Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
2.1 Linear Motion 2012
Transféré par
cikgusuriyatiCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2.1 Linear Motion 2012
Transféré par
cikgusuriyatiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
2.1
Linear motion is a study of moving object in a _______________ line. We need a _____________ _____________ to describe __________ and ___________ of objects.
Activity 1 (a) Distance & Displacement
(b) Speed & Velocity
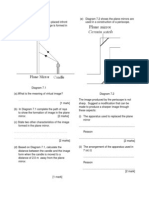
1. In groups of four, carry out these activities. Draw a diagram as below. Your task is to put a pencil at point C.
2. With a pencil take a ride from position A to B and to the final destination, C. Your total path of length = __________, this value is known as _____________ 3. Repeat step 2 but now from A direct to the final destination of C. This is your shortest path to the final destination, C. The value = _____________. This value is known as ______________ 4. If the time taken in step 2 is 4 seconds and the average speed is given as: Average speed, v = ____Total distance travel, s (m)__ Time taken, t (s) What is the average speed, v of your movement? ____________
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH 5. If the time taken in step 3 is 2 seconds and the average velocity is given as Average velocity, v = Displacement, s (m) Time taken, t (s) What is the average velocity, v of your movement? ______________ Distance is Define distance & displacement Displacement is
Diagram below shows the difference between distance and displacement. ___________ = Length of the road ___________ = Length of the line AB Example 1 Every day Rahim walks from his house to the junction which is 1.5 km from his house. Then he turns back and stops at warung Pak Din which is 0.5 km from his house. (a) What is Rahims displacement from his house when he reaches the junction.
When he is at warung Pak Din.
(b) After breakfast, Rahim walks back to his house. When he reaches home, (i) what is the total distance traveled by Rahim? what is Rahims total displacement from his house?
(ii)
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
Speed is the rate of change of _____________. Define speed & velocity Speed = Distance traveled Quantity: _________ SI unit: m s-1 Time taken Velocity is the rate of change of ______________. Velocity = Displacement Time taken Quantity :_________ SI unit: m s-1
Direction of velocity is the direction of displacement
Average speed : v = Total distant traveled, s Total time taken , t
Uniform speed Uniform velocity
Speed that remains the same in magnitude regardless of its direction. Velocity that remains the same in magnitude and direction. (a) the direction of motion changes or the motion is not linear. (b) The magnitude of its velocity changes.
Average velocity : v = Displacement , s Total time taken , t
An object has a nonuniform velocity if:
Example 2 An aeroplane flys towards the north with a velocity 300 km/hr in one hour. Then, the plane moves to the east with the velocity 400 km / hr in one hour. (a) What is the average speed of the plane?
(b) What is the average velocity of the plane?
(c) What is the difference between average speed and average velocity of the plane?
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH Example 3 The speedometer reading for a car traveling north shows 80 km/hr. Another car traveling at 80 km/hr towards south. Is the speed of both cars same? Is the velocity of both cars same?
Define acceleration and Deceleration Acceleration, a is defined as
Formula & SI unit:
+ve a: The velocity of an object __________ from an initial velocity, u, to a higher final velocity, v -ve a: The velocity of an object ____________ from an initial velocity, u, to a lower final velocity, v. Zero Acceleration means:
Example 4 A bicyclist starts from rest and increases his velocity at a constant rate until he reaches a speed of 4.0 m/s in 5.0 s. What is his average acceleration? Strategy: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) state the initial velocity = state the final velocity = state the time taken = apply formula
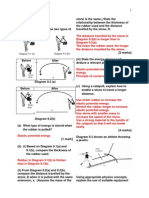
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH Example 5 Observe the motion of a car in Diagram 1 (a) and Diagram 1(b).
Diagram 1(a) (i)
Diagram 1(b)
Describe the changes in velocity of a car in Diagram 1(a). Is the car accelerate or decelerate?
(ii)
Describe the changes in velocity of a car in Diagram 1(b). Is the car accelerate or decelerate?
(iii)
Explain your answers in (i) and (ii) above.
Exercise 1 1. In table below state the comparisons between the terms given. Distance Displacement Speed Velocity
2. You walk along a long straight school corridor for 55 m, then you turn around and walk 30 m in the opposite. Finally, you turn again and walk 39 m in the original direction and stop. What is your displacement from your starting point?
