Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
United Nations Economic and Social Commission For Western Asia
Transféré par
Rahul KulkarniDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
United Nations Economic and Social Commission For Western Asia
Transféré par
Rahul KulkarniDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
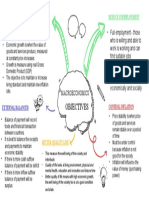
IMPACTS OF GLOBALIZATION ON INDIAN ECONOMY
INTRODUCTION TO GLOBALIZATION:
Globalization has many meanings depending on the context and on the person who is talking about. It refers to the increasing global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Guy Brainbant: says that the process of globalisation not only includes opening up of world trade, development of advanced means of communication, internationalisation of financial markets, growing importance of MNCs, population migrations and more generally increased mobility of persons, goods, capital, data and ideas but also infections, diseases and pollution. The term globalization refers to the integration of economies of the world through uninhibited trade and financial flows, as also through mutual exchange of technology and knowledge. Ideally, it also contains free inter-country movement of labour. The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia defines globalization as: "a widely-used term that can be defined in a number of different ways. When used in an economic context, it refers to the reduction and removal of barriers between national borders in order to facilitate the flow of goods, capital, services and labour... although considerable barriers remain to the flow of labour... Globalization is not a new phenomenon. It began towards the end of the nineteenth century, but it slowed down during the period from the start of the first World War until the third quarter of the twentieth century. This slowdown can
be attributed to the inward-looking policies pursued by a number of countries in order to protect their respective industries... however, the pace of globalization picked up rapidly during the fourth quarter of the twentieth century. INDIAN ECONOMY: Indian economy had experienced major policy changes in early 1990s. The new economic reform, popularly knownas, Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization (LPGmodel) aimed at making the Indian economy as fastest growing economy and globally competitive. The series of reforms undertaken with respect to industrial sector,trade as well as financial sector aimed at ma king theeconomy more efficient.With the onset of reforms to liberalize the Indianeconomy in July of 1991, a new chapter has dawned for India and her billion plus population. This period of economic transition has had a tremendous impact on the overall economic development of almost all major sectors of the economy, and its effects over the last decade can hardly be overlooked. Besides, it also marks the advent of the real integration of the Indian economy into the global economy.This era of reforms has also ushered in a remarkablechange in the Indian mindset, as it deviates from the traditional values held since Independence in 1947, suchas self reliance and socialistic policies of economicdevelopment, which mainly due to the inward lookingrestrictive form of governance, resulted in the isolation,overall backwardness and inefficiency of the economy,amongst a host of other problems. This, despite the fact that India has always had the potential to be on the fast track to prosperity. In context to India, this implies opening up theeconomy to foreign direct investment by providingfaci lities to foreign companies to invest in different fields of economic activity in India, removing constraints and obstacles to the entry of MNCs in India, allowing Indian companies to enter into foreign collaborations and also encouraging them to set up joint ventures abroad; carrying out massive import liberalization programs by switching over from quantitative restrictions to tariffs and import duties, therefore globalization has been identified with the policy reforms of 1991 in India. The Important Reform Measures (Step Towards liberalization privatization and Globalization)
Indian economy was in deep crisis in July 1991, when foreign currency reserves had plummeted to almost $1billion.
IMPACTS OF GLOBALIZATION:
The implications of globalization for a national economy are many. Globalization has intensified interdependence and competition between economies in the world market. These economic reforms have yielded the following significant benefits: Globalization in India had a favourable impact on the overall growth rate of the economy. This is major improvement given that Indias growth rate in the 1970s was very low at 3% and GDP growth in countries like Brazil, Indonesia, Korea, and Mexico was more than twice that of India. Though Indias average annual growth rate almost doubled in the eighties to 5.9%, it was still lower than the growth rate in China, Korea and Indonesia. The pickup in GDP growth has helped improve Indias global position. Consequently Indias position in the global economy has improved from the 8th
position in 1991 to 4th place in 2001; when GDP is calculated on a purchasing power parity basis. During 1991-92 the first year of Raos reforms program, The Indian economy grew by 0.9%only. However the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth accelerated to 5.3 % in 1992-93, and 6.2% 199394. A growth rate of above 8% was an achievement by the Indian economy during the year 2003-04. Indias GDP growth rate can be seen from the following graph since independence.
