amount earned by one unit of principal during a unit of time. I = Pin Where: I total interest earned by the principal, P amount of the principal I- rate of interest expressed in decimal form, n number of interest periods F = P + I = P (1 + in) Where: F - total amount to be repaid. Ordinary simple interest computed on the basis of one bankers year, or 1 bankers year = 12 months, each consisting of 30 days = 360 days. Exact Compound Interest based on the exact number of days, 365 for an ordinary year and 366 days for a leap year. Ordinary simple interest = Pi (d/360) Exact simple interest = Pi (d/365) For ordinary year = Pi (d/360) For leap year Compound Interest the interest earned by the principal if not paid at the end of each interest period (considered as added to the principal that will also earn interest for the succeeding periods). F = P (1 + I) n, where the factor (1 + n) n = (F/P, i%, n) or Single Payment Compound Amount Factor (SPCAF). Derivation Interest Period 1 2 n Principal at start of period P P (1 + I) P (1 + I) exp(n-1) Interest earned during period Pi P (1 + I) I P (1 + I) exp (n-1) I Compound amount at end of the period P (1+I) exp (n-1) + P (1+I) exp (n-1) = P (1+I) exp n = F
Continuous Compounding F = P (1 + r/m) mn Where: r nominal annual interest rate, m number of interest period each year i = r/m interest rate per interest period, m number of interest periods in n years. Nominal Rate of Interest the rate of interest in compound interest that specifies the rate of interest and the number of interest periods per year. Effective Rate of Interest the actual rate of interest on the principal for one year. Effective rate of interest(ERI) = (1+I)n -1 Present Value (P) the value of the compound amount F at present, or the present value of the amount F, or the amount which when invested now will become F after n periods. P = F (1+I) n = F/(1+I)n where the factor (1+I) n is the Single Payment Present Worth Factor or SPPWF = (P/F, i%, n). Discount (d) the difference between what is worth in the future and its present worth. Rate of discount the discount on one unit of principal per unit time. d = 1 1/(1+I) = 1 (P/F, i%, 1) or d = i/(1+i) = (P/F, i%, 1)I Equivalent rate of interest corresponding to the rate of interest I, I = d/(1-d) = d/(P/F, i%, 1) Problems: 1. Determine the exact and ordinary simple interests on P1200 for the period from January 16 to November 26, 1992, if the rate of interest is 24%. 2. A man borrows P10,000 from a loan firm. The rate of simple interest is 15%, but the interest to be deducted from the loan at the time the money is borrowed. At the end of one year he has to pay back P10,000. What is the actual rate of interest? 3. A man borrows P6400 from a loan association. In repaying this debt he has to pay P400 at the end of every 3 months on the principal and a simple interest of 16% on the principal outstanding at that time. Determine the total amount he has paid after paying all his debt. 4. A man possesses a promissory note, due 3 years hence, whose maturity value is P6,700.48. If the rate of interest is 10% compounded semi-annually, what is the value of this note now? 5. If you are investing your money which is better: 12% compounded monthly or 12.5% compounded annually? 6. An advertisement of an investment firm states that if you invest P500 in their firm today you will get P1000 at the end of 4 years. What nominal rate is implied if interest is compounded quarterly?