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH 3. A boy walks finish the following path AB. Find (a) total distance traveled
(b) displacement
4. Fill in the blanks: A steady speed of 10 m/s A steady velocity of -10 m/s the left. A steady acceleration of 4 ms-2 A steady deceleration of 4 ms-2 A steady velocity of 10 m/s
A distance of _____ is traveled every ______ A ________ of 10 m is traveled every _____ to
Speed goes up by 4 m/s every ________ speed goes _______ by 4 m/s every ____ _______________________________________
Note: KINEMATIC is the study of motion of objects but does not consider the causes of motion . It came from the Greek word kinema , meaning motion the same root from which we get the word cinema.
Relating Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration and Time Ticker timer: It is connected to an _____ power supply of 50 Hz. When it is turned on, the iron strip will vibrate 50 times per second. The time taken to make 50 dots on the ticker tape is 1 second. Hence, the time interval between 2 consecutive dots is 1/50 = 0.02 s. 1 tick is defined as __________________ __________________________________.
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH Activity 2:Method of calculation To investigate motion in laboratory mean Ive to determine distance / displacement, speed/ velocity, time and acceleration/ deceleration
STEP 1 : Determination of time / time taken for 1 tick. Time taken for 50 ticks = 1 second Time taken for 1 tick = _______ s Time taken from A to B = _______ ticks = _______ s STEP 2 : Determination of displacement The displacement of the object is determined by measuring the length of the ticker tape that is pulled through the ticker time Displacement from A to B = _________ cm STEP 3 : Determination of velocity Velocity, v = displacement Time = _____/ _________ cm/s = ______ cm/s STEP 4 : Determination of acceleration
From the first strip: Initial velocity, u at AB = From the last strip: Final velocity, v at DE =
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
The time interval, for the change in the velocity, t = Acceleration, a =
Making a speed-time graph Ticker tape gain from the experiment:
Can you describes motions from these tapes?
__________________
__________________
_____________________
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
Exersice 2 1
Based on the figure above, calculate the acceleration . Solution
The figure above shows a ticker tape contains 5 ticks for every interval AB.BC.CD and DE .Calculate the acceleration. Solution
3 The diagram above shows a ticker tape chart for a moving trolley. The frequency of the ticker-timer used is 50 Hz. Each section has 10 dots-spacing. (a) What is the time between two dots.
(b) What is the time for one strips.
(c) What is the initial velocity
(d) What is the final velocity.
(e) What is the time interval to change from initial velocity to final velocity?
(f) What is the acceleration of the object
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH 4 .The following figure shows a tape chart. Calculate (a) (b) Solution the acceleration the average velocity
Activity 3 : To identify the types of motion TICKER TAPE AND CHARTS Type of motion: ________________________________ Distance between the dots:
Distance between the dot ___________ uniformly the velocity is of the object is ___________ uniformly The object is moving at a uniform ____________.
Distance between the dots ____________ uniformly The velocity of the object is ____________ uniformly The object is experiencing uniform _______________
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH Activity 4: To determine displacement, average velocity and acceleration Apparatus: Ticker timer, trolley, 12 V power supply, runway, ticker tape, ruler Procedure: 1. Raise one end of runway to a reasonable height. 2. Pass the ticker tape through the ticker timer and attach it to a trolley at the top of the runway. 3. Switch on the ticker timer and release the trolley. 4. When the trolley comes to a stop, cut the tape.
5. Mark and cut the tape into 10-tick strips from the start of the first clear dot 6. Paste the 10-tick strips side-by-side on a paper to make a tape chart. Find The displacement of the 10-tick 1st strip Last strip
The time covered for the 10-tick strip
Average velocity over the 10-tick Strip Change in velocity between the two 10-tick strip Time taken for the change in velocity Acceleration
Conclusion: When an object with ______________ velocity, it experiences ______________
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH Paste your chart tape here.
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
Solve problems on linear motion with uniform acceleration v = u + at s= .(1) Where s : u :... u + v t ..(2) 2 v :... a : t :
s = ut + at2 ..(3) v2 = u2 + 2as ..(4)
Exercise 3 1. A car accelerates from rest to 25 m s-1 in 4 s. Find the acceleration of the car.