Structure of the Economy :
Due to globalization not only the GDP has increased but also the direction of growth in the sectors has also been changed. Earlier the maximum part of the GDP in the economy was generated from the primary sector but now the service industry is devoting the maximum part of the GDP. The services sector remains the growth driver of the economy with a contribution of more than 57 per cent of GDP. India is ranked 18th among the worlds leading exporters of services with a share of 1.3 per cent in world exports. The services sector is expected to benefit from the ongoing liberalization of the foreign investment regime into the sector. Software and the ITES-BPO sectors have recorded
an exponential growth in recent years. Growth rate in the GDP from major sectors of the economy can be seen from the following Table.
(% Of GDP) Agriculture Industry Services
1984-85 35.2 26.1 38.7
2002-3 26.5 22.1 51.4
2003-4 21.7 21.6 56.7
2004-5 20.5 21.9 57.6
Source: Economic Survey 2000 &2005
Foreign Direct investment inflows : FDI increased from around US$100 million in 1990/91 to USD 5536 million in 2004-5. Foreign Trade (Export- Import) Indias imports in 2004-05 stood at US$ 107 billion recording an increase of 35.62 percent compared with US$ 79 billion in the previous fiscal. Export also increased by 24 percent as compared to previous year. It stood at US $ 79 billion in 2004-05 compared with US $ 63 billion in the previous year. Oil imports zoomed by 19 percent with the import bill being US $ 29.08 billion against USD 20.59 billion in the corresponding period last year. Non-oil imports during 2004-05 are estimated at USD 77.036 billion, which is 33.62 percent higher than previous year's imports of US $ 57.651 billion in 2003-04.
Foreign Trade (US $ Million) Trade Total Exports 1990-91 18477 2002-3 52719 2003-4 63843 2004-5 79247
Total Imports Trade Balance
27915 -9438
61412 -8693
79149 -14307
107066 -27819
Source Reserve Bank of India Annual Report 2004-05
Thus we find that the economic reforms in the Indian economy initiated since July 1991 have led to fiscal consolidation, control of inflation to some extent, increase in foreign exchange reserve and greater foreign investment and technology towards India. This has helped the Indian economy to grow at a faster rate. Presently more than 100 of the 500 fortune companies have a presence in India as compared to 33 in China.
INDIAN ECONOMY: FUTURE CHALLENGES
Simplifying procedures and relaxing entry barriers for business activities and providing investor friendly laws and tax system. Checking the growth of population; India is the second highest populated country in the world after China. However in terms of density India exceeds China as India's land area is almost half of China's total land. Due to a high population growth, GNI per capita remains very poor. It was only $ 2880 in 2003 (World Bank figures). Boosting agricultural growth through diversification and development of agro processing. Expanding industry fast, by at least 10% per year to integrate not only the surplus labour in agriculture but also the unprecedented number of women and teenagers joining the labour force every year. Developing world-class infrastructure for sustaining growth in all the sectors of the economy Allowing foreign investment in more areas. Effecting fiscal consolidation and eliminating the revenue deficit through revenue enhancement and expenditure management.
Some regard globalization as the spread of western culture and influence at the expense of local culture. Protecting domestic culture is also a challenge. Global corporations are responsible for global warming, the depletion of natural resources, and the production of harmful chemicals and the destruction of organic agriculture. The government should reduce its budget deficit through proper pricing mechanisms and better direction of subsidies. It should develop infrastructure with what Finance Minister P Chidambaram of India called ruthless efficiency and reduce bureaucracy by streamlining government procedures to make them more transparent and effective. Empowering the population through universal education and health care, India must maximize the benefits of its youthful demographics and turn itself into the knowledge hub of the world through the application of information and communications technology (ICT) in all aspects of Indian life although, the government is committed to furthering economic reforms and developing basic infrastructure to improve lives of the rural poor and boost economic performance. Government had reduced its controls on foreign trade and investment in some areas and has indicated more liberalization in civil aviation, telecom and insurance sector in the future.
CONCLUSION:
Indian economy has made rapid strides in the process of globalization Globalization is increasing the integration of national markets and the interdependence of countries worldwide for a range of goods, services and commodities.
Indias trade reform programme resulted in strong economic growth in the globalization age. In particular, difficult decisions are to redress the fiscal imbalance, by reducing subsidies, completing the process of tariff and tax reform, and stepping-up privatization of stateowned enterprises.
The efforts are needed to balance the trade and consider expansion of trade in other countries of the world.
A country must carefully choose a combination of policies that best enables it to take the opportunity while avoiding the pitfalls and utilising globalization to the fullest extent possible.
