Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
About Group 18 Elements
Transféré par
Hoi YanDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
About Group 18 Elements
Transféré par
Hoi YanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
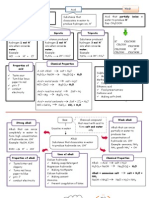
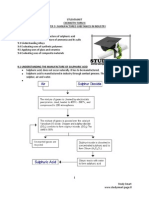
About Group 18 elements Group 18 - Noble gases - all are gases which are naturally occurring Noble gases
es are monoatomic
Physical properties Noble gases small atomic sizes Colourless gases at room temperature Atomic size increase going down the group, the force attraction between atoms of each element becomes stronger melting and boiling point increase to overcome the force attraction The density increase as the relatif atomic mass and size increases
Change of Physical Properties Atomic size Increase when go down the group The number of shell is increase Density All noble gas have low density. Because the position of atom are far among of them When go down the group, the density are increase Melting Point & Boiling Point Have lowest melting and boiling point. Because the atom of noble gas had attract by the weak of Van der Waals Force and a few energy used to overcome it. When go down the group: ~atomic size increase ~Van der Waals Force increase
Some other physical properties of noble gases Insoluble in water Cannot conduct electricity Poor conductors of heat All noble gases are inert and chemically unreactive. It is unreactive because no reaction occur when the atoms collides example:
It is inert because of the electron arrangement Helium has two electron valence called duplet Others have eight electron valence called octet These electron arrangements are very stable because the outermost shells are full this is why noble gas exist as monoatomic gases and unreactive.
Uses of inert gases Helium : Neon : Argon : Used in electric light bulbs and fluorescent tubes To supply inert atmosphere for welding process Found in atmosphere (one part in 55,000). Used in neon signs. Fluorescent lighting as it emits an orangered glow when an electric discharge passes through it at low pressure. Neon is used in advertising lights and television tubes. Found in atmosphere (one part in 200,000). Used in airship and balloons. Its is eight times less dense than air. Not inflammable
Krypton: Xenon : Radon : For treatment of cancer Use for electron tubes and stroboscopic lamps Bubble chambers in atomic energy reactors Radon is used in the treatment of cancer. Used in some laser and photographic flash lamps. Used in fluorescent tubes Used in the stroboscopic lights which flank airport runways. Krypton gas is used in lasers to repair the retina of the eye.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- BELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Document8 pagesBELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Anis Wahida Mohamad100% (1)
- 6 Displacement of Halogen From Its Halide SolutionDocument9 pages6 Displacement of Halogen From Its Halide SolutionJedidah JongPas encore d'évaluation
- EJSK SK025 Physical PropertiesDocument30 pagesEJSK SK025 Physical PropertieschiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufactured Subtances in Industry: By: Nurfarahain Binti Ahmad 4ST SMK SG AbongDocument73 pagesManufactured Subtances in Industry: By: Nurfarahain Binti Ahmad 4ST SMK SG AbongSanthiya MadhavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 SchemeDocument41 pagesChemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 Schemespm_victim2010100% (5)
- 5 6116152494587379984Document98 pages5 6116152494587379984dharwinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseDocument7 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseAngie Kong Su MeiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Atoms and MoleculesDocument43 pages1.1 Atoms and MoleculesDinie BidiPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFDocument12 pagesSPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFNurulPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry SPM State Trial Papers-Form5chap2Document16 pagesChemistry SPM State Trial Papers-Form5chap2Law Jin YaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition Chemistry Form 4 KSSMDocument4 pagesDefinition Chemistry Form 4 KSSMprebasubah100% (1)
- Form 4 Chapter 8Document60 pagesForm 4 Chapter 8Rabbi 08Pas encore d'évaluation
- SaltsDocument34 pagesSaltscar_yii100% (1)
- Chemistry SPMDocument20 pagesChemistry SPMJacob ChowPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Chemistry PracticesDocument122 pagesForm 4 Chemistry PracticesVANESSA VOON MoePas encore d'évaluation
