Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Building Services Project (Electrical 2) Auto Saved)
Transféré par
Asyraf RobaniDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Building Services Project (Electrical 2) Auto Saved)
Transféré par
Asyraf RobaniDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
electrical appliance electrical plan method of wiring sequence of supply control regulations/standard being applied
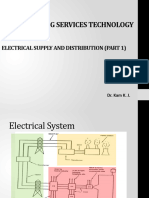
INTRODUCTION KJC 325 is a building service subject that teach us how to manage and learn how to recognize the part and the system are used in the building. In this project, we construct project to design a quarters house 3 phase wiring installation. But we just make a anlysis in one house because all the design is same.Each house have 3 bedroom,1 kitchen room,2 toilet room,1 dining room,1balcony,1 living hall and 1 stor,in each house just need single phase wiring installation.The location for this plan is been secured due to certain reasons.
recessed down light
mounted/surface down light
METHOD OF WIRING Conduit system In this electrical wiring plan, we used metal and non-metal tube which a PVC tube. This is used to provide protection to the cables and it is a permit for wiring. The tube act as earth conductor if the conduit is a metal. The size of conductor used is based on the current capacity. Cable is used to connect to the source energy to electric loads. In the conduit system, they have three component cables which is conductor, insulation and mechanical protection.
Conductor Type: cooper Size: 1.5mm, 2.5mm and 4mm We chose this type of conductor because it is durable and the conductivity is better than aluminium. This type is commonly used in construction. The size is based on the current carrying. copper has low resistance where it is a good material and can make electron move easily. Copper has low cross-section area that can save our cost of installation wiring. Insulation Type: PVC Its specific name is Polyvinyl Chloride. This type of insulation is commonly used for low and medium voltage. It made of synthetic rubber where the max temperature is 65c and it will easily bended if the temperature more than that. PVC unaffected by water, acids, oils and soils and can be safely buried in concrete, plaster or lime. PVC is light, smooth and easy to install and will not ignite.
Mechanical protection Type: light-gauge steel conduit (Grade A) This type usually used for low-voltage (not exceeding 250 V) installation. The conduit made up from steel strip with the joint welded, brazed or butted, the latter known as close-conduit. This conduit is protected from corrosion inside and outside by black bituminous enamel paint. The conduit cannot be formed into bend shape because of the thin tube wall, therefore special bends have to be used. Fitting for this type of conduit are elbows and tees by mean of a lug-grip connection, which is tightened on to the conduit. All black enameling must be removed before the fitting to ensure earth continuity Method of securing conduit The conduit can be secured by using saddles (hospital saddles, space bar, plain) crampet. We also secured the conduit in the concrete and timber floor.
SEQUENCES OF SUPPLY CONTROL Ring-circuit A ring circuit is a final sub-circuit. The power ring start and finishing at the consumer board. It is a multi-core cable carrying live, neutral and earth, looping in and out of the socket in each room. Appliances plugged into the socket are in parallel. The circuit being connected to a 30A, 20A, 10A and 6A miniature circuit-breaker(MCB) or a fuse. If a metal conduit system is used the earth wire is unnecessary, providing that the conduit joints are electrically sound and the conduit is earthed. It is permissible to cut the conductors where they loop into the terminals of the socket outlets, providing that the joint are electrically sound. A large house might have a power ring to the high-load appliances in the kitchen and separate power in to the each floor.
Earth leakage circuit-breaker (ELCB) A circuit-breaker which disconnect the supply when the voltage or current with respect to earth, reaches a predetermined limit. The current will operate with no direct earthling connection. 2 types of ELCB, there are 1- and 3-. The operation are as follow : 1. when the live and neutral current balance, they produce same and opposite fluxes in transformer. 2. when the earthed metalwork flow of current passing through the earth, more current flow in live side than neutral and make out of balance flux detected by fault-detector coil. Fuse and MCB Needed for safety reason. Its function is to cut out current due to excess current at certain temperature excess and produce heat and smoke. The advantages of using the fuses are as follow : Cheap Replaceable Other circuit can still be used Unlike the miniature circuit breaker (MCB) when excess current occur, the MCB will cut the circuit and can be adjust to its original position. Earthing The fuse protects the circuit but earth primarily protect the user. A loose wire make the outer casing of an appliance live. Provide the casing has its own low-resistance connection back to earth, the circuit will immediately complete, short circuiting and blowing the fuse on the live side, and making system safe.