2. A car accelerates from rest at 3 ms-2 along a straight road. How far has the car traveled after 4 s?
3. A car is traveling at 20 m/s along a straight road. The driver puts the brakes on for 5 s. It this causes a deceleration of 3 m s-2 , what is the cars final velocity?
4. A car moving with constant velocity of 40 ms-1. The driver saw and obstacle in front and he immediately stepped on the brake pedal and managed to stop the car in 8 s. The distance of the obstacle from the car when the driver spotted it was 180 m. How far is the obstacle from the car after it stops.
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH TUTORIAL 2.1 :LINEAR MOTION 1. Which physical quantity is equal to displacement? (2010) Time A. Speed B. Velocity C. Distance D. Acceleration 2. The acceleration of a car moving with a constant velocity will be A. increased B. constant C. zero D. decreased 3. An object which decelerates will move with . velocity A. a negative B. a positive C. an increasing D. a decreasing 4. Muthu cycles from his house to the shop. While coming back, he stops at Ahmads house. C. The object is at rest or moves with uniform velocity D. The object is moving with maximum velocity. 6. A tick from a ticker timer is A. time interval between two consecutive dots on a ticker tape. B. distance between two consecutive dots on a ticker tape. C. frequency of vibration from the ticker timer D. velocity of vibration from the ticker timer. 7. Which statement is true about the ticker tape shown below?
A. Velocity between CD is low. B. Velocity between DE and velocity between AB are equal. C. Frequency between BC is higher than DE D. Time between AB is equal with the time between DE 8. The diagram shows a ticker tape which is pulled by a trolley through a ticker-timer of frequency 50 Hz.
What is his displacement from his house? A. 300 m B. 400 m C. 1 100 m 5. Which of the following is true regarding the motion of an object having zero acceleration? A. The object is not moving B. The object is moving with uniform velocity
The average speed of the trolleys motion is A. 0.2 ms-1 B. 0.3 ms-1 C. 0.4 ms-1 D. 0.5 ms-1
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH 9. Average velocity from P to Q in the ticker tape below is
A. B. C. D.
85 cms-1 170 cms-1 200 cms-1 240 cms-1
10. Based on the ticker tape below, calculate the acceleration.
What is the trolleys acceleration? (1994) A. 20 cm s-2 B. 200 cm s-2 C. 240 cm s-2 D. 400 cm s-2 13. Which of the following motion charts shows a motion of uniform acceleration? Each section of the ticker tape consists of 10 ticks.
A. B. C. D.
2 ms-2 4 ms-2 5 ms-2 10 ms-2
11. Calculate the acceleration.
A. B. C. D.
- 50 ms-2 - 500 ms-2 50 ms-2 500 ms-2 14. A motorcycle is moving with velocity of 10 ms-1 and reaches a velocity of 25 m s-1 after 3 seconds. What is its acceleration? A. 15 ms-2 B. 8.3 ms-2 C. 11.7 ms-2
12. The diagram below shows a tape chart which is produced by a moving trolley. The frequency of the ticker-tape timer is 50 Hz and each stripe of ticker tape contains 5 ticks.
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH 15. A trolley starts from rest and reaches a velocity of 12 cms-1 after 5 seconds. The distance traveled by the trolley is A. 16 cm B. 24 cm C. 28 cm D. 30 cm 16. A lorry is moving with a velocity of 20 ms-1 brakes suddenly and stops after traveling 40 m. The time taken to stop is A. 10 seconds B. 8 seconds C. 6 seconds D. 4 seconds 17. Diagram below shows the path travelled by a car from P to S. 18. Question 1: Melaka Mid 08 Ali walks to the north for a distance of 300 m. He then turns west and walks for another distance of 400 m to reach Pak Kassims stall. Diagram 1 shows the path taken by Ali.
