Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Anatomy of the Vertical Jump in Basketball
Transféré par
ewer27Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Anatomy of the Vertical Jump in Basketball
Transféré par
ewer27Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Anatomy of Basketball and the Vertical Jump Posted on 20.
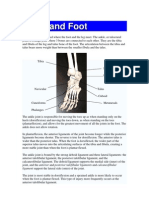
Jul, 2011 by David McCready in Building Muscle,Cardio/Conditioning, Misc Like most things I blog about, playing Basketball involves muscles throughout your body. The main movements inbasketball which are, running, pivoting and jumping utilize a full range of muscles in the feet, legs and trunk, with particular concentration in the quadriceps and hamstring muscles. The vertical jump in basketball is critical to your performance and involves a wide range of muscles, particularly: Abdominals: These muscles are flexible, and help to support your back through a range of motion. In particular,
the abdominal muscles on the sides, which assist in turning and twisting, better known as the obliques, work the hardest, especially during the execution of your jump shot. Calf muscles: Located at the back of the lower leg, these muscles are used intensively to achieve vertical height when jumping. Gluteus Muscles: Known as glutes, these muscles, are responsible for a large portion of the upward thrust necessary in your vertical jump. The gluteus maximus originates along the crests of the pelvic bone crests and attaches to the rear of the femur. Its primary function is hip extension (as the thigh moves to the rear). Hamstrings: These powerful muscles run along the back of the thigh, from the lower pelvis to the back of the shin bone. Hamstrings function to extend the hip joint and flex the knee joint. Quadriceps:
Located in the knee, the large thigh muscles known as quadriceps muscles are connected to the patella (kneecap) by the quadriceps tendon, while a separate tendon the infrapatellar tendon connects the patella to the top of the tibia (shin bone). Quadriceps are a focus of training for basketball players, especially when it comes to improving your jumping capacity. As a strong vertical jump gives the athlete considerable advantage in scoring, all five of these muscle groups should be equally targeted when it comes to basketball training. During the free throw in basketball, numerous upper body muscles are employed, including rotator cuff muscles, deltoids, coracobrachialis, latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major, biceps brachii, brachialis, brachioradialis, triceps brachii, anconeus, pronator teres, and pronator quadratus. A multitude of muscles in the hands and fingers come into play, including the flexor capri radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi radialis longus, flexor digitorium superficialis, flexor digitorum profoundus, flexor pollicus longus, extensor digitorum, extensor indicis, extensor digiti minimi, extensor pollicus longus, extensor pollicus brevis, and the abductor pollicus longus. These are the official names for various muscles heavily utilized when it comes to playing and training for basketball. I will include a more detailed diagram of the muscles soon. In the meantime feel free to look any of them up to harnes a better understanding of your body mechanics. Most Common Basketball Injuries: Like many athletic injuries, those occurring in basketball may often times be classified as overuse injuries and/or traumatic injuries. Overuse injuries Overuse injuries occur when a particular area is put under prolonged stress and becomes damaged in the process, causing pain, loss of movement, in many cases, swelling. One such injury common to the sport is patellar tendonitis, also known as jumpers knee, which is characterized by pain in the tendon just below your kneecap.Another typical overuse injury is Achilles tendonitis, involving the tendon connecting the muscles in the back of the calf to the heel bone. The result of this injury is pain in the back of your leg, slightly above the heel. In more severe cases, the Achilles tendon can tear, requiring medical treatment and immobilization of the injury to allow proper healing.Shoulder injuries involving overuse are not uncommon in basketball and may involve the tendons in their shoulders. The rotator cuff of the shoulder is made up of four muscles, attached by tendons to the shoulder bones. Inflammation and pain can result from overhead activities, including throwing the basketball. Traumatic injuries
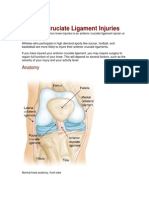
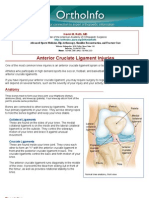
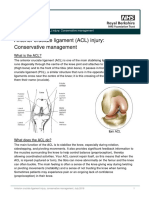
Unlike repetitive or overuse injuries, traumatic injuries result from a sudden forceful event. Among
