Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
A. Patient's Information
Transféré par
Camille Quilao PantoniDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
A. Patient's Information
Transféré par
Camille Quilao PantoniDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
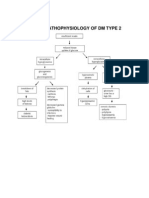
Introduction Diabetes Mellitus is one of the fastest serious health problems not only in the country but also
worldwide. It has been in the top 10 leading causes of mortality in the Philippines according to the latest statistics done by the Department of Health. A person with diabetes has a condition in which the quantity of glucose in the blood is too elevated (hyperglycemia). This is because the body does not produce enough insulin, produces no insulin, or has cells that do not respond properly to the insulin the pancreas produces. This results in too much glucose building up in the blood. This excess blood glucose eventually passes out of the body in urine. So, even though the blood has plenty of glucose, the cells are not getting it for their essential energy and growth requirements. There are two major classifications of Diabetes. First, the Type 1 diabetes mellitus which results from -cell destruction which usually leads to absolute insulin deficiency. And the Type 2 which results from a progressive insulin secretory defect on the background of assistance. Others include, genetic defects on the -cell and Gestational diabetes mellitus which is diagnosed during the pregnancy.
I. OBJECTIVES This study entails to seek appropriate strategies and management for the resolution of the case, Diabetes Mellitus. Also this study seek to know and investigate a phenomenon within its real life context.
II. METHODOLOGY
III. DATA GATHERING A. Patients Information The patients name is Mrs. Zenaida Hogar, 76 years old. She was admitted last Januray 15, 2012 at Manila Doctors Hospital. She was diagnosed with Type 2 DM, Diabetic Nephropathy. Patients past medical history/illness consists of Hypertension (20 years), Diabetes Mellitus.
B. Anthropometric Data Height Weight BMI BMI Interpretation IBW CBW TER
C. Dietary Assessment
48- Hour Food Recall Food Items Amount Breakfast A.M Snack Lunch P.M Snack Dinner Breakfast A.M Snack Lunch P.M Snack Dinner TOTAL
CHO
CHON
Fat
Kcal
DAY 1
DAY 2
D. Biochemical Data Markers
Test: Hematology
Date: Jan. 15, 2012 Pxs Laboratory Values Normal Value 123-153/L 0.36-0.45 4.10-5.10x101/2L 4.10-5.10x109/2L 0.00-0.01 0.01-0.04 0.2-0.12 0.36-0.66 0.24-0.44 0.02-0.12 150,000-450,000 x10^9/L 12.00-17.00% 80-96 27.50-53.20 pg 33.,40-35.50 g/dl Variance Normal Normal Normal High Normal Normal Low High Low Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal
Hemoglobin Hematocrit RBC WBC Basophil Eosinophil STAB Neutrophil Lymphocytes Monocyte Platelets RDW MCV MCH MCHC
127 0.39 4.60 19.64 0 0.01 0 0.84 0.08 0.07 222 15.1 84.3 27.6 32.7
Capillary Blood Glucose Date 1/15/2012 Time 1240H refused 0500H 0800H 1/16/2012 0900H 1100H 1700H 2100H 0500H 1100H 1700H 2100H 0500H Result 70 mg/dL 54 mg/dL 132 mg/dL 122 mg/dL 144 mg/dL 113 mg/ dL 87 mg/dL 120 mg/dL 92 mg/dL 104 mg/dL 102 mg/dL Pxs Laboratory Values FBS Cholesterol Triglycerides HDL LDL Alkaline Phosphatase 2.70 3 .90 1 1.6 121 Insulin d5050 1/2 vial IV ad. to eat -
1/17/2012 1/18/2012
Normal Value 3.90-5.55 mmol/L 100-200 mg/dL
Variance Low
FLUID INTAKE 1-15-12 INPUT Time 6-2 2-10 10-6 Oral 210 NPO IVF 500 700 Blood TOTAL Parenteral Others Total 710 700 1410 OUTPUT Urine 800 Total 800 800
1-16-12 INPUT Time 6-2 2-10 10-6 Oral 210 420 100 IVF 400 350 Blood TOTAL Parenteral Others Total 610 420 450 1480 OUTPUT Urine 450 450 Total 450
1-17-12 INPUT Time 6-2 2-10 10-6 Oral 210 420 100 IVF 400 350 Blood TOTAL Parenteral Others Total 610 420 450 1480 420 1800 800 OUTPUT Urine Total 420 1800 800 2000
Urinalysis Color: Dark Transparency: Turbid pH: 6.5 Specific Gravity: 1.020 Glucose: (-) Protein: 1.0 g/L Pxs Laboratory Values 8.2 167 136 2.8 100 1.9 .70 53.3 23.80 29.5 0.8:1
Date: 1-16-12 Blood: 80 ery/ L Ketone: (-) Nitrite: (-) Bilirubin: small Urobilirogen: 7.2 mol/L Leukocytes: 20 leu/ L Normal Value 3.0-9.2 mmoL/L 62-115 mmol/L 135-148 mmol/L 3.50-5.30 mmol/L 110 to 250(mEq/day 100 to 300 mg/day 1.5 - 2.5 mg/dL 64-83 g/L 35-50 g/L 29-33 g/L 1.2:1.5 Variance Normal High Normal Low Low Low Low Low Low Normal Low
BUN Creatinine Sodium Potassium Chlorine Calcium Magnesium Total Protein Albumin Globulin A/G ratio
E. Clinical Manisfestations 2 days PTC, patient had fever documented at 38C and had been noticed with a swelling on her right foot.
