Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Velammal Engineering College, Chennai - 600066.: Department of Mechanical Engineering University Question Bank
Transféré par
murugesanvDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Velammal Engineering College, Chennai - 600066.: Department of Mechanical Engineering University Question Bank
Transféré par
murugesanvDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Velammal Engineering College, Chennai 600066.
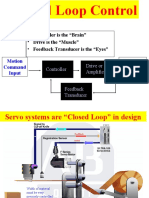
Department Of Mechanical Engineering University Question Bank
Subject code/Name : ME2305/Applied Hydraulics and pneumatics, Sem/Year : 05/III B section Part A 1. Define the term fluid power. Fluid power technology is a means to convert, transmit, control and apply fluid energy to perform useful work. Fluid power includes hydraulics and pneumatics 2. What are the properties of hydraulic fluid? Viscosity, oxidation stability, lubricity, flash point and fire point, viscosity index, demulsibility, rust prevention, neutralization number 3. What is the classification of pump? Non-positive displacement pump centrifugal pump & axial flow pumps Positive displacement pump gear pump, vane pump, lobe pump, screw pump 4. Differentiate hydraulic power supply and pneumatic power supply. Hydraulic power supply 1. The source is liquid 2. Operating cost is high 3. Output power is high 4. Liquid is incompressible 5. Requires more space for installation 5. What are control valves? State its types. The device which is used to meter, monitor & direct the fluids in a flow path is called as control valves Control valves are classified into: Relief valves, unloading valves, sequence valves, counter balance valve, check valve, directional control valve, flow control valve 6. What are fluid conditioning elements? In many plants, closed loop control is achieved by electronic devices based on different logic functions such as AND, OR, NOT and MEMORY. Logic controls can be defined as design of control system based on reasoning arising out of deductive principle. However, the electronic control system is not only control system used in industries. If the pneumatic control system using low-pressure air is used to achieve the above logic control functions, then it is known as Fluidic Logic Control. 7. What are the four important factors that should be considered while designing a fluid power circuit? Pneumatic power supply 1. The source is air 2. Operating cost is low as air is readily available in nature 3. Output power is low 4. Air is compressible 5. Requires less space for installation
Safety of operation, performance of desired function, efficiency of operation and cost 8. What is the use of regenerative circuit? A Regenerative circuit is used to speed up the extending speed of a double acting cylinder. This is attained by connecting the return flow from cylinder to pump flow 9. What is PLC? State its elements. A PLC can be defined as a digital electronic device that uses a programmable memory to store instructions such as logic, sequencing, timing, counting and arithmetic to control machines, or processes. Central processing unit (CPU), programmer/monitor (PM), input/output module (I/O). 10. Define proximity sensors. The object which is to be sensed at greater distances is possible only through proximity sensors for an equivalent amount of flow consumption 11. List any four applications of accumulators. Accumulator is used as an auxiliary power source. Accumulator is used as a compensator for an internal (or) external leak Accumulator is used as an emergency power source Accumulator is used as a hydraulic shock absorber. 12. List the components associated with PLC system. PLC can be defined as a digital electronic device that uses a programmable memory to store instructions such as logic, sequencing, timing, counting and arithmetic to control machines, or processes. Central processing unit with an associated memory, input modules, output modules. 13.Define viscosity and bulk modulus of a hydraulic fluid. Resistance experienced by the fluid to flow is called as viscosity Liquids are incompressible and so their volume does not change with pressure changes. This is not exactly true, for the change in volume due to pressure is so small that it is ignored. The compressibility is measured by Bulk Modulus. The higher the bulk modulus, the less compressible the fluid or vice versa. 14. What is a relay? Relay is a switch whose contacts open or close when its coil is energised. Relays are used for energising and de-energising solenoids 15. State the effect of temperature and pressure on viscosity of gases. The viscosity of gases increases with increase in temperature. Over the normal range of pressures, the viscosity of gases is found to be independent of pressure 16. How do you specify a pump? A pump can be specified by its capacity, discharge pressure and speed of rotation
