Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pipe Joint
Transféré par
imrankhan22Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pipe Joint
Transféré par
imrankhan22Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Engineering Standard
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components Piping Standards Committee Members
Nasri, Nadhir Ibrahim, Chairman Dib, Tony Georges, Vice Chairman Balhareth, Nasser Mohammad Bannai, Nabeel Saad Fadley, Gary Lowell Holland, Brad John Khashab, Jaafar M. Lewis, Trevor Mahmoud, Khalid Ahmed Phan, Howard Cong Rao, Sanyasi Rasheed, Mahmood A. Sharif, Talal Mahmoud Shiha, Saad Mohammed Swar, Ahmad H. (ABQ PLANTS)
18 May 2008
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Table of Contents 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Scope............................................................. 2 Conflicts and Deviations................................. 2 References..................................................... 2 Definitions....................................................... 4 Welded Joints................................................. 5 Prohibited Piping Joints and Components..... 6 Threaded Joints.............................................. 6 Flanged Joints................................................ 7 Seal Welding of Threaded Joints................... 8 Pipe Fittings General Requirements............... 9 Threaded and Socket Welding Fittings.......... 9 Steel Butt Welding Fittings............................ 10 Branch Connection Type and Fittings.......... 10 Specialty and Proprietary Couplings............. 11
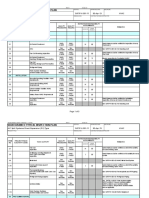
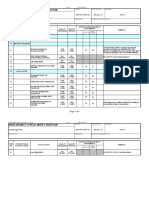
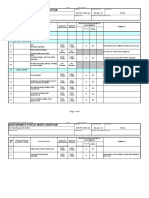
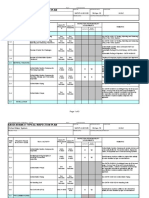
Chart 1 Branch Connections............................ 12
Previous Issue: 24 January 2007 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013 Revised paragraphs are indicated in the right margin Primary contact: Nasri, Nadhir Ibrahim on 966-3-8734525
CopyrightSaudi Aramco 2008. All rights reserved.
Page 1 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
Scope 1.1 This Standard covers the limitations on various types of piping joints and components used in metallic piping for pressure piping systems within the context of SAES-L-100. This Standard covers additional requirements to ASME B31.1, B31.3, B31.4 and B31.8 piping codes and defines requirements governing the selection of metallic pipe fittings, bends, miters, laps, and branch connections for plant piping and pipelines. Tube fittings and other specialty fittings are outside the scope of this standard.
1.2
Conflicts and Deviations 2.1 Any conflicts between this standard and other applicable Saudi Aramco Engineering Standards (SAESs), Materials System Specifications (SAMSSs), Standard Drawings (SASDs), or industry standards, codes, and forms shall be resolved in writing by the Company or Buyer Representative through the Manager, Consulting Services Department (CSD) of Saudi Aramco, Dhahran. Direct all requests to deviate from this standard in writing to the Company or Buyer Representative, who shall follow internal company procedure SAEP-302 and forward such requests to the Manager, Consulting Services Department of Saudi Aramco, Dhahran.