References: Engg Economy by M. Arreola, Engg Economy by E. Paul De Garmo, Engg Economics by C. S. Park
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Orca Share Media1533208944176Document90 pagesOrca Share Media1533208944176Christian Jimenez Reyes0% (1)
- Lecture 33434434313545Document10 pagesLecture 33434434313545Christelle Marie Aquino Beroña100% (3)
- Eseneco L2Document5 pagesEseneco L2Jennifer Elizabeth Yambao100% (1)
- Engineering Economy Lecture2Document32 pagesEngineering Economy Lecture2Jaed CaraigPas encore d'évaluation
- Interest & DiscountDocument5 pagesInterest & DiscountThur MykPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises 1 and 2Document3 pagesExercises 1 and 2Raymond Gicalde RementillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economy: Cheerobie B. AranasDocument27 pagesEngineering Economy: Cheerobie B. AranasCllyan ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- TLA 8.4 Sample Problems On Types of Annuities - Types of Annuity Group No. 6 PDFDocument10 pagesTLA 8.4 Sample Problems On Types of Annuities - Types of Annuity Group No. 6 PDFGian SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economics Upm Samples 10Document4 pagesEngineering Economics Upm Samples 10Cesia MontelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Interest Compound InterestDocument6 pagesSimple Interest Compound InterestKaye OleaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pagli Naw AnDocument17 pagesPagli Naw AnErgie PaglinawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Equation of Value For Ceit-04-501aDocument9 pagesEquation of Value For Ceit-04-501aAngeli Mae SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- InstallDocument2 pagesInstallNoreen Stella EbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Ii. The Time Value of MoneyDocument21 pagesUnit Ii. The Time Value of MoneyGrachelle Ann PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise No. 7 in ECON 11 Capitalized CostDocument3 pagesExercise No. 7 in ECON 11 Capitalized CostMarlon BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution 1-5 1Document4 pagesSolution 1-5 1Dan Edison RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Eeco Chapter 2Document3 pagesEeco Chapter 2Erika Herrera0% (2)
- Basic EE Week 8 Lesson - 864873286Document33 pagesBasic EE Week 8 Lesson - 864873286Reinier FrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple InterestDocument14 pagesSimple InterestVillanueva Moshe50% (2)
- Economy Problem Set 1Document4 pagesEconomy Problem Set 1jung biPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economics Learning Module 4Document14 pagesEngineering Economics Learning Module 4Oliver Jr SabadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemset EconceDocument10 pagesProblemset EconceGerly Joy MaquilingPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3.3 - Cashflow and Continuous Compounding Sample ProblemsDocument14 pagesChapter 3.3 - Cashflow and Continuous Compounding Sample ProblemsArin ParkPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machines 1 EE05: Engr. Ruben J. Dichoso InstructorDocument17 pagesElectrical Machines 1 EE05: Engr. Ruben J. Dichoso InstructorAngeli Mae SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems of EconomyDocument31 pagesProblems of EconomyJun Jun0% (2)
- c2 Selection of Present EconomyDocument12 pagesc2 Selection of Present EconomyJen67% (3)
- Engineering Economy: Kiv Ryan A. Albino, Ece, EctDocument51 pagesEngineering Economy: Kiv Ryan A. Albino, Ece, EctRoss Sonny Cruz100% (2)
- BES4 Assignment4Document2 pagesBES4 Assignment4look porrPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - Interest and Money Time Relationships Week 4Document5 pagesChapter 2 - Interest and Money Time Relationships Week 4Jouryel Ian Roy TapongotPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4dssfdDocument12 pagesLecture 4dssfdChristelle Marie Aquino Beroña0% (2)
- Chapter 12-Eneman20Document3 pagesChapter 12-Eneman20Reynald John PastranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economy Lecture 1 PDFDocument2 pagesEngineering Economy Lecture 1 PDFMichael Angelo Jugador Bas100% (1)
- Economics AnnuityDocument2 pagesEconomics AnnuityGeodetic Engineering FilesPas encore d'évaluation
- Amortization and Uniform Arithmetic GradientDocument20 pagesAmortization and Uniform Arithmetic GradientCyril Jay G. OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital Recovery CostDocument2 pagesCapital Recovery CostShahnaz NadivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ c3Document51 pagesEcon c3larra100% (1)
- ENGECODocument3 pagesENGECOmgoldiieeee20% (5)
