Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Booting Up The Router and Locating The Cisco IOS
Transféré par
Tinu ThykurinjiyilDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Booting Up The Router and Locating The Cisco IOS
Transféré par
Tinu ThykurinjiyilDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CCNA-INTERVIEW What is a router?
A router is a device that connects more than one physical network, or segments of a network, using IP routing software. As packets reach the router, the router reads them and forwards them to their destination. CISCO ROUTER BOOTUP PROCESS Booting up the Router Cisco routers can boot Cisco IOS software from these locations: 1. Flash memory 2. TFTP server 3. ROM (not full Cisco IOS) Locating the Cisco IOS Software Default boot sequence for Cisco IOS software: 1. NVRAM 2. Flash (sequential) 3. TFTP server (network boot) 4. ROM (partial IOS)
Booting up the router and locating the Cisco IOS
1. POST (power on self test) 2. Bootstrap code executed 3. Check Configuration Register value (NVRAM) which can be modified using the config-register command 0 = ROM Monitor mode 1 = ROM IOS 2 - 15 = startup-config in NVRAM
4. Startup-config file: Check for boot system commands (NVRAM)
If boot system commands in startup-config
a. Run boot system commands in order they appear in startup-config to locate the IOS b. [If boot system commands fail, use default fallback sequence to locate the IOS (Flash, TFTP, ROM) If no boot system commands in startup-config use the default fallback sequence in locating the IOS: a. Flash (sequential) b. TFTP server (netboot) c. ROM (partial IOS) or keep retrying TFTP depending upon router model 5. If IOS is loaded, but there is no startup-config file, the router will use the default fallback sequence for locating the IOS and then it will enter setup mode or the setup dialogue. 6. If no IOS can be loaded, the router will get the partial IOS version from ROM
Default (normal) Boot Sequence
Power on Router - Router does POST - Bootstrap starts IOS load Check configuration register to see what mode the router should boot up in (usually 0x102 to 0x10F to look in NVRAM) - check the startup-config file in NVRAM for bootsystem commands (normally there aren't any) - load IOS from Flash.
Boot System Commands
Router (config)# boot system flash IOS filename - boot from FLASH memory Router (config)# boot system tftp IOS filename tftp server ip address - boot from a TFTP server Router (config)# boot system rom - boot from system ROM Configuration Register Command Router (config)# config-register 0x10x (where that last x is 0-F in hex) When the last x is: 0 = boot into ROM Monitor mode 1 = boot the ROM IOS 2 - 15 = look in startup config file in NVRAM
ROM Monitor (ROMMON)
The ROM monitor is a bootstrap program that initializes the hardware and boots the Cisco IOS-XR software when you power on or restart a Cisco router. This mode is accessed only manually interrupting the boot process and placing the system in ROMMON access this mode. Once in ROMMON, you can perform ROM monitor tasks, including reinstalling the Cisco IOS-XR software, recovering passwords etc. Two ways to enter ROM monitor mode are provided:
Reset the Configuration Register and Reload the Router Manually Halt the Initialization Process During System Reload
Discuss WAN (wide area network)
A WAN is extended over longer distances that a LAN (local area network). It can range from a few miles to across the world. TCP/IP is
the primary WAN protocol and was developed to provide reliable, secure data transmissions over long distances.
Static routing
It is simply the process of manually entering routes into a device's routing table. These routes can be entered by a network administrator who configures the routes manually. Admin overhead.
Dynamic Routing
A routing protocol is used find the best path to the destination Router overhead.
RIP
1. The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance-vector protocol that uses hop count as its metric 2. It is an interior gateway protocol (IGP), which means that it performs routing within a single autonomous system 3. RIP routers maintain only the best route (the route with the lowest metric value) to a destination. 4. RIP is a dynamic, distance vector routing protocol. 5. RIP is a classful routing protocol. 6. RIP cannot handle more than 15 hops. 7. RIP is inefficient because RIP prefers paths with the shortest hop count. The path with the shortest hop count might be over the slowest link in the network.
EIGRP
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is an advanced distance vector routing protocol Advanced operational efficiency Capabilities of both link state and distance vector A classless routing protocol EIGRP uses bandwidth, delay, load and reliability to calculate the metric for its routing table. EIGRP uses a DUAL algorithm to avoid loops.
OSPF
Open Shortest Path First is a routing protocol that supports the concept of a core area to which everything attaches. It uses a link state routing. An OSPF domain is divided into areas. Areas are logical groupings of hosts and networks, including their routers having interfaces connected to any of the included networks. Each area maintains a separate link state database whose information may be summarized towards the rest of the network by the connecting router. Thus, the topology of an area is unknown outside of the area. This reduces the amount of routing traffic between parts of an autonomous system. OSPF selects the best routes by finding the lowest cost paths to a destination Area 0 is known as backbone area. All other OSPF areas must be connected to backbone area.