17. What is the purpose of an air pressure regulator? An air pressure regulator is used to meter the compressed air, to regulate the flow of air and to maintain the system pressure 18.What is the purpose of failsafe circuit? The fail safe circuit is used to safe guard the men, work and machines 19. What is bistable flip-flop? A bistable flip-flop provides controlled assurance as to which of the two ouput ports will deliver the power stream. It is normally used as a memory device 20.What are servo valves? Write their purpose in fluid power systems? Servo valves are nothing but DC valves having infinitely variable positioning capability The servo valves are used to control not only the direction of fluid flow, but also the amount of flow 21. State the coanda effect. when a stream of fluid meets other stream, the effect is to change its direction of flow and effect is the fluid sticks to the wall Part-B 1. What are the essential and desirable properties of a hydraulic fluid? Discuss fluid. (10) (6) 2. List the precautions to be taken when a mineral oil based fluid is changed into fire resistant 3. Explain how bernoullis equation can be used to determine the pressure drop between two stations in a hydraulic system. Assume that there are some number of bends, tees, elbows, globe and gate valves in between these two ststion separated by a long distance. 4. Discuss the factors to be considered in the selection of hydraulic fluids 5. With neat sketch explain the hydraulic and pneumatic flui power systems. 6. Discuss the properties of hydraulic fluids. 7. How to calculate frictional losses in common valves and fittings 8. Define Reynolds number. 9. Differentiate laminar and turbulent fluid flow. 10. Compare and contrast hydraulic, pneumatic and electromechanical power systems. 11. Write briefly about the following hydraulic fluids. i) petroleum oils, ii) emulsions, iii) glycols. 12. Explain how positive displacement pimps build pressure compared to rotodynamic pumps. What are the advantages of positive displacement pumps? plate type. atleast six types of cylinder mounts available. (6) (10) (16) 13. Using a neat sketch explain the construction and operation of an axial piston pump of swash 14. Explain using a neat sketch end cushioning provided in hydraulic cylinders. Also sketch (10) (8) (12) (4) (8) (2) (6) (10) (6)
15. Explain the followings: Pump characteristic curves Pump cavitation Pump noise Pump selection 16. With a neat sketch, explain the end cushion provided in hydraulic cylinder. 17. Explain with neat sketch, the principle of operation of telescopic cylinder. 18. Explain the working principle of external gear pump and determine its performance Measures. 19. Write short notes on variable displacement pumps, 20. Explain the various mechanisms of hydraulic cylinder mountings with neat diagram. 21. Explain a hydraulic press circuit which employs double pump unloading principle. and performance features of different types of hydraulic pumps. the specification of them. 24. Give any two applications circuits employing accumulator for different purposes. 25.Develop a two handed safety circuit for the operation of a press and explain. 26. Explain typical hydraulic and pneumatic systems with neat sketches. 27. Explain the working of hydraulic jack. 28. Draw iso symbols for the following. 4/3 DCV, pressure reducing valve, lever type actuation, variable displacement pump.
(16)
(8) (8) (12) (4) (16) (8) (8) (8) (8) (8) (12) (4) (8)
22. Explain the factors which affect the selection of pumps and discuss in detail the classification 23.Draw a single cylinder continuous reciprocation circuit using suitable components and give
29. Explain the construction and working principle of a bend axial pump with a neat sketch. (8) 30. Enumerate the construction and working principle of an external gear pump with a neat sketch. 31. Discuss the construction and working of a vane type hydraulic motor with a neat Sketch. 32. Explain the construction and working of a two stage air compressor with a neat sketch. flow control valve. system. (8) (8) (8) 33. Explain with the neat sketch the construction and working of a non-pressure compensated 34. Explain with the neat sketch the construction and working of a hydro mechanical servo valve 35.What is accumulator? Mention its types and applications in a hydraulic circuit. Explain any one of the circuit where in accumulator is used. Also explain its functions with help of a diagram. A+ B+ A- B- . (16) (16) 36.What is a cascade system? Design a pneumatic circuit using cascade method for the sequence (8) (8)
37. Explain how to control speed in a hydraulic system with neat diagram. diagrams. i) switches, ii) solenoids, iii) relays, iv) timers sequencing circuit with ladder diagram.
