Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Formulae Modulation
Transféré par
Satyanarayana RajuDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Formulae Modulation
Transféré par
Satyanarayana RajuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1.
(a + b)(a b) = a2 b2
2. (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2(ab + bc + ca)
3. (a b)2 = a2 + b2 2ab
4. (a + b + c + d)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + d2 + 2(ab + ac + ad + bc + bd + cd)
5. (a b)3 = a3 b3 3ab(a b)
6. (a b)(a2 + b2 m ab) = a3 b3
7. (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 -ab bc ca) = a3 + b3 + c3 3abc =
1/2 (a + b + c)[(a - b)2 + (b - c)2 + (c - a)2]
8. when a + b + c = 0, a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc
9. (x + a)(x + b) (x + c) = x3 + (a + b + c) x2 + (ab + bc + ac)x + abc
10. (x a)(x b) (x c) = x3 (a + b + c) x2 + (ab + bc + ac)x abc
11. a4 + a2b2 + b4 = (a2 + ab + b2)( a2 ab + b2)
12. a4 + b4 = (a2 2ab + b2)( a2 + 2ab + b2)
13. an + bn = (a + b) (a b n-1)
n-1
n-2
b+ a
n-3
b2 a
n-4
b3 +.. +
(valid only if n is odd) 14. an bn = (a b) (a b n-1)
n-1
+a
n-2
b+ a
n-3
b2 + a
n-4
b3 + +
{where n N) 15. (a b)2n is always positive while -(a b)2n is always negative, for any real values of a and b
16. (a b)2n = (b a)2 and (a b)2n+1 = (b a)2n+1
17. if and are the roots of equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, roots of cx + bx + a = 0 are 1/ and 1/. if and are the roots of equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, roots of ax2 bx + c = 0 are - and -.
18. n(n + l)(2n + 1) is always divisible by 6.
32n leaves remainder = 1 when divided by 8
n3 + (n + 1 )3 + (n + 2 )3 is always divisible by 9
102n
+ 1
+ 1 is always divisible by 11
n(n2- 1) is always divisible by 6
n2+ n is always even
23n-1 is always divisible by 7
152n-1 +l is always divisible by 16
n3 + 2n is always divisible by 3
34n 4
3n
is always divisible by 17
n! + 1 is not divisible by any number between 2 and n
(where n! = n (n l)(n 2)(n 3).3.2.1) for eg 5! = 5.4.3.2.1 = 120 and similarly 10! = 10.9.8.2.1= 3628800
19. Product of n consecutive numbers is always divisible by n!.
20. If n is a positive integer and p is a prime, then np n is divisible by p.
21. |x| = x if x 0 and |x| = x if x 0.
22. Minimum value of a2.sec2 + b2.cosec2 is (a + b)2; (0 < < 90)
for eg. minimum value of 49 sec2 + 64.cosec2 is (7 + 8)2 = 225. 23. among all shapes with the same perimeter a circle has the largest area.
24. if one diagonal of a quadrilateral bisects the other, then it also bisects the quadrilateral.
25. sum of all the angles of a convex quadrilateral = (n 2)180
26. number of diagonals in a convex quadrilateral = 0.5n(n 3)
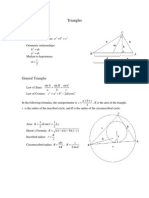
27. let P, Q are the midpoints of the nonparallel sides BC and AD of a trapezium ABCD.Then, APD = CQB.
Modulation
Modulation is an important step of communication system. Modulation is defined as the process whereby some characteristic (line amplitude, frequency, phase of a high frequency signal wave (carrier wave) is varied in accordance with instantaneous value intensity of low frequency signal wave (modulating wave.) Need for modulation : (i) To separate signal from different transmitters :Audio frequencies are within the range of 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Without modulation all signals at same frequencies from different transmitters would be mixed up. There by giving impossible situation to tune to any one of them. In order to separate the various signals, radio stations must broadcast at different frequencies. Each radio station must be given its own frequency band. This is achieved by frequency translation as a result of modulation process. (ii) Size of the antenna : For efficient transmission the transmitting antennas should have length at least equal to a quarter of the wavelength of the signal to be transmitted. For an electromagnetic wave of frequency 15 kHz, the wavelength is 20 km and one-quarter of this will be equal to 5 km. Obviously, a vertical antenna of this size is impractible. On the other hand, for a frequency of 1 MHz, this height is reduced to 75m. Also, the power radiated by an antenna of length l is proportional to (l/)2. This shows that for the same antenna length, power radiated is large for shorter wavelength. Thus, our signal which is of low frequency must be translated to the high frequency spectrum of the electromagnetic wave. This is achieved by the process of modulation.
Types of modulation :A sinusoidal carrier wave can be expressed as
ec = Ec cos(c t + )
Its three distinct characteristics are (i) Amplitude (Ec) (ii) angular frequency (c) (iii) phase angle ().
