Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
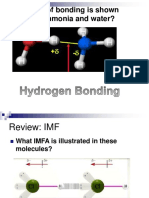
Dipole Induced Dipole: CH C O CH
Transféré par
vennicesumoDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Dipole Induced Dipole: CH C O CH
Transféré par
vennicesumoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES OF ATTRACTION (IMFA) explains
are compounds between outside and weak attraction due to
physical properties
partial charges
solubility farther distance
physical states
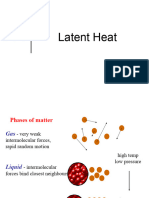
KINDS OF IMFAS KINDS OF IMFA electrostatic Ion dipole H bond Dipole-dipole Ion-induced dipole Dipole induced diploe Dispersion COMPOUNDS THAT FORMED THEM Ionic with ionic Ion with polar Polar H terminal with lone pairs of small electronegative atoms Polar with polar Ion with non polar Dipole with non polar Non polar with non polar
Examples
electrostatic NaCl NaCl
Na
H2O
ion dipole
CH 3 C = O
H- bond
CH 3
CH3 C=O
H 2O H 2O
CH3
dipole-dipole
ion induced dipole O = O e' movement O = O e' movement Cl
-
Na
dipole induced dipole O= O H2O
dispersion O = O O = O
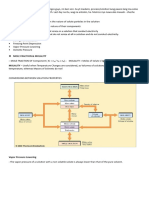
IMFA and Solubility For dissolving to happen, 3 processes must occur 1. Dissolved substance (solute) must separate (IMFA breaking- endothermic heat) 2. Dissolving substance (solvent) must separate (IMFA breaking-endothermic heat) 3. Solute and solvent must mix (IMFA forming-exothermic heat)
IMFA between solute and solvent > IMFA among solute and or IMFA among solvent _
Summarized as : LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE ; polar solvent dissolves polar solute Non polar solvent dissolves non polar solute
IMFA and Physical State
Physical State interplay between IMFA Kinetice Energy
draws molecules together
separates molelcules apart
Kinds Solid IMFA >>> Gas liquid IMFA <<< IMFA is continuously being formed and continuously being broken
KE
KE
Phase Changes are
MELTING is s >>>> l when temp > IMFA
EVAPORATION is l >>>> g when
CONDENSATION is g >>>> l when
FREEZING is l >>>> s when temp << IMFA
temp >> IMFA are
temp < IMFA
are exothermic heat makes warm sorrounding
endothermic heat makes cold sorrounding
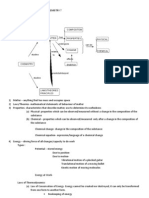
ENERGY CURVE DURING PHASE CHANGE (OF WATER)
g 100
l - g 540 cal/g
TEMP 25 0 s -4 80 cal/g
s - l
ENERGY
LATENT HEATS Heat of Fusion- amount of energy needed to melt 1 gram of a substance at its melting point H fusion water = 80 cal/g Q= mass X H fusion Heat of Freezing = energy released to change 1 gram of liquid to solid Heat of Fusion (endo) = Heat of Freezing (exo)
Heat of Vaporization amount of energy needed to evaporate 1 gram of a substance at its boiling point H vap water = 540 cal/g Q = mass X H vap Heat of Condensation= energy released to convert 1 gram of gas to liquid
Heat of Vaporization (endo) = Heat of Condensation(exo)
SPECIFIC HEATS= Energy needed to change the temperature of 1 gram of a substance 10Celsius For water: Sp. Heat = 1 cal/g-0C
UNIQUE PROPERTIES OF LIQUIDS
1. Surface Tension 2. Capillarity 3. Viscosity
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Gen Chem 2 Week 1 PDFDocument10 pagesGen Chem 2 Week 1 PDFantonio louise anjella monPas encore d'évaluation
- Surrounding Air Cools: Latent Heat of Fusion and VaporizationDocument2 pagesSurrounding Air Cools: Latent Heat of Fusion and VaporizationPutriInggitIstiqomahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Review Test 1Document2 pagesChem Review Test 1Rachel BaumgartenPas encore d'évaluation
- PHASEDocument57 pagesPHASEKarl SiaganPas encore d'évaluation
- calorimeterDocument18 pagescalorimeternorewa9632Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Laboratory#4 CHEM1103L CalorimetryDocument3 pagesPre-Laboratory#4 CHEM1103L CalorimetryMarielleCaindecPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry ThermochemistryDocument6 pagesChemistry ThermochemistryWiktoria KaczmarzykPas encore d'évaluation
- CHM2046 Chapter 11Document64 pagesCHM2046 Chapter 11wbryant2013Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 11 Energetics NotesDocument5 pagesGrade 11 Energetics NotesJodi DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry For Engineers 1 Energy Topic 03 EnthalpyDocument12 pagesChemistry For Engineers 1 Energy Topic 03 EnthalpyKristine AlcantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase ChangeDocument28 pagesPhase ChangeYomiko Danise P. EloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculate heat required to raise aluminum temperature from 300K to 400KDocument32 pagesCalculate heat required to raise aluminum temperature from 300K to 400KSudheerkhan MuhammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Molar Enthalpy WorksheetDocument2 pagesMolar Enthalpy WorksheetRanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Form5Document23 pagesChapter 4 Form5Nuzaher Qhussaen Omar AlliPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase ChangesDocument6 pagesPhase ChangesRoselle ParedesPas encore d'évaluation
- Latent Heat of VaporizationDocument11 pagesLatent Heat of VaporizationEsther Faith GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- GENCHEM Last ExamDocument5 pagesGENCHEM Last Examsunshayneee16Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions - : Solute SolventDocument4 pagesSolutions - : Solute SolventLawn94Pas encore d'évaluation
