Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Inherited Human Diseases Chart
Transféré par
Antidote4LifeDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Inherited Human Diseases Chart
Transféré par
Antidote4LifeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Inherited Human Diseases
Name
Fragile X Syndrome
Page One Symptoms
Developmental delay Hyperactivity Speech delay, perseverative speech Poor gross motor coordination Sterotypies, e.g., talking to self,spinning,hand flapping Gaze aversion Seizures
Cause
Genetic anomaly, labeled FMR1, on X chromosome at Xq27.3, the same position as the fragile site
Treatments
Psychosocial support Genetic counseling Regular well-child exams Enroll in early intervention Speech/language therapy Sensory/motor therapy Appropriate educational support
Results
Early intervention with help to develop to their full potential. Will depend on how affected they are by this syndrome
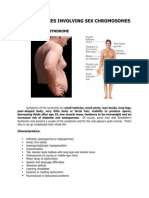
Turners syndrome
Nondisjunction during meiotic division Usually maternal; more than half have A mosaic chromosomal complement (45,XO/46/XX) 1:1500 to 1:2500 live births; most common sex-chromosomes anomaly affecting embryos do not survive to term
Short stature with square appearance Low hairline Chronic ear infections Learning disabilities Lack of development of secondary sexual characteristics
Klinefelter Syndrome
Maternal meiotic nondisjunction resulting in contributions of two X chromosomes to maternal zygote (ova);when over is fertilized by sperm Containing one Y chromosomes resulting embryo has klinfelter karyotype
Refer to endocrinology Growth hormone therapy beginning when growth falls below 5th percentile on normal female child growth charts Hormone,estrogen, replacement therapy beginning about 11 years of age Monitor for hypothyroidism Genetic counseling Psychological support Assistance in school for learning disabilities Referral to cardiologist Tall mate, especially at a adolescence Early intervention for leaning disorder and beyond Counseling / therapy for behavioral Slow, incomplete pubertal development disorders Behavioral and psychiatric disorders Psychosocial support for family (shy), immature, anxious, aggressive, Genetic counseling antisocial Refer to endocrinologist for Thin child,often overweight as consideration of testosterone at age 11 adolescent or12 Language impairment Screen for breast cancer Reduction mammoplasty for gynecomastia Normal development until age 3 to 6, then progressive deterioration Listlessness Muscle weakness Slow neurological development, loss of development milestone Feeding problems Frequent upper respiratory infections Apathy, irritability Seizures Deafness/blindness
Hormone therapy will help to minimize symptoms. Women can lead full productive lives.
Nearly 100% of the males are sterile. Testosterone injections can minimize symptoms and can lead full productive lives.
Tay-sachs disease
Autosomal recessive single gene disorder,deficiency of hexosaminidase A which is necessary for breakdown of ganglioside gm2; as glycoside accumulates in neurons, axons degenerate and demyelination occurs 3:10,000 live births; mainly in ashkenazic Jewish population; gene carrier frequency in U.S 1:27 among Jews and 1:380 among non-Jews
Genetic counseling Poor prognosis Primary prevention via carrier screening Early demise Secondary prevention via prenatal diagnosis elective termination of pregnancy No known treatment for underlying metabolic deficiency Psychosocial support for parents and family
Inherited Human Diseases
Name
Canavan disease
Page Two Symptoms Treatments Results
Poor prognosis Disease degeneration Early demise A family history of canavan disease Genetic counseling Decreased muscle tone (hypotonia) Symptomatic treatments especially in the neck muscles Abnormal posture with flexed arms and straight legs Feeding difficulties Nasal reguration Swallowing difficulties Reflux with vomiting Increasing head size (macrocephaly) Head lag Failure to meet milestones Seizures Severe mental retardation Blindness Death often by 18 months Family history of parent with waardenburg syndrome Externally pale blue eyes or eye colors dont match White forelock of hair or early graying hair Deafness Possible slight decrease in intellectual functioning Occasional cleft lip Constipation may occur May have difficulty with completely straitening joints Bruising at injection sights Bleeding following circumcision Excessive bruising after child begins walking Prolonged bleeding in any part of the body after child begins walking Prolonged bleeding in any part of the body Treatment for hearing disabilities Diet to decrease constipation
