Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Renal Failure Diagram
Transféré par
Michelle BarojaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Acute Renal Failure Diagram
Transféré par
Michelle BarojaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
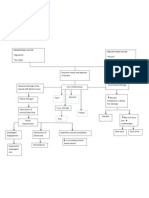
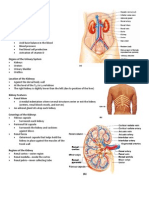
ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Non-Modifiable Risk Factor Advanced Age
Modifiable Risk Factor: Atherosclerosis Heart Disorders Low Blood Pressure Kidney Disorders
Prerenal Causes: Hypotension Hypovolemia (Shock) Decreased cardiac output Dehydration Hepatorenal syndrome Liver failure Atheroembolic disease Renal vein thrombosis Nephrotic syndrome Obstetrical Complications Diabetes type I and type II
Intrarenal Causes: Nephrotoxic episodes Infection Systemic inflammation Injured red blood cells Hemolytic blood transfusion reactions Glomerular diseases (systemic lupus, glomerulonephritits) Rhabdomylolysis Pancreatitis Hypercalcemia
Postrenal Causes: Medication that interferes with normal bladder emptying. Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) Prostate cancer Ovarian cancer Obstruction of a urinary catheter Renal calculi Bladder/pelvic neoplasms Urethral strictures Spinal disease
Constriction of urethra
Obstruction in urine flow
oliguria
Fluid accumulation and retention in the bladder
Bladder distension
Urine backflow to the Kidneys
Damage of cells in the tubules
Trauma to the bladder
GFR
Pain in the Lower abdomen
Filtrate components are not filtered Cell necrosis and ischemia
Blood filtrates are excreted
hematuria
blood volume
Creatinine, urea, uric acid retained and backflow to system
serum Creatinine and BUN
Nausea, Vomiting, bitter taste
uremia ANEMIA Edema esp. in lower extremities
Mr. Oriented is a 66-year-old male and was diagnosed having Benign Prostate Hyperplasia. Prostate enlargement obstructs the urine flow out of the bladder. Excretion then is impaired. Oliguria is present. As urine accumulates in the bladder, fluid retention and abdominal distention occur. Pain is present in the lower midline abdomen. Bladder cannot accommodate urine volume. Urine moves back ward going to the kidney causing the tubular cells to slough and blocks the membrane. GFR decreases. As it decreases, nitrogeneous waste are retained and while blood components are excreted. Increase nitrogeneous waste will cause increase serum BUN and Creatinine. Blood urea will cause nausea, vomiting, anemia, and when severe seizure and pruritus. Blood components that cross the semi permeable membrane will be excreted and hematuria will manifest. There will be increase in fluid volume due to impaired urinary elimination. Third spacing may occur.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Renal Diet Cookbook: 100 Simple & Delicious Kidney-Friendly Recipes To Manage Kidney Disease (CKD) And Avoid Dialysis (The Kidney Disease Cookbook)D'EverandRenal Diet Cookbook: 100 Simple & Delicious Kidney-Friendly Recipes To Manage Kidney Disease (CKD) And Avoid Dialysis (The Kidney Disease Cookbook)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionD'EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver CirrohosisDocument157 pagesLiver CirrohosisSeema SachdevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDocument22 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorJorie RocoPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Document8 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie RocoPas encore d'évaluation
- Presented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureDocument40 pagesPresented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureRavanshi ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney Injurymariaclaramutya100% (1)
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument106 pagesCirrhosis of LiveraahadPas encore d'évaluation
- MetabolismDocument39 pagesMetabolismTiffany KnepperPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute-Renal-Failure Lecture OnlyDocument17 pagesAcute-Renal-Failure Lecture OnlyeyesontheskyPas encore d'évaluation
- Complications of CirrhosisDocument2 pagesComplications of CirrhosisDanielle DiorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternative NamesDocument67 pagesAlternative NamespashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complications of Cirrhosis MbbsDocument16 pagesComplications of Cirrhosis MbbsNadun MethwadanePas encore d'évaluation
- Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas ProblemsDocument95 pagesLiver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas ProblemsBav VAansoqnuaetzPas encore d'évaluation
