Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Activity Intolerance Related To Amenia
Transféré par
Siti Syazana Mohamad MogriDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Activity Intolerance Related To Amenia
Transféré par
Siti Syazana Mohamad MogriDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Activity Intolerance Related To Amenia
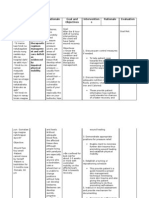
NURSING DIAGNOSIS INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION Assess patient ability to Influences choice of Activity Report an increase perform ADLs interventions and needed Intolerancerelated to in activity assistance. Monitor vital sign (Blood Anemia tolerance, Pressure, pulse, and Cardiopulmonarymanifestations including ADLs. respirations) during and after result from attempts by the Demonstrate a activity heart and lungs to supply Suggest client change position adequate amounts of oxygen to decrease in slowly; monitor for dizziness. the tissues. physiological signs Postural hypotension or Provide or recommend of intolerance cerebral hypoxia may assistance with activities and cause dizziness, fainting, and pulse, respirations, ambulation as necessary, and BP remain allowing client to be an active increased risk of injury. participant as much as Although help may be within clients possible. necessary, self-esteem is normal range. enhanced when client does Identify and implement Display laboratory some things for self. energy-saving techniques values (Hgb/Hct) Instruct client to stop activity Encourages client to do as within acceptable much as possible, while if palpitations,chest pain, conserving limited energy and range. shortness of breath, weakness,
ordizziness occur
Collaborative
Monitor laboratory studies, such as Hgb/Hct, RBC count, and arterial blood gases (ABGs). Provide supplemental oxygen as indicated. Administer the following, as indicated: Whole blood, packed RBCs (PRCs); blood products as indicated. Monitor closely for transfusion reactions. Prepare for surgical intervention, if indicated.
preventing fatigue. Cellular ischemia potentiates risk of infarction, and excessivecardiopulmonary strai n and stress may lead to decompensation and failure Identifies deficiencies in RBC components affecting oxygen transport, treatment needs, and response to therapy. Maximizing oxygen transport to tissues improves ability to function Increases number of oxygencarrying cells; corrects deficiencies to reduce risk of hemorrhage in acutely compromised individuals. Surgery is useful to control bleeding in clients who are anemic because of bleeding, such as in ulcers and uterine bleeding; or to remove spleen as treatment ofautoimmune hemolytic anemia. Bone marrow andstem cell transplantationmay be done in presence of bone marrow failure aplastic anemia.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerancejanelee2824Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP LocDocument2 pagesNCP LocMel RodolfoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJezza RequilmePas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearancePatrick Arvin Ballesteros BarcarsePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoPas encore d'évaluation
- Altered Renal Perfusion CRFDocument4 pagesAltered Renal Perfusion CRFKristel Anne Nillo ZepolPas encore d'évaluation
- Self Care DeficitDocument4 pagesSelf Care DeficitEllaine RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusionsyderman999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For MGDocument1 pageNCP For MGSandra MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesFluid Volume DeficitRuby AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeNica RespondoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPKyla Carbonel100% (1)
- NCP Arra AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP Arra AnemiaShin GuevaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- Nursing Care to Prevent Suffocation in BabiesDocument2 pagesNursing Care to Prevent Suffocation in BabiesKimberly Subade Mandilag100% (2)
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficitprickybiik100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthAna Ramos LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ate Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Document2 pagesAte Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Kimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionMitsika AnadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiodular non toxic goiter nursing care planDocument1 pageMultiodular non toxic goiter nursing care plankzbreakerrPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPRose AnnPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Impaired SkinDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocument5 pagesNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- Altered Renal Perfusion CRFDocument5 pagesAltered Renal Perfusion CRFGen Ramos- SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntolerancedohblePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Activity Intolerancelouie roderos0% (1)
- Daily NCPDocument5 pagesDaily NCPKuennie SabalPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceDocument8 pagesNCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceWyen Cabatbat100% (1)
- PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA Nursing Care Plan for 78yo Female CVD PatientDocument3 pagesPAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA Nursing Care Plan for 78yo Female CVD PatientpromilokidPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJhel NabosPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 pagesNCP PancreatitisJeanelle GenerosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheDocument14 pagesAnswer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheMikeePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessing and Managing Risk of AspirationDocument6 pagesAssessing and Managing Risk of AspirationaianrPas encore d'évaluation
- Bilirubin Assessment and Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesBilirubin Assessment and Nursing DiagnosisJonica CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 pagesAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan for GastroenteritisDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan for GastroenteritisChris Denver BancalePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 pageNCP Impaired Physical MobilityCharmaine SolimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Betty Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesBetty Impaired Skin IntegrityBenjie DimayacyacPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Urinary Tract Obstruction Nursing InterventionsDocument8 pagesManaging Urinary Tract Obstruction Nursing Interventionsjyaba0% (1)
- CC-Concept Map 2Document5 pagesCC-Concept Map 2MDCITY50% (2)
- HypertensionDocument3 pagesHypertensionAgnes Marie RendonPas encore d'évaluation
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument6 pagesDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarPas encore d'évaluation
- Care Plan Exercise: Cristi Day RN, MSN, FNP-C Texas A&M University - Corpus ChristiDocument19 pagesCare Plan Exercise: Cristi Day RN, MSN, FNP-C Texas A&M University - Corpus ChristiPhyu Lin0% (1)
- NCP 1Document5 pagesNCP 1Charm TanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivebanyenye25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study 9Document7 pagesCase Study 9Lindsay WishmierPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageCyrus De Asis92% (25)
- Sickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesSickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanArisa Vijungco100% (4)
- COMMON MCQ Hematology 2017Document25 pagesCOMMON MCQ Hematology 2017علي. احمد0% (1)
- Bone Marrow Biopsy Nursing Care StepsDocument40 pagesBone Marrow Biopsy Nursing Care StepsGaras AnnaBernicePas encore d'évaluation
- Acquired Hemolytic Anemia Presentation For BPharmDocument24 pagesAcquired Hemolytic Anemia Presentation For BPharmHiren Pathak100% (2)
- Approach To The Adult With Anemia - UpToDate PDFDocument66 pagesApproach To The Adult With Anemia - UpToDate PDFJuliana Salerno100% (1)
- Evaluation of Pallor in ChildrenDocument23 pagesEvaluation of Pallor in ChildrenFlorie Lei BulosPas encore d'évaluation
- Haematology MedicineDocument25 pagesHaematology MedicineSami Ur RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Normocytic Normochromic AnemiaDocument18 pagesNormocytic Normochromic AnemiaElaizha PagulayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemoglobin MetabolismDocument80 pagesHemoglobin MetabolismSurya BudikusumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument7 pagesAutoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentHoopmen SilaenPas encore d'évaluation
- Acquired Hemolytic AnemiaDocument48 pagesAcquired Hemolytic AnemiaJeena RajPas encore d'évaluation
- RBC & It's DisorderDocument101 pagesRBC & It's DisorderSPas encore d'évaluation
- Autoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaDocument55 pagesAutoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaNicky SebastianPas encore d'évaluation
- HEMOGLOBINOPATHY GUIDEDocument3 pagesHEMOGLOBINOPATHY GUIDEChatie PipitPas encore d'évaluation
- Anisocytosis (Variation in Size) : RBC AbnormalitiesDocument25 pagesAnisocytosis (Variation in Size) : RBC AbnormalitiesJam RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaemiaDocument70 pagesAnaemiaapi-3822841Pas encore d'évaluation
- Must To Know HemaDocument44 pagesMust To Know HemaKaycee Gretz LorescaPas encore d'évaluation
- RBC Count: Why The Test Is PerformedDocument3 pagesRBC Count: Why The Test Is PerformedFahmi SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Complete Blood Cell Count A PowerfulDocument16 pagesThe Complete Blood Cell Count A PowerfulGabriele VitorPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology: Done By: Ahmed AlsolamiDocument52 pagesHematology: Done By: Ahmed AlsolamiEmad Manni100% (1)
- Prepare & Interpret Blood SmearsDocument26 pagesPrepare & Interpret Blood Smearsstudent2013Pas encore d'évaluation
- PLASMA AND URINE HB TESTINGDocument12 pagesPLASMA AND URINE HB TESTINGAvi VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Assignment 3Document3 pagesPathology Assignment 3mah_heroPas encore d'évaluation
- LECTURE NOTES ON HAEMATOLOGYDocument94 pagesLECTURE NOTES ON HAEMATOLOGYAnmar ZawahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal Urine Analysis-01!12!2018Document28 pagesAbnormal Urine Analysis-01!12!2018ramesh joshiPas encore d'évaluation
- HypersensitivityDocument20 pagesHypersensitivityJAIRA RIEYELLE LIPANAPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology FinalDocument14 pagesHematology FinalTop Music100% (1)
- Study Stack - Hematology Tests 3-4 Table ReviewDocument5 pagesStudy Stack - Hematology Tests 3-4 Table Review장주연Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hemolytic AnemiaDocument1 pageHemolytic AnemiaTeus FatamorganaPas encore d'évaluation
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethyldopa Drug Studymilkv100% (14)
- Nguyen 2021Document8 pagesNguyen 2021Yaseen MohamnadPas encore d'évaluation