Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Q
Transféré par
Jose Marie SalmingoDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Q
Transféré par
Jose Marie SalmingoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Imperial system
Main article: Imperial units Before SI units were widely adopted around the world, the British systems of English units and later imperial units were used in Britain, the Commonwealth and the United States. The system came to be known as United States customary units in the United States and is still in use there and in a few Caribbean countries. These various systems of measurement have at times been called foot-pound-second systems after the Imperial units for length, weight and time even though the tons, hundredweights, gallons, and nautical miles, for example, are different for the U.S. units. Many Imperial units remain in use in Britain which has officially partially switched to the SI system. Road signs are still in miles, yards, miles per hour; milk, beer and cider are sold by the pint; people measure their height in feet and inches and their weight in stone and pounds, to give just a few examples. Imperial units are used in many other places, for example, in many Commonwealth countries that are considered metricated, land area is measured in acres and floor space in square feet, particularly for commercial transactions (rather than government statistics). Similarly, gasoline is sold by the gallon in many countries that are considered metricated.
Metric system
Main articles: Metric system, History of the metric system, and Introduction to the metric system The metric system is a decimal system of measurement based on its units for length, the metre and for mass, the kilogram. It exists in several variations, with different choices of base units, though these do not affect its day-to-day use. Since the 1960s, the International System of Units (SI) is the internationally recognized metric system. Metric units of mass, length, and electricity are widely used around the world for both everyday and scientific purposes. The metric system features a single base unit for many physical quantities. Other quantities are derived from the standard SI units. Multiples and fractions of the units are expressed as Powers of 10 of each unit. Unit conversions are always simple because they are in the ratio of ten, one hundred, one thousand, etc., so that convenient magnitudes for measurements are achieved by simply moving the decimal place: 1.234 metres is 1234 millimetres or 0.001234 kilometres. The use of fractions, such as 2/5 of a metre, is not prohibited, but uncommon. All lengths and distances, for example, are measured in metres, or thousandths of a metre (millimetres), or thousands of metres (kilometres). There is no profusion of different units with different conversion factors as in the Imperial system which uses, for example, inches, feet, yards, fathoms, rods.
International System of Units
Main article: International System of Units The International System of Units (abbreviated as SI from the French language name Systme International d'Units) is the modern revision of the metric system. It is the world's most widely used system of units, both in everyday commerce and in science. The SI was developed in 1960
from the metre-kilogram-second (MKS) system, rather than the centimetre-gram-second (CGS) system, which, in turn, had many variants. During its development the SI also introduced several newly named units that were previously not a part of the metric system. The original SI units for the six basic physical quantities were:[2] Unit Abbreviation Quantity measured metre m length second s time kilogram kg mass ampere A electric current kelvin K thermodynamic temperature candela cd luminous intensity The mole, the unit of amount of substance, was subsequently added to this list and the degree Kelvin renamed the kelvin. There are two types of SI units, base units and derived units. Base units are the simple measurements for time, length, mass, temperature, amount of substance, electric current and light intensity. Derived units are constructed from the base units, for example, the watt, i.e. the unit for power, is defined from the base units as m2kgs3. Other physical properties may be measured in compound units, such as material density, measured in kgm-3. Converting prefixes The SI allows easy multiplication when switching among units having the same base but different prefixes. To convert from metres to centimetres it is only necessary to multiply the number of metres by 100, since there are 100 centimetres in a metre. Inversely, to switch from centimetres to metres one multiplies the number of centimetres by 0.01 or divide centimetres by 100. Note, however, that this is an unusual practice when measuring periods of time more than a second long, which are generally measured instead in minutes, hours, days, and similar units (see below), which require other conversion factors. Smaller periods of time are often measured in units corresponding to powers of ten of seconds, however (e.g. milliseconds, microseconds, nanoseconds).
Some special names and tools
Some special names for some multiples of some units are also used.