the most common traumatic injuries in basketball are jammed fingers, which can range in severity from minor injury of the ligaments, to a fractured bone. These types of injuries require adequate care and may need to be splinted to ensure proper healing. Muscle pulls or tears are also common basketball injuries, often occurring in the large muscles of the legs.Ankle sprains may be the most frequent basketball injury, often occurring when one player lands on anothers foot or during a rapid change of direction. The result causes the stretching or tearing of the ligaments connecting bones and supporting the ankle. Ligaments tearing may be partial or complete.Knee injuries are potentially dangerous and debilitating. The knee may be sprained, with a tearing of ligaments or joint capsule. Twisting the knee can tear the meniscus the tissue acting as a cushion between the bones of the upper and lower leg at the knee. This injury may require surgical treatment.Tears to ligaments supporting the knee may also be serious. A tear of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the more common ligament injuries. Tears in the ACL require prompt medical attention and may require surgery. Injury Prevention Strategies Proper warm-up is essential. Jumping jacks, stationary cycling, running or walking helps limber up muscles, preventing strains and other injuries.Be aware of the position of other players on the court, to avoid inadvertant collisions.Proper, snug-fitting and supportive footwear can help avoid injuries. Cotton socks absorb perspiration, also providing extra support to the foot. Use of ankle supports can reduce the incidence of ankle sprains.Use of a mouth guard helps protect the teeth and mouth.Safety glasses should be used by those wearing eyeglasses.Basketball courts, whether indoors or out must be free of obstructions and debris. I know that these prevention strategies are slightly generic, but they are useful and everybody can use a reminder now and then. I hope you found this post useful and if youd like to add anything or simply say hello, leave me a comment below.
o
Post to Digg
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Basketball Stretches and Flexibility ExercisesDocument6 pagesBasketball Stretches and Flexibility ExercisesfredericktingsyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sports Medicine InjuriesDocument20 pagesSports Medicine InjuriesSreenath SukumaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Upper CalvesDocument22 pagesUpper Calvesgabriel tbPas encore d'évaluation
- Healthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesD'EverandHealthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.shoulder Girdle (MSPT-SPT)Document87 pages1.shoulder Girdle (MSPT-SPT)Khushboo IkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotator Cuff Relief-Horwitz PDFDocument75 pagesRotator Cuff Relief-Horwitz PDFGafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bones of The KneeDocument6 pagesBones of The Kneesabrina aswanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lower Calves and Achilles TendonDocument21 pagesLower Calves and Achilles Tendongabriel tbPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report On ACL Injuries: BY: PiyushDocument42 pagesProject Report On ACL Injuries: BY: Piyushsagar111033Pas encore d'évaluation
- ACL Injuries: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument6 pagesACL Injuries: Causes, Symptoms, Treatmentalgebra234Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 PDFDocument9 pages2 PDFAZOZ 19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoulder Joint Replacement: AnatomyDocument15 pagesShoulder Joint Replacement: AnatomyChandan Kumar ChoubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy: Collateral LigamentsDocument6 pagesAnatomy: Collateral LigamentsmysdayantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sport Presentation: by Scott CadmoreDocument55 pagesSport Presentation: by Scott CadmorescadmorePas encore d'évaluation
- Knee Ligament InjuriesDocument16 pagesKnee Ligament InjuriesBIJAY KRISHNA DASPas encore d'évaluation
- Sports Medicine Cadaver Demonstration Distance Learning ProgramDocument5 pagesSports Medicine Cadaver Demonstration Distance Learning Programaims_slusomPas encore d'évaluation
- Pro Quest DocumentsDocument47 pagesPro Quest Documentsvothihongnga05vtPas encore d'évaluation
- Foot AnkleDocument11 pagesFoot AnklelassieladdiePas encore d'évaluation
- Ankle SprainDocument11 pagesAnkle SprainAnonim AlexPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The AnkleDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Ankleallie343343Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bursae: Synovial Bursae Provide A Gliding Surface and A Cushion For Soft Tissues As They PassDocument3 pagesBursae: Synovial Bursae Provide A Gliding Surface and A Cushion For Soft Tissues As They PassazeemPas encore d'évaluation