2.2
References The selection of material and equipment, and the design, construction, maintenance, and repair of equipment and facilities covered by this standard shall comply with the latest edition of the references listed below, unless otherwise noted. 3.1 Saudi Aramco References Saudi Aramco Engineering Procedure SAEP-302 Instructions for Obtaining a Waiver of a Mandatory Saudi Aramco Engineering Requirement
Saudi Aramco Engineering Standards SAES-B-017 SAES-L-100 Fire Water System Design Applicable Codes and Standards for Pressure Piping Systems
Page 2 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
SAES-L-101 SAES-L-109 SAES-L-136 SAES-L-350 SAES-W-011 SAES-W-012 SAES-W-013
Regulated Vendor Lit for Pipes, Fittings and Gaskets Selection of Flanges, Stud Bolts and Gaskets Pipe Selection and Restrictions Construction of Plant Piping Welding Requirements for On-plot Piping Welding Requirements for Pipelines Welding Requirements for Offshore Structures
Saudi Aramco Materials System Specifications 02-SAMSS-001 02-SAMSS-005 Piping Components for Low Temperature Service Butt Welding Pipe Fittings
Saudi Aramco Standard Drawings AD-036090 AE-036175 AC-036404 AE-036643 AB-036719 3.2 Industry Codes and Standards American Petroleum Institute API SPEC 6A API STD 602 Wellhead and Christmas Tree Equipment Compact Steel Gate Valves - Flanged, Threaded, Welding, and Extended-Body Ends Joints for Welding Cement Lined Pipe Detail of Welding Boss, Threaded Connection to Vessels and Lines Flame Impingement Shield for Flangeless Valve Heavy Welding Boss, Socket Weld Connections Reinforcement of Welded Branch Connections
American Society of Mechanical Engineers ASME B16.11 ASME B1.20.1 ASME B16.25 ASME B16.3 ASME B16.9 Forged Steel Fittings, Socket-Welding and Threaded Pipe Threads, General Purpose (Inch) Buttwelding Ends Malleable Iron Threaded Fittings Factory-Made Wrought Buttwelding Fittings
Page 3 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
ASME B31.1 ASME B31.3 ASME B31.4 ASME B31.8 ASME SEC VIII D2
Power Piping Process Piping Pipeline Transportation Systems for Liquid Hydrocarbons and Other Liquids Gas Transmission and Distribution Piping Systems Pressure Vessels, Alternative Design
American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM A105 ASTM A182 Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Forgings for Piping Applications Standard Specification for Forged or Rolled Alloy-Steel Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, and Valves and Parts for High-Temperature Service Standard Specification for Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel Forgings, Requiring Notch Toughness Testing for Piping Components
ASTM A350
Manufacturers Standardization Society MSS SP-43 MSS SP-75 MSS SP-79 MSS SP-83 MSS SP-95 MSS SP-97 Wrought Stainless Steel Butt-Welding Fittings Specification for High Test Wrought Butt Welding Fittings Socket-Welding Reducer Inserts Steel Pipe Unions, Socket-Welding and Threaded Swaged (d) Nipples and Bull Plugs Integrally Reinforced Forged Branch Outlet Fittings-Socket Welding, Threaded, and Buttwelding Ends
International Standardization Organization ISO 15156 Petroleum and Natural Gas industries Materials for use in H2S-Containing Environments in Oil and Gas Production
Definitions Metal to Metal Seal Joint: A joint that relies on the mechanical fit between metals to seal against pressure.
Page 4 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
Proprietary /Specialty Coupling: A joint that is developed and possibly patented by a particular firm and could be not covered by any Industry Code. LokRing: It is a proprietary coupling used to join two pipes together. It relies on the mechanical grip between the pipe (female) and the joint (male). Positive Seal Coupling: It is a proprietary coupling used to join two pipes together. It relies on the mechanical grip between the pipe (male) and the joint (female). 5 Welded Joints 5.1 Pipe Welds Welds in metallic piping shall conform to the requirements to the applicable welding standard which are SAES-W-011, SAES-W-012 and SAES-W-013 and other Standards referenced therein. 5.1.1 When wall thickness ratio of joined pipes is less than or equal to 1.5, joint design details shall comply with the respective ASME B31 design code. When wall thickness ratio of joined pipes is greater than 1.5, end preparations and geometry shall comply with ASME B16.25 "Butt Welding Ends". For all four piping codes stated in paragraph 5.1.2 above, refer to Figure 434.8.6(a)-(2) in ASME B31.4 or Figure 15 in ASME B31.8 for graphic details of joint designs. When the wall thickness of the fitting or pipe at the welding end exceeds the wall thickness of the matching pipe resulting in an unequal external and/or internal diameters, the welded joint design shall comply with Fig. 434.8.6(a)-(2) of ASME B31.4 (regardless of the design code).
5.1.2
5.1.3
5.1.4
5.2
Socket Welds 5.2.1 The maximum size of socket-welded joints in hazardous services shall be 1-inch for new construction. Maximum 2-inch may be used in hazardous service for maintenance, minor field modifications of existing piping systems, and when necessary to match existing equipment connections. For sour service, socket-welded joints should be avoided. In case they could not be avoided the maximum size of socket-welded joints shall be 1-inch.
5.2.2
Page 5 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013 Commentary Note:
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
Generally, socket welded joints should be avoided in any service where crevice corrosion, severe erosion, or cyclic loading may occur.
