Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Derivatives
Transféré par
Rajan Singh TanwarDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Types of Derivatives
Transféré par
Rajan Singh TanwarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Types
[edit]OTC
and exchange-traded
In broad terms, there are two groups of derivative contracts, which are distinguished by the way they are traded in the market: Over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives are contracts that are traded (and privately negotiated) directly between two parties, without going through an exchange or other intermediary. Products such as swaps, forward rate agreements, exotic options - and other exotic derivatives - are almost always traded in this way. The OTC derivative market is the largest market for derivatives, and is largely unregulated with respect to disclosure of information between the parties, since the OTC market is made up of banks and other highly sophisticated parties, such as hedge funds. Reporting of OTC amounts are difficult because trades can occur in private, without activity being visible on any exchange. According to the Bank for International Settlements, the total outstanding notional amount [14] is US$708 trillion (as of June 2011). Of this total notional amount, 67% are interest rate contracts, 8% are credit default swaps (CDS), 9% are foreign exchange contracts, 2% are commodity contracts, 1% are equity contracts, and 12% are other. Because OTC derivatives are not traded on an exchange, there is no central counter-party. Therefore, they are subject to counter-party risk, like an ordinary contract, since each counter-party relies on the other to perform. Exchange-traded derivative contracts (ETD) are those derivatives instruments that are traded via specialized derivatives exchanges or other exchanges. A derivatives exchange is a market where [15] individuals trade standardized contracts that have been defined by the exchange. A derivatives exchange acts as an intermediary to all related transactions, and takes initial margin from both sides [16] of the trade to act as a guarantee. The world's largest derivatives exchanges (by number of transactions) are the Korea Exchange (which listsKOSPI Index Futures & Options), Eurex (which lists a wide range of European products such as interest rate & index products), and CME Group (made up of the 2007 merger of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange and the Chicago Board of Trade and the 2008 acquisition of theNew York Mercantile Exchange). According to BIS, the combined turnover in the world's derivatives exchanges totaled USD 344 trillion during Q4 2005. Some types of derivative instruments also may trade on traditional exchanges. For instance, hybrid instruments such as convertible bonds and/or convertible preferred may be listed on stock or bond exchanges. Also, warrants (or "rights") may be listed on equity exchanges. Performance Rights, Cash xPRTs and various other instruments that essentially consist of a complex set of options bundled into a simple package are routinely listed on equity exchanges. Like other derivatives, these publicly traded derivatives provide investors access to risk/reward and volatility characteristics that, while related to an underlying commodity, nonetheless are distinctive.
Common derivative contract types
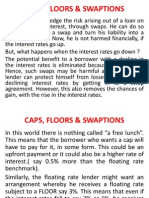
Some of the common variants of derivative contracts are as follows: 1. Forwards:A tailored contract between two parties, where payment takes place at a specific time in the future at today's pre-determined price.
2. Futures: are contracts to buy or sell an asset on or before a future date at a price specified today. A futures contract differs from a forward contract in that, while the former is a standardized contract written by a clearing house that operates an exchange where the contract can be bought and sold, the latter is a non-standardized contract written by the parties themselves. 3. Options are contracts that give the owner the right, but not the obligation, to buy (in the case of a call option) or sell (in the case of aput option) an asset. The price at which the sale takes place is known as the strike price, and is specified at the time the parties enter into the option. The option contract also specifies a maturity date. In the case of a European option, the owner has the right to require the sale to take place on (but not before) the maturity date; in the case of an American option, the owner can require the sale to take place at any time up to the maturity date. If the owner of the contract exercises this right, the counter-party has the obligation to carry out the transaction. Options are of two types: call option and put option. The buyer of a Call option although has a right to buy a certain quantity of the underlying asset, at a specified price on or before a given date in the future, he however has no obligation whatsoever to carry out this right. Similarly, the buyer of a Put option although has the right to sell a certain quantity of an underlying asset, at a specified price on or before a given date in the future, he however has no obligation whatsoever to carry out this right. 