Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Histology of Respiratory System Conducting Portion
Transféré par
Farahh ArshadDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Histology of Respiratory System Conducting Portion
Transféré par
Farahh ArshadDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Histology of respiratory system Conducting portion
Portion Larynx (hollow organ interposed between pharynx and trachea) Trachea (flexible tube continues with larynx above and bifurcates at its lower end to form bronchi) Bronchi (intrapulmonary bronchi) (Begins as bifurcation of trachea and may branch and decrease in size gradually) #Composed of airways located outside the lungs (primary bronchi, extrapulmonary bronchi) and airways located inside the lungs (secondary and tertiary bronchi, intrapulmonary bronchi) #Extrapulmonary bronchi have the same structure as trachea except smaller in diameter and thinner wall -Lined by respiratory epithelium -Smaller diameter than trachea -Lamina propria composed of loose fibroelastic CT Bronchioles
Mucosa
-2 pairs of mucosal folds: 1) Upper pair (vestibular fold) 2) Lower pair (vocal fold) -Lined by respiratory epithelium (pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium + goblet cells) -Lamina propria composed of loose CT and seromucous glands
-Lined by respiratory epithelium composed of: 1) Ciliated columnar cells 2) Goblet cells (contain mucinogen granules) 3) Basal cells (stem cells) 4) Brush cells (slender columnar cells with microvillous luminal border, less abundant than columnar and goblet cells, act as sensory cells) 5) Bronchial Kulchitsky cells (neuroendocrine function) -Lamina propria composed of loose CT rich in elastic fibres and lymphatic nodules. The elastic fibres condense to form elastic membrane separating lamina propria from submucosa
-Lined by ciliated columnar cells without goblet cells -The cilia gradually disappear and the cells become lower as bronchioles become smaller -The non-ciliated cells (Clara cells) characterized by apical microvilli and secretory granules. The granules secrete a fluid of protein nature that continuous with surfactant layer of alveoli that helps bronchioles patent during expiration -Neuroendocrine chemoreceptor cells present either separately (small granule cells) or in group (neuroepithelial bodies) giving a local active secretion -Lamina propria composed of loose CT rich in elastic fibres surrounded by circumferential smooth muscles
Created by Qosru Iskandariah
Submucosa
Muscularis Externa
-Kept open by hyaline cartilage (thyroid, cricoids, inferior aspect of arytenoids) and elastic cartilage (epiglottis, cuneiform, corniculate, superior aspect of arytenoids -Epiglottis projects upwards and backwards to close the larynx during swallowing -The core of vocal cord is made up of elastic tissue (vocal ligament) and skeletal muscle fibres in parallel bundles (vocal muscle). No gland
-Dense fibroelastic CT with seromucous glands -The ducts extend through elastic lamina (elastic membrane) to open onto the surface -Reinforced by 16-20 c-ring cartilaginous on its ventral and lateral aspects -Each ring is separated by fibroelastic CT to prevent over distension -At posterior aspect contains transversely arranged interlacing bundles of smooth muscles (trachealis muscles) connecting the 2 ends of c-ring
-Loose CT and mucoserous glands
-Smooth muscles are spirally arranged encircling the entire lumen between mucosa and cartilage -Its contraction during fixation results in longitudinal folds formation in mucosa -Discontinuous layer of hyaline cartilaginous plates that become smaller as bronchi become smaller. The plates are distributed around entire lumen giving bronchi circularshaped -Dense CT that continuous with adjacent structures -Lymph nodules are distributed in outer fibrous layer of bronchi
-No cartilaginous plate, no gland, no lymphatic nodule
Adventitia
-Fibroelastic CT -Most feature is hyaline cartilage (cshaped ring) and intervening fibrous CT -May anchor trachea to adjacent structures
Created by Qosru Iskandariah
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1st Lecture of Respiratory Histology by DR RoomiDocument24 pages1st Lecture of Respiratory Histology by DR RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Lung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesD'EverandLung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesAlain JunodPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine Notes - All in One FileDocument182 pagesEndocrine Notes - All in One FilekjPas encore d'évaluation
- IMD - Step-Up To USMLE Step 3 - Chapter 1 - CardiologyDocument124 pagesIMD - Step-Up To USMLE Step 3 - Chapter 1 - CardiologyAly SherifPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine: Ftplectures Endocrine System Lecture NotesDocument50 pagesEndocrine: Ftplectures Endocrine System Lecture NotesArif Setyawan100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagn Approach of Abdominal PainDocument53 pagesDiagn Approach of Abdominal PainNuriPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Cardiovascular System: Describe The Systemic Circulation in The Body and Give Its ImportanceDocument28 pages2 Cardiovascular System: Describe The Systemic Circulation in The Body and Give Its ImportanceBhavin ChangelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advances in Cattle WelfareD'EverandAdvances in Cattle WelfareCassandra TuckerPas encore d'évaluation
- Physio Coursepack 2016Document282 pagesPhysio Coursepack 2016Amanda KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesEpithelial TissueJoan PaulinePas encore d'évaluation
