Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Periop Pretest
Transféré par
Johnryl FranciscoDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Periop Pretest
Transféré par
Johnryl FranciscoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1. After obtaining 3 L of fluid from a client via parecentesis, the nurse would be alert for which complication? a.
Respiratory distress b. Bleeding from the site c. Encephalopathy d. Vascular collapse Rationale: The removal of large amount of fluid, such as 2-3 L, via paracentesis may lead to acute fluid shifting and hypotension, subsequently leading to vascular collapse. 2. Open glove method is preferred to use except: a. In the emergency department when donning sterile gloves for suturing lacerations b. Intravenous cutdown or administering of spinal anesthesia c. Changing a glove during an operation d. When donning gloves for procedures requiring gown Rationale: Open glove technique is used when only sterile gloves are worn, as far intravenous cutdown or administering of spinal anesthesia, or in the emergency department when donning sterile gloves for suturing lacerations. It is also for changing a glove during an operation and for procedures not requiring gown. 3. Correction of a drooping upper eyelid: a. Excision of chalazion b. Blepharaptosis repair c. Correction of entropion d. Canthotomy Rationale: Blepharaptosis repair is the Correction of a drooping upper eyelid. Correction of Entropion is the correction of an eversion and drooping of the lower eyelid. Canthotomy is the incision of the canthus. Exicision of the chalazion is the incision and curettage if a granulomatous swelling of the meibomian glands. 4. Which statement best explains the scientific rationale for performing urinary catheterization on a client following an abdominal hysterectomy if she is unable to void within 8 hours? a. Temporary atony may result from surgical manipulation in the area b. The bladder is removed along with the uterus c. Infection from surgery interferes with the clients ability to void d. Surgically induced menopause impairs the client urinary function Rationale: With a hysterectomy, the area around the bladder typically undergoes surgical manipulation. This causes edema and nerve trauma, possibly leading to temporary atony. Therefore if the client cannot void within 8 hours, urinary catheterization is performed to prevent urinary retention. 5. A client arrives at the clinic for a routine physical examination. During the examination, the nurse performs as otoscopic examination. Which finding would nurse expect as normal? a. Pale optic disk b. Pearly gray tympanic membrane c. Tactile fremitus d. Positive red reflex Rationale: An otoscopic examination uses an otoscope to inspect the external canal and middle ear, specifically the tympanic membrane and its landmarks. Normally, the tympanic membrane appears pearly gray ad intact. A pale optic disk is an abnormal fining during an ophthalmoscopic examination of the eyes. A positive red reflex is a normal finding with an ophthalmoscopic examination, not an otoscopic examination.
Tactile frmitus is an abnormal finding when the chest is palpated. 6. Following a bee sting a client who develops shortness of breath and hives on his face and neck receives an epinephrine injection. Which assessment data would indicate that the epinephrine is effective? a. Increased itching b. Drowsiness c. Easier breathing d. Reduced pain at the sting site Rationale: The client is exhibiting allergi reaction to the beesting. Epinephrine acts as a bronchodilator to ease the clients breathing. It has no effect on pain and will not cause drowsiness or increase itching. 7. An adult client has the following laboratory results: white blood cells 6,300/ mm3; platelets 250,000 mm3; serum sodium 140 mEq/L; serum potassium 6 mEq/L. which condition is present? a. Leukocytosis b. Hyperkalemia c. Hypernatremia d. Thrombocytopenia Rationale: The clients serum potassium level is above the normal range of 3.5 to 5.5 mEq/L. indicating hyperkalemia. 8. It is the resection of the half of the colon and a segment of the terminal ileum and their mesenteries. a. Ileostomy b. Hemicolectomy c. Transverse colectomy d. Colostomy Rationale: Hemicolectomy is the resection of the half of the colon and a segment of the terminal ileum and their mesenteries. Colostomy is the formation of a permanent or temporary opening into the colon brought out onto the abdominal wall as a stoma. Transverse colectomy is the resection of a segment of the transverse colon with an end-toend anastomosis to reestablish continuity of the colon. 9. Which instruction is most important to provide when discharging a client from the emergency department following penetrating foot injury? a. Call the health care provider at the first signs of any red streaks appearing on the foot or leg b. Watch for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis from the tetanus toxoid c. Avoid smoking until the entire wound is no longer open to the air d. Refrain from crossing the legs at the knee or ankle Rationale: The appearance of red streaks indicates lymphadenitis and evidence of spreading infection. The client should call the health care provider because further treatment is necessary. Not crossing the legs will aid in venous return but foot edema is not a serious threat to health as a spreading infection. Avoiding smoking is always an important health consideration. However, their effect is not an immediate as those of the spreading infection. Signs and symptoms of anaphylactic shock would most likely occur immediately after the administration of tetanus toxoid while the client is still in the health care facility. 10. Following a thyroidectomy, the client experiences hemorrhage. The nurse would prepare for which emergency intervention? a. I.V administration of thyroid hormone