- The Periodic TableDocument33 pagesThe Periodic TableIra MunirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Rate of Reaction NotesDocument27 pagesRate of Reaction NotesYong SiewkuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 62 Rate of Reaction Concentration Effect - DwiDocument2 pagesModule 62 Rate of Reaction Concentration Effect - Dwirudi_zPas encore d'évaluation
- REDOXDocument67 pagesREDOXLeo PietroPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document22 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Ck OoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v13Document29 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v13Khoa DangPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 9 Manufactured Substances in Industry: 9.6 Composite MaterialsDocument5 pagesTopic 9 Manufactured Substances in Industry: 9.6 Composite MaterialsPutri MalayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument16 pagesChapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionKavitha ThayagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Tble TeacherDocument24 pagesCHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Tble Teacherangie0812Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Paper 3 ExperimentDocument15 pagesChemistry Paper 3 ExperimentTan Yi Ning100% (3)
- Modul Galus Chem 2014Document83 pagesModul Galus Chem 2014Juni Farhana100% (2)
- Nota Kimia Carbon Compoun Form 5Document16 pagesNota Kimia Carbon Compoun Form 5akusabrina2012Pas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013Document11 pagesAnswer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013ryder1man6433Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerDocument6 pages2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerSiti Nursahidah0% (1)
- Elements in Period 3Document13 pagesElements in Period 3FAthiyah Abdul RahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 4 PDFChuahSiewHoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Skor A+ StudentDocument21 pagesSeminar Skor A+ StudentSora HikaruPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Notes: Form 5 Chemistry: Rate or ReactionDocument20 pagesShort Notes: Form 5 Chemistry: Rate or Reactioncashewnut_mishPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Document2 pagesChemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Daniel Wong Sai Meng100% (1)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) AlkeneDocument98 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Alkeneridwan100% (4)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9: Manufactured Substances in IndustryDocument20 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9: Manufactured Substances in IndustryRozaini Ermi100% (6)
- Form 4 Science Chapter 8Document6 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 8elinePas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Chap 2 ChemF4 Bil 2018 (CSY3p) PDFDocument27 pages02 Chap 2 ChemF4 Bil 2018 (CSY3p) PDFalanislnPas encore d'évaluation
- Relative Atomic Mass & Relative Molecular MassDocument11 pagesRelative Atomic Mass & Relative Molecular Masscikgu aisyah100% (1)
- C18 PolymersDocument31 pagesC18 PolymersKris DookharanPas encore d'évaluation
- A CidDocument3 pagesA CidJerry Pui Chaw MinPas encore d'évaluation
- Rate of ReactionDocument20 pagesRate of ReactionQueen BlehPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Group 17 Elements UpdatedDocument8 pages4 Group 17 Elements Updatedkarim100% (1)
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 9 MANUFACTURED SUBSTANCES IN INDUSTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 9 MANUFACTURED SUBSTANCES IN INDUSTRYJay Bee100% (9)
- Form 4 Revision QuizDocument80 pagesForm 4 Revision QuizEnvira LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Form FiveDocument23 pagesChemistry Form FiveNorazlin Ujang100% (1)
- CHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Table StudentDocument23 pagesCHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Table Studentangie0812Pas encore d'évaluation
- Salts - Short Notes Form 4 ChemistryDocument3 pagesSalts - Short Notes Form 4 Chemistryhalizayani73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document13 pagesChapter 9Nadira AtiqahPas encore d'évaluation
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Document8 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Ismaliza IshakPas encore d'évaluation
- The Reactivity Series of Metals and Its ApplicationsDocument14 pagesThe Reactivity Series of Metals and Its ApplicationsSaadiah MohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsRoty005100% (4)
- SPM ChemistryDocument46 pagesSPM Chemistrysaz14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Patterns in Period 3 ElementsDocument18 pagesPatterns in Period 3 ElementsDania Dobbs100% (2)
