Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
EIGRP
Transféré par
Amrxh LatifiDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
EIGRP
Transféré par
Amrxh LatifiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
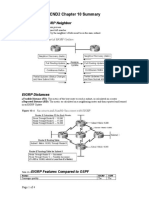
EIGRP( Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) )
Purpose of RTP: Used by EIGRP to transmit and receive EIGRP packets Characteristics of RTP: Involves both reliable & unreliable delivery of EIGRP packet Packets can be sent unicast and Multicast Neighbors learn about new routes, unreachable routes, and rediscovered routes through exchange of these packets: Hello: Unicast to discover neighbor, timers, unreliable Acknowledgement: in reply to Update, request, reply Update: 1) Unicast If a new neighbor is found 2) Multicast to indicate routing change Query: Unicast or multicast, to request info about neighbor or new successor Reply : Reply to a query and always uni-cast.
METRIC: EIGRP uses a composite metric value to determine the best path to a destination.
[ K1 * bandwidth + (K2*bandwidth)/(256-load)+K3]*delay] * [K5/(reliability+K4)]
Network Summerisation: Its basically the operation at which you summarize different subnets into
a single larger subnet which gets advertised to neighboring routers to conserve router resources.
If a single route goes down that is contained within a summary route, updates are not sent throughout the entire routed domain. Only the router advertising the summary route will know that the more specific route has went down. For EIGRP, this will prevent unwanted queries and potentially SIA in the EIGRP autonomous system. Router Authentication:1) Implement security to the routing protocol by supporting authentication. 2) A router authenticates the source of each routing update packet that it receives. 3) Prevent false routing updates from updating the routing table MD5 authentication: This authentication is secure, as described in RFC 1321. This authentication does not include confidentiality (content not encrypted). The router generates a message digest. The message digest is sent with the packet.
The key is not sent.
Requirements for EIGRP Authentication: IGRP AS number Authentication mode One or more keys Key lifetimes (optional)
key chain routerR1chain key 1 key-string firstkey accept-lifetime 04:00:00 Jan 1 2009 infinite send-lifetime 04:00:00 Jan 1 2009 04:00:00 Jan 31 2009 key 2 key-string secondkey
ip authentication mode eigrp 110 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 110 routerR1chain show ip eigrp neighbors: used to view neighbor table and verify that EIGRP has established adjacencies with neighbors show ip protocols: command is also used to verify that EIGRP is enabled show ip route: command is also used to verify EIGRP. EIGRP automatically summarizes routes at major network boundary The Null0 Summary Route By default, EIGRP uses the Null0 interface to discard any packets that match the parent route but do not match any of the child routes DUAL Purpose of DUAL: To prevent routing loops Successor: Primary route to a destination Feasible successor: Backup route to a destination Feasible distance: Lowest calculated metric to a destination Reported distance: The distance towards a destination as advertised by an upstream neighbor
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Informatica Cloud Real Time Service Technology and Security OverviewDocument16 pagesInformatica Cloud Real Time Service Technology and Security OverviewLakshminarayana SamaPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRPDocument5 pagesEIGRProkanPas encore d'évaluation
- Clase 14. EIGRPDocument70 pagesClase 14. EIGRPLinux0ecPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRPDocument21 pagesEIGRPAli MohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRP TutorialDocument3 pagesEIGRP TutorialAsim NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Cis82 SN EIGRPDocument135 pagesCis82 SN EIGRPAhmad AbidPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRPDocument16 pagesEIGRPmatthew_mk_au2271Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eigrp CCNP - Draft BDocument9 pagesEigrp CCNP - Draft BsubuecePas encore d'évaluation
- Capt2 RespuestasDocument8 pagesCapt2 Respuestasedwin4arroyo4colonPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRP Lab SimDocument2 pagesEIGRP Lab SimADILPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNP-ROUTE Chapter 2 EIGRP NotesDocument5 pagesCCNP-ROUTE Chapter 2 EIGRP Notesar0520Pas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRP Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesEIGRP Interview QuestionshamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei MBSC ST 1.07Document28 pagesHuawei MBSC ST 1.07abdirashiidPas encore d'évaluation
