Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
201HW2
Transféré par
ojhaaaaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
201HW2
Transféré par
ojhaaaaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Problems
67
2.9
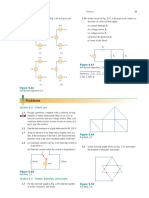
Which of the circuits in Fig. 2.66 will give you Vab 7 V?
5V + 3V + + 1V (a) 5V + 3V + + 1V (c) b a b a 5V + 3V + + 1V (b) 5V + 3V + + 1V (d) b a b a
2.10 In the circuit of Fig. 2.67, a decrease in R3 leads to a decrease of, select all that apply: (a) current through R3 (b) voltage across R3 (c) voltage across R1 (d) power dissipated in R2 (e) none of the above
R1
Vs
R2
R3
Figure 2.67
For Review Question 2.10.
Answers: 2.1c, 2.2c, 2.3b, 2.4c, 2.5c, 2.6b, 2.7a, 2.8d, 2.9d, 2.10b, d.
Figure 2.66
For Review Question 2.9.
Problems
Section 2.2 Ohms Law
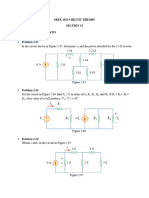
2.1 Design a problem, complete with a solution, to help students to better understand Ohms Law. Use at least two resistors and one voltage source. Hint, you could use both resistors at once or one at a time, it is up to you. Be creative. Find the hot resistance of a light bulb rated 60 W, 120 V. A bar of silicon is 4 cm long with a circular cross section. If the resistance of the bar is 240 at room temperature, what is the cross-sectional radius of the bar? (a) Calculate current i in Fig. 2.68 when the switch is in position 1. (b) Find the current when the switch is in position 2.
1 2 i + 40 V
2.2 2.3
Figure 2.69
For Prob. 2.5.
2.4
2.6
In the network graph shown in Fig. 2.70, determine the number of branches and nodes.
100
250
Figure 2.68
For Prob. 2.4.
Section 2.3 Nodes, Branches, and Loops
2.5 For the network graph in Fig. 2.69, nd the number of nodes, branches, and loops.
Figure 2.70
For Prob. 2.6.
68
Chapter 2
Basic Laws
2.7
Determine the number of branches and nodes in the circuit of Fig. 2.71.
1 4
2.11 In the circuit of Fig. 2.75, calculate V1 and V2.
+ + V1 1V + + 5V 2V + V2
12 V +
2A
Figure 2.71
For Prob. 2.7.
Figure 2.75
For Prob. 2.11. 2.12 In the circuit in Fig. 2.76, obtain v1, v2, and v3.
+ 30 V
Section 2.4 Kirchhoffs Laws
2.8 Design a problem, complete with a solution, to help other students better understand Kirchhoffs Current Law. Design the problem by specifying values of ia, ib, and ic, shown in Fig. 2.72, and asking them to solve for values of i1, i2, and i3. Be careful to specify realistic currents.
ia
50 V +
+ 20 V
+ v2
+ 40 V i1
+ v1
+ v3
ib i2 ic
i3
Figure 2.76
For Prob. 2.12. 2.13 For the circuit in Fig. 2.77, use KCL to nd the branch currents I1 to I4.
2A
Figure 2.72
For Prob. 2.8. 2.9 Find i1, i2, and i3 in Fig. 2.73.
4A
I2 1A 5A A i1 6A C B 7A i2 i3 I1
7A
I4
3A
I3
4A
2A
Figure 2.73
For Prob. 2.9. 2.10 Determine i1 and i2 in the circuit of Fig. 2.74.
Figure 2.77
For Prob. 2.13. 2.14 Given the circuit in Fig. 2.78, use KVL to nd the branch voltages V1 to V4.
V2 + + 2V + V4 + 5V
8 A i2 i1
4A 3V
+ 4V + + V3
+ V1
6 A
Figure 2.74
For Prob. 2.10.
Figure 2.78
For Prob. 2.14.
Problems
69
2.15 Calculate v and ix in the circuit of Fig. 2.79.
2.19 From the circuit in Fig. 2.83, nd I, the power dissipated by the resistor, and the power supplied by each source.
10 V + 12 V + + 8 V
12 +v 10 V + + 4V
+ 16 V ix + 3i x
I 3
Figure 2.79
For Prob. 2.15.