5.2.3
Socket weld joints are not permitted in location where high vibration can occur (such as high velocity gas control valves and reciprocating pumps). The axial gap between male and female component, as shown in Figure 328.5.2C of ASME B31.3 code, shall be maximum of 3 mm and minimum of 1.5 mm. This gap is required prior to welding.
Commentary Note: This axial gap requirement is only applicable to new installation of socket welds for new construction, maintenance and modification. It does not apply to piping already installed and welding was completed successfully.
5.2.4
5.3
Fillet Welds The use of sleeve couplings per Standard Drawing AD-036090 shall be limited to cement lined pipe in water services such as fire fighting piping systems and oily water service.
Prohibited Piping Joints and Components The following piping components are not allowed and shall not be used in pressure piping system within the scope of SAES-L-100. a) b) c) d) Caulked joints. Soldered, brazed, and braze-welded joints. Expanded joints: They are slip on type of joints using O-ring to seal the pressure. Bell-type and packed joints
Threaded Joints 7.1 The thread joints shall be taper pipe thread (NPT) conforming to ASME B1.20.1 unless otherwise required by specifications for specific connections. Threaded connections for fire services are exempted and shall be in accordance with SAES-B-017.
Commentary Note: Generally, threaded joints should be avoided in any service where crevice corrosion, severe erosion, or cyclic loading may occur.
Page 6 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
7.2
In hazardous services, the maximum size of threaded connections shall be 1-inch for standard fittings and valves, and 2-inch maximum when required for maintenance, minor field modifications of existing piping systems, and to match threaded specialty devices such as scraper signals and access fittings for corrosion monitoring. In non-hazardous services, the maximum size of threaded connections shall be 3-inch for standard fittings and valves, and 4-inch maximum on special items such as fire hydrants unless a larger size is approved by the assigned Chairman, Piping Standards Committee for the specific application. The minimum length of the engaged threads pipe shall meet the requirements of ASME B1.20.1 for taper pipe thread. The minimum number of engaged pipe threads shall meet the requirements of Table 1. Table 1 Thread Engagement Requirements for Taper Pipe Threads
Nom. Pipe Size 1/2" & 3/4" 1" through 1-1/2" 2" through 3" 4" Number of Threads Engaged 6 7 8 10
7.3
7.4
7.5
PTFE (Teflon) tape shall not be used for service temperature greater than 204C on threaded connections.
Flanged Joints 8.1 Flanged connections shall be avoided when butt-welded joints can be used in services and locations where leaks are likely to occur (e.g., cyclic or vibration services), or will cause serious hazard (e.g., potentially toxic material), or are difficult to control, such as the following: a) b) c) d) Steam in ASME class 900 pressure rating In the fully restrained portion of cross-country pipelines and in underwater pipelines In locations where the piping will be subjected to large bending or other external loads On buried piping system
Page 7 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
8.2
Flanged connections with long exposed bolts for sandwiched components, other than standard spectacle plates and blinds, shall not be used in fire hazardous areas unless the bolting is protected by a fire resistant shield such as illustrated on Standard Drawing AC-036404 or equivalent method. (Ref. SAES-B-006). Selection of flanges shall be in accordance with SAES-L-109.
8.3 9
Seal Welding of Threaded Joints 9.1 9.2 Seal welds are permitted to be used to prevent leakage of threaded joints. It shall not be considered as contributing factor to the strength of the threaded joints. Seal welding of all threaded joints up to the first block valve is required in the following services and applications: a) b) c) d) e) f) 9.3 All hydrocarbons. Boiler feed water, condensate, and steam systems utilizing ASME Class 300 and higher flange ratings. Toxic materials such as chlorine, phenol, hydrogen sulphide, etc. Corrosive materials such as acid, caustic, etc. Oilfield chemicals (e.g., corrosion inhibitors, emulsifiers, electrolytes, etc.) Piping which is subject to vibration, whether continuous or intermittent
Seal welding is not required for the following services and applications: a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) Thermowells Bar stock plugs downstream of a seal-welded block valve. Special devices such as access fittings and scraper signals. Joints which require frequent disassembly and are located downstream of a seal welded block valve, e.g., sample connections. Instrument piping downstream of the primary instrument isolation valve. Pipe union ring threads and joints with elastomer o-rings. Threaded joints, downstream of a seal welded root valve, which discharge directly to an open drainage system or to the atmosphere. Extended body valves with integrally reinforced welding end per API STD 602.