(16) (16) (16)
38.Explain the working principles of the following electrical control devices with suitable 39.What is meant by ladder diagram? Explain the working principle of a dual cylinder 40.Develop a circuit involving two double acting cylinders A and B operating with the following sequence: A+ B+ A- B- where + represents extension of the rod and represents retraction. Use only sequence valves to obtain the sequencing and explain the procedure to arrive at the size of the accumulator. 42. Draw a circuit employing accumulator for supplying emergency hydraulic power. 40) are determined. 44. Using a neat sketch explain the construction and working of a pneumatic regulator. Also give its graphical symbol. 45.A double acting pneumatic cylinder is required to provide the following operation: fast extensions till the mid stroke, slow extension till the end of stroke and on sensing the stroke end provide rapid return. Develop a pneumatic circuit employing a shuttle valve and suitable flow control and other valves. 46. Draw a neat sketch of an electro hydraulic servo valve and indicate all the gain for this valve. 47. Explain various locations at which filters and strainers are fitted giving reasons. internal pilot. What happens? Explain. 49. Explain how the pressure relief valve and its variants could be used for unloading applications. 50. List the need and application of synchronising circuits. 51. With simple sketches, explain the various types of synchronising circuits. graphical symbol. switches and relays. 55. Explain the working principle of any two types of pneumatic position sensing devices. 56. Explain with block diagram the components present in a PLC and give their functions. 57. What is cascade control? Explain giving suitable example circuit. (6) (4) (12) (6) (10) (6) (8) (8) (8) 48. If a hydraulic circuit has pump inlet and exit ports interchanged, unloading valve given (16) (16) (16) (6) (10) (6) (10) 41. Consider the charging and discharging of a hydro pneumatic accumulator to be isothermal
43.Explain how the size of the air receiver and pressure drop in pneumatic pipe lines (scheduled
Components and give their functions. Also develop the transfer function for the open loop
52. Draw a neat sketch of pneumatic filter and explain its construction and working. Also give the 53.Develop a continuous single cylinder reciprocation circuit for pneumatic system using limit 54. Draw a neat sketch of an electro-hydraulic for sequencing drilling and clamping cylinders(10)
58. Briefly explain the maintenance requirements for hydraulic power packs. traps and pressure regulation. 60. Explain the principle of low cost automation. 61. Explain the operational features of the check valve with neat diagram. 62. Write short notes on shuttle valve. 63.Explain air over oil intensifier system with suitable example. 64. With neat sketch explain the weight loaded accumulator. sketch. 66.What is synchronizing? Explain the synchronizing circuit with suitable approaches. 67.Explain the hydro mechanical servo system with suitable application. 68. How PLC is used in fluid power control? Explain with a suitable application. 69. Explain the construction and working of pilot operated sequence valve. 71. Draw and explain the ladder diagram connections for a regenerative circuit. 72. Write and explain the working principle of pressure intensifier, with neat diagram. m3/min at 8 bar gauge. The overall efficiency of the compressor is 74%. 74. Make a circuit sketch for the control of a double-acting hydraulic cylinder. diagram. 76. What are proportional control valves? Write the types of proportional control valves? 77. Describe the various selection criteria for pneumatic components. 78. Explain the working principle of a PLC with neat block diagram.
(6) (6) (4) (10) (6) (10) (6) (16) (16) (16) (16) (8) (10) (6)
59. Explain the layout of pneumatic systems with emphasis on sizing of conductors, cleanliness,
65. What is compressor? Explain the working principle of piston type compressor with neat
70. Make a circuit sketch, showing the use of an accumulator, as a hydraulic shock absorber. (8)
73.Determine the actual power required to drive a compressor that delivers air at 3.5 standard (8) (12) (6) (10)
75. Explain the construction and working principle of hydro mechanical servo calves with neat
