Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cancer Marker
Transféré par
Anita BhattiDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cancer Marker
Transféré par
Anita BhattiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
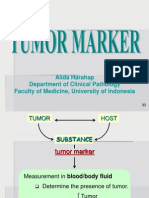
CANCER MARKER
Tumour marker is substance present in or produced by a tumour itself or produced by the host in response from normal tissue or to determine the presence of a tumour based on measurement in blood or secretion . it is measured qualitative or quantitatively by chemical ,immunological or molecular method to identify cancer presence . ideally tumour marker should occur only in patient white malignancy , should correlate with stage and response to treatment and should be easily and reproducibly measured . no tumour marker has met this ideal yet . tumour marker are either polypeptide , protein ,hormones ,surface antigen ,cytokines ,oncogenes or gene product .Baseline level measured prior to therapeutic intervention and followed later by serial periodic measurement help to periodic outcome therapy .toumor marker also help in early detection of recurrence , replace and metastasis . however ,it is the rate of change the tumor marker level which is more important then its absolute value .these test should not be used as screening test but should be correlated with other clinical criteria .
Clinical Application:-
mass screening ,differential diagnosis in symptomatic
patients ,clinical staging ,estimating tumor volume , prognostic indicator of disease progression , detecting recurrence ,evaluating the success of treatment and monitoring response to therapy .
Alpha Fetoprotein ( AFT ):AFT (A glycoprotein) is one of best known oncofetal antigen .it is elevated in 80% of patient with hepatocellular carcinoma and 60-80% of patient with testicular germ cell tumour .about 55100% cases of yolk sac tumours are AFP positive .this fact is helpful in distinguishing solid patterns of yolk sac tumours from seminomas as the seminomas are AFP negative .False positive resulthave been noticed in many non-neoplastic condition like cirrhosis ,massive liver necrosis ,chronic hepatitis etc. plasma AFP is elevated to a laser extent in carcinomas of colon , lung and pancreas .in early stage ,its level correlates with tumour size .Except pregnancy ,levels 1000micro g/l indicate cancer .the AFP levels decline rapidly after surgical resection of liver cancer or treatment of germ cell tumor .serial post therapy measurement of AFP provide a sensitive index of response to therapy and recurrence , good prognostic indicator of survival . AFP can be used for screening in high risk cases .
MARKERS Hormones
ASSOCIATED CANCERS
HCG Trophoblastic tumour,non seminomatous testicular tumor Calcitonin medullary thyroid carcinoma Catecholamines and metabolites Pheochromocytoma Ectopic Hormones:ACTH small cell carcinoma lung, pancreatic carcinoma and neural . tumour ADH/ANH small cell carcinoma lung intracranial neo plasma PTH-rP Squamous cell carcinoma lung ,breast, ovarian renal .. carcinoma and adult T-cell lymphoma Insulin Fibrosarcoma ,mesenchymal sarcomas hepatocellular . .. carcimoma Serotonin Bronchial adenoma ,pancreatic and gastric carcinoma Erythropoietin Renal carcinoma , cerebellar hemangioma ,heptocelloular . .. carcinoma Ferritin Acute leukemia ,Hodgkin disease ,multipale myeloma .. ,malignant lymphoma ,liver and prostate carcinoma ONCOFETAL ANTIGEN :AFP Hepatocellular carcinoma ,nonseminomatous germ cell testicular tumour CEA Isoenozmey prostate cancer phosphate (PAP) small cell carcinoma lung ,neuroblastoma Carcinoma of colon ,pancreas ,lung ,stomach and breast
Prostatic acid Neuron specific enolase Specific proteins Immunoglobulins Beta 2 Prostate specific Thyroglobulin IGFBP-2
Multiple myeloma Multiple Myeloma microgloubulin Prostate cancer antigen (PSA) ,total ,free and ratio Differentiated thyroid carcinoma Prostate cancer