- AnkleDocument6 pagesAnkleitoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Ball-and-socket hip joint anatomyDocument6 pagesBall-and-socket hip joint anatomyIshimaru ThorPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HipDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HipJayson OlilePas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Wrist and Hand Injuries in Sport Acute Soft Tissue InjuriesDocument65 pages04 Wrist and Hand Injuries in Sport Acute Soft Tissue InjuriesKhushboo IkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Equinus ContracturesDocument7 pagesEquinus Contracturesa013bsy2496Pas encore d'évaluation
- 01.Week-I Introduction To Shoulder (MSPT-SPT)Document38 pages01.Week-I Introduction To Shoulder (MSPT-SPT)Khushboo IkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Hip Pain TreatmentDocument19 pagesHip Pain TreatmentLev KalikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Knee Joint: What Are The Four Bones That Make Up The Knee Joint?Document41 pagesKnee Joint: What Are The Four Bones That Make Up The Knee Joint?nishantsinghbmePas encore d'évaluation
- Knee AnatomyDocument44 pagesKnee AnatomyYanti WijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries-Orthoinfo - AaosDocument5 pagesAnterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries-Orthoinfo - Aaosapi-228773845Pas encore d'évaluation
- Part 1: What Different Parts Make Up The Ankle?Document8 pagesPart 1: What Different Parts Make Up The Ankle?api-279497243Pas encore d'évaluation
- Knee ProblemsDocument10 pagesKnee ProblemsXeeshan AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Knee Replacement Surgery ExplainedDocument1 pageKnee Replacement Surgery ExplaineddrpagrawPas encore d'évaluation
- ArthroplastyDocument64 pagesArthroplastyAmit Kochhar75% (4)
- Knee PainDocument10 pagesKnee Painhis.thunder122100% (2)
- Pfeiffer 5 IM Chapter15Document16 pagesPfeiffer 5 IM Chapter15cjbthegeniusPas encore d'évaluation
- Relieve Pain and Improve Mobility With Knee ImplantsDocument6 pagesRelieve Pain and Improve Mobility With Knee ImplantsMoses DhinakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotator Cuff SyndromeDocument14 pagesRotator Cuff SyndromeRatu Suci Angraini HasibuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiotherapy in Portage La Prairie and Emerald Park For FootDocument11 pagesPhysiotherapy in Portage La Prairie and Emerald Park For Footdrrabe3Pas encore d'évaluation
- ACL Injury Conservative Management - Jul19Document4 pagesACL Injury Conservative Management - Jul19Tejesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of MovementDocument18 pagesAnalysis of MovementEfren Jonicel Daguio Domingo50% (2)
- Fitness & Exercise: Image Collection: Human AnatomyDocument3 pagesFitness & Exercise: Image Collection: Human Anatomysadaq84Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bones of The KneeDocument5 pagesBones of The KneeJessica AdhykaPas encore d'évaluation
- Foot and AnkleDocument4 pagesFoot and AnkleDonna EnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Rehab Individual (Achilles Tendon Injury) - Raihan Naqibah Binti Mohamed (2021515847)Document21 pagesRehab Individual (Achilles Tendon Injury) - Raihan Naqibah Binti Mohamed (2021515847)Jalal NasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Knee InjuryDocument44 pagesKnee Injuryvamshi reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Urdaneta City University Graduate School UrdanetaDocument13 pagesUrdaneta City University Graduate School UrdanetaMa Theresa PunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases or ConditionsDocument3 pagesDiseases or ConditionsRao SahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Are You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsD'EverandAre You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Common Tennis Injuries and 4 Ways To Prevent ThemDocument4 pages5 Common Tennis Injuries and 4 Ways To Prevent ThemTitser AyMiPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoulder PainDocument21 pagesShoulder PainAnna FrankfurtPas encore d'évaluation
- Sports Injuries in Wrist & Hand.Document72 pagesSports Injuries in Wrist & Hand.salmankhan09215Pas encore d'évaluation
- Patella Injuries: Pain Associated With The KneecapDocument5 pagesPatella Injuries: Pain Associated With The KneecapmarkositozPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of LEG TrainingDocument53 pagesAnatomy of LEG TrainingDiego Tzompa AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Foot Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesFoot Anatomy and PhysiologyMarta BłaszczykPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder ProblemsDocument14 pagesShoulder Pain and Common Shoulder ProblemsRatnaPrasadNalamPas encore d'évaluation