REFERENCES:
1. Globalisation Trend and Issues - T.K.Velayudham, Page 3, 66. 2. "Globalisation and Liberalisation" Prospects of New World Order - Dr.A.K.Ojha, Third Concept - An International Journal of Ideas, Aug 2002. 3. The Indian and Global Business - Jan 2004, Page 30. 4. Globalisation: Imperatives, Challenges and the Strategies, Page 39. 5. Goyal K A. & P.K.Khicha, Globalization of Business: Future Challenges, Third concept, An 6. International Journal of Ideas 7. Indian Government, Economic survey, 2002-03-04-05
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- GLOBALIZATIONDocument12 pagesGLOBALIZATIONFloydCorreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yy Yy Yy YyDocument8 pagesYy Yy Yy YyArjun YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Globalization On Indian EconomyDocument32 pagesImpact of Globalization On Indian EconomyAbhijeet Kulshreshtha88% (25)
- The Impact of Globalization On Indian EconomyDocument15 pagesThe Impact of Globalization On Indian Economyronik25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Globalization On Developing Countries (With Special Reference To India)Document7 pagesImpact of Globalization On Developing Countries (With Special Reference To India)manojbhatia1220Pas encore d'évaluation
- IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON INDIAN AGRICULTURE: AN OVERVIEW OF THE INDIAN ECONOMY - Dr. B. NAGARAJUDocument10 pagesIMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON INDIAN AGRICULTURE: AN OVERVIEW OF THE INDIAN ECONOMY - Dr. B. NAGARAJUBandameedi Nagaraju Ph DPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation 2Document11 pagesPresentation 2Akash ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Globalization On Indian EconomyDocument11 pagesImpact of Globalization On Indian EconomyShanthan NellutlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Globalization On IndianDocument2 pagesImpact of Globalization On IndianMaruko ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Globalization On Indian EconomyDocument2 pagesImpact of Globalization On Indian EconomysheenakrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Globalization and India: Iipm SMDocument24 pagesGlobalization and India: Iipm SMRAJIV SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- DR - Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University: SociologyDocument7 pagesDR - Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University: SociologySaroj adityaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Globalization in Bangalore: Arpan Lakhani DI 10006Document8 pagesImpact of Globalization in Bangalore: Arpan Lakhani DI 10006arplakhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- India Since 1991: AssignmentDocument9 pagesIndia Since 1991: AssignmentAnurag BishnoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2 Development Process and Social Movements in Contemporary IndiaDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 Development Process and Social Movements in Contemporary Indiasmriti goelPas encore d'évaluation
- Globalization and Its Impact On IndiaDocument3 pagesGlobalization and Its Impact On IndiaJananee Rajagopalan100% (1)
- Globalization ProjDocument40 pagesGlobalization ProjSurabhi SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Name of The School: Project DetailsDocument4 pagesName of The School: Project DetailsAbhinand PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Report: I: Subject: Business Environment Mba Sy Sem IiiDocument5 pagesSeminar Report: I: Subject: Business Environment Mba Sy Sem IiipankajkapsePas encore d'évaluation
- BE SeminarDocument5 pagesBE SeminarpankajkapsePas encore d'évaluation
- Stratergic ManagementDocument31 pagesStratergic ManagementSamir ParikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Implications of Reforms On The Economic Growth of India: AbstractDocument9 pagesImplications of Reforms On The Economic Growth of India: AbstractManju NathPas encore d'évaluation
- India'S Economic Reforms: Lessons For South Africa: PDF StrydomDocument4 pagesIndia'S Economic Reforms: Lessons For South Africa: PDF StrydomsilberksouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- IEPDocument50 pagesIEPK.muniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cultural 2. Demographic 3. Economic 4. Natural 5. Political 6. TechnologicalDocument17 pagesCultural 2. Demographic 3. Economic 4. Natural 5. Political 6. TechnologicalChinmay KhetanPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Review of New Economic Policy On Indian EDocument6 pagesCritical Review of New Economic Policy On Indian EthepeooplesoftheworldPas encore d'évaluation
- GlobalizationDocument14 pagesGlobalizationAnmol GargPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Economics Case StudyDocument9 pages12 Economics Case StudyconnorPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Globaliza Tion in IndiaDocument22 pagesHistory of Globaliza Tion in IndiaJoycelyn Glipa BetcherPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic Liberalisation: The Mckinsey Quarterly States ThatDocument13 pagesEconomic Liberalisation: The Mckinsey Quarterly States ThatramakntaPas encore d'évaluation
- Globalisation: Effect of Globalisation in IndiaDocument4 pagesGlobalisation: Effect of Globalisation in IndiaARYA S PILLAIPas encore d'évaluation