- AP Chem CalorimetryDocument19 pagesAP Chem Calorimetrysumire shiny dartokPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of Stable Isotopes in Geosciences and BiologyDocument45 pagesApplications of Stable Isotopes in Geosciences and BiologyMalik ArsalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6-Enthalpy ChangesDocument18 pagesChapter 6-Enthalpy ChangesClarize Soo Hoo0% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesThermodynamicsBavinaya ArunthavarasaPas encore d'évaluation
- EnergeticsDocument11 pagesEnergeticsMuhammadJahangirAlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal PhysicsDocument38 pagesThermal Physicsamoh1534Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample ChapterDocument7 pagesSample ChapterhugeamountPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermochemistry: Prepared By: Ron Eric B. LegaspiDocument42 pagesThermochemistry: Prepared By: Ron Eric B. LegaspiRon Eric Legaspi100% (1)
- Advanced Mechanical Vapor-Compression Desalination System: Jorge R. Lara, Omorinsola Osunsan and Mark T. HoltzappleDocument20 pagesAdvanced Mechanical Vapor-Compression Desalination System: Jorge R. Lara, Omorinsola Osunsan and Mark T. Holtzappleayman jummaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating Exothermic and Endothermic Enthalpy ChangesDocument76 pagesCalculating Exothermic and Endothermic Enthalpy ChangesLalitha KurumanghatPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled NotebookDocument71 pagesUntitled NotebookGouthamkri MsPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 NotesDocument28 pagesUnit 2 NotesMuhammad ZaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Enthalpy ChangesDocument14 pagesEnthalpy ChangesBoodhonee AvinashPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4 Phase Change and EnthalpyDocument14 pagesLesson 4 Phase Change and EnthalpyKibet TumPas encore d'évaluation
- Level 2 Basic Facts Worksheet AnswersDocument9 pagesLevel 2 Basic Facts Worksheet Answersapi-218511741Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Year Chemistry Lecture 6Document97 pages1st Year Chemistry Lecture 6Sarosh NaqviPas encore d'évaluation
- Minimum Learning Material XiiDocument27 pagesMinimum Learning Material XiiSmv KumPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem - Week - 2Document44 pagesChem - Week - 2cadaxeshpatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermochemistry GuideDocument3 pagesThermochemistry GuideLena ChoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument27 pagesChemical Energeticsraghavi luthraPas encore d'évaluation
- PHASE CHANGE Hand OutDocument8 pagesPHASE CHANGE Hand Outjoel rosalPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 19Document90 pagesCH 19Heidi ParkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermochemistry Energy ChangesDocument19 pagesThermochemistry Energy ChangesSahada KanapiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Enthalpy of A ReactionDocument3 pagesEnthalpy of A ReactionFelicia LingPas encore d'évaluation
- Enthalpy of VaporizationDocument5 pagesEnthalpy of VaporizationMikhail LópezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reactions: Exothermic vs EndothermicDocument18 pagesChemical Reactions: Exothermic vs EndothermicAngelika Bernal100% (1)
- 6-Ch6 (Energy Dan Termodinamika)Document80 pages6-Ch6 (Energy Dan Termodinamika)NiaKurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- LATENT HEAT NotesDocument4 pagesLATENT HEAT NotesSowndaryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermochemistry TeacherDocument20 pagesThermochemistry TeacherjiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Humidification/ DehumidificationDocument29 pagesHumidification/ DehumidificationCharles Arthel ReyPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermochemistry UnitDocument33 pagesThermochemistry Unitissa sherryPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Notes on ThermodynamicsDocument18 pagesPhysics Notes on ThermodynamicsSahil baggaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No - 7: Aim of The ExperimentDocument6 pagesExperiment No - 7: Aim of The ExperimentRITZ SANDYPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation: By: Allie E. Fuentebella-Pomperada, Che, Mengr, PHDTMDocument49 pagesEvaporation: By: Allie E. Fuentebella-Pomperada, Che, Mengr, PHDTMjantskie100% (2)
- What Type of Bonding Is Shown Between Ammonia and Water?Document34 pagesWhat Type of Bonding Is Shown Between Ammonia and Water?Beverly DatuPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit: 1 Refrigeration System and Refrigeration EquipmentsDocument13 pagesUnit: 1 Refrigeration System and Refrigeration EquipmentsrajasekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Colligative Properties Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesColligative Properties Cheat SheetRishi Sinha25% (4)
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Chemical Thermodynamics Important Questions With AnswersDocument15 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Chemical Thermodynamics Important Questions With AnswersMinato NamikazePas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Recovery MethodsDocument38 pagesThermal Recovery MethodsQaiser HafeezPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Thermodynamics - Lecture 8Document19 pages8 - Thermodynamics - Lecture 8Ramy MaamounPas encore d'évaluation