9.4
Where seal welding is required, the seal weld shall be a fillet weld going from the outer diameter of the female part, and it should be smooth with slight
Page 8 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
concavity as allowed by ASME B31, to the male part covering all exposed threads without undercut. 9.5 PTFE (Teflon) tape or joint compounds shall not be used in threaded connections requiring seal welding.
10
Pipe Fittings General Requirements 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 All metallic pipe fittings shall be fully compatible with the adjoining pipe and shall be subject to the limitations of SAES-L-136 for carbon steel line pipe. The pipe fittings shall be sourced from an approved manufacturer per SAES-L-101. Carbon steel fittings shall be in accordance with the requirements of 02-SAMSS-005. For service with design minimum temperature between minus 18C to minus 45C, the fittings shall comply with additional requirements of 02-SAMSS-001.
11
Threaded and Socket Welding Fittings 11.1 11.2 For steel piping in hazardous services, threaded and socket welding fittings shall conform to ASME B16.11 Class 3000, Class 6000 or higher. Pipe unions in hazardous services shall be limited to Class 3000 threaded or socket welding forged steel unions in accordance with MSS SP-83. The material shall be carbon steel per ASTM A105, ASTM A350 or alloy steel per ASTM A182. Pipe unions shall not be installed in the pipe section between the main pipe run and root valve. Threaded bushings with one size reduction shall not be used. When bushings are allowed, only hex head steel bushings shall be used. Flush steel bushings are not permitted. Welding bosses shall be forged steel ASTM A105, ASTM A350 or ASTM A182, as applicable, as shown on Standard Drawings AE-036175 or AE-036643. Integrally reinforced welding outlets of approved design (such as Weldolets, Threadolets, Sockolets, etc.) in Class 3000, 6000 or higher, as applicable, which abut the pipe wall with a full penetration weld are acceptable.
11.3
11.4
11.5
Page 9 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
11.6
Malleable iron screwed fittings shall conform to ASME B16.3 Class 150 and shall be galvanized and limited to non-hazardous services, except that pipe unions shall be Class 300. Pipe plugs for use in metallic piping shall be solid body, bar-stock, or forged steel plugs in accordance with ASME B16.11.
11.7
12
Steel Butt Welding Fittings 12.1 The material and purchasing requirements of carbon steel buttweld fittings to: ASTM A234 Grade WPB and MSS SP-75 shall conform to the requirements of 02-SAMSS-005. Steel butt welding fittings shall conform to 02-SAMSS-005. Integrally reinforced welding outlets not listed in SAMS Catalog shall be of a design approved by the Chairman of the Piping Standards Committee. Refer to SAES-L-350 for post weld heat treatment requirements for welding outlets. Miter elbows are not permitted. In case miter bends have to be used prior approval by the Chairman of the Piping Standards Committee is required.
12.2 12.3
12.4
13
Branch Connection Type and Fittings 13.1 Selection of the tee branch connections type and fittings shall be as follows: 13.1.1 13.1.2 For new construction of metallic piping selection shall be made in accordance with the Chart 1. In case a branch connection with reinforcement has been selected according to paragraph 13.1.1, the size of the reinforcement pad shall be per the applicable code. For field modifications to existing piping, the branch connections as shown on SASD AB-036719 with proper reinforcement are acceptable.
13.1.3 13.2
Laterals and crosses 13.2.1 Crosses are not permitted. Laterals shall be used only when required by Saudi Aramco standards. They should be used for low pressure system (less than 150 psig) such as flare lines. Laterals fittings shall be designed for a bursting strength at least equal to the bursting strength of the adjoining pipe.
13.2.2
Page 10 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
13.2.3
Laterals made by welding the branch pipe directly to the run pipe shall be designed according to the code and shall have complete encirclement reinforcement. Laterals shall be shop fabricated according to 01-SAMS-010 and subjected to minimum 90% SMYS hydrotest pressure.