4. Warrants: Apart from the commonly used short-dated options which have a maximum maturity period of 1 year, there exists certain long-dated options as well, known as Warrant (finance). These are generally traded over-the-counter. 5. Swaps are contracts to exchange cash (flows) on or before a specified future date based on the underlying value of currencies exchange rates, bonds/interest rates, commodities exchange, stocks or other assets. Another term which is commonly associated to Swap is Swaption which is basically an option on the forward Swap. Similar to a Call and Put option, a Swaption is of two kinds: a receiver Swaption and a payer Swaption. While on one hand, in case of a receiver Swaption there is an option wherein you can receive fixed and pay floating, a payer swaption on the other hand is an option to pay fixed and receive floating.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Pendekanti Institute of Management: DerivativesDocument86 pagesPendekanti Institute of Management: DerivativesRajeshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- FIS Remote-Prophet-Training-SubscriptionDocument15 pagesFIS Remote-Prophet-Training-Subscriptionpalmkodok0% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Swap and SwaptionsDocument21 pagesSwap and SwaptionsMalkeet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Cash-Settled Swaptions A Review of Cash-Settled Swaption PricingDocument15 pagesCash-Settled Swaptions A Review of Cash-Settled Swaption PricingRaphaël FromEverPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Cash-Settled Swaptions: How Wrong Are We?Document15 pagesCash-Settled Swaptions: How Wrong Are We?finalscourgePas encore d'évaluation
- Bermudan Swaption: 1.0 ScenarioDocument2 pagesBermudan Swaption: 1.0 ScenarioadityaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fabozzi Ch29 BMAS 7thedDocument43 pagesFabozzi Ch29 BMAS 7thedPropertywizzPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Convexity and Volatility PDFDocument20 pagesConvexity and Volatility PDFcaxapPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Interest Rate Risk Management: Learning OutcomesDocument16 pagesInterest Rate Risk Management: Learning OutcomesAnil ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Chapter 4: Interest Rate Derivatives: 4.3 SwaptionsDocument12 pagesChapter 4: Interest Rate Derivatives: 4.3 Swaptionsz_k_j_vPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- YieldBook MBS Volatility Skew and Valuation of MTG (2005)Document25 pagesYieldBook MBS Volatility Skew and Valuation of MTG (2005)fengn100% (1)
- Introduction To Financial DerivativesDocument81 pagesIntroduction To Financial DerivativesFinancial Management by Dr MujahedPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- EarningRiskPremiaIRVol PDFDocument16 pagesEarningRiskPremiaIRVol PDFkiza66Pas encore d'évaluation
- Midcurve Swaption PDFDocument17 pagesMidcurve Swaption PDFchinicoco100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- (Columbia Business School Publishing) Howard Corb - Interest Rate Swaps and Other Derivatives (2012, Columbia University Press)Document623 pages(Columbia Business School Publishing) Howard Corb - Interest Rate Swaps and Other Derivatives (2012, Columbia University Press)Leyti Dieng100% (2)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Opti Uni BursaDocument54 pagesOpti Uni BursaCristian ErimiaPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Cancellable SwapDocument1 pageCancellable SwapdltanevPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- History of DerivativesDocument29 pagesHistory of Derivativeshanunesh100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- 9.products CAPS SWAPTIONS New (1207)Document28 pages9.products CAPS SWAPTIONS New (1207)Luca DiboPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Interest Rate Modeling With Libor Market Model and Cva CalculationDocument30 pagesInterest Rate Modeling With Libor Market Model and Cva CalculationNemani Sri Harsha MBA KOL 2015-44Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Bermudan Swaptions Pricing OdysseyDocument32 pagesThe Bermudan Swaptions Pricing Odyssey楊約翰Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hull White PDFDocument64 pagesHull White PDFstehbar9570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Valuation and Hedging of Inv Floaters PDFDocument4 pagesValuation and Hedging of Inv Floaters PDFtiwariaradPas encore d'évaluation
- Nat West Case StudyDocument4 pagesNat West Case StudyMuzna MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Company Profile 1Document45 pagesCompany Profile 1VIJAYA SURYANPas encore d'évaluation
- Pratik Tibrewala (Final Report)Document52 pagesPratik Tibrewala (Final Report)Kushal ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Five-Caps, Floors & Swaptions 8Document8 pagesFive-Caps, Floors & Swaptions 8Akhilesh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Options: Minimum Correct Answers For This Module: 3/6Document14 pagesOptions: Minimum Correct Answers For This Module: 3/6Jovan SsenkandwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mba ProjectDocument73 pagesMba Projectjaya sai sree harishPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Razor Financial PrincipalsDocument373 pagesRazor Financial PrincipalsoptimistevePas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)