- SolutionsDocument5 pagesSolutionsvennicesumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic TableDocument4 pagesPeriodic TablevennicesumoPas encore d'évaluation
- GasesDocument2 pagesGasesvennicesumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Writing NomenclatureDocument3 pagesFormula Writing NomenclaturevennicesumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mole ConceptDocument2 pagesMole ConceptvennicesumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Composition Has Undergoes Relates Can BeDocument3 pagesComposition Has Undergoes Relates Can BevennicesumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesChemical BondsvennicesumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesAtomic StructurevennicesumoPas encore d'évaluation
- 101 CompositionDocument3 pages101 CompositionvennicesumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Java MCQ QuestionsDocument11 pagesJava MCQ QuestionsPineapplePas encore d'évaluation
- Android Attendance Management SystemDocument54 pagesAndroid Attendance Management Systemskpetks75% (12)
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument42 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionShola ayipPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal SepsisDocument87 pagesNeonatal Sepsisyhanne100% (129)
- Motivations for Leaving Public Accounting FirmsDocument33 pagesMotivations for Leaving Public Accounting Firmsran0786Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aquafine Optivenn Series Data SheetDocument8 pagesAquafine Optivenn Series Data SheetKenz ZhouPas encore d'évaluation
- Compare and Contrast High School and College EssayDocument6 pagesCompare and Contrast High School and College Essayafibkyielxfbab100% (1)
- LLM DissertationDocument94 pagesLLM Dissertationjasminjajarefe100% (1)
- Impact of Recruitment & Selection on Employee RetentionDocument39 pagesImpact of Recruitment & Selection on Employee RetentiongizawPas encore d'évaluation
- Conserve O Gram: Understanding Histograms For Digital PhotographyDocument4 pagesConserve O Gram: Understanding Histograms For Digital PhotographyErden SizgekPas encore d'évaluation
- Legal Principles and The Limits of The Law Raz PDFDocument33 pagesLegal Principles and The Limits of The Law Raz PDFlpakgpwj100% (2)
- Believer - Imagine Dragons - CIFRA CLUBDocument9 pagesBeliever - Imagine Dragons - CIFRA CLUBSilvio Augusto Comercial 01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Global 6000 SystemsDocument157 pagesGlobal 6000 SystemsJosé Rezende100% (1)
- Assessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistDocument7 pagesAssessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistNicole NipasPas encore d'évaluation
- COT EnglishDocument4 pagesCOT EnglishTypie ZapPas encore d'évaluation
- 277Document18 pages277Rosy Andrea NicolasPas encore d'évaluation
- A Systematic Scoping Review of Sustainable Tourism Indicators in Relation To The Sustainable Development GoalsDocument22 pagesA Systematic Scoping Review of Sustainable Tourism Indicators in Relation To The Sustainable Development GoalsNathy Slq AstudilloPas encore d'évaluation
- BMXNRPDocument60 pagesBMXNRPSivaprasad KcPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Organ DonationDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Organ Donationsheeliya whitePas encore d'évaluation
- Caribbean Examinations Council Caribbean Secondary Certificate of Education Guidelines For On-Site Moderation SciencesDocument9 pagesCaribbean Examinations Council Caribbean Secondary Certificate of Education Guidelines For On-Site Moderation SciencesjokerPas encore d'évaluation
- Genre Worksheet 03 PDFDocument2 pagesGenre Worksheet 03 PDFmelissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nature and Scope of Marketing Marketing ManagementDocument51 pagesNature and Scope of Marketing Marketing ManagementFeker H. MariamPas encore d'évaluation
- Startups Helping - India Go GreenDocument13 pagesStartups Helping - India Go Greensimran kPas encore d'évaluation
- ArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Document14 pagesArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Sultonmurod ZokhidovPas encore d'évaluation
- D257272 1200 FDD 002 R1 PDFDocument420 pagesD257272 1200 FDD 002 R1 PDFTap Toan100% (1)
- LGFL Service GuideDocument24 pagesLGFL Service GuideThe Return of the NoiristaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maximizing modular learning opportunities through innovation and collaborationDocument2 pagesMaximizing modular learning opportunities through innovation and collaborationNIMFA SEPARAPas encore d'évaluation
- EE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherDocument23 pagesEE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherMirza Azhar HaseebPas encore d'évaluation
- Hotel Design Planning and DevelopmentDocument30 pagesHotel Design Planning and DevelopmentTio Yogatma Yudha14% (7)
- E-banking and transaction conceptsDocument17 pagesE-banking and transaction conceptssumedh narwadePas encore d'évaluation