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyD'EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Embryology of Respiratory System NotesDocument3 pagesEmbryology of Respiratory System NotesJulienne Sanchez-SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs in Medicine by Medad Team FinalDocument5 pagesDrugs in Medicine by Medad Team Finalعبد الرحمن100% (2)
- Pain MedicationsDocument2 pagesPain MedicationsimirelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Gastroenterology and Hepatology Board Review ToolkitD'EverandPractical Gastroenterology and Hepatology Board Review ToolkitKenneth R. DeVaultPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebral Spinal Fluid & The MeningesDocument25 pagesCerebral Spinal Fluid & The MeningeschintyamontangPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Congenital Heart Disease: Eisenmenger’s Syndrome - A Global PerspectiveD'EverandPulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Congenital Heart Disease: Eisenmenger’s Syndrome - A Global PerspectivePas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of The Circulatory System Table-AnswersDocument2 pagesDisorders of The Circulatory System Table-Answersapi-281108263Pas encore d'évaluation
- Using The ACLS Primary Survey For A Patient in Respiratory ArrestDocument34 pagesUsing The ACLS Primary Survey For A Patient in Respiratory Arrest강기연100% (1)
- PRES (Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome) and Eclampsia-ReviewDocument5 pagesPRES (Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome) and Eclampsia-ReviewAvicena M IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case-Based Approach to Interventional Pulmonology: A Focus on Asian PerspectivesD'EverandA Case-Based Approach to Interventional Pulmonology: A Focus on Asian PerspectivesJamalul Azizi Abdul RahamanPas encore d'évaluation
- MS2 Cards Wigger DiagramDocument1 pageMS2 Cards Wigger DiagramCharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Ans 2 PDFDocument101 pagesAns 2 PDFrab yoPas encore d'évaluation
- Short and Long Term Regulation and Determinants of BPDocument90 pagesShort and Long Term Regulation and Determinants of BPDan Tristam MicabaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids&Lytes PediatricDocument33 pagesFluids&Lytes Pediatricnugraha_esaPas encore d'évaluation
- HistoryandPhysicalExamDocument105 pagesHistoryandPhysicalExamsilentscream0618Pas encore d'évaluation
- Uworld JournalDocument3 pagesUworld JournalJayPas encore d'évaluation
- Pericardial EffusionDocument3 pagesPericardial EffusionNita Hurek100% (1)
- Assessment of The Chest and LungsDocument46 pagesAssessment of The Chest and LungsSumathi GopinathPas encore d'évaluation
- Neet PG 2021 Q&A Medical JunctionDocument144 pagesNeet PG 2021 Q&A Medical JunctionKk bhaiPas encore d'évaluation
- EndocrineDocument23 pagesEndocrinensvickneswaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Thrombolytics - Hematology - Medbullets Step 1Document5 pagesThrombolytics - Hematology - Medbullets Step 1aymen100% (1)
- 3.0 Grand Physiology Finals Compilation - Batch 2017Document89 pages3.0 Grand Physiology Finals Compilation - Batch 2017Sheryl Layne Lao-SebrioPas encore d'évaluation
- Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed (2015) - 974-1006Document33 pagesGuyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed (2015) - 974-1006siñthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument29 pagesPeripheral Vascular DiseaseEva Bella100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Nursing: Study Online atDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Nursing: Study Online atLilly DayePas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced 12-Lead InterpretationDocument30 pagesAdvanced 12-Lead InterpretationRohini SelvarajahPas encore d'évaluation
- Head To Toe Checklist (Masroni)Document13 pagesHead To Toe Checklist (Masroni)hillary elsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Chest Pain in Primary Care Patients-AAFPDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Chest Pain in Primary Care Patients-AAFPnouval_iqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdomen Engl PDFDocument51 pagesAbdomen Engl PDFShuler0071Pas encore d'évaluation
- Epithelial TissueDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissuememe bolongonPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of AirwaysDocument6 pagesAnatomy of Airwaysgdubs215Pas encore d'évaluation
- Common Bacteria by Site of Infection: Mouth Skin/Soft Tissue Bone and JointDocument72 pagesCommon Bacteria by Site of Infection: Mouth Skin/Soft Tissue Bone and JointMuthia FadhilaPas encore d'évaluation
- PharynxDocument2 pagesPharynxameerabest0% (1)
- 2014 SHC ABX Dosing GuideDocument4 pages2014 SHC ABX Dosing GuideisnaeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Diuretic eDocument2 pagesDiuretic ejustme_adryPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemcatchivanPas encore d'évaluation
- Body CavitiesDocument22 pagesBody Cavitiesapi-421876553Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular Physiology 4 - Gomez MD PDFDocument65 pagesCardiovascular Physiology 4 - Gomez MD PDFMelissa SalayogPas encore d'évaluation
- Abx FinalDocument3 pagesAbx Finalyanks1120Pas encore d'évaluation