IV. ASSESSMENT
A. Nutritional Diagnosis
B. Medical Diagnosis Definition
Diabetes mellitus is a kind of metabolic disease that is brought about by either the insufficient production of insulin or the inability of the body to respond to the insulin formed within the system. In response to this, the body also produces symptoms of polyuria or frequent urination, polyphagia or increased hunger and polydipsia or increased thirst. Read on and get to know what is diabetes mellitus and the underlying processes that produce such conditions. The disease can be classified into three different categories: the type 1, type 2 and the gestational diabetes. Diabetes mellitus type 1 is caused by the loss of beta cells found in the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Beta cells primarily produce insulin and hence, their loss will lead to huge insulin deficiencies in the body.In most cases, the loss of the beta cells is caused by an autoimmune attack mediated by the bodys own T-cells. Another type of diabetes mellitus is the type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is generally characterized by the bodys resistance to insulin. This is primarily attributed to the loss of certain insulin receptors in the tissues that are supposed to mediate the entrance of insulin into the bodys cells. This particular kind of diabetes is the most common kind that afflicts most of the reported cases of the disease. Type 2 diabetes usually leads to hyperglycemia which can be treated by a series of medications that can either improve the bodys insulin sensitivity or improve the livers production of insulin in the system.
Drug Name
Frequency
Rationale
Contraindication
Co- amoxiclav
600 mg; q8
treatment of infections cellulites, Painkiller
Renal failure. Pregnancy & lactation. Neonates. Elderly. Active peptic ulcer, cerebrovascular disease, hemorrhagic diatheses, Patients in bronchospasm, angioedema whom
Ketrolac
30 mg IV; q8
Paracetamol
500 mg q4
For fever
Cefepime
1g IV; q12
For low WBC; and Hypersensitivity antibiotic cefepime or cephalosporins For pain
to other
Algesia
q8
Hypersensitivity to codeine or opioids. Acute intoxication w/ alcohol, hypnotics, narcotics Renal insufficiency, hyperkalemia, untreated Addison's disease, constriction of the esophagus Pregnancy
Kalium Durule
IT P.O; TID
For hypokalemia
Losartan
50 mg P.O.; BID
For HTN & diabetic nephropathy in type 2 DM. For HTN
Metroprolol
50 mg P.O; BID
Bronchospasm or asthma, history of obstructive airway disease Sick sinus syndrome.
Catapres Demerol
75 mcg SL 50 mg
HTN
Relief of moderate to Alcohol, narcotic severe pain analgesics
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Managing Diabetes Through Proper Treatment and MonitoringDocument10 pagesManaging Diabetes Through Proper Treatment and Monitoringjoeln_9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes MellitusDocument44 pagesDiabetes MellituslkristinPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes PPT FianlDocument31 pagesDiabetes PPT FianlUqba MishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Report on Diabetes Mellitus at University of Muthanna CollegeDocument12 pagesNursing Report on Diabetes Mellitus at University of Muthanna CollegeAbbas AwfiPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Perspectives and TreatmentsDocument32 pagesDiabetes Perspectives and TreatmentsyellahfellahPas encore d'évaluation
- DIABETES CorrectedDocument16 pagesDIABETES CorrectedBlaise PascalPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 s2.0 B9780128158449000075 MainDocument35 pages3 s2.0 B9780128158449000075 MainBlanca LozanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Childhood Diabetes and Treatment UpdatesDocument51 pagesTypes of Childhood Diabetes and Treatment UpdatesJulie Carnetion DPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument12 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosispolaris_027Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes MellitusDocument18 pagesDiabetes Mellitusrajirajesh100% (1)
- Pope, B. CCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Endocrine and BehavioralDocument14 pagesPope, B. CCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Endocrine and BehavioralKeisha JenkinsPas encore d'évaluation
- C C C CDocument51 pagesC C C CpixiemedicPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study: Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document48 pagesCase Study: Diabetes Mellitus Type 2John Carlo GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology ScribdDocument8 pagesPathophysiology ScribdTamil VillardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 16 Pediatric t1dmDocument12 pagesCase 16 Pediatric t1dmapi-501730091Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes PresentationDocument32 pagesDiabetes PresentationsgolbariPas encore d'évaluation
- DR ZegeyeDocument1 254 pagesDR ZegeyesirawPas encore d'évaluation