Either of these three characteristics can be varied in accordance with the modulating signal. These result in three types of modulation. (i) Amplitude modulation (AM) (ii) Frequency modulation (FM) (iii) Phase modulation (PM)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Physics 21 SolutionsDocument92 pagesPhysics 21 SolutionsOğuzhan Odbay100% (1)
- FormulaDocument2 pagesFormulaRajsekhar ToletyPas encore d'évaluation
- Important FormulasDocument3 pagesImportant FormulasAnurag ChokassPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Transmission: Solutions To Odd-Numbered Review Questions and ExercisesDocument4 pagesAnalog Transmission: Solutions To Odd-Numbered Review Questions and ExercisesshahabzaheerPas encore d'évaluation
- NET Past Papers MathsDocument49 pagesNET Past Papers Mathserum shomail100% (1)
- Trig Identities and Ratio Wts PDFDocument9 pagesTrig Identities and Ratio Wts PDFAshwin JambhulkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Kerala Set - 1Document18 pagesKerala Set - 1Yamini DhanabalanPas encore d'évaluation
- KEE - Model Question PaperDocument19 pagesKEE - Model Question PaperPremKumarKalikiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Jee Mains FormulasDocument17 pagesJee Mains FormulasdevenderPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics FormulasDocument2 pagesMathematics FormulasgopalmyneniPas encore d'évaluation
- ARML TheoremsDocument27 pagesARML Theoremsfreefall014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kvpy Paper XiiDocument25 pagesKvpy Paper XiiVishank RustagiPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Formulas For CatDocument2 pagesMaths Formulas For Catvickychauhan250% (2)
- Basic Maths FormulaeDocument10 pagesBasic Maths FormulaeAns DevPas encore d'évaluation
- AMC Formulas PDFDocument17 pagesAMC Formulas PDFYounger Boxer MetalicPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 Winter Camp - Mock Olympiad - SolutionsDocument5 pages2010 Winter Camp - Mock Olympiad - SolutionsAltananyPas encore d'évaluation
- All Maths FormulasDocument4 pagesAll Maths FormulasSAMUEL.SPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDocument9 pagesNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryJarnice Ling Yee ChingPas encore d'évaluation
- Essential FormulaeDocument16 pagesEssential FormulaeMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- Some Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in MathematicsDocument12 pagesSome Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in Mathematicsparchure123100% (1)
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDocument7 pagesEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebraShinigami01001Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Vector in The Direction of Vector That Has Magnitude 15 IsDocument8 pagesA Vector in The Direction of Vector That Has Magnitude 15 IsANKUR GHEEWALAPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Olympiad Set 3Document35 pagesMathematics Olympiad Set 3Senthilnathan SomasundaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Metz GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- CIRCLEA Theory Solved Example IitjeeDocument11 pagesCIRCLEA Theory Solved Example IitjeeShashank ShekharPas encore d'évaluation
- XVII APMO - March, 2005: Problems and SolutionsDocument8 pagesXVII APMO - March, 2005: Problems and SolutionsSơn TèoPas encore d'évaluation
- XVII APMO - March, 2005: Problems and SolutionsDocument57 pagesXVII APMO - March, 2005: Problems and Solutionscyoung36Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eklavyats-2023-Part Test 5 (Math) : Abc IsDocument27 pagesEklavyats-2023-Part Test 5 (Math) : Abc IsSaptarshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution20for20Midterm 201420fallDocument5 pagesSolution20for20Midterm 201420fall3.14159265Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coplex Number FormulasDocument7 pagesCoplex Number FormulasMohan KhedkarPas encore d'évaluation
- If A: B:: C: D, Then Ad BC: Ratio - Proportion - VariationDocument14 pagesIf A: B:: C: D, Then Ad BC: Ratio - Proportion - VariationMegha ShrimankarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2006 ISRO ECE Question Paper PDFDocument19 pages2006 ISRO ECE Question Paper PDFKD0% (1)
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ellipse 2012Document10 pagesEllipse 2012SantoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Tunedmassdamper PDFDocument3 pagesTunedmassdamper PDFJinho JungPas encore d'évaluation
- Rec3 SolutionsDocument6 pagesRec3 SolutionsOscar Martinez0% (1)
- 15 Maths in PhysicsDocument6 pages15 Maths in PhysicsmvhokoPas encore d'évaluation
- X-STB-Geomerty - Prelim - I - SET B - QPDocument4 pagesX-STB-Geomerty - Prelim - I - SET B - QPSAID SAYALIPas encore d'évaluation
- TrigonometryDocument23 pagesTrigonometryTitis PohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Illustrative Examples Physics Vectors RDocument20 pagesIllustrative Examples Physics Vectors RVishal KalraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ellipse orDocument23 pagesEllipse orTEJA SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM AddMath Formula List NOT GivenDocument10 pagesSPM AddMath Formula List NOT GivenYoke Hock Seow100% (1)