- Male Genital System - Pathology (Lect 10-12)Document83 pagesMale Genital System - Pathology (Lect 10-12)Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Cervical Polyp and Carcinoma - Pathology (Lect22-11)Document29 pagesCervical Polyp and Carcinoma - Pathology (Lect22-11)Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Ovary (Lect 19-11)Document28 pagesOvary (Lect 19-11)Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Semen Practical BiochemDocument51 pagesSemen Practical BiochemFarahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- PERINEUM and Urogenital Triangle (Lect 18-11)Document29 pagesPERINEUM and Urogenital Triangle (Lect 18-11)Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- SectionDocument1 pageSectionFarahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S9Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S9Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S1Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S1Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S2Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S2Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S7Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S7Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
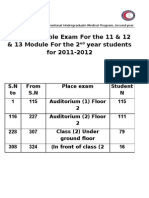
- Jadual ExamDocument1 pageJadual ExamFarahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Tempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S8Document2 pagesTempahan Gambar Batch (FINALE) S8Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Price List (Unit Economy ACE 2012)Document2 pagesPrice List (Unit Economy ACE 2012)Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Week (IUMP)Document2 pages1st Week (IUMP)Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Week (IUMP)Document2 pages2nd Week (IUMP)Farahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 11. 12 - 13 ExamDocument1 pageModule 11. 12 - 13 ExamFarahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of Adrenal GlandDocument20 pagesDiseases of Adrenal GlandFarahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormones & MetabolismDocument3 pagesHormones & MetabolismFarahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology BacteriaDocument4 pagesMicrobiology BacteriaFarahh ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- RESPI QuestionsDocument15 pagesRESPI QuestionsKim Anulacion100% (1)
- Biosys Katalog ENDocument12 pagesBiosys Katalog ENOğuzhanÖçbePas encore d'évaluation
- Cap NCPDocument6 pagesCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- Analisa Jurnal PneumoniaDocument14 pagesAnalisa Jurnal PneumoniaSindy OctaPas encore d'évaluation
- BRONCHOSDocument6 pagesBRONCHOSrajnishpathak648Pas encore d'évaluation
- Consenso Chileno de Técnicas de Kinesiología Respiratoria en PediatríaDocument15 pagesConsenso Chileno de Técnicas de Kinesiología Respiratoria en PediatríaRobert CerdaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsiaeclampsia - Hellp SyndromeDocument23 pagesNCP: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsiaeclampsia - Hellp SyndromeKath100% (2)
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument8 pagesCase Study PneumoniaThesa FedericoPas encore d'évaluation
- Decrease in Paco2 With Prone Position Is Predictive of Improved Outcome in Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument7 pagesDecrease in Paco2 With Prone Position Is Predictive of Improved Outcome in Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromedarwigPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 11 Laboratory Exercise The Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesWeek 11 Laboratory Exercise The Respiratory SystemEricka ElloPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For High Acuity Nursing 6th Edition Kathleen Dorman WagnerDocument18 pagesTest Bank For High Acuity Nursing 6th Edition Kathleen Dorman WagnerDavidRobinsonfikq100% (35)
- Pneumothorax: DR - Naveen Vennilavan R Pg-IiiDocument95 pagesPneumothorax: DR - Naveen Vennilavan R Pg-Iiinaveen vennilavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Care of Client With Respiratory System DisordersDocument17 pagesCare of Client With Respiratory System DisordersAYTONA, JAMAICA F.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tatalaksana Kegawatan Di UGD Dan Faskes PrimerDocument52 pagesTatalaksana Kegawatan Di UGD Dan Faskes PrimerBudiman BahagiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen InsufficiencyDocument24 pagesOxygen InsufficiencyAnusha VerghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Breathing and Coughing ExercisesDocument14 pagesBreathing and Coughing Exercisesanulalparayil2003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vaka TustimeDocument887 pagesVaka TustimeMohamed AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- NursingBulletin Notes On PneumothoraxDocument27 pagesNursingBulletin Notes On Pneumothoraxseigelystic100% (11)
- Greys-Anatomy-Student (1) - CompressedDocument2 pagesGreys-Anatomy-Student (1) - CompressedKaranPas encore d'évaluation
- EpistaxisDocument21 pagesEpistaxisgoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Covidien TrachProduct Poster PDFDocument1 pageCovidien TrachProduct Poster PDFsimoncoPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen TherapyDocument25 pagesOxygen Therapypolosan123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ventilator Waveform AnalysisDocument96 pagesVentilator Waveform AnalysisVeerapong Vattanavanit100% (11)
- Newborn Resuscitation..Document125 pagesNewborn Resuscitation..Rahul DhakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study On AtelectasisDocument14 pagesCase Study On AtelectasisSanhati Ghosh BanerjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Preparing MedicationsDocument18 pagesPreparing MedicationsJuliezel IringanPas encore d'évaluation
- Absen Pembacaan Telaah Jurnal Suci RamadhaniDocument2 pagesAbsen Pembacaan Telaah Jurnal Suci Ramadhanisuci ramadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 Biology 11Document36 pagesChapter 11 Biology 11ax1lePas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen Therapy - Facemask, Nasal ProngDocument47 pagesOxygen Therapy - Facemask, Nasal ProngLimYiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - Drugs For AsthmaDocument75 pages5 - Drugs For Asthmanica velano100% (1)