Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pityriasis Versicolor
Transféré par
Iqbal AminDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pityriasis Versicolor
Transféré par
Iqbal AminDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pityriasis Versicolor Pityriasis (tinea) versicolor (PV) is a chronic asymptomatic scaling epidermomycosis associated with the superficial overgrowth
of the hyphal form of Malassezia furfur, characterized by well-demarcated scaling patches with variable pigmentation, occurring most commonly on the trunk. Epidemiology and Etiology Etiology M. furfur (previously known as Pityrosporum ovale, P. orbiculare) is a lipophilic yeast that normally resides in the keratin of skin and hair follicles of individuals at puberty and beyond. It is an opportunistic organism, causing pityriasis versicolor and Malassezia folliculitis and is implicated in the pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis. Malassezia infections are not contagious; rather, overgrowth of resident cutaneous flora occurs under certain favorable conditions. Age of Onset
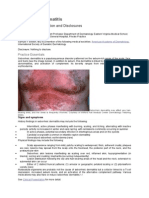
Skin Symptoms Usually none. Occasionally, mild pruritus. Individuals with PV usually present because of cosmetic concerns about the blotchy pigmentation. Physical Examination Skin Lesions Macules, sharply marginated (Figs. 23-36, 23-37, and 23-38), round or oval in shape, varying in size. Fine scaling is best appreciated by gently abrading lesions with a no. 15 scalpel blade or the edge of a microscope slide. Treated or burnedout lesions lack scale. Some patients have findings of Malassezia folliculitis and seborrheic dermatitis. In untanned skin, lesions are light brown. On tanned skin, white. In darkskinned individuals, dark brown macules. Brown of varying intensities and hues (Fig. 23-36); off-white macules (Figs. 2337 and 23-38). Some PV lesions are red (Fig. 23-38). In time, individual lesions may enlarge, merge, forming extensive geographic areas. Figure 23-36
Young adults. Less common when sebum production is reduced or absent; tapers off during fifth and sixth decades. Predisposing Factors High temperatures/relative humidity, oily skin, hyperhidrosis, hereditary factors, glucocorticoid treatment, and immunodeficiency. Application of oils such as cocoa butter predisposes young children to PV. Season Temperate zones, appears in summertime, affecting 2% of population; may regress during cooler months; in physically active individuals, may persist year round. Subtropical and tropical zones: year around in 20%. Pathogenesis Malassezia changes from the blastospore form to the mycelial form under the influence of predisposing factors. Dicarboxylic acids formed by enzymatic oxidation of fatty acids in skin surface lipids inhibit tyrosinase in epidermal melanocytes and thereby lead to hypomelanosis. The enzyme is present in the organism. History Duration of Lesions Months to years. Pityriasis versicolor Multiple, small-to-medium-sized, welldemarcated hypopigmented macules on the back of a tanned individual with white skin. Figure 23-38 Pityriasis versicolor Sharply marginated brown macules on the trunk. Fine scale was apparent when the lesions were abraded with the edge of a microscope slide. Figure 23-37
Pityriasis versicolor Follicular, hypopigmented macules on the upper chest of an individual with black skin. Distribution Upper trunk, upper arms, neck, abdomen, axillae, groins, thighs, genitalia. Facial, neck, and/or scalp lesions occur in patients applying creams/ointments or topical glucocorticoid preparations. Differential Diagnosis
Hypopigmented PV Vitiligo, pityriasis alba, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, tuberculoid leprosy. Scaling Lesions Tinea corporis, seborrheic dermatitis, pityriasis rosea, guttate psoriasis, nummular eczema. Laboratory Examinations Direct Microscopic Examination of Scales Prepared with KOH Scale is best obtained with two microscope slides, using one to raise scale and move it onto the other. The harvested scale is moved into a small pile in the center of the slide and covered with a coverslip. KOH solution (15 to 20%) is added at the edge of the coverslip; the slide is gently heated and examined. Filamentous hyphae and globose yeast forms, termed spaghetti and meatballs, are seen (Fig. 23-39). Figure 23-39
Management Topical agents Selenium sulfide (2.5%) lotion or shampoo Apply daily to affected areas for 10 to 15 min, followed by shower, for 1 week Applied same as selenium sulfide shampoo Apply qd or bid for 2 weeks