13.3
Branch connections, such as those for drain and vent connections, on tees, elbows and reducers are not permitted. When not avoidable, the piping design shall be reviewed and approved by the Chairman of Piping Standards Committee.
14
Specialty and Proprietary Couplings 14.1 Any new proprietary or specialty mechanical joints regardless of service shall be evaluated and approved by the Chairman of Piping Standards Committee, prior to specification and installation. Examples are Victaulic couplings and Dresser couplings. Metal to Metal Seal Coupling The following proprietary pipe couplings are acceptable within the limitations specified for each one: 14.2.1 Positive Seal Coupling The use of Positive Seal Coupling is limited to on shore pipelines for non-hazardous service and limited to 12 inch maximum diameter. 14.2.2 LokRing Coupling The use of LokRing coupling is limited to piping 2 inch maximum for instrument air, nitrogen gas, and water service. 14.3 Clamp-type connectors for high pressure services shall conform to API SPEC 6A or shall be proprietary connectors of a design based on ASME SEC VIII and approved by the Chairman, Piping Standards Committee in the Consulting Services Department (for example, Grayloc, Techlok, etc.). Proprietary couplings for pipeline repair, such as Plidco, Weld + Ends couplings, proprietary swivel joints, such as Chiksan, or similar specialties shall be of a design approved by the Chairman, Piping Standards Committee in the Consulting Services Department.
14.2
14.4
Page 11 of 12
Document Responsibility: Piping Issue Date: 18 May 2008 Next Planned Update: 18 May 2013
SAES-L-110 Limitations on Pipe Joints and Components
Chart 1 Branch Connections
18 May 2008
Revision Summary Revised the "Next Planned Update". Reaffirmed the contents of the document and reissued with minor revision.
Page 12 of 12
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Piping Design Requirements PDFDocument6 pagesPiping Design Requirements PDFkarunaPas encore d'évaluation
- SP PI PP 001 (General Piping System)Document49 pagesSP PI PP 001 (General Piping System)Ari IndrajayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Specification For GRP Pipes and Piping ComponentDocument43 pagesTechnical Specification For GRP Pipes and Piping ComponentngoctuanPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview Of: Piping Material SpecificationDocument60 pagesAn Overview Of: Piping Material SpecificationNeeraj Bora100% (10)
- Module 8 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingDocument4 pagesModule 8 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingSheila Mae Paltep100% (3)
- Saes L 136Document8 pagesSaes L 136kartik_harwani4387Pas encore d'évaluation
- 04-SAMSS-002 Globe Valves PDFDocument11 pages04-SAMSS-002 Globe Valves PDFSaeed KazemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Piping Materials Brochure PDFDocument9 pagesSpecial Piping Materials Brochure PDFshankarmech04@gmail.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Tech. Spec. For Flanges and Spectacle BlindsDocument6 pagesTech. Spec. For Flanges and Spectacle Blindssanjay421Pas encore d'évaluation
- C-31-Rubber Lined Piping System PDFDocument6 pagesC-31-Rubber Lined Piping System PDFvedadonPas encore d'évaluation
- When Should Category M Fluid Service Be Selected For ASME B31Document2 pagesWhen Should Category M Fluid Service Be Selected For ASME B31gpskumar22Pas encore d'évaluation
- UHDE-Specs Section-9 PaintingDocument12 pagesUHDE-Specs Section-9 PaintingDivyansh TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sour Service Pipes - Annexure HDocument6 pagesSour Service Pipes - Annexure HSubhajit Bhattacharya100% (1)
- Types of Stresses in Piping Systems - Pressure Vessel EngineeringDocument7 pagesTypes of Stresses in Piping Systems - Pressure Vessel EngineeringLorenzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Buried Pipes and Fittings Painting SpecDocument5 pagesBuried Pipes and Fittings Painting SpecRohan Sharma50% (2)
- 7hfkqlfdouhsruw Dvnhwvirusro/Hwk/Ohqh3 (SLSHFRQQHFWLRQV: A Technical Paper Presented by James Walker Australia Pty LTDDocument16 pages7hfkqlfdouhsruw Dvnhwvirusro/Hwk/Ohqh3 (SLSHFRQQHFWLRQV: A Technical Paper Presented by James Walker Australia Pty LTDthmaraishriPas encore d'évaluation