- Group 8A ElementsDocument27 pagesGroup 8A ElementsNesa Salsabila BahriPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Group 18 - Nobel GasesDocument10 pages10 - Group 18 - Nobel Gasesfriasereca22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Group 18 Presentation - Noble GasesDocument8 pagesGroup 18 Presentation - Noble GasesKah WaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 18bce0227 VL2018191000937 Adl PDFDocument24 pages18bce0227 VL2018191000937 Adl PDFReghunaath A APas encore d'évaluation
- Helium-Neon Lasers: A.A.REGHUNAATH: 18BCE0227 A.V.Abhishek Arjun: 18bce0232 ARJUN.S: 18BCE0236Document24 pagesHelium-Neon Lasers: A.A.REGHUNAATH: 18BCE0227 A.V.Abhishek Arjun: 18bce0232 ARJUN.S: 18BCE0236Reghunaath A APas encore d'évaluation
- Naming Inorganic Compounds WorksheetDocument2 pagesNaming Inorganic Compounds WorksheetDaniah AllemaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.VA Group Elements 171-175Document12 pages10.VA Group Elements 171-175eamcetmaterials100% (3)
- GRP 15 - PBlock CHEMHACKDocument10 pagesGRP 15 - PBlock CHEMHACKSATYA PRAKASH SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- Inert GasesDocument8 pagesInert Gasesbiswajit.ghoshPas encore d'évaluation
- 11th Chemistry Simple Salts English Medium PDFDocument39 pages11th Chemistry Simple Salts English Medium PDFDeenu RamenjesPas encore d'évaluation
- Files - Complete Soylent Nutrition Facts PDFDocument1 pageFiles - Complete Soylent Nutrition Facts PDFrp1858009462Pas encore d'évaluation
- GROUP - 7 - COE 102 LABRATORY EXERCISE No. 3 WEEK 3 Chemical NomenclatureDocument4 pagesGROUP - 7 - COE 102 LABRATORY EXERCISE No. 3 WEEK 3 Chemical NomenclatureAlbert MariquitPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 The P-Block Elements: Level - IDocument22 pages7 The P-Block Elements: Level - IFasahatPas encore d'évaluation
- Parameter Pengujian AirDocument4 pagesParameter Pengujian AirtiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sulfuric Acid Manufacturing ProcessDocument10 pagesSulfuric Acid Manufacturing ProcessMg HPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 Past Year Question (Combination)Document6 pagesChapter 10 Past Year Question (Combination)angelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Group 16 in P Block ElementsDocument4 pagesChemistry of Group 16 in P Block Elementsakino.mitsunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Balancing Equations AssignmentDocument10 pagesBalancing Equations AssignmentShifa RizwanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1a WORD EQUATION QUESTIONSDocument3 pages1a WORD EQUATION QUESTIONSWu YiruiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Document4 pagesChemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Lama DebanaPas encore d'évaluation
- DPP 1 Atomic Radius 1639722834709Document3 pagesDPP 1 Atomic Radius 1639722834709Vivek SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Problems For Naming Inorganic CompoundsDocument2 pagesPractice Problems For Naming Inorganic CompoundsViswak BalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Limiting Reactants: Name - Chem Worksheet 12-3Document1 pageLimiting Reactants: Name - Chem Worksheet 12-3qwrewe0% (1)
- Atomic Masses of First 30 Elements: Hydrogen HDocument4 pagesAtomic Masses of First 30 Elements: Hydrogen HPrithvi Bhardwaj94% (31)
- Chemical CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesChemical CharacteristicsDiana BunaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Displacement Worksheet ExtraDocument2 pagesDisplacement Worksheet ExtraMalooka AlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Vii The HalogensDocument58 pagesGroup Vii The HalogensYuanWei SiowPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic TableDocument69 pagesPeriodic Tablesofiea hazriPas encore d'évaluation
- Tablas TermodinámicasDocument5 pagesTablas TermodinámicasSarahí CabreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 Making SaltsDocument46 pagesChapter 11 Making SaltsSumi VjPas encore d'évaluation
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan - JhsDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan - JhsMoises Von Rosauro De GraciaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Microorganisms in The Nitrogen Cycle: BiodiversityDocument1 pageThe Role of Microorganisms in The Nitrogen Cycle: BiodiversityAzween SabtuPas encore d'évaluation
- QuizDocument1 pageQuizApril Mergelle LapuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Mrs. Uma Sathish TutorialsDocument4 pagesMrs. Uma Sathish TutorialsSSE MECHPas encore d'évaluation
- S-Block ElementDocument62 pagesS-Block Elementabc9999999999Pas encore d'évaluation