79. Fluid is flowing through a tapering pipe having diameters 50 mm and 25mm at sections 1 and 2 respectively. The discharge through the pipe is 7.5 Lps (litres per second). The section 1 is 3m above datum and section 2 is 1.25m above datum. If the pressure at section 1 is 200 kpa, find the pressure at section 2. The specific gravity of the fluid is 0.9. (10) 80.A hydraulic pump delivers oil at 60 bar, 120 lpm into a circuit laid on a horizontal plane. There are 4 elbows (k=0.75), one globe valve fully open (k=10) and a DCV (pressure drop =3bar) with the inside diameter of the pipe as 30mm. the total length of the straight run pipe is 20 m and specific gravity of the oil is 0.9. The kinematic viscosity of the oil is 0.0001 m2/sec. determine the pressure in bar at the exit point of the pipe. (10) 81.Oil with a specific gravity 0.9 enters a Tee, as shown in fig 1, with velocity V1=5m/s. the diameter at section 2 is 7cm and the diameter at section 3 is 6cm. if equal flow rates are to occur at section 2 and 3, find V2 and V3 (8)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics ME1305Document8 pagesApplied Hydraulics and Pneumatics ME1305kv19852009Pas encore d'évaluation
- ME 2305 Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics: Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Instuitute of Research and TechnologyDocument10 pagesME 2305 Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics: Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Instuitute of Research and TechnologyAnonymous p8bHAAxPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Hydralics and Pneumatics 2 MarksDocument10 pagesApplied Hydralics and Pneumatics 2 MarksVignesh VickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2hariharanbookPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4& 5Document9 pagesUnit 4& 5hariharanbook0% (1)
- Unit - I: Two Mark Questions & AnswersDocument8 pagesUnit - I: Two Mark Questions & Answerssmg26thmayPas encore d'évaluation
- Me55 - Applied Hydraulics & Pneumatics PDFDocument12 pagesMe55 - Applied Hydraulics & Pneumatics PDFPandiya RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic & Pneumatic Two Mark QuestionsDocument7 pagesHydraulic & Pneumatic Two Mark QuestionsVVCET - MechPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 1305 Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument6 pagesME 1305 Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsSuresh VeluPas encore d'évaluation
- AMEE310 Lab5Document12 pagesAMEE310 Lab5tsunaseetPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 1305 - Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument7 pagesME 1305 - Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsUva ShruthikaPas encore d'évaluation
- BMT7L1-Fluid Power Automation LabDocument37 pagesBMT7L1-Fluid Power Automation LabvamshimohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Power DME 6TH SEMDocument58 pagesFluid Power DME 6TH SEMAman Ahmed MokamiPas encore d'évaluation
- AHP Question BankDocument11 pagesAHP Question Bankduraiprakash83Pas encore d'évaluation
- ED7004-Design of Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Question BankDocument10 pagesED7004-Design of Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Question Bankkannanviknesh086319Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mechatronics Lab ManualDocument54 pagesMechatronics Lab ManualAjay Chacko100% (1)
- Lab Report 2: BTM 2243 Fluid Power TechnologyDocument5 pagesLab Report 2: BTM 2243 Fluid Power TechnologyIbrahim AdhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Amta6 7 Using Hydraulic SystemsDocument26 pagesAmta6 7 Using Hydraulic SystemsMohammed Al-OdatPas encore d'évaluation
- HYDRAULICS AND PNEUMATICS 2 MarksDocument34 pagesHYDRAULICS AND PNEUMATICS 2 MarksAnirudhan RPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 - Hydraulic Operation Circuit and ApplicationDocument19 pagesChapter 7 - Hydraulic Operation Circuit and ApplicationMuhammad AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Questions For Industrial Fluid PowerDocument3 pagesOral Questions For Industrial Fluid PowerEswara RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic System:-: Chapter-2 Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electrical Telemetry SystemsDocument7 pagesHydraulic System:-: Chapter-2 Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electrical Telemetry SystemsMayur ParmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument1 pageApplied Hydraulics and PneumaticsSoni Mishra Tiwari0% (1)
- 7 Hydraulic CKT 18P1Document23 pages7 Hydraulic CKT 18P1M Razzaque100% (2)
- Fluid Power with ApplicationsDocument9 pagesFluid Power with ApplicationstadiwosPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulics NotesDocument16 pagesHydraulics NotesMadhusudhan ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document86 pagesUnit 1Kalaiselvan PunniyamoorthyPas encore d'évaluation