Cause
Canavan disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait and has higher incidence among ashkenazi Jews than the general population a deficient enzyme,aspartoacylase, results in the accumulation of n-acetylaspartic acid in the brain and subsequent degeneration of the white matter typical cases have onset of symptoms in the first year of life with loss of developmental milestone and death before 18 months of age
Waardenburg syndrome
Its inherited as an autosomal dominant trait; only one parent has to pass on the gene for a child to be affected75
Lead full productive lives
hemophilia
Caused by congenital deficiency of either clotting factor VIII or XI
Collaborative interdisciplinary approach Life expectancy 10 years less than facilitated by regional hemophilia average treatment center Factor replacement therapy Antifibrinolytic therapy Physical therapy Genetic counseling
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Impact of Training On The Performance of Employeees in The Public Sector - A Case Study of MoWTDocument56 pagesImpact of Training On The Performance of Employeees in The Public Sector - A Case Study of MoWTJJINGO ISAAC100% (2)
- Characteristic of Human LanguageDocument1 pageCharacteristic of Human LanguageSatya Permadi50% (2)
- PWS, AgDocument12 pagesPWS, Agmohadese.hnprPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic DisordersDocument20 pagesGenetic Disorderszaryabali771Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chromosomal DisordersDocument4 pagesChromosomal DisordersYoussry JaranillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Disorders: Problem PregnanciesDocument18 pagesGenetic Disorders: Problem PregnanciesNandithPas encore d'évaluation
- Pisharody Genetic CounselingDocument15 pagesPisharody Genetic Counselingapi-228136529Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Chromosomal DisordersDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Chromosomal DisordersKathleenJoyGalAlmasinPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Disorders in Humans PresentationDocument16 pagesGenetic Disorders in Humans PresentationKaty W. IvesPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Provide A Safe and Stimulating Classroom Environment For Students With Down Syndrome-A Medical and Educational PerspectiveDocument40 pagesHow To Provide A Safe and Stimulating Classroom Environment For Students With Down Syndrome-A Medical and Educational PerspectiveHuy Hữu NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Chromosomal DisordersDocument4 pagesChromosomal DisordersMatth N. ErejerPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic DisordersDocument26 pagesGenetic DisorderscamsfPas encore d'évaluation
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument32 pagesChromosomal AbnormalitieszahraaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic DisordersDocument39 pagesGenetic DisordersSuho Leexokleader Kim100% (1)
- Human Genetic Disorders: Photos Are From Smith's Recognizable Patterns of HumanDocument49 pagesHuman Genetic Disorders: Photos Are From Smith's Recognizable Patterns of HumanJessie AzarragaPas encore d'évaluation
- Birth DefectsDocument15 pagesBirth Defectsobgynmaret 2016Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic DisordersDocument37 pagesGenetic DisordersAmalia Solehah (Nim: 2048201110145)Pas encore d'évaluation
- 08 Birth Defects and Prenatal DiagnosisDocument29 pages08 Birth Defects and Prenatal DiagnosisOsman Saidu SesayPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics 3Document32 pagesGenetics 3Dipesh KhadkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chromosomal DisorderDocument19 pagesChromosomal DisorderPriyesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument45 pagesUntitledMary Grace SunioPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Disorders: U Me and SocietyDocument23 pagesGenetic Disorders: U Me and SocietyDeepansh GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Birth DefectDocument35 pagesBirth DefectAdvocate subhan abbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Teratology (Birth Defect) (Birth Defect) : Lecture NoteDocument36 pagesTeratology (Birth Defect) (Birth Defect) : Lecture NoteTofik MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Turner's SyndromeDocument21 pagesTurner's Syndromedindasudibya96100% (1)