Mucins and Glycoprotins:CA125 CA19.9 CA72.4 CA15.3 Cyfra 21.1 Viruses Human papilloma virus (HPV) .. Cervical carcinoma Epstein Barr virus (EVB) .. Burkitt,s lymphoma ,nasopharyngeal carcinoma and some lymhoproliferative disorders Ovarian cancer Pancreas and colon cancer Gastric and colon cancer Breast cancer Non small cell lung cancer
Tumor markers According to Tissue of Tissue of Origin:Breast Cancer . Prostate Cancer Colorectal cancer Gastric cancer Pancreatic cancer ., .. Liver cancer Lung cancer Ovarian cancer Cervical cancer Trophoblastic cancer Testicular cancer Urinary Blader cancer CA15.3,CA27.29,CEA,ERandPR, pS2,HER-2/neu ,catheepsin .. D,p53,DNA ploidy,S phase,EGFr PAP ,PSA,DNA polidy,IGFBP-2 CEA,p53 CA72.4,CEA CA19.9,CEA (carcinoma); glucagon (glucagonama); insulin .. proinsulin ,cpeptide and IGFBP-1(insulinoma);pancreatic . polypeptide (endocrine tumor) AFP,CEA ,ferritin Cyfra-21.1(NSCLC);neuron specific enolase (SCLC) CA125,CEA(epithelial);urinary gonadotropin peptide . .. .(endometroid); inhibin (granulosa cell) HPV,squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC-Ag) Beta hCG AFP(yolk sac tumour) ,beta hCG (Trophoblast) DNA polidy,s-phase
Thyroid cancer
Calcitonin (medullary carcinoma thyroglobulin (differentiated) Squamous cell carcinoma antigen N-myc oncogene, .neuron specific enolase ,HPV Chromogranin a VMA, catecholamines , metanephrines
Head and Neck cancer neuroblastoma . Pheochromocytoma
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument1 pageRenal Cell CarcinomaBobet ReñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Marrow Biopsy Interpretive GuidelinesDocument19 pagesBone Marrow Biopsy Interpretive Guidelinesdtoxic1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2022Document98 pages2022JkPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument10 pagesRenal Cell Carcinoma'asyura Mohd RezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 2 Exam Sample Q 2015Document194 pagesPart 2 Exam Sample Q 2015Abdul QuyyumPas encore d'évaluation
- Crohn's DiseaseDocument14 pagesCrohn's DiseaseNader Smadi100% (2)
- Pancreatic Cancer (Cancer of The Pancreas) : Patient Discussions: FindDocument13 pagesPancreatic Cancer (Cancer of The Pancreas) : Patient Discussions: FindMoses ZainaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor MarkersDocument18 pagesTumor MarkersHafizur RashidPas encore d'évaluation
- Papaya Leaf Cancer CureDocument34 pagesPapaya Leaf Cancer CureFrancisca_nida75% (4)
- Respiratory DiseasesDocument11 pagesRespiratory DiseasesMichael Angelo SeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- General SurgeryDocument50 pagesGeneral Surgerykllo_85Pas encore d'évaluation
- TUMOR MARKER - ModulpptDocument30 pagesTUMOR MARKER - Modulpptnouval_iqbal100% (1)
- Difficult Decisions in Colorectal PDFDocument578 pagesDifficult Decisions in Colorectal PDFDenise Guevara100% (1)
- HerniaDocument11 pagesHerniaHapsari Wibawani 'winda'100% (1)
- ShockDocument21 pagesShockMin-Joo Esther ParkPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Strength TestingDocument3 pagesMuscle Strength TestingGiselle Chloe Baluya ico100% (1)
- Testicular CancerDocument24 pagesTesticular CancerJulianne LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)D'EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Therapy For CancerDocument7 pagesGene Therapy For Canceresraa elsharkawyPas encore d'évaluation
- Shock TypesDocument25 pagesShock TypesMuqeet76Pas encore d'évaluation
- Essay On Healthy EatingDocument10 pagesEssay On Healthy EatingAini Ulis100% (2)
- Oncology LectureDocument92 pagesOncology Lecturerustie26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Practice IV EdgeworthDocument9 pagesNursing Practice IV EdgeworthRichard Ines Valino100% (6)
- Gas GangreneDocument6 pagesGas GangreneIwan AchmadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Markers Dr. MarwaDocument36 pagesTumor Markers Dr. Marwakholoud220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Riaz Gul AHN Unit 1Document106 pagesRiaz Gul AHN Unit 1Riaz Gul RindPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemotherapeutic DrugsDocument4 pagesChemotherapeutic DrugsEditor IJTSRDPas encore d'évaluation
- Wound AssessmentDocument19 pagesWound Assessmentdrsonuchawla100% (1)