b. Creation of a tracheostomy c. Insertion of an oral airway d.I.V administration of calcium Rationale: Following a thyroidectomy, postoperative hemorrhage may cause compression of the trachea, necessitating an emergency tracheostomy to maintain airway patency. Calcium and thyroid hormones may be administered postoperatively, but these agents are unrelated to hemorrhage. Insertion of an oral airway would be ineffective in maintaining airway patency because the compression from the hemorrhage is below the airway insertion site. 11. Which intervention must be implemented first during the initial assessment of a client with major burn injury? a. Inserting a nasogastric tube b. Treating for burn shock c. Ensuring a patent airway d. Eliminating the source of the burn Rationale: Before any other action can be taken, the source of the burn injury must be eliminated. The airway patency is ensured, any associated injuries are assessed, and then burn shock is treated. 12. Prior the operation the nurse checks the client receiving warfarin sodium, an anticoagulant, has a prothrombin time of 22 and a partial thromboplastin time of 39. The control values are PT 12.9; and PTT 37. The International Normalized Ratio (INR) is 2.8. Which nursing intervention would be most appropriate? a. Notifying the health care provider immediately b. Administering the medication as ordered c. Holding the medication and assessing for bleeding d. Preparing to administer protamine sulfate Rationale: When a client is receiving warfarin, the PT value should be 1.5 to 2 times the control value. The INR should be between 2 to 3. The clients INR value is therapeutic, so the medication should be administered as ordered. 13. A client is 4 hours postoperative abdomino-peritoneal resection with sigmoid colostomy. He is complaining of rectal pain that ranks 8 on a scale of 1 to 10. Which interventions should he nurse implement? (select all that apply) a. Assisting the client with distraction to help the pain b. Notifying the health care provider that the stoma is pink c. Assessing the abdominal incision d. Assessing the clients blood pressure and pulse e. Medicating the client as ordered Rationale: The nurse should rule out surgical complications, such as hemorrhage, by assessing the clients blood pressure and pulse. The nurse also should medicate the client immediately because the client is only 4 hours postoperative. The client will not have an abdominal incision with the surgery (rectal dressing). The nurse would be concerned if the stoma is purple not pink. The clients need medication not distraction at 4 hours postoperative. Sitting on the side of the bed will not help the clients pain. 14. Which intervention should the nurse implement first when beginning preoperative teaching? a. Assessing the clients knowledge base related to the surgical procedure b.Describing the possible risks of the surgical procedure c. Having the client read the printed instructional booklet
d. Using a standardized preoperative teaching plan for consistency Rationale: Before beginning any teaching program; the nurse must first assess the clients knowledge base. Doing so allows the nurse to identify the clients teaching needs, avoid repetition of areas the client is already familiar with, and identify or correct in misconceptions or misinformation that the client might have. 15. Which topic would be most important to include in the postoperative teaching for the client scheduled for a vaginal hysterectomy? a. Lower-extremity exercises and deep breathing b. Pelvic muscle strengthening exercises c. Use of a bedpan and call light d. Availability of support persons Rationale: Use of lithotomy position for a vaginal hysterectomy predisposes the client to DVT. Additionally, atelectasis from surgery may also occur. Thus, the client needs instructions on lower extremity exercises to minimize the risk of DVT. She also needs deep breathing exercises to prevent atelectasis.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Smoking and Its EffectsDocument12 pagesSmoking and Its EffectsJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Competencies in Platform-Based Product Development: Antecedents and OutcomesDocument43 pagesUnderstanding Competencies in Platform-Based Product Development: Antecedents and OutcomesJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency NursingDocument52 pagesEmergency NursingJohnryl Francisco100% (1)
- 2 Mod Issue Brief Finalupdatedlogo Policy Oct2017 SMDocument2 pages2 Mod Issue Brief Finalupdatedlogo Policy Oct2017 SMJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Care For A Paralyzed PersonDocument2 pagesHow To Care For A Paralyzed PersonJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2022 New MCN PresentationDocument54 pages2022 New MCN PresentationJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormones and The Menstrual Cycle: Discussion GuideDocument11 pagesHormones and The Menstrual Cycle: Discussion GuideJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Es Sio N: W Fo RDDocument14 pagesEs Sio N: W Fo RDJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Grow and Glow FoodsDocument15 pagesGo Grow and Glow FoodsJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Assignment Problem: An Example: SinksDocument4 pagesThe Assignment Problem: An Example: SinksJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure and Function of The Reproductive SystemDocument48 pagesStructure and Function of The Reproductive SystemJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Buntis KitDocument2 pagesBuntis KitJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Philippine Cancer Control ProgramDocument10 pagesThe Philippine Cancer Control ProgramJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- The DOH Philippine Cancer Control Program CCCN1Document9 pagesThe DOH Philippine Cancer Control Program CCCN1Johnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
