Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Timeline of Atomic Structure
Transféré par
Haider AliDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Timeline of Atomic Structure
Transféré par
Haider AliDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
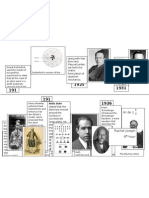
TIMELINE OF ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Greek Democritus era 1704 Isaac Newton "by convention bitter, by convention sweet, but in reality atoms and void"
Proposed a mechanical universe with small solid masses in motion. Proposed an "atomic theory" with spherical solid atoms based upon measurable 1803 John Dalton properties of mass. Studied the effect of electricity on solutions, coined term "electrolysis" as a splitting 1832 Michael Faraday molecules with electricity, developed laws of electrolysis. Faraday himself was not a proponent of atomism. 1859 J. Plucker Built one of the first gas discharge tubes ("cathode ray tube"). Arranged elements into 7 groups with similar properties. He discovered that the 1869 Dmitri Mendeleev properties of elements "were periodic functions of the their atomic weights". This became known as the Periodic Law. James Clerk 1873 Proposed electric and magnetic fields filled the void. Maxwell Discovered cathode rays had the following properties: travel in straight lines from t Sir William cathode; cause glass to fluoresce; impart a negative charge to objects they strike; ar 1879 Crookes deflected by electric fields and magnets to suggest a negative charge; cause pinwhee in their path to spin indicating they have mass. Used a CRT to study "canal rays" which had electrical and magnetic properties oppo 1886 E. Goldstein of an electron. Proposed that electricity was made of discrete negative particles he called electrons " 1894 G.J. Stoney (Link to info on electrons) Using a CRT he observed that nearby chemicals glowed. Further experiments found 1895 Wilhelm Roentgen very penetrating rays coming from the CRT that were not deflected by a magnetic fie He named them "X-rays". While studying the effect of x-rays on photographic film, he discovered some chemic 1896 Henri Becquerel spontaneously decompose and give off very pentrating rays. Used a CRT to experimentally determine the charge to mass ratio (e/m) of an electro 1897 J.J. Thomson =1.759 x 10 8 coulombs/gram. 1897 J.J. Thomson Studied "canal rays" and found they were associated with the proton H + . 1898 Rutherford Studied radiations emitted from uranium and thorium and named them alpha and be Studied uranium and thorium and called their spontaneous decay process Marie Sklodowska 1898 "radioactivity". She and her husband Pierre also discovered the radioactive elements Curie polonium and radium. Observed spontaneous disintegration of radioactive elements into variants he called 1900 Soddy "isotopes" or totally new elements, discovered "half-life", made initial calculations o energy released during decay. 1900 Max Planck used the idea of quanta (discrete units of energy) to explain hot glowing matter. Postulated a "Saturnian" model of the atom with flat rings of electrons revolving arou 1903 Nagaoka a positively charged particle.
Discovered that inert gases had a stable electron configuration which lead to their chemical inactivity. 1905 Albert Einstein Published the famous equation E=mc 2 1906 Hans Geiger Developed an electrical device to "click" when hit with alpha particles. Oil drop experiment determined the charge (e=1.602 x 10 -19 coulomb) and the mass 1909 R.A. Millikan (m = 9.11 x 10 -28 gram) of an electron. Using alpha particles as atomic bullets, probed the atoms in a piece of thin (0.00006 1911 Ernest Rutherford cm) gold foil . He established that the nucleus was: very dense,very small and positiv charged. He also assumed that the electrons were located outside the nucleus. Using x-ray tubes, determined the charges on the nuclei of most atoms. He wrote"Th atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus". This 1914 H.G.J. Moseley work was used to reorganize the periodic table based upon atomic number instead of atomic mass. 1919 Aston Discovered the existence of isotopes through the use of a mass spectrograph. Developed an explanation of atomic structure that underlies regularities of the perio 1922 Niels Bohr table of elements. His atomic model had atoms built up of sucessive orbital shells of electrons. Discovered that electrons had a dual nature-similar to both particles and waves. 1923 de Broglie Particle/wave duality. Supported Einstein. Described atoms by means of formula connected to the frequencies of spectral line 1927 Heisenberg Proposed Principle of Indeterminancy - you can not know both the position and veloc of a particle. Cockcroft / Built an early linear accelerator and bombarded lithium with protons to produce alph 1929 Walton particles Viewed electrons as continuous clouds and introduced "wave mechanics" as a 1930 Schrodinger mathematical model of the atom. Proposed anti-particles . Anderson discovered the anti-electron (positron) in 1932 an 1930 Paul Dirac Segre/Chamberlain detected the anti-proton in 1955.. Using alpha particles discovered a neutral atomic particle with a mass close to a proto 1932 James Chadwick Thus was discovered the neutron. Conducted experiments verifying that heavy elements capture neutrons and form Lise Meitner, 1938 unstable products which undergo fission. This process ejects more neutrons continui Hahn , Strassman the fission chain reaction. 1941 Synthesized 6 transuranium elements and suggested a change in the layout of the Glenn Seaborg 51 periodic table. 1942 Enrico Fermi Conducted the first controlled chain reaction releasing energy from the atoms nucleu 1950's New Follow this link to current theories about atomic stucture. findings/particles 1904 Abegg