Ketoconazole shampoo Azole creams (ketoconazole, econazole, micronazole, clotrimazole) Terbinafine 1% solution Systemic therapy (None of these agents is approved for use in PV in the United States) Ketoconazole Fluconazole Itraconazole Secondary prophylaxis
Apply bid for 7 days
400 mg stat (take 1 h before exercise) 400 mg stat 400 mg stat Ketoconazole shampoo once or twice a week Selenium sulfide (2.5%) lotion or shampoo Salicylic acid/sulfur bar Pyrithione zinc (bar or shampoo) Ketoconazole 400 mg PO monthly
Malassezia furfur: KOH preparation Round yeast and elongated pseudohyphal forms, so-called "spaghetti and meatballs." Wood's Lamp Blue-green fluorescence of scales; may be negative in individuals who have showered recently because the fluorescent chemical is water soluble. Vitiligo appears as depigmented, white, and has no scale. Dermatopathology Budding yeast and hyphal forms in the most superficial layers of the stratum corneum, seen best with PAS stain. Variable hyperkeratosis, psoriasiform hyperplasia, chronic inflammation with blood vessel dilatation. Diagnosis Clinical findings, confirmed by positive KOH preparation findings. Course and Prognosis Infection persists for years if predisposing conditions persist. Dyspigmentation persists for months after infection has been eradicated.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Dermatofitosis FitzpatrickDocument28 pagesDermatofitosis FitzpatrickFadli IlhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Gangguan Kulit Pada LansiaDocument28 pagesGangguan Kulit Pada LansianoviPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Abnormal KeratinizationDocument36 pagesDisorders of Abnormal KeratinizationdayangPas encore d'évaluation
- Derm Online Resource Pack PDFDocument81 pagesDerm Online Resource Pack PDFOlaPas encore d'évaluation
- articulo_ingles_2_ginaDocument8 pagesarticulo_ingles_2_ginassariedmartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Pigmentation 1Document56 pagesDisorders of Pigmentation 1Ahmed Noureldin AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Sebaceous GlandDocument54 pagesDisorders of Sebaceous GlandAnurag PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Meth Elab Topic N2Document19 pagesMeth Elab Topic N2Group M1869Pas encore d'évaluation
- Continuing Medical Education: Amanda M M Oakley MBCHB Fracp DiphealinfDocument4 pagesContinuing Medical Education: Amanda M M Oakley MBCHB Fracp DiphealinfCarol SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Hpe Final 110529Document98 pagesHpe Final 110529deeps.u.97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis of Common, Benign Neonatal Dermatoses: Daniel Wallach, MDDocument5 pagesDiagnosis of Common, Benign Neonatal Dermatoses: Daniel Wallach, MDDesi RatnaningtyasPas encore d'évaluation
- AcneDocument44 pagesAcneHitesh N RohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Fungal Infections-MlcDocument31 pagesFungal Infections-Mlcsamuel gathenyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Skinl3 WEB13 PDFDocument58 pagesSkinl3 WEB13 PDFDrAmit Verma100% (1)
- Treatment of Seborrheic Dermatitis PDFDocument7 pagesTreatment of Seborrheic Dermatitis PDFAhmed MawardiPas encore d'évaluation
- Superficial Mycoses Group 4Document38 pagesSuperficial Mycoses Group 4prudence azenaborPas encore d'évaluation
- Acne and Other Common Acneiform DisordersDocument6 pagesAcne and Other Common Acneiform DisordersSudesna Roy ChowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocument4 pagesPityriasis VersicolorLidya NazirPas encore d'évaluation
- Superficial Mycoses 3Document8 pagesSuperficial Mycoses 3Mohammad KaifPas encore d'évaluation
- ErytrasmaDocument17 pagesErytrasmaAndrean LinataPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi KuliitDocument40 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi KuliitZulfani AdhiyatmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Seborrheic Dermatitis From JurnalDocument6 pagesSeborrheic Dermatitis From JurnalindciwPas encore d'évaluation
- 19411-Article Text-62419-1-10-20180329 PDFDocument10 pages19411-Article Text-62419-1-10-20180329 PDFGreice BelfortPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Trauma (Koebner's Phenomenon) Is A Major Factor in Eliciting LesionsDocument12 pagesPhysical Trauma (Koebner's Phenomenon) Is A Major Factor in Eliciting LesionsNaomi AnastacioPas encore d'évaluation
- ACNEDocument28 pagesACNESalman AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- AcneDocument49 pagesAcnebismahPas encore d'évaluation