Figure 2.83
2.16 Determine Vo in the circuit in Fig. 2.80. For Prob. 2.19.
16 + 10 V + Vo
14
2.20 Determine io in the circuit of Fig. 2.84.
io + 25 V 54 V + + 5i o 22
Figure 2.80
For Prob. 2.16.
Figure 2.84
For Prob. 2.20.
2.17 Obtain v1 through v3 in the circuit of Fig. 2.81.
v1
2.21 Find Vx in the circuit of Fig. 2.85.
24 V +
v2 + + 12 V
+ v3
+ + 10 V 15 V +
Figure 2.81
For Prob. 2.17.
Figure 2.85
For Prob. 2.21.
2.18 Find I and Vab in the circuit of Fig. 2.82.
2.22 Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. 2.86 and the power absorbed by the dependent source.
10 I + Vo 10 25 A 2 Vo
30 V
Figure 2.82
For Prob. 2.18.
10 V
a + Vab b
5 +
8V
Figure 2.86
For Prob. 2.22.
5 + Vx
2 Vx
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Converting Between YUV and RGBDocument3 pagesConverting Between YUV and RGBumer40Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 2 - Neutron Chain Fission ReactorDocument45 pagesTopic 2 - Neutron Chain Fission ReactorSit LucasPas encore d'évaluation
- E01 33kV and 11 KV Lightning Arresters (1) - 2010Document12 pagesE01 33kV and 11 KV Lightning Arresters (1) - 2010Ashwin RaparthiPas encore d'évaluation
- EE2001 Tutorial 1Document3 pagesEE2001 Tutorial 1PeiXuan HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2 (All)Document16 pagesAssignment 2 (All)Shangkaran RadakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Electrodynamics: 12.1 Gauge Invariant Interacting TheoryDocument99 pagesQuantum Electrodynamics: 12.1 Gauge Invariant Interacting TheoryPedro SimoesPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP 03Document29 pagesCHP 03Gunadevan Chandrasekaran100% (1)
- Welding Carbon Steel Mech TubingDocument69 pagesWelding Carbon Steel Mech Tubingsatebekicot0% (1)
- 181003.takehome QuizDocument13 pages181003.takehome QuizYWKMSE10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ohm's LawDocument15 pagesOhm's Lawpaancute8982Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Analysis of Solenoid Coil in ANSYS and IES Software Case StudyDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Analysis of Solenoid Coil in ANSYS and IES Software Case StudyEditor IJRITCCPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit LabDocument46 pagesCircuit LabMiran SolankiPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Field Theory RadiationDocument5 pagesQuantum Field Theory RadiationieiediediediePas encore d'évaluation
- Thevenin and Norton EquivalentsDocument36 pagesThevenin and Norton EquivalentsJosé Guillermo De Chomón AranguenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gumsung Fire & SecurityDocument31 pagesGumsung Fire & Securityjuwinthir putra bengawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kee-552 Control System LabDocument55 pagesKee-552 Control System Labmat labPas encore d'évaluation
- SPLM #7 - Non-Sinusoidal WaveformDocument32 pagesSPLM #7 - Non-Sinusoidal WaveformSherwin PagpaguitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hazardous Area Classification Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesHazardous Area Classification Interview QuestionssuhailfarhaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Field Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesQuantum Field Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShiva MohammadzadehPas encore d'évaluation
- Spin 56-432 Spin LecDocument293 pagesSpin 56-432 Spin LecJacecosmozPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics PDFDocument23 pagesElectronics PDFCivil WarPas encore d'évaluation
- Klystron Testing LectureDocument36 pagesKlystron Testing LecturerajarpitPas encore d'évaluation
- EE4503 Power Engineering Design - OBTLDocument6 pagesEE4503 Power Engineering Design - OBTLAaron Tan100% (1)
- Ground Penetrating Radar - 2nd Edition: Edited by David J. DanielsDocument11 pagesGround Penetrating Radar - 2nd Edition: Edited by David J. DanielsVeron Pius RodriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 4 - Clippper and Clamper CircuitsDocument7 pagesLab 4 - Clippper and Clamper CircuitseyobPas encore d'évaluation