Mass: 100 kilograms = 1 quintal; 1000 kilograms = 1 metric tonne; Time: 60 seconds = 1 minute; 60 minutes = 1 hour; 24 hours = 1 day; 365 days = 1 year; 10 years = 1 decade; 100 years = 1 century; 1000 years = 1 millennium
Length measuring tools
A 2-metre carpenter's ruler A ruler or rule is a tool used in, for example, geometry, technical drawing, engineering, and carpentry, to measure lengths or distances or to draw straight lines. Strictly speaking, the ruler is the instrument used to rule straight lines and the calibrated instrument used for determining length is called a measure, however common usage calls both instruments rulers and the special name straightedge is used for an unmarked rule. The use of the word measure, in the sense of a measuring instrument, only survives in the phrase tape measure, an instrument that can be used to measure but cannot be used to draw straight lines. As can be seen in the photographs on this page, a two-metre carpenter's rule can be folded down to a length of only 20 centimetres, to easily fit in a pocket, and a five-metre-long tape measure easily retracts to fit within a small housing.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsDocument4 pagesThe International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsSamir ZaghloolPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Workbook Class 11 Geography PDFDocument135 pagesPractical Workbook Class 11 Geography PDFSurbhi SheoranPas encore d'évaluation
- EIM 11 - Q1 - W6 - Mod6Document14 pagesEIM 11 - Q1 - W6 - Mod6Mark Anthony BagaindocPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.creation and Development History of Unit SystemsDocument3 pages10.creation and Development History of Unit SystemsМурад ГусейнзадеPas encore d'évaluation
- Aeronautical ScienceDocument31 pagesAeronautical Sciencejorgerosas454Pas encore d'évaluation
- ES 112 Physics For Engineers Assignment 1Document2 pagesES 112 Physics For Engineers Assignment 1GB SoraPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Physics Notes Ch2Document2 pages11 Physics Notes Ch2Vijay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Derived Units and Unit Prefixes Derived UnitDocument15 pagesPhysics Derived Units and Unit Prefixes Derived UnitJohnRenzoMolinarPas encore d'évaluation
- FM 7910Document18 pagesFM 7910HiTechPas encore d'évaluation
- 2160 Zealstudy 8th Science 1st Lesson Unit Test 1 em Term - 1Document1 page2160 Zealstudy 8th Science 1st Lesson Unit Test 1 em Term - 1MuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Mechanics NotesDocument106 pagesEngineering Mechanics NotesVinodh GbPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.4 Measurement StandardDocument25 pages4.4 Measurement StandardMiles Paculba100% (1)
- 11th Physics Lesson 1 To 5 Question and Answer Study Material English MediumDocument49 pages11th Physics Lesson 1 To 5 Question and Answer Study Material English MediumMrDarkBéastPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Mechanics IDocument57 pagesEngineering Mechanics IsouhailPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFDocument6 pagesPhysical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFARAVINDPas encore d'évaluation
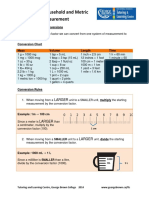
- Apothecary, Household and Metric Systems of MeasurementDocument4 pagesApothecary, Household and Metric Systems of MeasurementMANLANGIT, Bianca Trish A.100% (1)
- Module 1 (Mathematics, Science, and Technology) Bsba 2 (Final Copy)Document7 pagesModule 1 (Mathematics, Science, and Technology) Bsba 2 (Final Copy)frederick liponPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 - General Physics 1Document16 pagesWeek 1 - General Physics 1do san namPas encore d'évaluation
- ELeventh Physics Textbook SCERtDocument320 pagesELeventh Physics Textbook SCERtRoobala ChelladuraiPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL-G7 Q2 Week 2Document6 pagesDLL-G7 Q2 Week 2Gen-GenAlcantaraBaldado100% (1)
- Si Units: Nsci-6100 Physics For Engineers 1Document8 pagesSi Units: Nsci-6100 Physics For Engineers 1Yoo JungPas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics 1: Ms. ClariceDocument25 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Ms. ClariceHoneylyn V. ChavitPas encore d'évaluation
- Grades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level Teacher Mark A. Soliv A Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument9 pagesGrades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level Teacher Mark A. Soliv A Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterMark A. SolivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Units, Physical Quantities, Measurement, Errors and Uncertainties, Graphical Presentation, and Linear Fitting of DataDocument87 pagesUnits, Physical Quantities, Measurement, Errors and Uncertainties, Graphical Presentation, and Linear Fitting of DataAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Si Units EssayDocument8 pagesSi Units EssayRogger CarranzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5 Pharma Extra LectureDocument2 pagesLesson 5 Pharma Extra Lecturethe someonePas encore d'évaluation
- Physics XIDocument13 pagesPhysics XIArokiaraj RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Movin N Groovin Potm 8thDocument14 pagesMovin N Groovin Potm 8thapi-296863028Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Units, Measurement and Significant FiguresDocument33 pagesChapter 1 - Units, Measurement and Significant FiguresGhassan TerekPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Notes!Document45 pagesChapter 2 Notes!ronniego100% (2)