- CKD - For Concept MappingDocument7 pagesCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- Hepatic Cirrhosis (肝硬化): Yu BaopingDocument62 pagesHepatic Cirrhosis (肝硬化): Yu BaopingKurbulPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal SystemDocument20 pagesRenal SystemRahul DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument35 pagesCirrhosis of LiverShazia Parveen100% (1)
- Acute and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument20 pagesAcute and Chronic Kidney DiseaseCabdi WaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Renal FailureDocument28 pagesAcute Renal FailureAs SyarifPas encore d'évaluation
- CKDDocument3 pagesCKDMarc Lawrence Balderas CAra100% (2)
- Chronic Renal Failure-7Document5 pagesChronic Renal Failure-7GERA SUMANTHPas encore d'évaluation
- MS AddsDocument4 pagesMS Addsapi-3731294Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of Urogenital TractDocument170 pagesDiseases of Urogenital TractMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 CKDDocument53 pagesLecture 3 CKDPharmswipe KenyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Interpretive Summary: Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)Document3 pagesInterpretive Summary: Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)Wael SafwatPas encore d'évaluation
- Presented By: Medicine Unit 1Document95 pagesPresented By: Medicine Unit 1Abdullah Muceddidi100% (1)
- Renal FailureDocument4 pagesRenal FailureMunish DograPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Disorders, Renal Failure, & Renal Dialysis: Remerose C. Ragasa, R.NDocument41 pagesRenal Disorders, Renal Failure, & Renal Dialysis: Remerose C. Ragasa, R.NremerosePas encore d'évaluation
- AkiDocument42 pagesAkimarauder_popPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument23 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryBaraka SayorePas encore d'évaluation
- Cirrhosis: Petrus J. HasibuanDocument17 pagesCirrhosis: Petrus J. HasibuanAgustinus VincentPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Liver DiseaseDocument30 pagesChronic Liver Diseaseprajwal86% (7)
- BubreDocument10 pagesBubreharryPas encore d'évaluation
- CirrhosisDocument54 pagesCirrhosisYani86% (7)
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Document47 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Abinaya RanganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- GI Bleeding - Acute PancreatitisDocument67 pagesGI Bleeding - Acute PancreatitisandikaisnaeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersDocument72 pagesPediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersMarie Angelique Cruz CrestaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Portal HypertensionDocument23 pagesPortal HypertensionSumathi GopinathPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal - Pathophysiology 2020 PDFDocument89 pagesRenal - Pathophysiology 2020 PDFHardian HardianPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Renal FailureDocument4 pagesAcute Renal FailurePerrilyn PereyPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho of Liver Cirrhosis 22222 (Repaired)Document2 pagesPatho of Liver Cirrhosis 22222 (Repaired)Maxie PacadaPas encore d'évaluation
- CirrhosisDocument55 pagesCirrhosisFUTURE DOCTORPas encore d'évaluation
- Prezentare Ciroza Eng Semne Si SimptDocument64 pagesPrezentare Ciroza Eng Semne Si SimptDăscălașu CatalinaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) ?Document2 pagesWhat Is End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) ?Vecky TolentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument28 pagesChronic Renal FailuremarshmalouPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic RenalDocument5 pagesChronic Renaljazzy penzPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument4 pagesChronic Renal FailureHercy Emarie AnabePas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation Liver CirrhosisDocument26 pagesPresentation Liver CirrhosisFaye Dominique Roxas PalmaresPas encore d'évaluation
- CRF TextbookDocument5 pagesCRF TextbookThirdie LacortePas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Support in Hepatic Patient: by Mohammed Dabbour Lecturer of Anesthesia Ain Shams UniversityDocument36 pagesRenal Support in Hepatic Patient: by Mohammed Dabbour Lecturer of Anesthesia Ain Shams UniversityTrishenth FonsekaPas encore d'évaluation