Diagram 1 (a) Distance is a Tick () the correct answer in the box below x Scalar quantity Vector quuantity (b) On Diagram 1, mark an arrow to show the displacement made by Ali [1 mark]
What is the displacement of the car? (2007) A. 5.0 km B. 6.8 km C. 8.2 km D. 9.0 km
(c) What is the total distance travelled by Ali? .......................................................... [1 mark] (d) Ali then walks home for another distance of 500 m. What is the total displacement made by Ali. .......................................................... [1 mark]
SM SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
19. Question 3: N9 2010 Diagram 3 shows a diagram of stroboscopic photographs of a moving toy car.
Diagram 1.1 (a) Explain the type of motion from A to B and from B to C, shown by the car in Diagram 3. A to B : B to C: [2 marks] (b) What is the acceleration of the toy car from A to B? Explain your answer. .......................................................... [2 marks] (c) Distance from A to B is 6 meter and the toy car took 20 seconds to reach B. The mass of the toy car is 0.5 kg. (i) Calculate the velocity of the toy car from A to B. [2 marks] Diagram 1.2 (a) Underline the correct answer in the bracket to complete the sentence below. The type of current used in the ticker timer is (direct current, alternating current). [1 mark] (b) Based on Diagram 1.2, (i) one tick is represented by the time taken from point .......... to point .............. [ 1 mark] (ii) compare the distance between PQ and ST.
20. SPM 2011 Question 2 Diagram 1.1 shows a trolley moving down an inclined plane. The ticker timer vibrates at frequency 50 Hz. Diagram 1.2 shows the ticker tape produced by the motion of the trolley.
[1 mark] (iii) state the type of motion of the trolley. [ 1 mark]
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Document17 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Farain RashdiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 Linear MotionDocument66 pages2.1 Linear Motioncikgusuriyati100% (1)
- Kinematics Note Ws 2019 UpdatedDocument26 pagesKinematics Note Ws 2019 UpdatedHany WafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Velocity Acceleration Lab PDFDocument6 pagesVelocity Acceleration Lab PDFUltramixPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter2 ModuleDocument133 pagesChapter2 ModulePauling ChiaPas encore d'évaluation
- PrePHYSICS REVISION Quiz S1 MT For 2023-24Document3 pagesPrePHYSICS REVISION Quiz S1 MT For 2023-24Ngọc Thùy Vân NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Motion - KeyDocument7 pagesBasic Motion - KeyAli Ali AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 9 Q4 Intro To KinematicsDocument54 pagesScience 9 Q4 Intro To KinematicsSire WillPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion 2021 For GCRDocument24 pagesMotion 2021 For GCRkhuranahardikcr7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Motion (I) : Length and TimeDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Motion (I) : Length and TimeZhu JiankunPas encore d'évaluation
- Description of MotionDocument8 pagesDescription of MotionSel FortichPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 1a Motion - Ticker Timers Notes 2024Document27 pagesCH 1a Motion - Ticker Timers Notes 2024andilenbPas encore d'évaluation
- Cw-1d Kinematic Pair WorksheetDocument4 pagesCw-1d Kinematic Pair WorksheetCj PascualPas encore d'évaluation
- General PhysicsDocument5 pagesGeneral PhysicsKrizza Solis CataloctocanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ws - 201 Motion I Amended PDFDocument9 pagesWs - 201 Motion I Amended PDFL LHPas encore d'évaluation
- Year10 Motion SummaryDocument3 pagesYear10 Motion SummaryWet waterPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating SpeedDocument3 pagesCalculating SpeedMaridjan Wiwaha50% (2)
- Basic Motion - NotesDocument7 pagesBasic Motion - NotesparneetPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Linear MotionDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Linear MotionMuhd Faizal MdkPas encore d'évaluation
- Yr 11 Special Notes On FizzDocument54 pagesYr 11 Special Notes On FizzNayab ShahzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 4 Speed and VelocityDocument7 pagesModule 3 4 Speed and VelocityBaby-AnnieAquino-Ventura100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 8 MotionDocument21 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 8 MotionLAKHA PRASADPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Year 11 Prelim NotesDocument53 pagesPhysics Year 11 Prelim NotesZain Al-LoosPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Motion NotesDocument33 pagesLinear Motion NotesPotriyan SivanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDocument10 pagesPre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDaisy GamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces and MotionDocument150 pagesForces and MotionAz MYPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Unit Test Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesPhysics Unit Test Questions and Answerscarol janePas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Notes WS (GRADE 10)Document11 pagesExtra Notes WS (GRADE 10)aaliyahleshabanePas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics and Dynamics WorksheetsDocument49 pagesKinematics and Dynamics Worksheetsknoxphysics100% (1)