- India's Economic Performance - Globalisation As Its Key DriveDocument16 pagesIndia's Economic Performance - Globalisation As Its Key DriveludovicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Globalization & LiberalizationDocument12 pagesGlobalization & Liberalizationmitul-desai-8682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Political Environment of Business: Presented by Aun AhmedDocument18 pagesPolitical Environment of Business: Presented by Aun AhmedMdheer09Pas encore d'évaluation
- By: Neha Sharma Roll: PGP/22/088: TH THDocument2 pagesBy: Neha Sharma Roll: PGP/22/088: TH THNehas22Pas encore d'évaluation
- By: Neha Sharma Roll: PGP/22/088: TH THDocument2 pagesBy: Neha Sharma Roll: PGP/22/088: TH THNehas22Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4ab resPAperDocument2 pages4ab resPAperNehas22Pas encore d'évaluation
- MBA 205 - Legal Aspect - Unit 8 - Eco EnvironDocument7 pagesMBA 205 - Legal Aspect - Unit 8 - Eco EnvironSoumen SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- 17BCM1034 Research PaperDocument6 pages17BCM1034 Research PaperRao Paramjit singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth in Trade and Businesses in IndiaDocument15 pagesGrowth in Trade and Businesses in IndiaGaurishPas encore d'évaluation
- 3ab resPAperDocument2 pages3ab resPAperNehas22Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Pattern and Causes of Economic Growth in IndiaDocument2 pagesThe Pattern and Causes of Economic Growth in IndiaNehas22Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 AbDocument2 pages3 AbNehas22Pas encore d'évaluation
- India On MoveDocument6 pagesIndia On MoveN MPas encore d'évaluation
- EconomyDocument42 pagesEconomyZulaikha panhwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemant ADocument12 pagesHemant AhercuPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Industrilization On Regional and Community Welfare in The 21St CenturyDocument12 pagesImpact of Industrilization On Regional and Community Welfare in The 21St CenturySHAILVI GUPTAPas encore d'évaluation
- EMEA Group8 IndiaDocument15 pagesEMEA Group8 IndiaRAJARSHI ROY CHOUDHURYPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Globalisation: The Indian ExperienceDocument5 pagesImpact of Globalisation: The Indian ExperiencekumardattPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Global Is at Ion On India EconomyDocument3 pagesImpact of Global Is at Ion On India EconomygowrishankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics - II Project - Sumant Meena (217055) & Himanshu Cheeta (217089)Document31 pagesEconomics - II Project - Sumant Meena (217055) & Himanshu Cheeta (217089)Himanshu CheetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ReportDocument17 pagesProject Reportshiva7363Pas encore d'évaluation
- Subject 201 Business and Human Resource Management Ms - Jigna DesaiDocument5 pagesSubject 201 Business and Human Resource Management Ms - Jigna DesaiVrutika PathakPas encore d'évaluation
- India Needs Reforms AgainDocument3 pagesIndia Needs Reforms AgainGirijesh PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Macro Economics Project Report - Group 7.Document30 pagesMacro Economics Project Report - Group 7.Mayank Misra50% (2)
- India: 1991: By: Shashwat TiwariDocument21 pagesIndia: 1991: By: Shashwat TiwariPrithvi de VilliersPas encore d'évaluation
- Bpos and KposDocument95 pagesBpos and KposZoya ShabbirhusainPas encore d'évaluation
- 29 JulyDocument31 pages29 Julyapi-3728485Pas encore d'évaluation
- Meezan Bank Limited, FTC Branch, Shahrah e Faisal, KarachiDocument1 pageMeezan Bank Limited, FTC Branch, Shahrah e Faisal, Karachitumbin12k4Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1,000 Cases of Exam Paper Leak Reported - FIA Informs NA Body - Pakistan - Business RecorderDocument2 pages1,000 Cases of Exam Paper Leak Reported - FIA Informs NA Body - Pakistan - Business RecorderahmedlakhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Salvatore's International Economics - 10 Edition Test BankDocument4 pagesSalvatore's International Economics - 10 Edition Test BankMert CordukPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Release Goat Situation ReportDocument8 pagesSpecial Release Goat Situation ReportYumie YamazukiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dfi in IndiaDocument11 pagesDfi in IndiarishabhPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 7 - Global Divides - The North and The SouthDocument21 pagesWeek 7 - Global Divides - The North and The SouthGosu NaPas encore d'évaluation
- U.S. Dollar To Indian Rupee Exchange Rate History - 28 September 2019 (28 - 09 - 2019) UsdDocument6 pagesU.S. Dollar To Indian Rupee Exchange Rate History - 28 September 2019 (28 - 09 - 2019) UsdAnish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 11 - KeyDocument1 pageQuiz 11 - KeyAqail AlrajhPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of Foreign Portfolio InvestmentDocument15 pagesStructure of Foreign Portfolio InvestmentNisarg ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Globalisation and Indian Economy - Economics - CompressedDocument3 pagesGlobalisation and Indian Economy - Economics - CompressedNicky RoshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mind Map EcoDocument1 pageMind Map EcoJung JihyunPas encore d'évaluation
