Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Notes - Consumer and Culture
Transféré par
Himadri PalikheDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter Notes - Consumer and Culture
Transféré par
Himadri PalikheDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Group 3 Arjun Kumar Chhetri, Himadri Palikhe, Shrawan Tamrakar
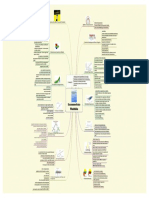
Chapter Notes_Influence of Culture on Consumer Behavior
Culture is a detailed examination of the character of the total society, including such factors as language, knowledge, laws, religion, food customs, music, art, technology, work patterns, products, and other artifacts that give a society its distinctive flavor. In a sense, culture is a societys personality. Culture is the sum total of learned beliefs, values, and customs that server to direct the consumer behavior of members of a particular society. It is the accumulation of shared meanings, rituals, norms, and traditions among the members of an organization or society and determines: Overall priorities a consumer attaches to different activities and products Success or failure of specific products and services
Consumers both view themselves in the context of their culture and react to their environment based upon the cultural frame work that they bring to that experience. Each individual perceives the world through his own cultural lens. Culture is also associated with what a societys members consider to be a necessity and what they view as a luxury. For instance, 55% of Americans adults consider a microwave to be a necessity and 36% consider a remote control for a TV or VCR to be necessity. The learning of ones own culture is known as enculturation. The learning of a new or foreign culture is known as acculturation. Culture is learned. At an early age, we begin to acquire from our social environment a set of beliefs, values, and customs that make up our culture. Anthropologists have identified three distinct forms of cultural learning: 1. Formal learning: in which adults and older siblings teach a young family member How to behave; 2. Informal learning: in which a child learns primarily by imitating the behavior of selected others, such as family, friends, or TV stars. 3. Technical Learning: Which teachers instruct the child in an educational environment about what, how and why it should be done. Advertising can influence all three types of cultural learning's.
Group 3 Arjun Kumar Chhetri, Himadri Palikhe, Shrawan Tamrakar
Culture is shared. Culture is viewed as group customs that link together the members of the society. Common language is the critical component that makes it possible for people to share values, experiences, and customs. Social Institutions transmitting the element of culture and sharing of culture 1. Family: primary agent for enculturation 2. Educational Institutions: imparts learning skills, history, patriotism, citizenship and technical training. 3. Religious Institutions: Perpetuate religious consciousness, spiritual guidance, and moral training. 4. Mass Media: wide range of cultural values. Culture is Dynamic. To fulfill the need gratifying role, culture continually must evolve if it is to function in the best interests of a society. The marketers must carefully monitor the socio culture environment in order to market an existing product effectively or to develop promising new products. Aspects of culture. A cultural system consists of 3 functional areas: Social Structure: Way in Which Orderly Social Life is Maintained Ecology: Way a System is Adapted to Its Habitat Ideology: Way in Which People Relate to Their Environment and Social Groups Other aspects of culture - Although every culture is different, 4 dimensions appear to account for much of this variability. Power distance - how interpersonal relationships form when power differences exist. Uncertainty avoidance - degree to which people feel threatened by ambiguous situations Masculinity/ femininity - degree to which sex roles are clearly delineated. Individualism - extent to which the welfare of the individual Vs the group is valued.
Group 3 Arjun Kumar Chhetri, Himadri Palikhe, Shrawan Tamrakar
Values are very general ideas about good and bad goals Enacted Norms - Explicitly Decided On Crescive Norms - Embedded in Culture. Like Customs, Mores, Conventions
A myth is a story containing symbolic elements that expresses the shared emotions and ideals of a culture. Myths serve 4 interrelated functions in a culture: Metaphysical Cosmological Psychological Sociological
A ritual is a set of multiple, symbolic behaviors that occur in a fixed sequence and that tend to be repeated periodically. A ritual is a type of symbolic activity consisting of a series of steps occurring in a fixed sequence and repeated over time. The standpoint of marketers is the fact that rituals tends to replete with ritual artifacts that are associated with or somehow enhance the performance of the ritual. The gift - giving ritual can be broken down into the following three distinct stages: Gestation - giver is motivated by an event to buy a gift Presentation - process of gift exchange Reformulation - bonds between parties are adjusted
Rites of passage can be construed as being special times marked by a change in social status. Stage 1. Separation detaching from the original group Stage 2. Liminality person is in-between statuses Stage 3. Aggregation person reenters society after rite-of-passage is complete Sacred and Profane Consumption Sacred consumption - involves objects and events that are set apart from normal activities, and are treated with some degree of respect or awe. Domains of Sacred Consumption:
Group 3 Arjun Kumar Chhetri, Himadri Palikhe, Shrawan Tamrakar
Sacred Places - May have religious or mystical significance. Others are created from the profane world and given special sacred qualities (i.e. Disney World, or shopping malls). The home is a particularly scared place.
Sacred People - Memorabilia can take on special meaning, from baseball cards to clothing the special person has touched or worn. Sacred Events Many consumers activities (events) have taken on special status. Examples would include the Super Bowl, the Olympics, the World Series, even family vacations. Personal mementos from sacred events can include: Local products (i.e. wine from California). Pictorial images (i.e. post cards). A piece of the event such as a rock or seashell. Symbolic shorthand (i.e. a miniature Statue of Liberty). Markers (i.e. Hard Rock Cafe T-shirts).