- Drafting Practices StandardDocument14 pagesDrafting Practices StandardJonathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil and Gas Pipeline Design and MaintenanceDocument27 pagesOil and Gas Pipeline Design and MaintenanceernmrajaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Samss 008Document11 pages02 Samss 008inatt101Pas encore d'évaluation
- Glass Fiber Reinforced Polyethylene (PE-GF) Spiral Wound Large Diameter PipeDocument8 pagesGlass Fiber Reinforced Polyethylene (PE-GF) Spiral Wound Large Diameter Pipemohamed senoussi100% (1)
- Piping Material Specification 2010014 00 l0 Gs 001Document215 pagesPiping Material Specification 2010014 00 l0 Gs 001Wilson Xavier Orbea Bracho100% (1)
- SLR Strainer Data Sheet PDFDocument7 pagesSLR Strainer Data Sheet PDFKailas NimbalkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping Design CriteriaDocument15 pagesPiping Design CriteriaSubash Chandrabose50% (2)
- Sharing Session Piping Material - Flame ArrestorDocument18 pagesSharing Session Piping Material - Flame ArrestorDinda Putri AmaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pip PNSM0105Document6 pagesPip PNSM0105romerobernaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6-44-0053 Rev 6 FlangesDocument7 pages6-44-0053 Rev 6 Flangesहेमंत कुमार मीणाPas encore d'évaluation
- Annexure To SOW 10 Standard Specification For Steam TracingDocument9 pagesAnnexure To SOW 10 Standard Specification For Steam TracingASHISH GORDEPas encore d'évaluation
- SAMSUNG SEM-3036E - Piping Design Manual (Rack Piping) PDFDocument48 pagesSAMSUNG SEM-3036E - Piping Design Manual (Rack Piping) PDFPrashant SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Din en Iso 16135Document26 pagesDin en Iso 16135Ahmed HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Samss 029Document23 pages01 Samss 029faisalPas encore d'évaluation
- L&T Process Ball Valves PDFDocument16 pagesL&T Process Ball Valves PDFUnna MalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Smith Fibercast Green Thread Performance Plus Fiberglass Pipe Piping BrochureDocument8 pagesSmith Fibercast Green Thread Performance Plus Fiberglass Pipe Piping BrochureWong Chung MengPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Industry Practices Piping: Pip Pnsmv005 Carbon Steel Check Valve DescriptionsDocument25 pagesProcess Industry Practices Piping: Pip Pnsmv005 Carbon Steel Check Valve DescriptionsRicardo Zárate GodinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Support Systems (2 PDH) Course No. M-2018Document17 pagesPipe Support Systems (2 PDH) Course No. M-2018arsssyPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Principles To Be Considered For An Aboveground GRP Piping SystemDocument35 pagesBasic Principles To Be Considered For An Aboveground GRP Piping SystemSantos SudhakerPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Samss 051 PDFDocument9 pages04 Samss 051 PDFJuned BagdadiPas encore d'évaluation
- 357-PressureEquivalentMethod 2007ASMESectionVIIIDivision2Document4 pages357-PressureEquivalentMethod 2007ASMESectionVIIIDivision2ZAZZERA125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Underground Piping Stress Analysis Procedure Using Caesar IIDocument7 pagesUnderground Piping Stress Analysis Procedure Using Caesar IIFandy SipataPas encore d'évaluation
- SP Item DatasheetsDocument21 pagesSP Item DatasheetsSELVAMANIPas encore d'évaluation
- About The CourseDocument2 pagesAbout The Coursemayur_lanjewar0% (1)
- JERES - Non Metalic PipingDocument12 pagesJERES - Non Metalic PipingDidit RizkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping Quiz AnsDocument13 pagesPiping Quiz Anssairam2234100% (1)
- Module1 Stress ObjectiveDocument48 pagesModule1 Stress ObjectivepalluraviPas encore d'évaluation
- CPI Technical-EngDocument22 pagesCPI Technical-EngMazwan Che MansorPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Thickness Calculation Internal Pressure Design Thickness As Per ASME B313Document7 pagesPipe Thickness Calculation Internal Pressure Design Thickness As Per ASME B313mohamed samyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fittings TrainingDocument61 pagesFittings TrainingsbmmlaPas encore d'évaluation