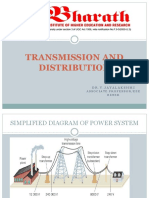
METHOD OF DISTRIBUTION This house use a radial System in method of ditribution.The service to subsidiary distribution panels originate from the main intake panel.Main panel consists of a main switche connected to fused switches through bus-bar chamber.Feeder cables run from the main intake panel to subsidiarydistribution panels located at point in the building or separate building.
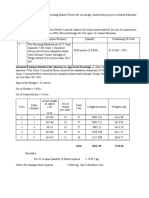
ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE Equipment Downlight fitting, 26W Fluo fitting, 18W Fluo fitting, 36W Ceiling fan fitting Single gang SSO, 13A Twin SSO, 13A (ring CCT) SSO for AC, 15A Quantity 16 3 1 5 8 3 1
DIVERSITY FACTOR The rate of current that passes through a cable or electrical equipment with assumption that not all loads used at the same time. Singlestory house 1 , 240V EQUIPMENT Downlight fitting, 26W Fluo fitting, 18W Fluo fitting, 36W Ceiling fan fitting, 100W Single gang SSO, 13A Twin SSO, 13A (ring CCT) SSO for AC, 15A
TOTAL LOAD 1.73A 0.23A 0.15A 2.08A 104A 39A 15A
FACTOR LOAD 1.14A 0.15A 0.1A 1.37A 49.4A 23.4A 15A
D.F = factored current Total current D.F = 90.56A_ x 100= 55.8% 162.19A
CALCULATION :
16, 26W recessed down light Total Load P = 26 x 16 = 416w I = P/V = 416 / 240 = 1.73A Factor Load 66% x 1.73 = 1.14A
3, 18W surface down light Total Load P = 18 x 3 = 54w I = P/V = 54 / 240 = 0.23A Factor load 66% x 0.23 = 0.15A
1, 36W surface down light Total Load P = 36 x 1 = 36w I = P/V = 36 / 240 = 0.15A Factor load 66% x 0.15 = 0.1A
1-gang 13A socket Total Load I = 8 13 = 104A Factor load 1 100/100 13 = 13 A 7 13 40/100 = 36.4 A = 49.4 A
Twin SSO 13A socket Total Load I = 3 13 = 39A Factor load 1 100/100 13 = 13 A 2 13 40/100 = 10.4 A = 23.4 A
SSO for AC socket Total Load I = 1 15 = 15A Factor load 1 100/100 15 = 15 A
SIZE OF CABLE : The size of conductor used is based on the current capacity. Cable is used to connect to the source energy to electric loads. In the conduit system, they have three component cables which is conductor, insulation and mechanical protection. Factors that influence the size of cable : Drop in voltage Variation factor Wiring system Surrounding Temperature Type of Cable Incoming cable length : From table 9D1 from the manual book; area = 70 mm2 Maximum nominal voltage = 4% = 4/100 voltage = 4/100 240 = 9.6 V Total Factor Load = 90.56A Incoming cable length Then voltage drop = total load voltage drop from table 9D1 Length 9.6 = 90.56 0.00062 L L= 138m Calculation of length cable: At L / R3 4 NOS PLC 18w surface down light P = 418W =72W I = 72/415 =0.17A Current =0.17 21A Voltage drop =4/100415=16.6A From table 9D1: area of cable =2.5mm2 Voltage drop=I voltage drop from table 9D1 length 16.6=210.015L L=52.7m
REGULATION/STANDARD BEING APPLIED all electrical wiring installation works shall comply to the latest edition of IEE wiring regulations all wiring works shall meet the SESCO standard practice requirement, to be tested and approve by SESCO all concealed conduit used shall be of high impact UPVC bomba approve type all exposed/surface run conduit shall be of G.I type
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Electrical WiringDocument11 pagesElectrical WiringRasydan AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm C469 - C469M - 14Document5 pagesAstm C469 - C469M - 14adil Rahman hassoon100% (1)
- Design Report XXXDocument41 pagesDesign Report XXXashikin100% (1)
- Ecm216 Building Services Bab 1.5 CableDocument3 pagesEcm216 Building Services Bab 1.5 CableAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (1)
- Electrical Installation in BuildingsDocument14 pagesElectrical Installation in BuildingsMasar Abdul Rakman100% (1)
- Lighting Circuits and Power Circuits Socket OutletsDocument13 pagesLighting Circuits and Power Circuits Socket OutletsLawrence Wahome ngariPas encore d'évaluation