- Maskless LithographyDocument8 pagesMaskless Lithographymarci_elgPas encore d'évaluation
- Chenming Hu Ch8Document34 pagesChenming Hu Ch8Roberto Rojas PizarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Qualification of Cables To Ieee StandardsDocument5 pagesQualification of Cables To Ieee StandardskrivitskiPas encore d'évaluation
- NCSLI Measure 2014 Sept PDFDocument84 pagesNCSLI Measure 2014 Sept PDFzafarhrehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review of Recent MOSFET VTH Extraction MethodsDocument14 pagesA Review of Recent MOSFET VTH Extraction Methodshpnx9420Pas encore d'évaluation
- EEE 3571 Assignment 3 and 4Document3 pagesEEE 3571 Assignment 3 and 4Emmanuel Nama HasalamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4 - Neutron Diffusion TheoryDocument46 pagesTopic 4 - Neutron Diffusion TheorySit LucasPas encore d'évaluation
- Eecs242 Lect3 RxarchDocument34 pagesEecs242 Lect3 Rxarchp3erezPas encore d'évaluation
- Final ResearchDocument29 pagesFinal Researchshubham dhakulkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Klystron SDocument17 pagesKlystron SNitin Suyan PanchalPas encore d'évaluation
- Xiao-Gang Wen - Introduction To Quantum Many-Boson Theory - A Theory of Almost EverythingDocument63 pagesXiao-Gang Wen - Introduction To Quantum Many-Boson Theory - A Theory of Almost EverythingSwertyyPas encore d'évaluation
- NUREG-0050 Recommendations Related To Browns Ferry FireDocument96 pagesNUREG-0050 Recommendations Related To Browns Ferry Firescott56794Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Evolution of IEC 62368-1: Keep Up With Changes in The 3rd EditionDocument5 pagesThe Evolution of IEC 62368-1: Keep Up With Changes in The 3rd EditionMickeyYS LongPas encore d'évaluation
- (FINAL) Gas Leakage Detection With Buzzer System Using AtmegaDocument3 pages(FINAL) Gas Leakage Detection With Buzzer System Using AtmegaYash Kapure100% (2)
- Laplace Table PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Table PDFMaxi EurekaPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulation Tester - HT7051 - EN1-01Document3 pagesInsulation Tester - HT7051 - EN1-01Muaf FaizudeenPas encore d'évaluation
- DetectorsDocument282 pagesDetectorsMoch. Syamsul AlamsyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Frequency RelayDocument2 pagesFrequency RelayAkhilesh JindalPas encore d'évaluation
- BETATRONDocument8 pagesBETATRONMhaithan Hernandez CaliuagPas encore d'évaluation
- CC1608 - Fire Systems Design GuideDocument20 pagesCC1608 - Fire Systems Design GuidePhạm Thanh Sơn0% (1)
- 352 - 17385 - EC233 - 2015 - 4 - 1 - 1 - Sheet 3Document2 pages352 - 17385 - EC233 - 2015 - 4 - 1 - 1 - Sheet 3Timothy KennedyPas encore d'évaluation
- Table 4D1A Single Core PVCDocument1 pageTable 4D1A Single Core PVCDarren KhooPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Comb Filter PPT - 2007Document19 pagesFinal Comb Filter PPT - 2007Subrat BarsainyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Charge Transport in Disordered Organic Field Effect TransistorsDocument144 pagesCharge Transport in Disordered Organic Field Effect Transistorsajayiitm05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 591 - B Analysis and Design of CSDocument2 pagesLab 591 - B Analysis and Design of CSDevine WriterPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentMatthew Baker100% (1)
- SDS Nytro LyraDocument2 pagesSDS Nytro LyraUmair Maqbool100% (1)
- Name and Formula: Merck Index, 8th Ed., P. 272Document2 pagesName and Formula: Merck Index, 8th Ed., P. 272drksaran100% (1)
- 665report - Design of CMOS Ring VCO and Quadrature LC VCO For 8 Phases GenerationDocument17 pages665report - Design of CMOS Ring VCO and Quadrature LC VCO For 8 Phases GenerationapplebeePas encore d'évaluation