- ElevatorDocument26 pagesElevatorChristine Joyce Bunyi17% (6)
- Activity A - Introduction To Engineering EconomyDocument2 pagesActivity A - Introduction To Engineering EconomySofia MonteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economy: University of Eastern Philippines College of EngineeringDocument34 pagesEngineering Economy: University of Eastern Philippines College of EngineeringFrqnz AyasivPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Problems in Engineering Economy AccountingDocument10 pagesSolved Problems in Engineering Economy Accountingsaleh gaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved ProblemsDocument44 pagesSolved ProblemsGlyzel Dizon0% (1)
- Eeco HWDocument19 pagesEeco HWRejed VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Problems Thermodynamics Plate 1Document2 pagesSample Problems Thermodynamics Plate 1Mahusay Neil DominicPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment 2 Adriano Belza Codilan Correa NaluisDocument13 pagesAssessment 2 Adriano Belza Codilan Correa NaluisLindsay DazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engg. EconomicsDocument2 pagesEngg. EconomicsStevenPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ 1Document15 pagesEcon 1Martin Laurence Garcia PlasabasPas encore d'évaluation
- Worktext in EE 006 (Basic EE For CE)Document232 pagesWorktext in EE 006 (Basic EE For CE)Jean Divinagracia100% (1)
- Ecoon PDFDocument9 pagesEcoon PDFJm T. Despabeladero100% (1)
- 6-Comparing AlternativesDocument7 pages6-Comparing AlternativesKlucifer XinPas encore d'évaluation
- Baldevino Assignment 1Document9 pagesBaldevino Assignment 1Nathaniel Baldevino100% (1)
- Engineering Economy Part 3Document13 pagesEngineering Economy Part 3Josiah FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economy: Annuity and Capitalized CostDocument22 pagesEngineering Economy: Annuity and Capitalized CostKì Hyö JüngPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometric GradientDocument20 pagesGeometric GradientDarkie DrakiePas encore d'évaluation
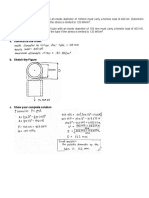
- The Outside Diameter of The Tube If The Stress Is Limited To 120 MN/MDocument19 pagesThe Outside Diameter of The Tube If The Stress Is Limited To 120 MN/MMa Rhena Salomon MagdasocPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Econ FinalsDocument10 pagesEngineering Econ FinalsIvan Morise AtienzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Question: A Cube 2.2 FT On An Edge Has Its Lower Half of S 1.6 and UpperDocument1 pageQuestion: A Cube 2.2 FT On An Edge Has Its Lower Half of S 1.6 and UpperLi RePas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 3.2Document3 pagesTopic 3.2Dave Jhaeson AlivioPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple and Compound Interest: Ryan Jeffrey P Curbano, PH.DDocument35 pagesSimple and Compound Interest: Ryan Jeffrey P Curbano, PH.DPrince RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economy Lecture21 WisDocument35 pagesEngineering Economy Lecture21 WisMelissa Delgado100% (1)
- Supply, Delivery, Installation, Testing and Commissioning of Pabx, Structured Cabling, CCTV and Access Control Installation WorksDocument189 pagesSupply, Delivery, Installation, Testing and Commissioning of Pabx, Structured Cabling, CCTV and Access Control Installation WorksChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Structured CablingDocument4 pagesStructured CablingChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- T-300 - Telecom Riser DiagramDocument1 pageT-300 - Telecom Riser DiagramChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- State of Ind Structured Cabling & Matl SpecificationsDocument91 pagesState of Ind Structured Cabling & Matl SpecificationsChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Community EducationDocument8 pagesCommunity EducationChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Z-Transform: ECON 397 Macroeconometrics CunninghamDocument22 pagesThe Z-Transform: ECON 397 Macroeconometrics CunninghamChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- EN Technical GuideDocument72 pagesEN Technical GuideChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Telephone Wiring BasicsDocument8 pagesTelephone Wiring BasicsChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Template1 HRDocument6 pagesTemplate1 HRChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 ECE Annex IV - Laboratory RequirementsDocument11 pages2018 ECE Annex IV - Laboratory RequirementsChris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Editorial 2Document26 pagesEditorial 2Chris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Enigma Pricelist As of July 23, 2011Document2 pagesEnigma Pricelist As of July 23, 2011Chris AlunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Materials FOR V: Aluation Concepts and MethodsDocument36 pagesInstructional Materials FOR V: Aluation Concepts and MethodsShahida Rodny NoronaPas encore d'évaluation