- PGHU-CV-LBDES-000002 R3 Technical Spec For Pipes, Fittings, and Flanges - WG 22sep16Document28 pagesPGHU-CV-LBDES-000002 R3 Technical Spec For Pipes, Fittings, and Flanges - WG 22sep16Riyan EsapermanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping Stress SpecificationDocument23 pagesPiping Stress Specificationpourang1361Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inspection Engineer Interview Points Piping: Commonly Used Construction CodesDocument39 pagesInspection Engineer Interview Points Piping: Commonly Used Construction CodesAshat Ul Haq100% (1)
- Branch Connection Fittings (MSS SP-97) - Weldolet®, Sockolet®, Thredolet®, Latrolet®, Elbolet®, Nipolet®, Sweepolet®Document3 pagesBranch Connection Fittings (MSS SP-97) - Weldolet®, Sockolet®, Thredolet®, Latrolet®, Elbolet®, Nipolet®, Sweepolet®dchz_62Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Samss 009Document13 pages02 Samss 009barouniaminePas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Samss 010Document12 pages01 Samss 010aamirtec301Pas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Samss 010Document12 pages01 Samss 010inatt101Pas encore d'évaluation
- Saes L 110Document12 pagesSaes L 110Karu 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Samss 010Document11 pages01 Samss 010biplabpal2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Samss 010 PDFDocument11 pages01 Samss 010 PDFAnonymous ZxJZoU0% (1)
- Saes S 050Document17 pagesSaes S 050Hamza ChPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials System SpecificationDocument12 pagesMaterials System SpecificationJeck MaquitedPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials System SpecificationDocument15 pagesMaterials System SpecificationZubair RaoofPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Samss 010Document12 pages01 Samss 010이진영Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comments Resolution Sheet: Fadhili Sulfur Recovery FacilitiesDocument1 pageComments Resolution Sheet: Fadhili Sulfur Recovery Facilitiesimrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- SATIP-K-001-11 - AC Split Systems - DX TypeDocument3 pagesSATIP-K-001-11 - AC Split Systems - DX Typeimrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- SATIP-K-001-08 - Air Filtration Devices and Grease FilterDocument2 pagesSATIP-K-001-08 - Air Filtration Devices and Grease Filterimrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- SATIP-K-001-01 Rev 6 Centrifugal FanDocument3 pagesSATIP-K-001-01 Rev 6 Centrifugal Fanimrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Satip-K-001-12 - Tab of Hvac SystemDocument2 pagesSatip-K-001-12 - Tab of Hvac Systemimrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- SATIP-K-001-02 Rev 6 Air-Handling Unit (AHU)Document4 pagesSATIP-K-001-02 Rev 6 Air-Handling Unit (AHU)imrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- SATIP-K-001-03 - HVAC Metal Duct System - Rev. 6Document3 pagesSATIP-K-001-03 - HVAC Metal Duct System - Rev. 6imrankhan220% (1)
- SATIP K 001 07 Refrigerant - PipingDocument2 pagesSATIP K 001 07 Refrigerant - Pipingimrankhan22100% (1)
- SATIP K 001 05 Chilled Water SystemDocument3 pagesSATIP K 001 05 Chilled Water Systemimrankhan220% (1)
- SATIP-K-001-01 Rev 6 Centrifugal FanDocument3 pagesSATIP-K-001-01 Rev 6 Centrifugal Fanimrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- !indx SaipDocument2 pages!indx Saipimrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAIC-A-2007 Rev 3Document12 pagesSAIC-A-2007 Rev 3imrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Visa ServicesDocument1 pageVisa Servicesimrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAIC-A-2001 Rev 3 Review Procedure Pressure Testing (All Applications)Document15 pagesSAIC-A-2001 Rev 3 Review Procedure Pressure Testing (All Applications)imrankhan2250% (2)
- SAIC-A-1005 Rev 3 Compaction TestingDocument2 pagesSAIC-A-1005 Rev 3 Compaction Testingimrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- 156532402-API-RP-571-Damag-10Document12 pages156532402-API-RP-571-Damag-10imrankhan22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ostrich RacingDocument4 pagesOstrich RacingalexmadoarePas encore d'évaluation