- Dental Management of Patients With Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesDental Management of Patients With Diabetes Mellitusاحمد سلامPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus Definition, Types, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument27 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Definition, Types, Symptoms, and Treatmentana chasanahPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentragavan86Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Task 2 Life-Threatening Hyperglycaemia & Health Care PromotionDocument6 pagesAssessment Task 2 Life-Threatening Hyperglycaemia & Health Care PromotionGundeepPas encore d'évaluation
- How EXERCISE Helps Control DiabetesDocument23 pagesHow EXERCISE Helps Control DiabetesApurba MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- DMCaseDocument45 pagesDMCaseNyell18Pas encore d'évaluation
- DMDocument20 pagesDMKC PalattaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes OutlineDocument7 pagesDiabetes OutlineJenny VarghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Dilated Eye Exam: An Eye Care Professional Uses Eye Drops To Temporarily Widen, orDocument5 pagesDilated Eye Exam: An Eye Care Professional Uses Eye Drops To Temporarily Widen, orClare LsyPas encore d'évaluation
- Grp.10 DiabetesDocument15 pagesGrp.10 DiabetesVanessa JannePas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Truth 2Document11 pagesDiabetes Truth 2gibrambo5770Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Reading On: Type 2 DiabetesDocument10 pagesA Reading On: Type 2 DiabetesPadilla, John AndrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Toddler With A Diaper RashDocument4 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis in Toddler With A Diaper RashKarl Angelo MontanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care and EducationDocument38 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care and EducationRegina PunPas encore d'évaluation
- DM Grand Case PresDocument24 pagesDM Grand Case PresBing Howell de GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus and Cho Dis.Document15 pagesDiabetes Mellitus and Cho Dis.abdo000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vol-2 DiabetesDocument50 pagesVol-2 DiabetesVishwanath SomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric DMDocument39 pagesPediatric DMmy Lord JesusPas encore d'évaluation
- DM FinaDocument3 pagesDM FinaChared LumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paeda DMDocument38 pagesPaeda DMAmanuel LemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument34 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAru VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis 508Document12 pagesDiagnosis 508Tri HarjonoPas encore d'évaluation
- 06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument47 pages06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismRizka NizarPas encore d'évaluation
- Aims and ObjectivesDocument13 pagesAims and Objectivesmamun183Pas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Abbreviation For Diabetes Mellitus With Endocrine System Abbreviation Medical Term Meaning / DefinitionDocument26 pagesMedical Abbreviation For Diabetes Mellitus With Endocrine System Abbreviation Medical Term Meaning / DefinitionCt AinnPas encore d'évaluation
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: EtiologyDocument9 pagesType 1 Diabetes Mellitus: EtiologyChristian diorPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism-Converted - WatermarkDocument82 pagesDisorders of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism-Converted - WatermarkAbhi VarnaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Diabetes? What Causes Diabetes?Document8 pagesWhat Is Diabetes? What Causes Diabetes?Khaleda FatmawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Type 1 DiabetesDocument11 pagesType 1 DiabetesLyne Paggic PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus, Often Simply Referred To As Diabetes, Is A Group of Metabolic Diseases inDocument28 pagesDiabetes Mellitus, Often Simply Referred To As Diabetes, Is A Group of Metabolic Diseases inKrissy GaluraPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabete Mellitus HandoutsDocument7 pagesDiabete Mellitus HandoutsSittie Nashieva A. UsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- All About DiabetesDocument6 pagesAll About DiabetesR-vin TanjecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Daibetes Mellitus: Dr. Siddaganga S MDocument45 pagesDaibetes Mellitus: Dr. Siddaganga S Msiddaganga sigiPas encore d'évaluation
- T31 - Types of Diabetes and Diagnosis - PTPDocument6 pagesT31 - Types of Diabetes and Diagnosis - PTPangela adelantarPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification: LiverDocument20 pagesClassification: LivertermskipopPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes NotesDocument10 pagesDiabetes Notestripj33Pas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix B Pathophysiology of DM Type 2Document20 pagesAppendix B Pathophysiology of DM Type 2Jennifer AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study in DMDocument34 pagesCase Study in DMKathrina Marie B. BinaraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Type 2 Diabetes GuideDocument50 pagesType 2 Diabetes GuideKimberly Jose100% (4)