Profane consumption - involves consumer objects and events that are ordinary, everyday objects and events that do not share the specialness of sacred ones. Some sacred things have become profane, and some profane things have become sacred. Desacralization occurs when a sacred item or symbol is removed from its special place or is duplicated in mass quantities, becoming profane as a result. Examples: Monuments, artwork, American flag, religion. Sacralization occurs when ordinary objects, events, and even people, take on sacred meaning to a culture or to specific groups within a culture. Examples: Super Bowl, or Elvis. Objectification occurs when sacred qualities are attributed to mundane objects. Collecting refers to the systematic acquisition of a particular object or set of objects.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Econometrics MadalaDocument1 pageEconometrics MadalaHimadri PalikhePas encore d'évaluation
- 716-1 Simple Regression Theory IDocument8 pages716-1 Simple Regression Theory IVu SangPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers CH 2Document4 pagesAnswers CH 2Cepade ProjectosPas encore d'évaluation
- 05.myers - Sat1100 - Chicago GWW Res Design MethodsDocument41 pages05.myers - Sat1100 - Chicago GWW Res Design MethodsManvendra Pratap SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Disney Consumer ProductsDocument5 pagesDisney Consumer ProductsHimadri PalikhePas encore d'évaluation
- Disney Consumer ProductsDocument5 pagesDisney Consumer ProductsHimadri PalikhePas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Why Organic AgricultureDocument40 pagesModule 1 Why Organic AgricultureHimadri Palikhe100% (2)
- Concepts of Self in MarketingDocument20 pagesConcepts of Self in MarketingHimadri PalikhePas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Valley Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesValley Lesson Planapi-258572357Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Moham Ed Hamed Ghazy: Mansoura UniversityDocument6 pagesDr. Moham Ed Hamed Ghazy: Mansoura UniversityMohamed Hamed GhazyPas encore d'évaluation
- Competency-standards-Training-RegulationDocument22 pagesCompetency-standards-Training-Regulationksj rembulatPas encore d'évaluation
- Code of Ethics SummaryDocument1 pageCode of Ethics SummaryHerceeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurse Practioner Syllabus RegulationsDocument69 pagesNurse Practioner Syllabus RegulationsSanthu SuPas encore d'évaluation
- HEALTH Mod. 12 Q3 LASDocument4 pagesHEALTH Mod. 12 Q3 LASHsiri IrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestion Des Services de Santé (Hah) : Vous Consultez La Version 2021-2022 Du CatalogueDocument3 pagesGestion Des Services de Santé (Hah) : Vous Consultez La Version 2021-2022 Du CatalogueBienvenue succèsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Lesson Plan-Elements of Poetry (Ubd) : That's What FriendsDocument1 pageSample Lesson Plan-Elements of Poetry (Ubd) : That's What FriendsAlphaa RevechePas encore d'évaluation
- Sara J. Bilhimer: 1141 Connecticut St. Lawrence, Ks 66044 - 785-917-0371 - Wildrnes@ku - EduDocument2 pagesSara J. Bilhimer: 1141 Connecticut St. Lawrence, Ks 66044 - 785-917-0371 - Wildrnes@ku - Eduapi-243278996Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 WholeDocument156 pages02 WholeNgvinh PiePas encore d'évaluation
- Agile SDLC (Wiki)Document12 pagesAgile SDLC (Wiki)ghar_dashPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Day Agile Essentials Refresher v1.2Document142 pages1 Day Agile Essentials Refresher v1.2pradeep6174Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classifying PolygonsDocument5 pagesClassifying PolygonsHarpreet KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- BIG DATA & Visual Analytics: Professional Program inDocument11 pagesBIG DATA & Visual Analytics: Professional Program inNiranjanAryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Monitoring Tool in ScienceDocument10 pagesMonitoring Tool in ScienceCatherine RenantePas encore d'évaluation
- ISE II WS 2 Task 1 Maths SkillsDocument2 pagesISE II WS 2 Task 1 Maths SkillsVicente Cristiano BarbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument4 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldMary Joy CasillaPas encore d'évaluation
- SITXHRM010 Student Assessment Task 3Document9 pagesSITXHRM010 Student Assessment Task 3Smile Reacts0% (1)
- Application Form: You Must Add Country Code, City Code Before Your Telephone, Mobile and Fax NumberDocument8 pagesApplication Form: You Must Add Country Code, City Code Before Your Telephone, Mobile and Fax NumbermisbayyPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 3 Performing Underchassis Preventive Converted RecoveredDocument126 pages3 3 Performing Underchassis Preventive Converted RecoveredEDEN JIMENEZPas encore d'évaluation
- PN Initial Assessment and Triage Questionnaire Coach VersionDocument13 pagesPN Initial Assessment and Triage Questionnaire Coach Versionpraveen100% (1)
- Q4 LP7 GenPysics2Document11 pagesQ4 LP7 GenPysics2ROMELYN GRACE BORBEPas encore d'évaluation
- Houchen Test On MatterDocument3 pagesHouchen Test On Matterapi-200821684Pas encore d'évaluation
- History TcuDocument8 pagesHistory TcuJulieann Bagunas KimPas encore d'évaluation
- COT - LP For GerundsDocument3 pagesCOT - LP For GerundsRalph LegoPas encore d'évaluation
- BEST STEPS - PhysicsDocument12 pagesBEST STEPS - PhysicsAlex GoldsmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Copy ReadingDocument54 pagesCopy ReadingGienniva FulgencioPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasound Guided Vascular AccessDocument19 pagesUltrasound Guided Vascular Accessdragon_hubo100% (2)
- Impromptu SpeechDocument13 pagesImpromptu Speechapi-327193447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Engineer Resume For FresherDocument5 pagesMechanical Engineer Resume For FresherIrfan Sayeem SultanPas encore d'évaluation