- The 5 Most Common Sports InjuriesDocument4 pagesThe 5 Most Common Sports InjuriesAngeline SahagunPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal Joint: Dr. Vareishang Tangpu Assistant Professor in Zoology RIE, Mysore - 06Document53 pagesSkeletal Joint: Dr. Vareishang Tangpu Assistant Professor in Zoology RIE, Mysore - 06Floriza de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Healthy Shoulder Handbook: Second Edition: 100 Exercises for Treating Common Injuries and Ending Chronic PainD'EverandHealthy Shoulder Handbook: Second Edition: 100 Exercises for Treating Common Injuries and Ending Chronic PainPas encore d'évaluation
- Yr7 Fitness BookletDocument8 pagesYr7 Fitness BookletAydaan PannuPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises To Lower Blood Sugar - LSDocument3 pagesExercises To Lower Blood Sugar - LSjferrell4380Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kinesiology Sample Cover Letter: Margaret MeadDocument1 pageKinesiology Sample Cover Letter: Margaret MeadmahsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Describe A Game or Sport You Enjoy PlayingDocument3 pagesDescribe A Game or Sport You Enjoy PlayingLong Bùi VănPas encore d'évaluation
- 1pages From The Anatomy of Stretching, Seco - Walker, BradDocument6 pages1pages From The Anatomy of Stretching, Seco - Walker, BradFatimah SalsabilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Leisure Activities and the First ConditionalDocument5 pagesLeisure Activities and the First ConditionalDeyan BrenesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan 2 Ped 356Document3 pagesLesson Plan 2 Ped 356api-533885137Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practice: Side A Side B Side CDocument1 pagePractice: Side A Side B Side ChomayoonPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP - 10 Training in SportsDocument49 pagesCHP - 10 Training in SportslakshrakeshkumarshahPas encore d'évaluation
- Gerunds and Infinitives Exercise 24 - ENGLISH PAGEDocument2 pagesGerunds and Infinitives Exercise 24 - ENGLISH PAGEgustavo oruePas encore d'évaluation
- Life Fitness Cardiovascular - NEW ELEVATION SERIES Discover Se & Si ConsolesDocument35 pagesLife Fitness Cardiovascular - NEW ELEVATION SERIES Discover Se & Si ConsolesMoges AberaPas encore d'évaluation
- (123doc) Dap An Full Doc Tieng Anh 6 Ehou En40Document1 456 pages(123doc) Dap An Full Doc Tieng Anh 6 Ehou En40Dang Quoc DuPas encore d'évaluation
- t1 Exam Booster PETDocument10 pagest1 Exam Booster PETTommt TuckeredingPas encore d'évaluation
- Ajnara Vice Royale Studios V1Document13 pagesAjnara Vice Royale Studios V1Zama KazmiPas encore d'évaluation
- DIRECTIONS: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument5 pagesDIRECTIONS: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerGilbert BuladoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sports Development Office: de La Salle LipaDocument3 pagesSports Development Office: de La Salle LipaTrisha SARMIENTOPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE PE 13 Prelim CoverageDocument16 pagesMODULE PE 13 Prelim CoveragebatanilanilynPas encore d'évaluation
- Shanda's 2018 Strategic PlanDocument1 pageShanda's 2018 Strategic Planbirhanu Ayenew AnleyPas encore d'évaluation
- 7th Grade PE Unit 1Document17 pages7th Grade PE Unit 1ahfiuahuifeubgiuwPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Awareness EssayDocument2 pagesHealth Awareness EssayDrake SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of Machine Learning Technique For Identification of Yoga PosesDocument4 pagesImplementation of Machine Learning Technique For Identification of Yoga PosesSatnam SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Worksheet 3Document9 pagesActivity Worksheet 3Tuanda TVsPas encore d'évaluation
- Manipulating Reps For Gains in Size and Strength by Charles PoliquinDocument6 pagesManipulating Reps For Gains in Size and Strength by Charles Poliquinnam nguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- User'S Manual: Questions?Document40 pagesUser'S Manual: Questions?scribnowherePas encore d'évaluation
- High Intensity Interval Training Is Not Superior To Contin - 2023 - Journal of EDocument10 pagesHigh Intensity Interval Training Is Not Superior To Contin - 2023 - Journal of ESherriPas encore d'évaluation
- P90X3 TrackerDocument55 pagesP90X3 Trackerazl100% (2)
- History of Physical Education in The PhilippinesDocument15 pagesHistory of Physical Education in The PhilippineszaiaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Rutgers FilesDocument7 pagesThe Rutgers Filesdada100% (2)
- Subic Bay Sports Master Plan - Beeyong SisonDocument28 pagesSubic Bay Sports Master Plan - Beeyong SisonBeeyong SisonPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 Strategies For Successful Fat LossDocument12 pages16 Strategies For Successful Fat LosstobyPas encore d'évaluation