- Soluzioni al Diabete e all'Ipoglicemia - Come prevenire e disfarsene naturalmente e senza medicineD'EverandSoluzioni al Diabete e all'Ipoglicemia - Come prevenire e disfarsene naturalmente e senza medicinePas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions to Diabetes and Hypoglycemia (Translated): How to prevent and get rid of it in a natural way, without resorting to medicines but adopting a correct way of lifeD'EverandSolutions to Diabetes and Hypoglycemia (Translated): How to prevent and get rid of it in a natural way, without resorting to medicines but adopting a correct way of lifePas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic Cookbook: Low Carb Diabetes Cookbook for Beginners: Diabetic CookbooksD'EverandDiabetic Cookbook: Low Carb Diabetes Cookbook for Beginners: Diabetic CookbooksÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The DronesDocument43 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of The DronesVysual ScapePas encore d'évaluation
- Scharlau Chemie: Material Safety Data Sheet - MsdsDocument4 pagesScharlau Chemie: Material Safety Data Sheet - MsdsTapioriusPas encore d'évaluation
- Testbanks ch24Document12 pagesTestbanks ch24Hassan ArafatPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of ISO/IEC 17020:2012 For The Accreditation of Inspection BodiesDocument14 pagesApplication of ISO/IEC 17020:2012 For The Accreditation of Inspection BodiesWilson VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 Bomet District Paper 2Document16 pages2007 Bomet District Paper 2Ednah WambuiPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiquity: Middle AgesDocument6 pagesAntiquity: Middle AgesPABLO DIAZPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Ing Kls 6Document5 pagesB. Ing Kls 6siskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems of Teaching English As A Foreign Language in YemenDocument13 pagesProblems of Teaching English As A Foreign Language in YemenSabriThabetPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiera Foods - Production SupervisorDocument1 pageFiera Foods - Production SupervisorRutul PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Equipment, Preparation and TerminologyDocument4 pagesEquipment, Preparation and TerminologyHeidi SeversonPas encore d'évaluation
- Recycle Used Motor Oil With Tongrui PurifiersDocument12 pagesRecycle Used Motor Oil With Tongrui PurifiersRégis Ongollo100% (1)
- Create a seat booking form with Google Forms, Google Sheets and Google Apps Script - Yagisanatode - AppsScriptPulseDocument3 pagesCreate a seat booking form with Google Forms, Google Sheets and Google Apps Script - Yagisanatode - AppsScriptPulsebrandy57279Pas encore d'évaluation
- Key formulas for introductory statisticsDocument8 pagesKey formulas for introductory statisticsimam awaluddinPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sound Collector - The Prepared Piano of John CageDocument12 pagesThe Sound Collector - The Prepared Piano of John CageLuigie VazquezPas encore d'évaluation
- General Separator 1636422026Document55 pagesGeneral Separator 1636422026mohamed abdelazizPas encore d'évaluation
- Impolitic Art Sparks Debate Over Societal ValuesDocument10 pagesImpolitic Art Sparks Debate Over Societal ValuesCarine KmrPas encore d'évaluation
- AVANTIZ 2021 LNR125 (B927) EngineDocument16 pagesAVANTIZ 2021 LNR125 (B927) EngineNg Chor TeckPas encore d'évaluation
- Planview Innovation Management Maturity Model PDFDocument1 pagePlanview Innovation Management Maturity Model PDFMiguel Alfonso Mercado GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Ss17 JALAN SS17/1, Subang Jaya English Scheme of Work Form 3Document11 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Ss17 JALAN SS17/1, Subang Jaya English Scheme of Work Form 3Rohana YahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Deluxe Force Gauge: Instruction ManualDocument12 pagesDeluxe Force Gauge: Instruction ManualThomas Ramirez CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Benjie Reyes SbarDocument6 pagesBenjie Reyes Sbarnoronisa talusobPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Communication Quantization OverviewDocument5 pagesDigital Communication Quantization OverviewNiharika KorukondaPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Istructe.pdf FIP UKDocument4 pagesWWW - Istructe.pdf FIP UKBunkun15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: The Critical Role of Classroom Management DescriptionDocument2 pagesChapter 1: The Critical Role of Classroom Management DescriptionJoyce Ann May BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ca. Rajani Mathur: 09718286332, EmailDocument2 pagesCa. Rajani Mathur: 09718286332, EmailSanket KohliPas encore d'évaluation
- Drafting TechnologyDocument80 pagesDrafting Technologyong0625Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basf Masterseal 725hc TdsDocument2 pagesBasf Masterseal 725hc TdsshashiPas encore d'évaluation
- SYNOPSIS - Impact of GST On Small Traders!Document21 pagesSYNOPSIS - Impact of GST On Small Traders!Laxmi PriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fong vs. DueñasDocument2 pagesFong vs. DueñasWinter Woods100% (3)
- Time Table For Winter 2023 Theory ExaminationDocument1 pageTime Table For Winter 2023 Theory ExaminationSushant kakadePas encore d'évaluation