- SCIENCE 7 Q3 Week 2Document9 pagesSCIENCE 7 Q3 Week 2Khryzha Mikalyn GaligaPas encore d'évaluation
- K00735 - 20200314121311 - Velocity Acceleration LabDocument6 pagesK00735 - 20200314121311 - Velocity Acceleration LabIsen HausPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 5 q3 Mod 1Document31 pagesScience 5 q3 Mod 1erikauclos856Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gen. Physics 1 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Kinematic QuantitiesDocument5 pagesGen. Physics 1 Unit 1 Lesson 3 Kinematic QuantitiesMary Love JuanicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys Int CC CH 2 - Motion in A Straight Line - AnswersDocument10 pagesPhys Int CC CH 2 - Motion in A Straight Line - AnswersKimberly OlivaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Lectures 2 General PhysicsDocument36 pagesLectures 2 General PhysicsMaliamungu EmmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys11-A Problem SetsDocument16 pagesPhys11-A Problem SetsResci Angelli Rizada-NolascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Booklet Prep 3 First Term 2015-2016Document50 pagesScience Booklet Prep 3 First Term 2015-2016Dina HafezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-General PhysicsDocument58 pages1-General PhysicsSamah HafezPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 2023 1-Merged 1 1Document216 pagesNotes 2023 1-Merged 1 1Quizz QuizzPas encore d'évaluation
- Physic WorksheetDocument82 pagesPhysic WorksheetJohn Lower100% (1)
- Grade 10 PhysicsDocument24 pagesGrade 10 PhysicsAutumn DeGraevePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - MotionDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - MotionDani PrimantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 7 Science Forces Activity PackDocument47 pagesYear 7 Science Forces Activity PackAnasua BasuPas encore d'évaluation
- SPH3U - Kinematics 2: Velocity and Speed: ReviewDocument6 pagesSPH3U - Kinematics 2: Velocity and Speed: Reviewlim05abcPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set. Kinematics One DimensionDocument3 pagesProblem Set. Kinematics One DimensionAlman MacasindilPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Linear MotionDocument10 pages1 - Linear Motionapi-242844746Pas encore d'évaluation
- SLK G7 Q3wk2 ZAcademia RevisedDocument13 pagesSLK G7 Q3wk2 ZAcademia RevisedJen-jen Ybanez BalderasPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 3-Kinematics PDF ModuleDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 3-Kinematics PDF ModuleLesther James CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion in One DimensionDocument4 pagesMotion in One DimensionmtsilmaroPas encore d'évaluation
- 2aprob Sol 1 PDFDocument6 pages2aprob Sol 1 PDFsbikmmPas encore d'évaluation
- ODU Mechanics Questions o Level A Level PhysicsDocument40 pagesODU Mechanics Questions o Level A Level Physicsduncon100% (1)
- KinematicsDocument13 pagesKinematicsiskenderbeyPas encore d'évaluation
- MotionDocument60 pagesMotionjoshua cerialesPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 S3Document6 pagesUnit 1 S3cyumadripPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion in a Straight Line (Physics) Question BankD'EverandMotion in a Straight Line (Physics) Question BankPas encore d'évaluation
- High School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsD'EverandHigh School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankD'EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankPas encore d'évaluation
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (10)
- 3.3 Atmospheric and Gas Pressure 2012Document12 pages3.3 Atmospheric and Gas Pressure 2012cikgusuriyati100% (1)
- 3.4 Pascal Principal IntensiveDocument33 pages3.4 Pascal Principal Intensivecikgusuriyati100% (1)
- Tutorial 3.3Document20 pagesTutorial 3.3cikgusuriyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.3 Gas Pressure IntensiveDocument33 pages3.3 Gas Pressure Intensivecikgusuriyati100% (1)
- 3.2 Liquid Pressure 2012Document12 pages3.2 Liquid Pressure 2012cikgusuriyati100% (1)
- Tutorial 3.2Document22 pagesTutorial 3.2cikgusuriyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 PressureDocument14 pages3.1 Pressurecikgusuriyati100% (1)