- 11-Step Procedure For A Successful Electrical Circuit Design (Low Voltage)Document7 pages11-Step Procedure For A Successful Electrical Circuit Design (Low Voltage)Mohammad Ather SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- About Power SupplyDocument17 pagesAbout Power SupplyAnonymous DjWqKpZ1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 220 KV Switchyard EquipmentsDocument3 pages220 KV Switchyard EquipmentsRaj Kumar Prajapati100% (1)
- House WiringDocument9 pagesHouse WiringhassjayawardanaPas encore d'évaluation
- BLD61304 (Week 7 - Eletricity Supply To Buildings 1)Document31 pagesBLD61304 (Week 7 - Eletricity Supply To Buildings 1)khoo chao siangPas encore d'évaluation
- Domestic Electrical InstallationsDocument9 pagesDomestic Electrical InstallationsgauravPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 10 Electrical Design Considrations For Residential BuildingDocument11 pagesLecture 10 Electrical Design Considrations For Residential BuildingBUKENYA BEEE-2026100% (1)
- Railway ProjectDocument38 pagesRailway Projectalankar123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual PDFDocument40 pagesLab Manual PDFAngelline MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Installation Technology IDocument34 pagesElectrical Installation Technology IMeja PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Installation Design - TESLA INSTITUTEDocument20 pagesElectrical Installation Design - TESLA INSTITUTEWa LidPas encore d'évaluation
- Underground Power CablesDocument64 pagesUnderground Power CablesAnonymous rWZ2WNh4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compact Integrated Distribution Substation CIDS CatalogDocument12 pagesCompact Integrated Distribution Substation CIDS Catalogalexns84Pas encore d'évaluation
- MV HV Cable ManufacturingDocument33 pagesMV HV Cable ManufacturingAris BudiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical InstallationDocument6 pagesElectrical InstallationEvans MuokiPas encore d'évaluation
- Flex& Spur OutletDocument9 pagesFlex& Spur OutletTehran KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Immersion LabDocument30 pagesEngineering Immersion LabSudeepPas encore d'évaluation
- EPT Final NotesDocument10 pagesEPT Final NotesHaris MemonPas encore d'évaluation
- 11-Step Procedure For A Successful Electrical Circuit Design (Low Voltage)Document11 pages11-Step Procedure For A Successful Electrical Circuit Design (Low Voltage)kisan singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2-Electrical Wiring CircuitsDocument43 pagesChapter 2-Electrical Wiring CircuitsyeabmotherPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser Security System For HomeDocument19 pagesLaser Security System For HomeSelvakumar SubramaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Installation - CircuitsDocument8 pagesElectrical Installation - CircuitsAmos KormePas encore d'évaluation
- 2.2.06 DiDocument5 pages2.2.06 DiMauro MarafonPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbo Generator at NalcoDocument13 pagesTurbo Generator at NalcoSanjay Kumar PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Mains WiringDocument5 pagesConsumer Mains WiringMsKarolyPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical V 2.0Document65 pagesElectrical V 2.0hahadu0% (1)
- Electronic Transformer For 12 V Halogen LampDocument15 pagesElectronic Transformer For 12 V Halogen LampWin KyiPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 6Document11 pagesCH 6Vikas UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Internship Report: Saqib AliDocument11 pagesInternship Report: Saqib AliSHAH RUKH KHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Report of Grid Substation: Presented byDocument11 pagesTraining Report of Grid Substation: Presented byତୁଷାର ମିଶ୍ର100% (1)