- 50 TOP ONCOLOGY Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF - SURGERY MCQs PDFDocument6 pages50 TOP ONCOLOGY Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF - SURGERY MCQs PDFaziz100% (4)
- Case Study CLD 1Document12 pagesCase Study CLD 1MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Improved Outcomes in Colon and Rectal SurgeryDocument432 pagesImproved Outcomes in Colon and Rectal SurgeryMiguel Angel AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Peptic UlcerDocument27 pagesTreatment of Peptic Ulcerapi-3761895100% (3)
- GI 2007 Exam QuestionsDocument47 pagesGI 2007 Exam QuestionsRoh JitenPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Diagnosis of Cervical LymphadenopathyDocument14 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Cervical LymphadenopathyKokila AbelPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor MarkersDocument14 pagesTumor MarkersPatrick LizarondoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fistula in AnoDocument21 pagesFistula in AnoHannah LeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatments and Drugs: by Mayo Clinic StaffDocument23 pagesTreatments and Drugs: by Mayo Clinic StaffJr D BayzPas encore d'évaluation
- ICSH Guidelines For Bone Marrow Lee Oct 2018Document16 pagesICSH Guidelines For Bone Marrow Lee Oct 2018Mia FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Report of Classical Hodgkin's Lymphoma Presented With Anemia of Chronic Disease As Microcytic Hypochromic TypeDocument3 pagesA Case Report of Classical Hodgkin's Lymphoma Presented With Anemia of Chronic Disease As Microcytic Hypochromic TypeIOSRjournalPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study For LeukemiaDocument5 pagesCase Study For LeukemiaGabbii CincoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Document3 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- BurnsDocument58 pagesBurnsMarie MayPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Asthma ExacerbationDocument13 pagesManagement of Asthma ExacerbationAini Shofa HaniahPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac TestsDocument17 pagesCardiac TestsGiorgiana pPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphoma Diagnosis BCSH 042010Document59 pagesLymphoma Diagnosis BCSH 042010DR_Alaa_FakhriPas encore d'évaluation
- Papillary CarcinomaDocument7 pagesPapillary Carcinomarazik89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Abdominal PainDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Abdominal PainCherry Faith Merisco LabtangPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor MarkersDocument9 pagesTumor MarkersDewi Puspita SariPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Case Presentation For A Patient With CABG: Subject: Medical Surgical Nursing-IIDocument10 pagesNursing Case Presentation For A Patient With CABG: Subject: Medical Surgical Nursing-IIanamika sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain TumorDocument50 pagesBrain TumorbudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute and Chronic Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument7 pagesAcute and Chronic Gastrointestinal BleedingMarwan M.100% (1)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia in PediatricDocument43 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia in PediatricSari HestiyariniPas encore d'évaluation
- UrolithiasisDocument29 pagesUrolithiasis143bbPas encore d'évaluation
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument37 pagesSystemic Lupus ErythematosusFirman Ichlasul AmalPas encore d'évaluation
- LA Myxoma Case PresentationDocument34 pagesLA Myxoma Case PresentationWiwik Puji LestariPas encore d'évaluation
- Tuberculosis: Dr. Kaem Shir AliDocument52 pagesTuberculosis: Dr. Kaem Shir AliMwanja MosesPas encore d'évaluation
- Assisting Bone Marrow Aspiration DraftDocument6 pagesAssisting Bone Marrow Aspiration Draftabcde pwnjabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Prepared By: Manisha Praharaj Msc. Nursing 2Nd YearDocument28 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: Prepared By: Manisha Praharaj Msc. Nursing 2Nd YearMaria YaseenPas encore d'évaluation