- CKD NotesDocument11 pagesCKD NotesMaria WibawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeDocument19 pagesHepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeRacha MougharbelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument5 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseFaye R. PelayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Kidney Failure FactsDocument19 pagesKidney Failure Factss.khan9211rediffmail.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Take Home Exam - Ali, Habiba L.Document5 pagesTake Home Exam - Ali, Habiba L.hally_lipPas encore d'évaluation
- Kidney FailureDocument2 pagesKidney Failuredanee しPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesD'EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Kidney Disease Case PresentationDocument14 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Case PresentationEmi EspinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Benefit of All Asanas. D. ShamikhaDocument47 pagesBenefit of All Asanas. D. Shamikhabiplav dassPas encore d'évaluation
- B Braun Vet SuturesDocument45 pagesB Braun Vet SuturesHisyam AdityaPas encore d'évaluation
- Punjab National Bank HRDD Cir. NO. 515 Human Resources Development DivisionDocument16 pagesPunjab National Bank HRDD Cir. NO. 515 Human Resources Development DivisionHIMANSHU SADANPas encore d'évaluation
- Elimination PatternDocument29 pagesElimination PatternShaheen Khowaja0% (1)
- Handouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Document7 pagesHandouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Kelly Trainor100% (2)
- Síndrome Adrenogenital e Alterações Anatômicas PDFDocument10 pagesSíndrome Adrenogenital e Alterações Anatômicas PDFFred SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bubbles HeDocument39 pagesBubbles HePerrilyn PereyPas encore d'évaluation
- Utis, Bacteria & Antibiotics: By: A Team of Health ProfessionalsDocument17 pagesUtis, Bacteria & Antibiotics: By: A Team of Health ProfessionalsAbdul QaharPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Urinary Disorders - 2012 - Small Animal Clinical Diagnosis by Laboratory Methods Fifth EditionDocument30 pages7 Urinary Disorders - 2012 - Small Animal Clinical Diagnosis by Laboratory Methods Fifth EditionNarvarte Hospital Veterinario de EspecialidadesPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQS, PelvisDocument23 pagesMCQS, PelvisICIKITI JOELPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis and Classification of Urethral InjuriesDocument13 pagesDiagnosis and Classification of Urethral Injuriesleo100% (2)
- Neurogenic BladderDocument4 pagesNeurogenic BladderBonna PakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Uti PathoDocument3 pagesUti PathoThrinPas encore d'évaluation
- RID - VesicolithotomyDocument30 pagesRID - VesicolithotomyDwiyanti Oktavia100% (2)
- Urinary System WorksheetDocument4 pagesUrinary System WorksheetTENNESSEE AYALAPas encore d'évaluation
- Symptomatology Clinical Manifestations Actual Ideal Significance Basis FeverDocument5 pagesSymptomatology Clinical Manifestations Actual Ideal Significance Basis FeveropxPas encore d'évaluation
- HLTAAP001 - Horia RevisedDocument74 pagesHLTAAP001 - Horia RevisedYouYou Tube80% (5)
- Urinary System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)Document44 pagesUrinary System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter (14) Assessment of Urinary System: Faculty of Nursing-IUGDocument8 pagesChapter (14) Assessment of Urinary System: Faculty of Nursing-IUGVeenasravanthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Urodynamic Testing ReportDocument25 pagesUrodynamic Testing Reportzharah180% (1)
- Studer Surgical - Images - of - Ileal - ConduitDocument11 pagesStuder Surgical - Images - of - Ileal - ConduitTomek RPas encore d'évaluation
- Micturition 2022Document20 pagesMicturition 2022Mohammad zreadPas encore d'évaluation
- A Nursing Case StudyDocument105 pagesA Nursing Case StudyStephen Tumbaga75% (4)
- The Human Renal SystemDocument8 pagesThe Human Renal SystemRobert CaseyPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd MDocument1 pageReflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd MTharani KumaraPas encore d'évaluation
- 3312 Adult Health Exam 4 Study GuideDocument15 pages3312 Adult Health Exam 4 Study GuideRyanne JPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurogenic Bladder: When Nerve Damage Causes Bladder ProblemsDocument3 pagesNeurogenic Bladder: When Nerve Damage Causes Bladder ProblemsmarselamgePas encore d'évaluation
- Brmedj07820 0019Document1 pageBrmedj07820 0019cleybismarPas encore d'évaluation
- Asuhan Keperawatan BPH - YunahDocument51 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan BPH - YunahYuds YudsPas encore d'évaluation