- Memo For Completed RubricDocument3 pagesMemo For Completed Rubricnisev2003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Culture Performance and Economic Return of Brown ShrimpDocument8 pagesCulture Performance and Economic Return of Brown ShrimpLuã OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Part-II Poem Article and Report For College Magazine-2015-16 Dr.M.Q. KhanDocument4 pagesPart-II Poem Article and Report For College Magazine-2015-16 Dr.M.Q. KhanTechi Son taraPas encore d'évaluation
- 热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远Document7 pages热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远小黄包Pas encore d'évaluation
- Canadian Solar-Datasheet-All-Black CS6K-MS v5.57 ENDocument2 pagesCanadian Solar-Datasheet-All-Black CS6K-MS v5.57 ENParamesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Copper For BusbarDocument60 pagesCopper For BusbarSunil Gadekar100% (3)
- VukcevicEtAl GhostFluidMethodInPolyhedralFV AnnotatedDocument19 pagesVukcevicEtAl GhostFluidMethodInPolyhedralFV AnnotatedputhenkulamPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesPhysics Cheat SheetJeremiah MoussaPas encore d'évaluation
- Free DMAIC Checklist Template Excel DownloadDocument5 pagesFree DMAIC Checklist Template Excel DownloadErik Leonel LucianoPas encore d'évaluation
- North Rig 4Document1 pageNorth Rig 4avefenix666Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pay Scale WorkshopDocument5 pagesPay Scale WorkshopIbraPas encore d'évaluation
- Apc 10kva Ups ManualDocument36 pagesApc 10kva Ups Manualraj rajPas encore d'évaluation
- Transfer CaseDocument46 pagesTransfer Casebantuan.dtPas encore d'évaluation
- Evelyn Arizpe - Teresa Colomer - Carmen Martínez-Roldán - Visual Journeys Through Wordless Narratives - An International Inquiry With Immigrant Children and The Arrival-Bloomsbury Academic (2014)Document290 pagesEvelyn Arizpe - Teresa Colomer - Carmen Martínez-Roldán - Visual Journeys Through Wordless Narratives - An International Inquiry With Immigrant Children and The Arrival-Bloomsbury Academic (2014)Lucia QuirogaPas encore d'évaluation
- Floating Solar Photovoltaic Systems - An Overview and Their Feasibility at Kota in Rajasthan - IEEE Conference Publication - IEEE XploreDocument3 pagesFloating Solar Photovoltaic Systems - An Overview and Their Feasibility at Kota in Rajasthan - IEEE Conference Publication - IEEE XploreJames KazoobaPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Star Env Audit Specification Amp Pre Audit ChecklistDocument20 pagesFive Star Env Audit Specification Amp Pre Audit ChecklistMazhar ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 Ford Fiesta 1.6l Sohc Fluid CapacitiesDocument1 page2013 Ford Fiesta 1.6l Sohc Fluid CapacitiesRubenPas encore d'évaluation
- Contingency Measures and ProceduresDocument25 pagesContingency Measures and ProceduresKaren Villapando LatPas encore d'évaluation
- Programmable Logic Controllers: Basic Ladder Logic ProgrammingDocument9 pagesProgrammable Logic Controllers: Basic Ladder Logic Programminganuradha19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Steel ConstructionDocument70 pagesModern Steel ConstructionohundperPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 My Hobbies Lesson 1 Getting StartedDocument14 pagesUnit 1 My Hobbies Lesson 1 Getting StartedhienPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Safety Installation Operations Tescom en 123946Document23 pagesManual Safety Installation Operations Tescom en 123946Karikalan JayPas encore d'évaluation
- Warranties Liabilities Patents Bids and InsuranceDocument39 pagesWarranties Liabilities Patents Bids and InsuranceIVAN JOHN BITONPas encore d'évaluation
- SIRMDocument9 pagesSIRMshailendra369Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3: Letters of RequestDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Letters of RequestMinh HiếuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Logistics XI - 2023Document45 pagesFundamentals of Logistics XI - 2023saiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Renr5908 08 01 All PDFDocument108 pages06 Renr5908 08 01 All PDFFrancisco Ospino Arrieta100% (2)
- Business ProposalDocument35 pagesBusiness ProposalMJ MacapagalPas encore d'évaluation