OSPF Router Types
Internal Routers An internal router connects only to one OSPF area. All of its interfaces connect to the area in which it is located and does not connect to any other area. Backbone Routers Backbone routers have one or more interfaces in Area 0 (the backbone area). Area Border Router (ABR) A router that connects more than one area is called an area border router or ABR. Usually an ABR is used to connect nonbackbone areas to the backbone
Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR)
If the router connects the OSPF Autonomous System to another Autonomous System, it is called an Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR).
Designated Router (DR)
The Designated Router (DR) is the router to which all other routers within an area send their Link State Advertisements. The Designated Router will keep track of all link state updates and make sure the LSAs are flooded to the rest of the network using Reliable Multicast transport.
Backup Designated Router (BDR)
The BDR takes over from the DR when the DR fails.
What is an autonomous system?
An autonomous system is one network or sets of networks under a single administrative control. It breaks up parts of the network into manageable chunks. An AS is a connected group of IP networks that follows to a single and clearly defined routing policy.
What is BGP?
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), performs routing between different autonomous systems. It is an exterior gateway routing protocol that enables groups of routers (called autonomous systems) to share routing information.
What mask would you use to supernet two class C addresses?
The subnet would be 255.255.254.03
ARP (ADDRESS RESOLUTION PROTOCOL)
It is used to find the MAC Address with known IP address. A host wishing to obtain a physical address broadcasts an ARP request onto the TCP/IP network. The host on the network that has the IP address in the request then replies with its physical hardware address.
Reverse ARP (RARP)
A host to discover its IP address can use it. In this case, the host
broadcasts its physical address and a RARP server replies with the host's IP address.
SUBNET
A subnet is a logical grouping of connected network devices When subnets are properly implemented, both the performance and security of networks can be improved.
DNS
The DNS translates Internet domain and host names to IP addresses.
DNS server
A DNS server is any computer registered to join the Domain Name System. A DNS server runs special-purpose networking software, features a public IP address, and contains a database of network names and addresses for other Internet hosts.
NAT definition
NAT translates the IP addresses of computers in a local network to a single IP address. It maps private IP addresses to public IP addresses Process of assigning a public address to a computer (or group of computers) inside a private network Used to access resources outside the Local Area Network, like the Internet
VLAN (Virtual LAN)
Logical grouping of networks Implementing VLAN increases the no. Of broadcast domains. Improved Administration Efficiency Virtual Groups Enhanced Network Security
Why not just subnet my network?
Each VLAN should be in its own subnet. The benefit that a VLAN provides over a subnetted network is that devices in different physical locations, not going back to the same router, can be on the same network. The limitation of subnetting a network with a router is that all devices on that subnet must be connected to the same switch and that switch must be connected to a port on the router.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Rouing ConceptsDocument211 pagesRouing ConceptsmntesnotPas encore d'évaluation
- NETWORK LAYER PROTOCOLS GUIDEDocument12 pagesNETWORK LAYER PROTOCOLS GUIDEelakya rageshPas encore d'évaluation
- Routing Questions-Part-IDocument7 pagesRouting Questions-Part-Isumai BagwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna NotesDocument67 pagesCcna NotesIrshad KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Exploration Module 2 Chapter 1 Static Networking V 4.0Document6 pagesCCNA Exploration Module 2 Chapter 1 Static Networking V 4.0tommylikiePas encore d'évaluation
- WXES2106 Network Technology Semester 1 2004/2005: RoutersDocument34 pagesWXES2106 Network Technology Semester 1 2004/2005: Routersapi-19663123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Static Routing Introduction To Dynamic Routing Protocols RIP v1 and RIP v2, OSPF Eigrp BGPDocument12 pagesStatic Routing Introduction To Dynamic Routing Protocols RIP v1 and RIP v2, OSPF Eigrp BGPShiv Pratap SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Static Routing Introduction To Dynamic Routing Protocols RIP v1 and RIP v2, OSPF Eigrp BGPDocument12 pagesStatic Routing Introduction To Dynamic Routing Protocols RIP v1 and RIP v2, OSPF Eigrp BGPShiv Pratap SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- CHSHTDocument13 pagesCHSHTAgnes BernardPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours ReseauDocument14 pagesCours ReseauNlend IsraëlPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna2 1Document6 pagesCcna2 1Ashutosh UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Code CIT 333Document53 pagesCourse Code CIT 333M Shumraiz SharifPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA2. Chapter 1Document11 pagesCCNA2. Chapter 1sashii09100% (1)