- Eigrp SummaryDocument8 pagesEigrp SummaryCCNAResourcesPas encore d'évaluation
- RobRiker EIGRPDocument55 pagesRobRiker EIGRPAhmed R. KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cis185 ROUTE Lecture2 EIGRP Part1Document113 pagesCis185 ROUTE Lecture2 EIGRP Part1samirandPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRPDocument4 pagesEIGRPRatheesh RavindranPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRPDocument26 pagesEIGRPKhaing myal HtikePas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRP FeaturesDocument14 pagesEIGRP Featuresathartanveer31Pas encore d'évaluation
- AyenewDocument55 pagesAyenewayenewPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccnav3.3 303Document63 pagesCcnav3.3 303Tung HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Route 2 Eigrp ImplementingeigrpDocument97 pagesRoute 2 Eigrp ImplementingeigrpAdrian AdmiPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRP OverviewDocument9 pagesEIGRP OverviewYusuf MahmoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Yap Chin Hoong Bsci05 - EIGRPDocument16 pagesYap Chin Hoong Bsci05 - EIGRPMohd RummanPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRPDocument102 pagesEIGRPNguyễn Mạnh ThếPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRP - NotesDocument2 pagesEIGRP - NotesDaniel DudleyPas encore d'évaluation
- A Reply That Is Received From Each Neighbor For Every Generated QueryDocument8 pagesA Reply That Is Received From Each Neighbor For Every Generated QueryRamandeep K BhumblaPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRP... : Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Is A Distance Vector, Classless Routing ProtocolDocument16 pagesEIGRP... : Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Is A Distance Vector, Classless Routing ProtocolAbhishek KunalPas encore d'évaluation
- Advance EigrpDocument42 pagesAdvance EigrpashdesantisPas encore d'évaluation
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing ProtocolDocument25 pagesEnhanced Interior Gateway Routing ProtocolRobinson JoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- DCUG EIGRP Class-2006-12-14Document52 pagesDCUG EIGRP Class-2006-12-14CPUHoggPas encore d'évaluation
- CcnaDocument19 pagesCcnaMavhungu MarvinPas encore d'évaluation
- ROUTE Chapter 2 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Document8 pagesROUTE Chapter 2 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205100% (2)
- EIGRP TutorialDocument18 pagesEIGRP TutorialGustavo Muñoz SuroPas encore d'évaluation
- Please Wait, CIS 185 Will Begin Shortly (5:30pm) There Will Be No Sound Until Class Begins. I Will Do A Sound Check at The Beginning of ClassDocument104 pagesPlease Wait, CIS 185 Will Begin Shortly (5:30pm) There Will Be No Sound Until Class Begins. I Will Do A Sound Check at The Beginning of ClassJaroslaw ZakPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRPDocument3 pagesEIGRPHiep TrinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP)Document17 pagesEnhanced IGRP (EIGRP)Fanani MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Eigrp?Document37 pagesWhat Is Eigrp?sinan sinanPas encore d'évaluation
- Enarsi - Chapter - 2 Eigrp (Done)Document36 pagesEnarsi - Chapter - 2 Eigrp (Done)teferihabtamu98Pas encore d'évaluation
- ICND2-Chapter10 Key IdeasDocument4 pagesICND2-Chapter10 Key Ideashoang nguyen baPas encore d'évaluation
- S2M09 Basic Router TroubleshootingDocument46 pagesS2M09 Basic Router TroubleshootingRamesh AlagarsamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol: Kmar Thaalbi Kmar - Thaalbi@tek-Up - deDocument16 pagesEnhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol: Kmar Thaalbi Kmar - Thaalbi@tek-Up - deHamzaJayariPas encore d'évaluation
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol: Naveen PatelDocument13 pagesEnhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol: Naveen PatelNishant MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- EIGRP TutorialDocument13 pagesEIGRP TutorialFurqan Ali KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 9tut NotesDocument19 pages9tut NotescleetusPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5Document6 pagesChapter 5decker360Pas encore d'évaluation
- +EIGRP Config - v3Document5 pages+EIGRP Config - v3Norwell SagunPas encore d'évaluation