- Problems On Math Methods - II: Compiled by JMDocument4 pagesProblems On Math Methods - II: Compiled by JMSourav RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- DPPS - 2 - VectorDocument2 pagesDPPS - 2 - VectormridulPas encore d'évaluation
- Cap. 32 PDFDocument75 pagesCap. 32 PDFwallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths General FunDASDocument10 pagesMaths General FunDASVinod ChintalapudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesD'EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsD'EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Newnes Mathematics Pocket Book for EngineersD'EverandNewnes Mathematics Pocket Book for EngineersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYD'EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionD'EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionPas encore d'évaluation
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankD'EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsD'EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Marantz Product Catalogue 2010 2011Document31 pagesMarantz Product Catalogue 2010 2011O M Gee100% (1)
- Reduced Chemical Kinetic Mechanisms For Methane Combustion Ino /N and O /co AtmosphereDocument51 pagesReduced Chemical Kinetic Mechanisms For Methane Combustion Ino /N and O /co Atmosphereariel zamoraPas encore d'évaluation
- STP Tender Document For 08.05.2018Document32 pagesSTP Tender Document For 08.05.2018Arunprasad DurairajPas encore d'évaluation
- CMMIDocument23 pagesCMMIChaithanya KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cap 1Document10 pagesCap 1Oscar Bello LemusPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Construction Article PDF - Site Casting Exposed Aggregate WallsDocument1 pageConcrete Construction Article PDF - Site Casting Exposed Aggregate WallssonofalexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Competitive Products Cross-Reference GuideDocument30 pagesCompetitive Products Cross-Reference GuideJeremias UtreraPas encore d'évaluation
- A Tracer Study On Btte GraduatesDocument15 pagesA Tracer Study On Btte GraduatesOzalleAngryBertPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions Supplychain RegalDocument2 pagesQuestions Supplychain RegalArikuntoPadmadewaPas encore d'évaluation
- L5 - Dipl in Computing International StudentsDocument6 pagesL5 - Dipl in Computing International StudentscuriousEnginePas encore d'évaluation
- Relais Bistable, 3 RT / 25 A: Relay Latch, 3 PDT / 25 AmpDocument4 pagesRelais Bistable, 3 RT / 25 A: Relay Latch, 3 PDT / 25 AmpXavier DevauxPas encore d'évaluation
- Sony Video Camera Manual PDFDocument118 pagesSony Video Camera Manual PDFGary Hoehler100% (1)
- Lutec Katalog PDFDocument166 pagesLutec Katalog PDFSpeedyPas encore d'évaluation
- Goldwallet 2.1.1Document16 pagesGoldwallet 2.1.1yanuarPas encore d'évaluation
- Python - Tutorial: #!/usr/bin/python Print "Hello, Python!"Document174 pagesPython - Tutorial: #!/usr/bin/python Print "Hello, Python!"ankitPas encore d'évaluation
- StatementDocument3 pagesStatementSachinBMetre87 SachinBMetrePas encore d'évaluation
- Premier MDocument44 pagesPremier Mthebetterman0511Pas encore d'évaluation
- Econ Ball Valves Stainless Steel 3 Way Port: Blow-Out Proof StemDocument1 pageEcon Ball Valves Stainless Steel 3 Way Port: Blow-Out Proof StemChristianGuerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machines (K-18EL101) (Mid-Term Presentation)Document11 pagesElectrical Machines (K-18EL101) (Mid-Term Presentation)Noor SabaPas encore d'évaluation
- ElinkDocument36 pagesElinkjosemanuelarangoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Compressed Air SystemDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Compressed Air SystemMohd Zulhairi Mohd NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Top Links October 2018Document122 pagesTop Links October 2018Andrew Richard ThompsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Gautam Buddha University: ID Card Form (Please Fill Up The Form in Block Letters)Document1 pageGautam Buddha University: ID Card Form (Please Fill Up The Form in Block Letters)ATUL SAXENAPas encore d'évaluation
- Sterling Trader Pro en PDFDocument91 pagesSterling Trader Pro en PDFAyush ChaudhariPas encore d'évaluation
- XII Bahasa Inggris No. 16-18Document3 pagesXII Bahasa Inggris No. 16-18Auryn AnastashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chandigarh Shep PDFDocument205 pagesChandigarh Shep PDFAkash ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Instructions For Using Biometric DevicesDocument6 pagesManual Instructions For Using Biometric DevicesramunagatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Notes On Building ConstructionDocument20 pagesShort Notes On Building Constructionlarnz0% (1)
- The Organization & Structure of Banks & Their IndustryDocument19 pagesThe Organization & Structure of Banks & Their Industryrachim04Pas encore d'évaluation
- Premium Protection Synthetic Motor Oils (AMO & ARO)Document2 pagesPremium Protection Synthetic Motor Oils (AMO & ARO)brian5786Pas encore d'évaluation