- Patterns: OF InheritanceDocument45 pagesPatterns: OF InheritanceMary Grace SunioPas encore d'évaluation
- Sindroma Down: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas - Wijaya Kusuma SurabayaDocument23 pagesSindroma Down: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas - Wijaya Kusuma SurabayaPrinces Mentari Dwi NurainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Birth DefectsDocument36 pagesBirth DefectsSohera NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Tay SachsDocument11 pagesTay Sachsarchitecture14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Disorders PDFDocument38 pagesGenetic Disorders PDFEllen Mae PrincipePas encore d'évaluation
- Down SyndromeDocument12 pagesDown SyndromeaksinuPas encore d'évaluation
- Klinefelter-Syndrome GenbioDocument3 pagesKlinefelter-Syndrome GenbioNeo RealyouPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurodevelopmental DisordersDocument6 pagesNeurodevelopmental DisordersNatalie LiPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Part1&2Document9 pagesGenetics Part1&2Tanveer aminPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Genetics LectureDocument81 pagesMedical Genetics LectureIMUSIC Corp.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jewish Genetic DiseasesDocument2 pagesJewish Genetic DiseasesReformJudaismPas encore d'évaluation
- Sindroma Down: DR - Ayling Sanjaya, M.Kes, Spa Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Wijaya Kusuma SurabayaDocument23 pagesSindroma Down: DR - Ayling Sanjaya, M.Kes, Spa Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Wijaya Kusuma SurabayaFarihatun NisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trisomy/ Down SyndromeDocument2 pagesTrisomy/ Down SyndromeDanah Grace SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine DisordersDocument106 pagesEndocrine DisordersMansur MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Down SyndromeDocument74 pagesDown Syndromeanumeha sharma100% (2)
- Angelman SyndromeDocument4 pagesAngelman SyndromeLee ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fragile X SyndromeDocument23 pagesFragile X SyndromeVincent ScorsinniPas encore d'évaluation
- Teratology: Definition: Branch of Science That Studies TheDocument27 pagesTeratology: Definition: Branch of Science That Studies TheSaba RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- DownsyndromeDocument20 pagesDownsyndromeAbraham AnaelyPas encore d'évaluation
- Down SyndromeDocument24 pagesDown SyndromePunit GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Klinefelter SyndromeDocument28 pagesKlinefelter SyndromeKimberly Anne Marica0% (1)
- Human Genetic Disorders: and PedigreesDocument51 pagesHuman Genetic Disorders: and Pedigreescm4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormalities Involving Sex ChromosomesDocument5 pagesAbnormalities Involving Sex ChromosomesManveth DawnAnne Narvaez BahunsuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alterations in ChromosomesDocument50 pagesAlterations in ChromosomesMaan LucsPas encore d'évaluation
- Some of The Genetic AbnormalitiesDocument11 pagesSome of The Genetic AbnormalitiesCarmsPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic and Chromosomal Abnormalities 1Document10 pagesGenetic and Chromosomal Abnormalities 1arcjendelaclanPas encore d'évaluation
- Autosomal RecessiveDocument19 pagesAutosomal RecessiveKomala KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Vignette 1Document9 pagesClinical Vignette 1Joanne Alyssa Hernandez LascanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 - Mutation & Genetic DisordersDocument30 pagesLesson 3 - Mutation & Genetic DisordersPaul Santos100% (2)
- Deletion Syndromes: By: Rania ZahoDocument55 pagesDeletion Syndromes: By: Rania ZahoRania ZahoPas encore d'évaluation
- Thea Brigette Vergara: Name: Date SubmittedDocument9 pagesThea Brigette Vergara: Name: Date SubmittedMj YuPas encore d'évaluation
- Down's Syndrome2Document18 pagesDown's Syndrome2fmarniePas encore d'évaluation
- Down SyndromeDocument26 pagesDown SyndromeJerralyn GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, Down SyndromeDocument78 pagesTurner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, Down SyndromeTasya100% (3)