- Topics Covered: Basics of EIGRP Configuration of EIGRP Troubleshooting EIGRPDocument4 pagesTopics Covered: Basics of EIGRP Configuration of EIGRP Troubleshooting EIGRPprashant patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Route NotesDocument17 pagesRoute NotesSDE NIBPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploration Routing Chapter 9Document65 pagesExploration Routing Chapter 9vildsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 7b - EigrpDocument17 pages7b - EigrpFachrizal Rizky FerdiansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Routing: Eng - Ahmed NabilDocument16 pagesRouting: Eng - Ahmed Nabilhooda3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Day 5Document32 pagesDay 5AlyDedenPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna 3 Chapter 5 (Version 4.0)Document8 pagesCcna 3 Chapter 5 (Version 4.0)_mika_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cis185 ROUTE Lecture2 EIGRP Part1Document104 pagesCis185 ROUTE Lecture2 EIGRP Part1Phil GarbettPas encore d'évaluation
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingD'EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingPas encore d'évaluation
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingD'EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingPas encore d'évaluation
- First Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolD'EverandFirst Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolPas encore d'évaluation
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkD'EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- Sec Usr Cts Xe 16 12 Book PDFDocument138 pagesSec Usr Cts Xe 16 12 Book PDFHamza AbdelsalamPas encore d'évaluation
- ArticleDocument769 pagesArticletesnimarapmoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Iub DimensioningDocument14 pagesIub DimensioningOcira Oyaro0% (1)
- HCNP-IENP en Lab Guide-ContentDocument159 pagesHCNP-IENP en Lab Guide-ContentAnton FortovPas encore d'évaluation
- NID4083 - 1.4.1 Designing An IP-Transport Network For DTTDocument25 pagesNID4083 - 1.4.1 Designing An IP-Transport Network For DTTtrucaitPas encore d'évaluation
- FortiSwitchOS-7.4.0-FortiLink Guide (FortiOS 7.4)Document254 pagesFortiSwitchOS-7.4.0-FortiLink Guide (FortiOS 7.4)José PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- PCRFDocument10 pagesPCRFvivekgeethaPas encore d'évaluation
- FS 24-Port Multi-Gigabit 10GBASE-T Switch - FSDocument12 pagesFS 24-Port Multi-Gigabit 10GBASE-T Switch - FSMai Tuấn CườngPas encore d'évaluation
- IP HeaderDocument1 pageIP HeaderbajjiboyPas encore d'évaluation
- Link Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachDocument66 pagesLink Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachMuhammad FaisalPas encore d'évaluation
- "Configuring Wireless Access Point" (Advanced Setup)Document22 pages"Configuring Wireless Access Point" (Advanced Setup)EurekaTwT100% (1)
- 1 I3OFPP Attachment en ENUDocument3 pages1 I3OFPP Attachment en ENUprudhvi rajuPas encore d'évaluation
- TCP and UDP - : Transport Layer ProtocolsDocument4 pagesTCP and UDP - : Transport Layer ProtocolsGabriel DeMarco100% (1)
- TCPIP Lecture16Document115 pagesTCPIP Lecture16Tuan BeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sip ProtocolDocument137 pagesSip Protocolramin_babaePas encore d'évaluation
- NPCI API Descriptionsb9bceb7Document74 pagesNPCI API Descriptionsb9bceb7Joinal AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - Subnetting Calculations Lab: Student NameDocument9 pagesLab - Subnetting Calculations Lab: Student NamesugapriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nokia 7750 SR Series Data Sheet enDocument10 pagesNokia 7750 SR Series Data Sheet enDiegoPas encore d'évaluation
- 0mnaccsa4enqb Man Acc Netman 204 QST enDocument2 pages0mnaccsa4enqb Man Acc Netman 204 QST enEka WijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2xo4u2nb3kys-LAB 3.4 PDFDocument5 pages2xo4u2nb3kys-LAB 3.4 PDFAneeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Secospace USG2110 V100R001C03SPC200 User Guide (English Document)Document10 pagesSecospace USG2110 V100R001C03SPC200 User Guide (English Document)Subarna GhimirePas encore d'évaluation
- Fortigate Sniffing Commands - MaxnetworkDocument3 pagesFortigate Sniffing Commands - Maxnetworkba31Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nano IP Series - Ipn920.Document2 pagesNano IP Series - Ipn920.PaMe LiTaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Solve Hik-Connect Offline IssueDocument3 pagesHow To Solve Hik-Connect Offline Issuedian_16Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Setup and Configure Elatec Tcpconv Network Hardware: Card ReaderDocument3 pagesHow To Setup and Configure Elatec Tcpconv Network Hardware: Card ReadersololoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aviat CTR 8540 Data Sheet - April 26 - 2018Document2 pagesAviat CTR 8540 Data Sheet - April 26 - 2018Sulaiman HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- WEB Setting - AR-727-CM Manual-EnDocument21 pagesWEB Setting - AR-727-CM Manual-EnJohnyTrinidadPas encore d'évaluation
- InformationSecuirty (Apr 09)Document5 pagesInformationSecuirty (Apr 09)MukeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna 200-301Document72 pagesCcna 200-301Adrian100% (1)