- Switch and Router ConfigurationDocument41 pagesSwitch and Router ConfigurationBroot KalPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Notes CCNA 3 EasyDocument40 pagesRevision Notes CCNA 3 EasyNur Dinah YeePas encore d'évaluation
- 22 - Static and Dynamic RoutingDocument21 pages22 - Static and Dynamic RoutingJana MassadehPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 3 Study Guide Answers-AllDocument33 pagesCCNA 3 Study Guide Answers-AllgeertvdhPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Router1Document22 pagesCCNA Router1kishoreplkPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA RoutingDocument4 pagesCCNA RoutingshiblyshahsadPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNAv3.3 206Document33 pagesCCNAv3.3 206Tung HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Routing in the Internet: Intra and Interdomain RoutingDocument6 pagesRouting in the Internet: Intra and Interdomain RoutingSmit prajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- CN-2022BCS005Document5 pagesCN-2022BCS005Akshat NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- W4 - Presentation-Chapter 4 Routing ConceptsDocument21 pagesW4 - Presentation-Chapter 4 Routing ConceptsWendellPas encore d'évaluation
- Router FundamentalsDocument22 pagesRouter Fundamentalsapi-3825972100% (4)
- Router: What Is A Router?Document6 pagesRouter: What Is A Router?Kumar KksPas encore d'évaluation
- ROUTERDocument26 pagesROUTERZEESHAN YTPas encore d'évaluation
- Routing Questions-Part-IIDocument6 pagesRouting Questions-Part-IIsumai BagwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Semester 2 Module 6 Routing and Routing Protocols: Click To Add Text Asian CollegeDocument58 pagesSemester 2 Module 6 Routing and Routing Protocols: Click To Add Text Asian CollegeR.k.ThapaPas encore d'évaluation
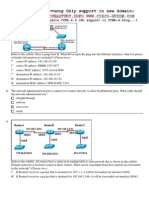
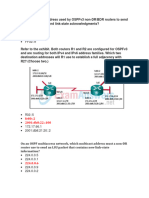
- Refer To The Exhibit. Host A PingsDocument7 pagesRefer To The Exhibit. Host A Pingskader7782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Routing Protocols and ConceptsDocument42 pagesRouting Protocols and ConceptsRoger EmbalsadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Routing RoutedDocument32 pagesRouting RoutedMangesh KakadePas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 2 Quizz#1Document7 pagesCCNA 2 Quizz#1Alberto Arrieta BaltodanoPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA2 - 1 - Configuring Network Devices and Introduction To RoutingDocument60 pagesCCNA2 - 1 - Configuring Network Devices and Introduction To RoutingDominic BeneditoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco ProtocolsDocument9 pagesCisco ProtocolsEric ResuelloPas encore d'évaluation
- cn_lab_2022BCS005Document5 pagescn_lab_2022BCS005Akshat NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER - 1 Introduction To Routing and Packet ForwardingDocument6 pagesCHAPTER - 1 Introduction To Routing and Packet ForwardingAlexandrosAristeridisPas encore d'évaluation
- CN_Lab_2022bcs035Document8 pagesCN_Lab_2022bcs035Akshat NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- Created With Novapdf Printer - Please Register To Remove This MessageDocument8 pagesCreated With Novapdf Printer - Please Register To Remove This MessagePhilipp FelderPas encore d'évaluation
- Routing Protocols: By: Er. Amit MahajanDocument30 pagesRouting Protocols: By: Er. Amit Mahajanamit mahajan100% (1)
- Basic of RoutingDocument56 pagesBasic of RoutingnjgregPas encore d'évaluation
- Minor Project Report-OSPF ChampDocument5 pagesMinor Project Report-OSPF Champsmrutiranjan1991100% (1)
- Presentation ON Ccna: TRAINED BY - Kundan Singh (Aptron Solutions PVT LTD)Document36 pagesPresentation ON Ccna: TRAINED BY - Kundan Singh (Aptron Solutions PVT LTD)Akshay Mishra BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- cn-2022BCS035Document5 pagescn-2022BCS035Akshat NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- Different WAN technologies and EIGRP tablesDocument8 pagesDifferent WAN technologies and EIGRP tablesSecdition 30Pas encore d'évaluation
- IP RoutingDocument14 pagesIP Routingjoannacatayoc12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Routing and Packet ForwardingDocument82 pagesIntroduction To Routing and Packet ForwardingJessica NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Router FinalDocument13 pagesRouter FinalhahahahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three of NetworkingDocument66 pagesChapter Three of NetworkinghailePas encore d'évaluation