- FLUID POWER SYSTEMS Theory and PracticeDocument37 pagesFLUID POWER SYSTEMS Theory and PracticeAchmad Ari Dwi P100% (2)
- The Source of Hydraulic PowerDocument16 pagesThe Source of Hydraulic Powersekar507Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2: Actuation SystemsDocument10 pagesUnit 2: Actuation SystemsNaga RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- ME416 LN 201617 Unit1Document66 pagesME416 LN 201617 Unit1rajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Me2305 - Ahp 2 Marks Q&ADocument11 pagesMe2305 - Ahp 2 Marks Q&ANavinsithi100% (1)
- Automotive Hydraulics & Pneumatic SystemsDocument2 pagesAutomotive Hydraulics & Pneumatic SystemsSiddhrajsinh ZalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulics Intro PDFDocument81 pagesHydraulics Intro PDFavinash babuPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumatic ViseDocument18 pagesPneumatic ViseSaravanan SaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Power Engineering FPE 18ME55 Syllabus 2018 19Document3 pagesFluid Power Engineering FPE 18ME55 Syllabus 2018 19ChinthanPas encore d'évaluation
- NPTEL Fluid Power Control CourseDocument2 pagesNPTEL Fluid Power Control Coursevitor_pedro100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Hydraulic SystemsDocument30 pagesFundamentals of Hydraulic SystemsMuhannad AbdulRaoufPas encore d'évaluation
- Aircrafts Hydraulic SystemDocument23 pagesAircrafts Hydraulic SystemPrinnia Zulfiqur BorshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulics Pneumatics QuestionDocument29 pagesHydraulics Pneumatics QuestionSenthilvel C100% (1)
- HPS Notes of Lecture PDFDocument63 pagesHPS Notes of Lecture PDFsbhalesh100% (2)
- Hydraulic SystemDocument7 pagesHydraulic SystemHamza Munir100% (1)
- Fluid Power Learning ObjectivesDocument40 pagesFluid Power Learning ObjectivesbmdbmdbmdPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Power EngineeringDocument2 pagesFluid Power EngineeringBhavesh PipaliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes On Fluid Power Systems: Unit IDocument10 pagesLecture Notes On Fluid Power Systems: Unit ItadiwosPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Circuits Lab ReportDocument13 pagesHydraulic Circuits Lab ReportklashincoviskyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 TroubleshootingDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Troubleshootingabdullatif_asPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Sim Hydraulics ReferenceDocument430 pages2 Sim Hydraulics ReferenceEnrico GambiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro-Pneumatics: Module EP-5: Sensors in Electro-Pneumatics (Proximity Switches and Pressure Switches)Document36 pagesElectro-Pneumatics: Module EP-5: Sensors in Electro-Pneumatics (Proximity Switches and Pressure Switches)Joesun LizardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Notes Pneumatic 2Document27 pagesExtra Notes Pneumatic 2olivia curtisPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems Test AnswersDocument5 pagesPneumatic and Hydraulic Systems Test AnswersZuhaila MohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Limits and FitsDocument6 pagesLimits and Fitscamohunter71Pas encore d'évaluation
- Closed Loop Control Systems ExplainedDocument33 pagesClosed Loop Control Systems ExplainedSgsksbskxvxk100% (1)
- Hydraulic CircuitsDocument45 pagesHydraulic Circuitsankita kamble50% (4)
- DRIVE SYSTEM Hydraulic and PneumaticDocument50 pagesDRIVE SYSTEM Hydraulic and PneumaticNor AzlanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic System ObjectivesDocument4 pagesHydraulic System ObjectivesMegha KharchePas encore d'évaluation
- ME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument79 pagesME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticselabalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil Hydraulics and Pneumatics Question BankDocument3 pagesOil Hydraulics and Pneumatics Question Bankkishan mauryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics Systems Components CircuitsDocument7 pagesHydraulics and Pneumatics Systems Components CircuitsdurgapriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Links To This Post First Year QP Mechanical QB Mechnical: Posted by N R Rejin Paul LabelsDocument8 pagesLinks To This Post First Year QP Mechanical QB Mechnical: Posted by N R Rejin Paul LabelsSuresh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Trane Chiller Plant Admapn014en - 0105Document4 pagesTrane Chiller Plant Admapn014en - 0105a_salehiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3.7 Cooling TowerDocument17 pagesChapter 3.7 Cooling TowermurugesanvPas encore d'évaluation