- Seborrheic Dermatitis EmedicineDocument10 pagesSeborrheic Dermatitis EmedicineIkram IkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Dermatitis SeborreicaDocument6 pagesDermatitis SeborreicaDiego Eraso IncaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lipoma 2. Sebaeceous Cyst 3.dermoid Cyst 4. Keloid 5.BCC: Surgical Short Cases 1Document86 pagesLipoma 2. Sebaeceous Cyst 3.dermoid Cyst 4. Keloid 5.BCC: Surgical Short Cases 1Nguyễn ThànhPas encore d'évaluation
- Acne Notes For MBBSDocument15 pagesAcne Notes For MBBSsobretilldawnPas encore d'évaluation
- Dermatology 1Document47 pagesDermatology 1Edwin OkonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric DermatosesDocument58 pagesPediatric DermatosesSajin AlexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- The Lichens in Vulvovaginal Disease 2015Document20 pagesThe Lichens in Vulvovaginal Disease 2015Vidini Kusuma AjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Keratosis Pilaris: Oleh: Queen Yosefin Mailoa, S.Ked 2018-84-035 Pembimbing: Dr. Hanny Tanasal, Sp. KKDocument34 pagesKeratosis Pilaris: Oleh: Queen Yosefin Mailoa, S.Ked 2018-84-035 Pembimbing: Dr. Hanny Tanasal, Sp. KKIin MailoaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acne and Rosacea: AetiologyDocument7 pagesAcne and Rosacea: AetiologyananPas encore d'évaluation
- $RG8JJJ1Document82 pages$RG8JJJ1Rasha mohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Acne VulgarisDocument40 pagesAcne VulgarisRabeea Khan100% (2)
- Speaker NotesDocument21 pagesSpeaker Noteschinnupepsi4allPas encore d'évaluation
- 2022 MIKRO - INTEGUMEN BakteriDocument47 pages2022 MIKRO - INTEGUMEN BakterifatharaniPas encore d'évaluation
- HB LSHBB WLDTRBT DHT LLQDocument62 pagesHB LSHBB WLDTRBT DHT LLQtricia isabellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cutaneous MycosesDocument30 pagesCutaneous MycoseshudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dandruff PDFDocument8 pagesDandruff PDFArthur ChietraPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Syndromic IcthyosisDocument109 pagesNon Syndromic IcthyosisSRIRAM CKPas encore d'évaluation
- Maryville NURS 623 ExamDocument14 pagesMaryville NURS 623 ExamWizzardPas encore d'évaluation
- Tinea Versicolor: Pathophysiology, Etiology in <40 CharsDocument4 pagesTinea Versicolor: Pathophysiology, Etiology in <40 Charswahyuni taslimPas encore d'évaluation
- By Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumDocument6 pagesBy Dr. Nouran Abou Khedr: Xeroderma PigmentosumBahaa ShaabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dermatitis Seborroeik: DR Maria Dwikarya SPKKDocument22 pagesDermatitis Seborroeik: DR Maria Dwikarya SPKKHendy MasjayantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dermatological Conditions KOROS E.k-1Document107 pagesDermatological Conditions KOROS E.k-1victorPas encore d'évaluation
- HERBAL PLANTS AND PROPIONIBACTERIUM ACNES - AN OVERVIEWDocument13 pagesHERBAL PLANTS AND PROPIONIBACTERIUM ACNES - AN OVERVIEWmskchoudhuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Burn Healing and GraftingDocument8 pagesSkin Burn Healing and GraftingCiullaePas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Dermatology Lecture HandoutDocument62 pagesPediatric Dermatology Lecture Handoutskin_docPas encore d'évaluation
- Acne Vulgaris: Audi Adibah - Affan Syafiqi - Amanina Nasir - Nurul Hidayu - Nik Nor Liyana - SathishwaranDocument38 pagesAcne Vulgaris: Audi Adibah - Affan Syafiqi - Amanina Nasir - Nurul Hidayu - Nik Nor Liyana - SathishwaransomnathPas encore d'évaluation
- Fungal InfectionsDocument9 pagesFungal InfectionsCoral Srinivasa RamaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Seborrhoeic Dermatitis: Search Dermnet Nz..Document13 pagesSeborrhoeic Dermatitis: Search Dermnet Nz..Thanushan BalasingamPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Skin InfectionsDocument53 pagesOverview of Skin Infectionsadamu mohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Diseases Presentation2Document40 pagesSkin Diseases Presentation2DaniTadePas encore d'évaluation