- OpTransactionHistory03 11 2023Document9 pagesOpTransactionHistory03 11 2023abhay singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Home S Currency Is The Peso and Trades at 1 PesoDocument1 pageSolved Home S Currency Is The Peso and Trades at 1 PesoM Bilal SaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- ECN 138. Chapter 12Document4 pagesECN 138. Chapter 12Louren Pabria C. PanganoronPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution of The Philippine Taxation, Taxation in Spanish PhilippinesDocument12 pagesEvolution of The Philippine Taxation, Taxation in Spanish PhilippinesAnge Napalia100% (2)
- AS - Marshall-Lerner ConditionDocument5 pagesAS - Marshall-Lerner ConditionDamion BrusselPas encore d'évaluation
- Holiday Homework - Worksheet Section 1Document2 pagesHoliday Homework - Worksheet Section 1Anavi KhoslaPas encore d'évaluation
- April Moth PayslipDocument1 pageApril Moth PayslipLoan LoanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ovo 1Document1 pageOvo 1Ashok Kumar PanigrahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sales Presentation - BankingDocument18 pagesSales Presentation - BankingdrifterliverPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas 2 Bahasa Inggris NiagaDocument2 pagesTugas 2 Bahasa Inggris NiagaBintang FazarraPas encore d'évaluation
- Macro AssignmentDocument2 pagesMacro AssignmentInocent ZakiPas encore d'évaluation
- AssamDocument88 pagesAssamRishi WadhwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- GST Rate On Packers and MoversDocument2 pagesGST Rate On Packers and MoversSaiRamPas encore d'évaluation
- International Trade at A Casual Environment Exercise & Script - Listening ComprehensionDocument2 pagesInternational Trade at A Casual Environment Exercise & Script - Listening ComprehensionFrancisco J. Salinas B.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Berger Paint ComptettionDocument6 pagesBerger Paint ComptettionRohit ParavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Billing Address: Tax InvoiceDocument1 pageBilling Address: Tax InvoiceAayush SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP 24Document2 pagesCHP 24Eeva The DivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Marcom PlanDocument2 pagesMarcom PlanSuhaib BaluchPas encore d'évaluation
- AlinaDocument10 pagesAlinakushathashreePas encore d'évaluation
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)D'EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (32)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaD'EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (14)
- The Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingD'EverandThe Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (17)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceD'EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (18)
- The Caesars Palace Coup: How a Billionaire Brawl Over the Famous Casino Exposed the Power and Greed of Wall StreetD'EverandThe Caesars Palace Coup: How a Billionaire Brawl Over the Famous Casino Exposed the Power and Greed of Wall StreetÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Ready, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successD'EverandReady, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (93)
- Venture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistD'EverandVenture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (73)
- Summary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisD'EverandSummary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (6)
- Joy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerD'EverandJoy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- 7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelD'Everand7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionD'EverandFinancial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (7)
- Financial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityD'EverandFinancial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- The Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursD'EverandThe Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (8)
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialD'EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (32)
- Startup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)D'EverandStartup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Mastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsD'EverandMastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsPas encore d'évaluation
- How to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessD'EverandHow to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (4)
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanD'EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (79)
- 2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSND'Everand2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSNÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialD'EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialPas encore d'évaluation
- The Synergy Solution: How Companies Win the Mergers and Acquisitions GameD'EverandThe Synergy Solution: How Companies Win the Mergers and Acquisitions GamePas encore d'évaluation
- Creating Shareholder Value: A Guide For Managers And InvestorsD'EverandCreating Shareholder Value: A Guide For Managers And InvestorsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (8)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceD'EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)