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Atomic Theories TimelineDocument3 pagesAtomic Theories TimelineTinray ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic TimelineDocument3 pagesAtomic TimelineCarlos WatsonPas encore d'évaluation
- A Timeline On Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesA Timeline On Atomic Structuresome onePas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure TimelineDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure TimelineNouman1203Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Atomic Model: History of The Atom Khalil SinclairDocument32 pagesThe Atomic Model: History of The Atom Khalil Sinclairangelgirl101096Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Enigmatic Electron: Electron Behaviour and How It Influences Our LivesD'EverandThe Enigmatic Electron: Electron Behaviour and How It Influences Our LivesPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectronDocument15 pagesElectronMukhammad Hermawan Mochenk AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical ChangesDocument3 pagesChemical ChangesFrankPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronological Table For The Development of Atomic and Molecular PhysicsDocument69 pagesChronological Table For The Development of Atomic and Molecular PhysicsFaisal Kamran MarwatPas encore d'évaluation
- Democrit Us: Early TheoriesDocument8 pagesDemocrit Us: Early TheoriesPinky EclarinalPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Principles of RadioactivityDocument143 pagesBasic Principles of RadioactivityBulu Chandra MahantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument7 pagesAtomic Theory Timelinem1e arZPas encore d'évaluation
- Electron 1561665Document18 pagesElectron 1561665johnny deppPas encore d'évaluation
- Timeline of Quantum Mechanics ManciaDocument2 pagesTimeline of Quantum Mechanics ManciaDianaJane HilokPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Nature TimelineDocument2 pagesAtomic Nature TimelinebokanegPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3Document5 pagesWeek 3Prima LebananPas encore d'évaluation
- Max Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert EinsteinDocument4 pagesMax Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert Einsteinkat morenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Brownian Motion: Geiger-Marsden ExperimentDocument3 pagesBrownian Motion: Geiger-Marsden Experimentrjohn 7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Johann Wilhelm HittorfDocument5 pagesJohann Wilhelm Hittorfkat morenoPas encore d'évaluation
- J. J. Thomson Cathode Ray TubesDocument1 pageJ. J. Thomson Cathode Ray TubesRainier RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Atomic TheoryDocument28 pagesAdvanced Atomic TheoryMohammed Sohail SamejaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Nuclear PowerDocument20 pagesA Nuclear Powermukesh8981Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Model Timeline: Quicktime™ and A Decompressor Are Need Ed To See This PictureDocument31 pagesAtomic Model Timeline: Quicktime™ and A Decompressor Are Need Ed To See This PictureNoman AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture - 2 Title:: Page - 1 ObjectivesDocument20 pagesLecture - 2 Title:: Page - 1 Objectivesr prathapPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of AtomDocument106 pagesStructure of AtomJayesh ChouhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fortaleza Vanesse G. ChemDocument3 pagesFortaleza Vanesse G. Chemvanesse fortalezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorg and Analytical Chemistry 1Document39 pagesInorg and Analytical Chemistry 1MhelvenePas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of AtomDocument107 pagesStructure of AtomDarshan Patil100% (1)
- Chem TimelineDocument1 pageChem TimelinejessicajackPas encore d'évaluation
- Early Atomic TheoryDocument10 pagesEarly Atomic TheoryMa. Ericca OrgaPas encore d'évaluation
- TimelineDocument3 pagesTimelineSiddharthPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nobel Prize in Physics 1901Document44 pagesThe Nobel Prize in Physics 1901Rudolf JasonPas encore d'évaluation
- A Timeline On Atomic StructureDocument8 pagesA Timeline On Atomic Structureashley ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- History of The AtomDocument13 pagesHistory of The Atomapi-457121591Pas encore d'évaluation
- Material AssignmentDocument12 pagesMaterial AssignmentstevePas encore d'évaluation
- Science WorksheetDocument13 pagesScience WorksheetRonilo ParagsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Around 460 BDocument2 pagesAround 460 BSydni JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of AtomDocument26 pagesStructure of AtomsyPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic TheoryDocument42 pagesAtomic TheoryMarvin RoselPas encore d'évaluation
- Timeline of Atomic NatureDocument19 pagesTimeline of Atomic NatureLesly Justin FuntechaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2 Structure of Atom 1Document109 pagesCH 2 Structure of Atom 1vhidulaaprakash18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Famous ScientistDocument10 pagesFamous Scientistafzal786435Pas encore d'évaluation