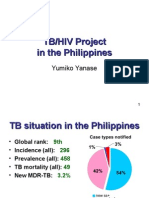
- TB/HIV Project in The PhilippinesDocument22 pagesTB/HIV Project in The PhilippinesJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Assignment Problem: An Example: Assignment Problems. These Problems Can, of Course, Be Solved byDocument5 pagesThe Assignment Problem: An Example: Assignment Problems. These Problems Can, of Course, Be Solved byJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gantt ChartDocument4 pagesGantt ChartJohnryl FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nle 2Document7 pagesNle 2Aijem RyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Clinical Optometry Primary Eye CareDocument3 pagesClinical Optometry Primary Eye CareDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study OrthopedicDocument15 pagesCase Study Orthopedicjoyevangelista100% (3)
- Improving Outpatient Clinic Operations: An Exploratory Case StudyDocument6 pagesImproving Outpatient Clinic Operations: An Exploratory Case Studynurul fatma diyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aurobindo Pharma Receives USFDA Approval For Norethindrone Acetate Tablets (Company Update)Document1 pageAurobindo Pharma Receives USFDA Approval For Norethindrone Acetate Tablets (Company Update)Shyam SunderPas encore d'évaluation
- Developing Geriatric Services For Incontinence in The ElderlyDocument5 pagesDeveloping Geriatric Services For Incontinence in The ElderlyrnrmmanphdPas encore d'évaluation
- Peace Corps MS 261 Policy 2017 - BackUp Medical ProviderDocument8 pagesPeace Corps MS 261 Policy 2017 - BackUp Medical ProviderAccessible Journal Media: Peace Corps DocumentsPas encore d'évaluation
- Tgas Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesTgas Bahasa Inggrisbilly jordiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Zodiac and The Salts of SalvationDocument32 pagesThe Zodiac and The Salts of Salvationrogerfpa100% (1)
- Paramedical E-BrochureDocument4 pagesParamedical E-BrochureMohil DaveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Weapons TestsDocument10 pagesBio Weapons TestsRaptorman1973Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anxiety NCPDocument3 pagesAnxiety NCPJulibeth Subong Dominguez50% (2)
- Dissertation Topics MidwiferyDocument4 pagesDissertation Topics MidwiferyCustomizedWritingPaperNewark100% (1)
- A Clear Label Strategy For Food AdditivesDocument6 pagesA Clear Label Strategy For Food AdditivesJerome DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Stimulus Piece PTSD AnswersDocument2 pagesStimulus Piece PTSD AnswerschandanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen AdministrationDocument29 pagesOxygen Administrationjembut300100% (2)
- Historical Development of Social Case Work Unit - 1Document10 pagesHistorical Development of Social Case Work Unit - 1आई सी एस इंस्टीट्यूट60% (5)
- Preface ReprintDocument19 pagesPreface ReprintMusfiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 ACPL Expanded Content OutlineDocument9 pages2016 ACPL Expanded Content OutlineiisforintheskyPas encore d'évaluation
- Relationship of Self-Regulation, Stress, and Life Satisfaction Among Middle School Students of Ekamai International School, Bangkok, ThailandDocument27 pagesRelationship of Self-Regulation, Stress, and Life Satisfaction Among Middle School Students of Ekamai International School, Bangkok, ThailandFrederick Edward FabellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emory IMDocument29 pagesEmory IMBeká BakhtadzePas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Injury in Relation To Voltage, "No Let Go" Phenomenon, Symptoms and Perceived Safety Culture: A Survey of Swedish Male ElectriciansDocument11 pagesElectrical Injury in Relation To Voltage, "No Let Go" Phenomenon, Symptoms and Perceived Safety Culture: A Survey of Swedish Male ElectriciansYopa Riyanda PuteriPas encore d'évaluation
- Corn Coffee FinalDocument85 pagesCorn Coffee FinalNhelia Santos Bañaga100% (1)
- Australian Indigenous People - EditedDocument8 pagesAustralian Indigenous People - EditedApril CliffordPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaccines By: Muhammad Haikal Bin Abd RahmanDocument3 pagesVaccines By: Muhammad Haikal Bin Abd RahmanMUHAMMAD HAIKALPas encore d'évaluation
- Twenty Tested and Safe Homeopathic RemediesDocument60 pagesTwenty Tested and Safe Homeopathic RemediesShekhar SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kuesioner Ndi PDFDocument4 pagesKuesioner Ndi PDFeloooyiyPas encore d'évaluation
- Prescription Pain MedicationDocument9 pagesPrescription Pain Medicationapi-409112773Pas encore d'évaluation
- ReportsDocument15 pagesReportsamandio silvaPas encore d'évaluation
- "Sin Taxes" and Health Financing in The Philippines - Case StudyDocument10 pages"Sin Taxes" and Health Financing in The Philippines - Case StudyMack ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Compass Is A Nutrient Profiling System Using Expanded Characteristics For Assessing Healthfulness of FoodsDocument10 pagesFood Compass Is A Nutrient Profiling System Using Expanded Characteristics For Assessing Healthfulness of FoodsANKITPas encore d'évaluation