- 3.1 Pressure 2012Document7 pages3.1 Pressure 2012cikgusuriyati50% (2)
- 3.2 Liquid Pressure IntensiveDocument22 pages3.2 Liquid Pressure IntensivecikgusuriyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3.1Document13 pagesTutorial 3.1cikgusuriyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Perfec Score MelakaDocument8 pagesPerfec Score MelakacikgusuriyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1 The Nucleus of An Atom IntensivesDocument20 pages10.1 The Nucleus of An Atom IntensivescikgusuriyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Perfec Score Melaka 2012 JawapanDocument11 pagesPerfec Score Melaka 2012 JawapancikgusuriyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 2 Section B and C Sample QuestionsDocument30 pagesPaper 2 Section B and C Sample Questionscikgusuriyati100% (4)
- Brochurer ESBDocument4 pagesBrochurer ESBcikgusuriyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Quest 9 ProblemsDocument2 pagesQuest 9 ProblemsAdmnUnpwndPas encore d'évaluation
- Far Field Near Filed AntennaDocument3 pagesFar Field Near Filed Antennaanirban pahariPas encore d'évaluation
- Momentum Problem SolvingDocument16 pagesMomentum Problem SolvingRokutodoari VenPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic JumpDocument15 pagesHydraulic JumpabbasjadoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture1530518026 PDFDocument130 pagesLecture1530518026 PDFMuhtasim FuadPas encore d'évaluation
- Interference of LightDocument3 pagesInterference of LightSuman_SamadderPas encore d'évaluation
- IIT JEE - Rotation Motion (MAINS)Document6 pagesIIT JEE - Rotation Motion (MAINS)yashsodhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- COLLISIONDocument26 pagesCOLLISIONFatima salasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pahang JUJ 2012 SPM PhysicsDocument134 pagesPahang JUJ 2012 SPM PhysicsJeyShidaPas encore d'évaluation
- 05729c454 PDFDocument6 pages05729c454 PDFManu ChakkingalPas encore d'évaluation
- MechanicsDocument47 pagesMechanicshitesh81Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanic 20152016 PDFDocument8 pagesMechanic 20152016 PDFAPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test 4.1-4.5 - NO CALC: Find The Value of The Trig Function IndicatedDocument3 pagesPractice Test 4.1-4.5 - NO CALC: Find The Value of The Trig Function Indicatedrust accPas encore d'évaluation
- CBR - Luni Karlina Manik - HSP in Multimedia - Pesp18Document19 pagesCBR - Luni Karlina Manik - HSP in Multimedia - Pesp18luni karlina manikPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective Type Questions For Units and DimensionsDocument5 pagesObjective Type Questions For Units and DimensionsDheeraj Kumar SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acoustics & Sound AttenuationDocument21 pagesAcoustics & Sound AttenuationbuddhikasatPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3 - Flow Over Supersonic AirfoilDocument14 pagesExperiment 3 - Flow Over Supersonic AirfoilSanthosh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch2 Aircraft LoadsDocument24 pagesCh2 Aircraft LoadsDragon ZNPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces Exam QsDocument27 pagesForces Exam Qsapi-422428700Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science 9: Quarter 4 Week 3Document13 pagesScience 9: Quarter 4 Week 3Lilacx ButterflyPas encore d'évaluation
- C03-001-Structural Steel CalculationsDocument166 pagesC03-001-Structural Steel CalculationsNguyễnBìnhPhươngPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensional Analysis Similarity Lesson2 Dimensional Parameters HandoutDocument11 pagesDimensional Analysis Similarity Lesson2 Dimensional Parameters HandoutRizqi RamadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3 WavesDocument148 pages2.3 WavesAhmed KhalilPas encore d'évaluation
- Eec130b 2019 HW8Document2 pagesEec130b 2019 HW8NGUYEN NGUYENPas encore d'évaluation
- Coherence and Width of Spectral Lines With Michelson InterferometerDocument5 pagesCoherence and Width of Spectral Lines With Michelson InterferometerJose GalvanPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOMECHANIC - Linear Kinematics Part IIIDocument68 pagesBIOMECHANIC - Linear Kinematics Part IIITanisha SekhonPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Unit 2 Fluid Kinematics & DynamicsDocument20 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery Unit 2 Fluid Kinematics & DynamicsPalaniVelRajanPas encore d'évaluation
- PTC A, B1.1 & B2 Basic Notes - Sub Module 8.4 (Flight StabilDocument25 pagesPTC A, B1.1 & B2 Basic Notes - Sub Module 8.4 (Flight StabildaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Uniform Rotary MotionDocument26 pagesUniform Rotary MotionMark RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Formula Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet PDFDirty PiloPas encore d'évaluation