- Development of Atomic TheoryDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Atomic TheoryPedro NepomucenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Che 101 NoteDocument39 pagesChe 101 Noteadebowalepeace502Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument3 pagesAtomic Theory TimelineYhan Brotamonte BoneoPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument49 pagesAtomic Structure PDFAshishPas encore d'évaluation
- AlcantaraDocument2 pagesAlcantaraJessica PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- The Structure of The AtomDocument28 pagesThe Structure of The AtomAnonymous dh6DITPas encore d'évaluation
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 03Document7 pagesClass IX Chemistry Chapter 03Sam FisherPas encore d'évaluation
- C8 History Tech IEC 2022Document22 pagesC8 History Tech IEC 2022Laveidem LNPas encore d'évaluation
- Final History of Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesFinal History of Atomic Theorybrowneyes_luke6052Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1008 - 5761141 - Punpun - PhysicsDocument15 pages1008 - 5761141 - Punpun - Physicsapi-276904981Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thinking About MatterDocument3 pagesThinking About MatterKim TaehyungPas encore d'évaluation
- History of The AtomDocument17 pagesHistory of The Atomali100% (1)
- Structure of Atoms and MoleculesDocument20 pagesStructure of Atoms and MoleculesIsrael EsmilePas encore d'évaluation
- The Cathode RaysDocument1 pageThe Cathode RaysLian ValenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Atomic StructureDocument109 pages2 Atomic Structuregnkstar50% (2)
- History of The Atom 1. J.J Thomson'S Experiment To Detect The ElectronDocument4 pagesHistory of The Atom 1. J.J Thomson'S Experiment To Detect The ElectronYeni SurantiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief History of Element Discovery, Synthesis, and AnalysisD'EverandA Brief History of Element Discovery, Synthesis, and AnalysisPas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Atomic StructureDocument13 pagesProject On Atomic Structureswati0611Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exp1 Sic180033 PDFDocument6 pagesExp1 Sic180033 PDFfara basar100% (1)
- Exp. - 9 Rotary FilterDocument4 pagesExp. - 9 Rotary Filterfayaz5uin1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Thermal Effect of The Reich's DOR BusterDocument16 pagesThe Thermal Effect of The Reich's DOR BusterAngel MalzonePas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogue CSM PDFDocument4 pagesCatalogue CSM PDFFran IgledominguezPas encore d'évaluation
- G4051 S40C Mechanical PropertiesDocument1 pageG4051 S40C Mechanical PropertiesLeonard EzraPas encore d'évaluation
- KCGM XD48 Presentation ProcessDocument152 pagesKCGM XD48 Presentation ProcessAnonymous ObQnrU100% (3)
- Welding F22 To F91 (09MAR2018)Document2 pagesWelding F22 To F91 (09MAR2018)Juan Shuna100% (2)
- UntitledDocument27 pagesUntitledapi-256504985Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science and Engineering of Materials 7th Edition Askeland Solutions ManualDocument29 pagesScience and Engineering of Materials 7th Edition Askeland Solutions Manualcrapevioloush1o97% (32)
- PneumaticDocument13 pagesPneumaticVikas RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- SC435418MFC16Document5 pagesSC435418MFC16javierPas encore d'évaluation
- KGL ManualDocument47 pagesKGL ManualAaron Shane IrvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Air To Fuel Ratio ControlDocument68 pagesAir To Fuel Ratio Controlvivek_genx4737100% (2)
- Centrifugal Compressor BasicsDocument45 pagesCentrifugal Compressor BasicsAnkit Gandhi100% (1)
- Kelvin Lau MWI +RRDocument18 pagesKelvin Lau MWI +RRUniversityJCPas encore d'évaluation
- GEO424 Lect08 Soil Water Snow PDFDocument38 pagesGEO424 Lect08 Soil Water Snow PDFAires Rafael Rutherford AiresPas encore d'évaluation
- FTIR Crystal Referance GuideDocument11 pagesFTIR Crystal Referance GuideberkahPas encore d'évaluation
- NSTSE Class 7 Solved Paper 2009Document23 pagesNSTSE Class 7 Solved Paper 2009swainanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Well Testing PresentationDocument24 pagesWell Testing PresentationSaid71% (7)
- Common Names (Organic Compounds)Document8 pagesCommon Names (Organic Compounds)Tushar100% (5)
- Gasket Brochure Complete MDS EngDocument20 pagesGasket Brochure Complete MDS EngAditya JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Spent Fuel Pool Safety and Performance Chan Young PaikDocument23 pagesSpent Fuel Pool Safety and Performance Chan Young PaikIAEAInformationPas encore d'évaluation
- BCSP CSP Exam Study GuideDocument578 pagesBCSP CSP Exam Study GuideengineeramujtabaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Potentiometry 2013Document52 pages2 - Potentiometry 2013AtikDwiOktavianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Slump Test or Slump Cone TestDocument4 pagesConcrete Slump Test or Slump Cone TestEljoy C. AgsamosamPas encore d'évaluation
- Well Classification SystemDocument2 pagesWell Classification SystemMuhammad Naufal Nazhib KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 〈1207.2〉 Package Integrity Leak Test TechnologiesDocument15 pages〈1207.2〉 Package Integrity Leak Test TechnologiesTranNguyenBaoKhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Conduction (Linear)Document7 pagesHeat Conduction (Linear)Yi Ling GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Kluber PresentationDocument79 pagesKluber PresentationZegera MgendiPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison Chart: (828 Ratings) (877 Ratings)Document11 pagesComparison Chart: (828 Ratings) (877 Ratings)RosePas encore d'évaluation