- Bulletin 09Document2 pagesBulletin 09VeeMugeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Culinary Arts Program Self Study ReportDocument655 pagesCulinary Arts Program Self Study Reportmurugesanv100% (3)
- E Mech and Mechanics of Solids SyllabusDocument4 pagesE Mech and Mechanics of Solids SyllabusmurugesanvPas encore d'évaluation
- Two Dimensional Random VariablesDocument6 pagesTwo Dimensional Random VariablesmurugesanvPas encore d'évaluation
- Adams Slider CrankDocument22 pagesAdams Slider CrankarslanPas encore d'évaluation
- TamilnaduDocument13 pagesTamilnadubalachandar19kPas encore d'évaluation
- RefrigerantsDocument66 pagesRefrigerantsargyreniaPas encore d'évaluation
- MM-18 - Bilge Separator - OPERATION MANUALDocument24 pagesMM-18 - Bilge Separator - OPERATION MANUALKyaw Swar Latt100% (2)
- TITLE 28 United States Code Sec. 3002Document77 pagesTITLE 28 United States Code Sec. 3002Vincent J. Cataldi91% (11)
- P.E 4 Midterm Exam 2 9Document5 pagesP.E 4 Midterm Exam 2 9Xena IngalPas encore d'évaluation
- Labov-DIFUSÃO - Resolving The Neogrammarian ControversyDocument43 pagesLabov-DIFUSÃO - Resolving The Neogrammarian ControversyGermana RodriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- Marlissa - After School SpecialDocument28 pagesMarlissa - After School SpecialDeepak Ratha50% (2)
- The Five Laws of Light - Suburban ArrowsDocument206 pagesThe Five Laws of Light - Suburban Arrowsjorge_calvo_20Pas encore d'évaluation
- UG022510 International GCSE in Business Studies 4BS0 For WebDocument57 pagesUG022510 International GCSE in Business Studies 4BS0 For WebAnonymous 8aj9gk7GCLPas encore d'évaluation
- Kedudukan Dan Fungsi Pembukaan Undang-Undang Dasar 1945: Pembelajaran Dari Tren GlobalDocument20 pagesKedudukan Dan Fungsi Pembukaan Undang-Undang Dasar 1945: Pembelajaran Dari Tren GlobalRaissa OwenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Commuter Cleaning - Group 10Document6 pagesCommuter Cleaning - Group 10AMAL ARAVIND100% (1)
- AVK Butterfly Valves Centric 75 - TADocument1 pageAVK Butterfly Valves Centric 75 - TANam Nguyễn ĐứcPas encore d'évaluation
- Housekeeping NC II ModuleDocument77 pagesHousekeeping NC II ModuleJoanne TolopiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Classen 2012 - Rural Space in The Middle Ages and Early Modern Age-De Gruyter (2012)Document932 pagesClassen 2012 - Rural Space in The Middle Ages and Early Modern Age-De Gruyter (2012)maletrejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10-2nd Periodical Test 2018-19Document2 pagesScience 10-2nd Periodical Test 2018-19Emiliano Dela Cruz100% (3)
- Data FinalDocument4 pagesData FinalDmitry BolgarinPas encore d'évaluation
- Astrology - House SignificationDocument4 pagesAstrology - House SignificationsunilkumardubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Java Interview Questions: Interfaces, Abstract Classes, Overloading, OverridingDocument2 pagesJava Interview Questions: Interfaces, Abstract Classes, Overloading, OverridingGopal JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Areas Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Areas Teaching Dates and Time QuarterKhesler RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Reviewer in PmlsDocument10 pagesLesson 1 Reviewer in PmlsCharisa Joyce AgbonPas encore d'évaluation
- Md. Raju Ahmed RonyDocument13 pagesMd. Raju Ahmed RonyCar UsePas encore d'évaluation
- Ten - Doc. TR 20 01 (Vol. II)Document309 pagesTen - Doc. TR 20 01 (Vol. II)Manoj OjhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comal ISD ReportDocument26 pagesComal ISD ReportMariah MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Product Development - SurveyDocument4 pagesFood Product Development - SurveyJoan Soliven33% (3)
- SCMReport Group4 MilmaDocument10 pagesSCMReport Group4 MilmaJyotsna Gautam0% (1)
- CSR of Cadbury LTDDocument10 pagesCSR of Cadbury LTDKinjal BhanushaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtue Ethics: Aristotle and St. Thomas Aquinas: DiscussionDocument16 pagesVirtue Ethics: Aristotle and St. Thomas Aquinas: DiscussionCarlisle ParkerPas encore d'évaluation
- ROCKET STOVE DESIGN GUIDEDocument9 pagesROCKET STOVE DESIGN GUIDEfrola5100% (2)
- Poetry Recitation Competition ReportDocument7 pagesPoetry Recitation Competition ReportmohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- 2Document5 pages2Frances CiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nazi UFOs - Another View On The MatterDocument4 pagesNazi UFOs - Another View On The Mattermoderatemammal100% (3)
- Supply Chain AssignmentDocument29 pagesSupply Chain AssignmentHisham JackPas encore d'évaluation