- Datacom ReportDocument50 pagesDatacom ReportACDC TeamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document30 pagesChapter 4misikir zenebePas encore d'évaluation
- IP RoutingDocument11 pagesIP Routingmaria bashirPas encore d'évaluation
- FinaoDocument48 pagesFinaoEdwin HPas encore d'évaluation
- Typical CCNA QuestionDocument4 pagesTypical CCNA QuestionkeoghankPas encore d'évaluation
- Take Assessment - Erouting Chapter 1 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Document7 pagesTake Assessment - Erouting Chapter 1 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)wingn1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Routing Protocol Selection Guide - IGRP, Eigrp, Ospf, Is-Is, BGPDocument9 pagesRouting Protocol Selection Guide - IGRP, Eigrp, Ospf, Is-Is, BGPFred MadisonPas encore d'évaluation
- First Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolD'EverandFirst Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolPas encore d'évaluation
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkD'EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIOND'EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONPas encore d'évaluation
- Nmap - Scanning The InternetDocument45 pagesNmap - Scanning The InternetDDN1967Pas encore d'évaluation
- IS-IS Networking ProtocolDocument4 pagesIS-IS Networking ProtocolKrishnakumar SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Agara IndustriesDocument2 pagesAgara IndustriesLaxmikant VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Network AddressingDocument11 pagesWhat Is Network AddressingArgyll GalanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring IP Multicast Routing: Finding Feature InformationDocument24 pagesConfiguring IP Multicast Routing: Finding Feature InformationJoão CuglerPas encore d'évaluation
- MIKROTIK MTCNeDocument2 pagesMIKROTIK MTCNeGilang SyahidanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) : Gurjot Singh Ug201113013 Revti Raman Singh Ug201110026Document35 pagesHypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) : Gurjot Singh Ug201113013 Revti Raman Singh Ug201110026Sunitha ManamPas encore d'évaluation
- Template Script Mikrotik Routing Game Online: Ip Address Lokal - . Gateway Modem Game .Document6 pagesTemplate Script Mikrotik Routing Game Online: Ip Address Lokal - . Gateway Modem Game .Deny IryantoPas encore d'évaluation
- VersionDocument27 pagesVersioninfinitwebturboPas encore d'évaluation
- Three powerful route manipulation toolsDocument3 pagesThree powerful route manipulation toolsAmit kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Example Tunneling IPv6 Traffic Over MPLS IPv4 Networks - TeDocument6 pagesExample Tunneling IPv6 Traffic Over MPLS IPv4 Networks - TeLeonardo HutapeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 04-Network LayerDocument66 pagesChapter 04-Network LayerLy VuPas encore d'évaluation
- RTS Feature of BluecoatDocument4 pagesRTS Feature of BluecoatpskroyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Standardization Who's Who in The Telecommunication World?Document4 pagesNetwork Standardization Who's Who in The Telecommunication World?anjali prasadPas encore d'évaluation
- EchoLife EG8141H5 Datasheet 01Document3 pagesEchoLife EG8141H5 Datasheet 01Marucho MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- BRKMPL 2115Document93 pagesBRKMPL 2115luisPas encore d'évaluation
- DRC Technical Bid Form for Internet ServicesDocument2 pagesDRC Technical Bid Form for Internet ServicesSimon PolycarpePas encore d'évaluation
- CAMP002-3 Emails and Other Conferencing ToolsDocument23 pagesCAMP002-3 Emails and Other Conferencing ToolsTavisLeaPas encore d'évaluation
- MikroTik Configuration PDFDocument19 pagesMikroTik Configuration PDFdaraPas encore d'évaluation
- 0008 Remote Triggered Black Hole RTBH 2017-07-24Document142 pages0008 Remote Triggered Black Hole RTBH 2017-07-24B18DCVT310-Trần Thị NgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Threat Report 1h2023Document16 pagesThreat Report 1h2023GG PlanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between CIDR and VLSMDocument11 pagesDifference Between CIDR and VLSMStojan KitanovPas encore d'évaluation
- Baru 4Document2 pagesBaru 4Rian KoezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document159 pages1Vjik61Pas encore d'évaluation
- SonicOS 6.5 System Setup PDFDocument903 pagesSonicOS 6.5 System Setup PDFCao Chi KienPas encore d'évaluation
- Junos Pppoe XDocument22 pagesJunos Pppoe Xpaulo h100% (2)
- Netstat CommDocument2 pagesNetstat CommMirza CerimPas encore d'évaluation
- Velocloud Admin Guide 33Document409 pagesVelocloud Admin Guide 33Amir MajzoubPas encore d'évaluation
- MTCNA Sample ExamDocument6 pagesMTCNA Sample ExamJorge CopaPas encore d'évaluation
- ISWA Unit1pptx 2023 08 28 19 47 11Document47 pagesISWA Unit1pptx 2023 08 28 19 47 11shivanibabhatti21Pas encore d'évaluation