- Building ServicesDocument31 pagesBuilding ServicesRoop TejaPas encore d'évaluation
- 400 KV Metal Oxide Surge Arrestor CigreDocument12 pages400 KV Metal Oxide Surge Arrestor CigreDilip ARPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Design Report Dormitory CYT-T1Document8 pagesElectrical Design Report Dormitory CYT-T1Freedom Love NabalPas encore d'évaluation
- System Specification / Details of SPV Power Plant Kavaratti: Load Location PV ArrayDocument9 pagesSystem Specification / Details of SPV Power Plant Kavaratti: Load Location PV ArrayankitPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Materials On Electrical Layout For StudentsDocument27 pagesReading Materials On Electrical Layout For Studentsbeng tahoPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit Breakers: Carla Cristine Pillejera Bet-Mect3ADocument25 pagesCircuit Breakers: Carla Cristine Pillejera Bet-Mect3Akanye eastPas encore d'évaluation
- ECM346 1.2.3 Function of Protection Devices HBI 02Document50 pagesECM346 1.2.3 Function of Protection Devices HBI 02Tiffany's LovePas encore d'évaluation
- B. Tech (Elect) AnujDocument19 pagesB. Tech (Elect) AnujMansi MansiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 IesDocument93 pagesUnit 1 Iesbhanupathania02Pas encore d'évaluation
- 35kW Active RectifierDocument6 pages35kW Active RectifierndcongPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8&9-Electric and LightningDocument62 pagesLecture 8&9-Electric and LightningMuhammad FakhriPas encore d'évaluation
- Domestic Electrical WiringDocument4 pagesDomestic Electrical WiringSyed Showkath AliPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER TWO-WPS Office NewDocument12 pagesCHAPTER TWO-WPS Office NewSayp dPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee04 801-EsdeDocument222 pagesEe04 801-EsdeChandra Bose Kn50% (2)
- EEE - BEE601 - TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION - Dr. V. JayalakshmiDocument21 pagesEEE - BEE601 - TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION - Dr. V. JayalakshmikrishnandrkPas encore d'évaluation
- Domestic InstallatiuonDocument10 pagesDomestic InstallatiuonJoseph MvurachenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 04 ElectricityDocument61 pagesLec 04 ElectricityNandini BhattPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 6 Electrical Services To BuildingsDocument14 pagesTopic 6 Electrical Services To Buildingsullhan84100% (1)
- Lastactivity NapiliDocument10 pagesLastactivity NapiliMArk BarenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Workshop - ExperimentsDocument7 pagesElectrical Workshop - ExperimentsMirza Bilal100% (1)
- Neutral Wires. These Wires Are Color Coded For Easy Identification. Hot Wires Are Black or RedDocument17 pagesNeutral Wires. These Wires Are Color Coded For Easy Identification. Hot Wires Are Black or Redvalerie candoPas encore d'évaluation
- Switchgear Lab ManualDocument40 pagesSwitchgear Lab ManualZeeshan Ahmed100% (2)
- Services 2 Reading MaterialDocument16 pagesServices 2 Reading MaterialDhyey VaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Transmission TowerDocument25 pagesTransmission TowerAkshay MalviyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test-Ch 6 v2Document3 pagesTest-Ch 6 v2api-188215664Pas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance For Accelerated Testing and Reliability - For Electrical and Electronic Parts and EquipmentDocument7 pagesGuidance For Accelerated Testing and Reliability - For Electrical and Electronic Parts and EquipmentHans HsiehPas encore d'évaluation
- Shreyas Pawale ResumeDocument1 pageShreyas Pawale ResumeRahulRajGoldyPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems Based On AgesDocument2 pagesProblems Based On AgesHarish Chintu100% (1)