- 668 1051 1 SMDocument7 pages668 1051 1 SMSigit KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Derm Quick ReviewDocument124 pagesDerm Quick ReviewRohit NalamasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyper-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment, And Related ConditionsD'EverandHyper-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment, And Related ConditionsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsD'EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Kampu NganDocument1 pageKampu NganIqbal AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Translate KacoDocument2 pagesTranslate KacoIqbal AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Baden Powell QuotesDocument2 pagesBaden Powell QuotesPaul LimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal KulitDocument3 pagesJurnal KulitIqbal AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Don't Study Grammar Guys..Document6 pagesDon't Study Grammar Guys..Iqbal AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Obat-Obat Emergency: DR T. Mamfaluti, SPPDDocument36 pagesObat-Obat Emergency: DR T. Mamfaluti, SPPDIqbal AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Efect of Drying Rate On CoffeeDocument7 pagesEfect of Drying Rate On CoffeeIqbal AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Japanese Mom And Young Flash Video FileDocument1 pageJapanese Mom And Young Flash Video FileIqbal AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocument2 pagesPityriasis VersicolorIqbal AminPas encore d'évaluation
- By The Sun and Its BrightnessDocument1 pageBy The Sun and Its BrightnessIqbal AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Neutriderm Anti Dandruff ShampooDocument6 pagesNeutriderm Anti Dandruff ShampooUASPharmaceuticalsPas encore d'évaluation
- Dermatophytes - Medical Research Institute - Alexandria UniversityDocument129 pagesDermatophytes - Medical Research Institute - Alexandria Universityማላያላም ማላያላምPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Etiologic Facets of Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis: Malassezia Fungi, Sebaceous Lipids, and Individual SensitivityDocument3 pagesThree Etiologic Facets of Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis: Malassezia Fungi, Sebaceous Lipids, and Individual SensitivityAhmed MawardiPas encore d'évaluation
- Micoses Superficiais - GlobalDocument19 pagesMicoses Superficiais - GlobalJosé Paulo Ribeiro JúniorPas encore d'évaluation
- Dapus 13Document9 pagesDapus 13Mega UtariPas encore d'évaluation
- Antifungal Activity of Plant Extracts Against DandDocument3 pagesAntifungal Activity of Plant Extracts Against DandmasdfgPas encore d'évaluation
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocument4 pagesPityriasis VersicolorLidya NazirPas encore d'évaluation
- Tinea Versicolor: Pathophysiology, Etiology in <40 CharsDocument4 pagesTinea Versicolor: Pathophysiology, Etiology in <40 Charswahyuni taslimPas encore d'évaluation
- Malassezia Furfur - Microbewiki PDFDocument4 pagesMalassezia Furfur - Microbewiki PDFDr-Shubhaneel NeogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Systematic Review On Herbs With Antidandruff PropertyDocument13 pagesSystematic Review On Herbs With Antidandruff PropertyIJRASETPublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocument10 pagesPityriasis Versicolorketty putriPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation and Identification of Malassezia GlobosaDocument8 pagesIsolation and Identification of Malassezia GlobosanahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Okra Shampoo Effectiveness Against Dandruff (OSEADDocument11 pagesOkra Shampoo Effectiveness Against Dandruff (OSEADGlaiza Dalayoan Flores100% (1)
- Identification of Malassezia SpeciesDocument3 pagesIdentification of Malassezia SpeciesSJ IraaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study On Pityriasis Versicolor in Patients Referred To Clinics in TabrizDocument5 pagesStudy On Pityriasis Versicolor in Patients Referred To Clinics in TabrizMiranda Yudhi CyubidubiduuPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 MalasseziaDocument7 pages04 MalasseziaResty Agiastuty Eka PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Pityriasis Versicolor 1 PDFDocument5 pagesPityriasis Versicolor 1 PDFanwarfuadiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pityrosporum Folliculitis: Yeast Overgrowth Causes Itchy BumpsDocument6 pagesPityrosporum Folliculitis: Yeast Overgrowth Causes Itchy BumpsAndy Sugiharto WonodiharjoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dandruff Scalp Advanced Care Guide-HAIRQAREDocument91 pagesDandruff Scalp Advanced Care Guide-HAIRQAREralucaxjsPas encore d'évaluation
- Superficial Mycoses: Diseases Causative Organisms IncidenceDocument4 pagesSuperficial Mycoses: Diseases Causative Organisms IncidencePatricia Marie M. AgnesPas encore d'évaluation