- SPE Introduction To E&P Petroleum Economics & Commercial: November 28, 2019 Lamé VerreDocument43 pagesSPE Introduction To E&P Petroleum Economics & Commercial: November 28, 2019 Lamé Verrejhon berez223344Pas encore d'évaluation
- IMC Unit 2 Mock Exam 1 V18 March 2021Document33 pagesIMC Unit 2 Mock Exam 1 V18 March 2021SATHISH SPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 Risks and Returns - BobadillaDocument24 pagesChapter 10 Risks and Returns - BobadillaJohn Rey EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Report and Accounts 2013Document36 pagesReport and Accounts 2013MdBelaluddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Value of MoneyDocument32 pagesTime Value of MoneyHariom Singh100% (1)
- Chapter 1:-The Nature of Capital MarketDocument9 pagesChapter 1:-The Nature of Capital MarketJaideep SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- ESENECO (2) Interest Money Time RelationshipDocument50 pagesESENECO (2) Interest Money Time Relationshipjhonel guinto100% (3)
- Smart Beta: Hatsun Agro Products LTD 12 Month Target: INR 806.6 Last Close (27/09/19) : INR 725.4E Upside: 11.2%Document8 pagesSmart Beta: Hatsun Agro Products LTD 12 Month Target: INR 806.6 Last Close (27/09/19) : INR 725.4E Upside: 11.2%akash srivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes - FAR - Loans and Receivables (Financial Assets at Amortized Cost)Document10 pagesNotes - FAR - Loans and Receivables (Financial Assets at Amortized Cost)ElaineJrV-IgotPas encore d'évaluation
- ACF Course OutlineDocument8 pagesACF Course OutlineRashi AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital BudgetingDocument44 pagesCapital BudgetingMohammad Rakiv75% (4)
- Risk and Refinement in Capital BudgetingDocument51 pagesRisk and Refinement in Capital BudgetingRitesh Lashkery0% (1)
- Financial Management:: Stock ValuationDocument57 pagesFinancial Management:: Stock ValuationSarah SaluquenPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting For Merchandising Businesses Chp. 6 Group 4 FIXDocument78 pagesAccounting For Merchandising Businesses Chp. 6 Group 4 FIXboba milk100% (1)
- CB With FC Saiful Sir Class SmaDocument23 pagesCB With FC Saiful Sir Class SmaFahadPas encore d'évaluation
- FINC521-Most Important QuestionsDocument24 pagesFINC521-Most Important QuestionsAll rounder NitinPas encore d'évaluation
- Preface To The Third Edition: Life Contingencies by C.W. Jordan, Our Text Has Become The Only OneDocument59 pagesPreface To The Third Edition: Life Contingencies by C.W. Jordan, Our Text Has Become The Only OneAelin IsmailovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition and Type DebenturesDocument4 pagesDefinition and Type DebenturesAshutosh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 01.payback Period and NPV Their Different Cash FlowsDocument7 pages01.payback Period and NPV Their Different Cash FlowsAndryPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounts Payable - SDD - 001Document95 pagesAccounts Payable - SDD - 001KrishaPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Funds Management - Integration With FIDocument27 pagesSAP Funds Management - Integration With FIKathiresan NagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- IBS Session 1 With SolutionDocument16 pagesIBS Session 1 With SolutionMOHD SHARIQUE ZAMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Resto-Bar Customer SatisfactionDocument23 pagesFactors Affecting Resto-Bar Customer SatisfactionAETHEL JOY SERNICULAPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Mathematics Quarter 1 Week 6: NAME: - GRD. & SEC.Document10 pagesBusiness Mathematics Quarter 1 Week 6: NAME: - GRD. & SEC.Nìcole NabasPas encore d'évaluation
- Interest Rate Risk I (CH 8)Document13 pagesInterest Rate Risk I (CH 8)Mahbub TalukderPas encore d'évaluation
- Acctg 201 Midterm Quiz 3Document10 pagesAcctg 201 Midterm Quiz 3Minie KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Startup Valuation Guide: September 2018Document42 pagesStartup Valuation Guide: September 2018adsadPas encore d'évaluation
- Credit Default Swap Pricing ModelDocument34 pagesCredit Default Swap Pricing ModeldovidsteinbergPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4 - Equity ValuationDocument45 pagesLecture 4 - Equity Valuationchenzhi fanPas encore d'évaluation