- EE276 Test 8Document3 pagesEE276 Test 8fred francisPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 6154457525488977613Document5 pages5 6154457525488977613ankith sPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Containemt IsolatorsDocument72 pagesDesign of Containemt IsolatorsSweekar Borkar50% (2)
- Probability Theory & Stochastic Processes - BITSDocument12 pagesProbability Theory & Stochastic Processes - BITSAllanki Sanyasi RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wartsila o e W 50df TRDocument16 pagesWartsila o e W 50df TRNoel MejiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lewis David On The Plurality of WorldsDocument279 pagesLewis David On The Plurality of Worldsdjoseph_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- XXX Book of Aquarius XXXDocument163 pagesXXX Book of Aquarius XXXlesgrantonline100% (1)
- A Solar Chimney Power Plant TULJAPURDocument16 pagesA Solar Chimney Power Plant TULJAPURDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (3)
- SIMS ManuscriptDocument6 pagesSIMS ManuscriptViraj EdirisinghePas encore d'évaluation
- Material Estimate Details With Reference To Approved Drawings. A Cable Shall Consist of 12 Nos 12.7mmDocument2 pagesMaterial Estimate Details With Reference To Approved Drawings. A Cable Shall Consist of 12 Nos 12.7mmepe civil1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1.constrution of Flying Quad Rotor With Video Surveillance SystemDocument45 pages1.constrution of Flying Quad Rotor With Video Surveillance SystemakhilPas encore d'évaluation
- Anhua New Energy Introduction 2014Document62 pagesAnhua New Energy Introduction 2014maradonagolPas encore d'évaluation
- Shaft Model With Mathlook EquationsDocument112 pagesShaft Model With Mathlook EquationsMoisés MachadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Enhanced Degradation of Persistent Pharmaceuticals Found in Wastewater Treatment Ef Uents Using Tio2 Nanobelt PhotocatalystsDocument14 pagesEnhanced Degradation of Persistent Pharmaceuticals Found in Wastewater Treatment Ef Uents Using Tio2 Nanobelt PhotocatalystsSourav SutradharPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 6: Simulations of Photonic Crystal StructuresDocument11 pagesExperiment 6: Simulations of Photonic Crystal StructuresKishlay KushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aztech LightsDocument4 pagesAztech Lightskhan4luvPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study of Verbs Compounded With Aus, Ein, Etc., As Contrasted With Those Compounded With Heraus, Hinaus, Herain, Hinein, EtcDocument152 pagesA Study of Verbs Compounded With Aus, Ein, Etc., As Contrasted With Those Compounded With Heraus, Hinaus, Herain, Hinein, EtcEnkindooPas encore d'évaluation
- Biplots of Compositional Data: University of Glasgow, UKDocument18 pagesBiplots of Compositional Data: University of Glasgow, UKStefhany ArdilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report Strength Tensile TestDocument3 pagesLab Report Strength Tensile TestAbdul KarimPas encore d'évaluation
- DE38#######KS###: Data Sheet and Instruction Manual DE38 Digital Differential Pressure Transmitter / SwitchDocument12 pagesDE38#######KS###: Data Sheet and Instruction Manual DE38 Digital Differential Pressure Transmitter / SwitchAmirouche BenlakehalPas encore d'évaluation
- CUOBOGASDocument4 pagesCUOBOGASDiego Fernando Pedroza UribePas encore d'évaluation
- 2Nd Experiment "Coagulation - Floculation Analysis Using Jar - Test Method"Document15 pages2Nd Experiment "Coagulation - Floculation Analysis Using Jar - Test Method"garum_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Einstein's Third Postulate PDFDocument5 pagesEinstein's Third Postulate PDFHerczegh TamasPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard S Ific Ion For: - !' N G :.. F.Ld'.Tita"Ilj.MDocument6 pagesStandard S Ific Ion For: - !' N G :.. F.Ld'.Tita"Ilj.MIgnacio Hiram M RoquePas encore d'évaluation