- Chap1 The Physics of Solar CellsDocument16 pagesChap1 The Physics of Solar Cellsmin_yu_6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 4Document9 pagesTutorial 4sreekantha reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- ProblemsDocument14 pagesProblemsĐỨC HẬUPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1javi.alberto.torrucoPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 2Document3 pagesHW 2gavinilaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2, Solution 4 I 15/100 150 Ma I 15/150 100 Ma Chapter 2, Solution 7Document4 pagesChapter 2, Solution 4 I 15/100 150 Ma I 15/150 100 Ma Chapter 2, Solution 7Asad Ur RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 14121Document31 pages14121Pankaj Kumar SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Uc 1526 ADocument12 pagesUc 1526 Agameel alabsiPas encore d'évaluation
- MN04020003EDocument204 pagesMN04020003EElderJoaoPas encore d'évaluation
- (Datasheet) MLX90614Document43 pages(Datasheet) MLX90614leonardorqPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Transmission of Electricity PDFDocument13 pagesWireless Transmission of Electricity PDFcrazymangeshPas encore d'évaluation
- TransputersDocument12 pagesTransputersNihit VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Order PDFDocument126 pagesWork Order PDFJohnPatrickRamirezCuevas0% (1)
- PIC Development System (Compilers, Simulator andDocument42 pagesPIC Development System (Compilers, Simulator andPirapuraj PonnampalamPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE104L Exp 4Document7 pagesECE104L Exp 4Diana Jane Terez LazaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Phase Three Leg Ac/ac ConverterDocument8 pagesSingle Phase Three Leg Ac/ac ConvertermycatalystsPas encore d'évaluation
- Negative Voltage of Bently NevadaDocument2 pagesNegative Voltage of Bently NevadaSamir FertasPas encore d'évaluation
- TH L32a10s2Document124 pagesTH L32a10s2Nilo Magno0% (1)
- Mips IsaDocument79 pagesMips Isaphan_vinh_20Pas encore d'évaluation
- SJSU EE288 Lecture18 SAR ADCDocument15 pagesSJSU EE288 Lecture18 SAR ADCZulfiqar AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Diod S A0004145376 1-2542498 PDFDocument9 pagesDiod S A0004145376 1-2542498 PDFJajang SaprudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cables y Conectores - AES14-1992-r2004Document5 pagesCables y Conectores - AES14-1992-r2004Juan Felipe LópezPas encore d'évaluation
- GT Relay Testing FormatDocument7 pagesGT Relay Testing FormatVk Sumanth100% (1)
- Satellite CommunicationDocument11 pagesSatellite CommunicationRamPas encore d'évaluation
- Beyond Uvm For Soc Verification PDFDocument15 pagesBeyond Uvm For Soc Verification PDFSudha Mahesh GPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 Microwave FiltersDocument53 pagesChapter 8 Microwave FilterskhyatichavdaPas encore d'évaluation
- EX NO 1 Micro Controller 7segmentDocument5 pagesEX NO 1 Micro Controller 7segmentsrgperumalPas encore d'évaluation
- Bidirectional Visitor CounterDocument56 pagesBidirectional Visitor CounterRahul Verma100% (4)
- Hospital Management Using Circular Queue Linked ListDocument22 pagesHospital Management Using Circular Queue Linked ListRam Kiran Devireddy0% (2)
- AN - ST - Aplicacoes AutomotivasDocument12 pagesAN - ST - Aplicacoes AutomotivasDaniel MartinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Double Side Band Suppressed Carrier: Professor Z GhassemlooyDocument13 pagesDouble Side Band Suppressed Carrier: Professor Z GhassemlooyUmaraDissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prist University - Ece 2nd Year Detailed SyllabusDocument21 pagesPrist University - Ece 2nd Year Detailed SyllabusPrist UniversityPas encore d'évaluation
- MultivibratorsDocument12 pagesMultivibratorsInam Rajj100% (1)
- NCM-W, NCM-F Onyx®: Series Network Communications ModulesDocument2 pagesNCM-W, NCM-F Onyx®: Series Network Communications Modulescarlos yepezPas encore d'évaluation
- The Fundamentals of Signal Analysis - 5952-8898EDocument65 pagesThe Fundamentals of Signal Analysis - 5952-8898Efabry8080Pas encore d'évaluation