- Genetics Plabable PDFDocument5 pagesGenetics Plabable PDFTirtha TaposhPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Presentation:: Inheritance DisordersDocument11 pagesBio Presentation:: Inheritance DisordersRaeed khanPas encore d'évaluation
- VONG 1 - 2020-2021 - Key - CTDocument2 pagesVONG 1 - 2020-2021 - Key - CTKhánh LinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Case Study - Jupyter NotebookDocument10 pagesDiabetes Case Study - Jupyter NotebookAbhising100% (1)
- 1.gilbert Et Al (Everything You Read)Document33 pages1.gilbert Et Al (Everything You Read)simiflorPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutech University Admission SlipDocument3 pagesNutech University Admission SlipaliiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- WMS - IV Flexible Approach Case Study 2: Psychiatric DisorderDocument2 pagesWMS - IV Flexible Approach Case Study 2: Psychiatric DisorderAnaaaerobiosPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 Lesson Plan 1 2Document9 pagesUnit 6 Lesson Plan 1 2Thuy Quynh BuiPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative-And-Superlative-Survey Activity 6Document2 pagesComparative-And-Superlative-Survey Activity 6Neisa SantamariaPas encore d'évaluation
- CFA Exam Dates & Schedule - WileyCFADocument1 pageCFA Exam Dates & Schedule - WileyCFASudipto PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Support Vector Machines and Artificial Neural Networks: Dr.S.Veena, Associate Professor/CSEDocument78 pagesSupport Vector Machines and Artificial Neural Networks: Dr.S.Veena, Associate Professor/CSEvdjohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Web Based Gamo Gofa AgricultureDocument4 pagesWeb Based Gamo Gofa AgricultureAnonymous vNvtJIPas encore d'évaluation
- Level of Effectiveness of Online Teaching and Learning in Facilitating Instruction For Grade One Learners: Basis For A Proposed Teaching ModelDocument11 pagesLevel of Effectiveness of Online Teaching and Learning in Facilitating Instruction For Grade One Learners: Basis For A Proposed Teaching ModelPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- Thaarinisudhakaran (4 3)Document1 pageThaarinisudhakaran (4 3)vineeth rockstar1999Pas encore d'évaluation
- SpringDocument24 pagesSpringRiya IndukuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Duncan Clancy ResumeDocument1 pageDuncan Clancy Resumeapi-402538280Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fampulme - The Planning Functions of The ControllershipDocument22 pagesFampulme - The Planning Functions of The ControllershipCarla Pianz FampulmePas encore d'évaluation
- Ultimate Customer ServiceDocument10 pagesUltimate Customer ServicesifPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 8. New Ways To Learn: Part I. PhoneticsDocument15 pagesUnit 8. New Ways To Learn: Part I. PhoneticsTrúc LinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Eyes Open 1.2 A Unit 7 TestDocument4 pagesEyes Open 1.2 A Unit 7 TestDorota SmolinskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Academic Achievement Scholarships For Current Students 2019/20Document5 pagesNon-Academic Achievement Scholarships For Current Students 2019/20Ho Ming ChoPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 7 Lesson Plans 2Document4 pagesWeek 7 Lesson Plans 2api-334646577Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan - Nguyen Tran Minh Anh - Nguyen Thanh NamDocument7 pagesLesson Plan - Nguyen Tran Minh Anh - Nguyen Thanh NamNguyễn Ngọc Mai KhanhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes: Introduction To Linear FunctionsDocument4 pagesLecture Notes: Introduction To Linear Functionsapi-544591906Pas encore d'évaluation
- Emergence of OBDocument4 pagesEmergence of OBBhavya VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutritional Status of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders (Asds) : A Case-Control StudyDocument14 pagesNutritional Status of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders (Asds) : A Case-Control StudyyeyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Book ReviewDocument2 pagesBook ReviewTrishaPas encore d'évaluation
- Language Development: Educational Implications.: January 2018Document31 pagesLanguage Development: Educational Implications.: January 2018Tengku AimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Is WealthDocument100 pagesKnowledge Is WealthmustaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook Addendum: Student & ParentDocument42 pagesHandbook Addendum: Student & ParentExam PurposePas encore d'évaluation