- Juvenile CataractDocument12 pagesJuvenile CataractSofea Mustaffa100% (1)
- Cardiac MyxomaDocument4 pagesCardiac MyxomaAve FenixPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument3 pagesAcute Myeloid LeukemiaKathleen Marie ChuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmn FINAL WORDDocument16 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysmn FINAL WORDErica P. ManlunasPas encore d'évaluation
- OncologyDocument5 pagesOncologymitzi019Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fat Embolism SyndromeDocument26 pagesFat Embolism SyndromeAzni MokhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Examination of A StomaDocument3 pagesExamination of A StomaChloe100% (1)
- PancreatitisDocument12 pagesPancreatitismardsz100% (5)
- UnconsciousnessDocument16 pagesUnconsciousnessAkhilesh BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Markers: Universiti Kuala Lumpur (Unikl) - Where Knowledge Is Applied and Dreams RealizedDocument29 pagesTumor Markers: Universiti Kuala Lumpur (Unikl) - Where Knowledge Is Applied and Dreams RealizedNida RidzuanPas encore d'évaluation
- K8.Tumor Marker'sDocument47 pagesK8.Tumor Marker'sDwi Meutia IndriatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructor's Presentation-Tumor MarkersDocument57 pagesInstructor's Presentation-Tumor MarkersMACOB, ETHELHYN JHANEPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 67 Lecture SyllabusDocument22 pagesNCM 67 Lecture SyllabusRichard Allan SolivenPas encore d'évaluation
- Malignant Growth of Tumor That Begins From The Inner Wall of The Colon or Rectum. Can Also Involve The Anal CanalDocument55 pagesMalignant Growth of Tumor That Begins From The Inner Wall of The Colon or Rectum. Can Also Involve The Anal CanalJojo JustoPas encore d'évaluation
- დნმ-ის დაზიანების მექანიზმები კანცეროგენეზისა და კიბოს მკურნალობის დროსDocument1 pageდნმ-ის დაზიანების მექანიზმები კანცეროგენეზისა და კიბოს მკურნალობის დროსEMD GROUPPas encore d'évaluation
- American Dietetic Association FiberDocument8 pagesAmerican Dietetic Association FiberroomforsquaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 16Document15 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 16sarasjunk100% (1)
- Cancer ClassificationDocument10 pagesCancer ClassificationMuhamad Asymawi SuhaiminPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 MLH1Document6 pages2007 MLH1Mericia Guadalupe Sandoval ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ales 04 96Document8 pagesAles 04 96Daniel Gonzales LinoPas encore d'évaluation
- ACG Clinical Guidelines: Colorectal Cancer Screening 2021Document22 pagesACG Clinical Guidelines: Colorectal Cancer Screening 2021Julianne GRPas encore d'évaluation
- Colorectal CancerDocument3 pagesColorectal CancerFarah FarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of The ColonDocument59 pagesDiseases of The ColonElvisPas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions of Benign Vs MalignantDocument4 pagesDefinitions of Benign Vs MalignantMitreswaran SelvakumaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Info - PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesInfo - PathophysiologyRupert BassigPas encore d'évaluation
- New Hire Med. Assessment Study GuideDocument24 pagesNew Hire Med. Assessment Study GuideNada PersonalPas encore d'évaluation
- Colonic Inertia With Tortuous Colon Is Surgery MyDocument18 pagesColonic Inertia With Tortuous Colon Is Surgery MyMisa AjversonPas encore d'évaluation
- A Sigmoidoscopy Only Examines Up To The Sigmoid. The Most Distal Part of The Colon, While Colonoscopy Examines The Whole Large BowelDocument5 pagesA Sigmoidoscopy Only Examines Up To The Sigmoid. The Most Distal Part of The Colon, While Colonoscopy Examines The Whole Large BowelMa. Ydela MeradoresPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer TreatmentDocument6 pagesCancer TreatmentJoshua DauzPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Cancer StagingDocument28 pagesPrinciples of Cancer StagingAnonymous PKE8zOXPas encore d'évaluation
- QUIZDocument14 pagesQUIZhahaha0% (1)