Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Conlaw Outline
Transféré par
Laurie YoonDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Conlaw Outline
Transféré par
Laurie YoonDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FEDERAL JUDICIAL POWER
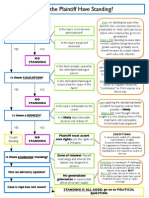
Standing o P suffered an injury o For declaratory and injunctive relief, P must show a likelihood of future harm to themselves o Ps problem must be resolvable by a favorable court ruling. o P cant stand in the shoes of another plaintiff, unless: The two plaintiffs have a special relationship The other plaintiff is unlikely to assert his own rights The asserting plaintiff is an organization and: The members have standing as individuals, The interests are germane to the organizations purpose The individual members need not participate in the suit o No generalized grievances allowed Ripeness o What hardship will be suffered if no preenforcement review? o Does the federal court have all it needs to decide the case now? Mootness o Case will be decided anyway if The wrong is capable of repetition and each time is resolved before review. If defendant voluntarily halts the offending practice If the name plaintiffs claim in a class action becomes moot, the suit will continue so long as one member of the class has an ongoing injury. Political question o Disputes under the Republican Form of Government clause (Article 4, section 4) o Challenges to Presidents conduct of foreign policy o Challenges to impeachment and removal process o Challenges to partisan gerrymandering
SUPREME COURT REVIEW
o
o o
General path to USSC o the highest court of a state (if a reversal on the federal law issues would materially affect the outcome) o a US court of appeals, or o a panel of 3 federal district court judges (usually, here, a statutory right of appeal will be provided) Writ of Certiorari o Most common method to get to USSC. Used to go from state courts and federal courts of appeal. o USSC has discretion on whether to hear it. Statutory appeals o If statute provides for USSC appeal, the USSC must hear it. Sovereign immunity o Established by 11th amendment. States cannot be sued.
Exceptions to sovereign immunity State can waive it State can be sued under federal laws adopted under section 5 of 14th amendment Federal government can sue the state State can be dragged into a bankruptcy proceeding o State officials (governor, etc) can be sued, but only if they would be personally liable. If any judgment would come from the state, sovereign immunity applies. Abstention o A federal court can hear a case, but declines to within its discretion. o Only mandatory abstention a federal court cannot enjoin a pending state court proceeding on the same issue. Not sure why this is under Supreme Court Review and not Federal Judicial Power
FEDERAL LEGISLATIVE POWER
o
Congressional authority to act o An express or implied power granted to Congress o The necessary and proper clause o Taxing and Spending power, or the Commerce power. o The 10th amendment (prevents Congress from compelling states to act) o Congressional power under section 5 of 14th amendment to remedy violations of existing rights. Delegation of powers o No limit on what powers Congress can delegate o One exception Congress cannot delegate executive powers to itself or its officers. o Vetoes Of executive actions both the House and Senate must act together (i.e. bicameralism) and the veto must be presented to the President Line-item veto is unconstitutional.
FEDERAL EXECUTIVE POWER
o
Limits of Presidential Executive Power o Most power when President acts with implied or express Congressional action o Less power President can act where Congress is silent, unless it: Usurps power from another governmental branch, or Prevents another governmental branch from carrying out its tasks. o Least power when President acts against the express will of Congress. Foreign policy o Treaties Senate must ratify, but President can repudiate unilaterally. o Executive Agreements o Executive Orders
Commander-In-Chief power broad. Domestic affairs o Appointment power o Removal power Congress cannot limit the Presidents ability to fire, but it can limit it. Congress may limit President ability to fire if independence from the President is desirable. o Impeachment and removal from office Impeached if House approves by a majority. Convicted by 2/3 of Senate o Presidential immunity from civil suit for actions taken while in office o Papers and conversations can be protected by Presidential privilege, but must yield to other governmental interests o Pardon For federal offenses only, not state law offenses Cannot pardon an offense for which an official was impeached
o
FEDERALISM
o
Preemption o Express statute explicitly says so o Implied preemption if: State and federal laws are mutually exclusive State law impedes achievement of a federal objective Congress evidences a clear intent to preempt o States cannot tax or regulate federal government activity Dormant Commerce Clause & Privileges and Immunities o Definitions: Dormant commerce clause states cannot pass laws to regulate interstate commerce in areas that Congress has left silent. Article 4 P&I states cannot discriminate based on state citizenship by treating instate residents more favorably than out-of-staters Corporations and aliens cannot use Article 4 P&I, but can use dormant commerce clause instead 14th amendment P&I States cannot deny their own residents rights of national citizenship, like the right to vote or the right to travel. Passed after the Civil War to prevent states from passing laws which treated blacks as inferior. o Analysis: If state law does not discriminate on its face against out-of-staters Article 4 P&I doesnt apply. If burden on interstate commerce, violates dormant commerce if burdens exceed benefits. If state law does discriminate on its face against out-of-staters and burdens interstate commerce:
it violates dormant commerce clause unless necessary to achieve an important government purpose, like protecting natural resources (fish, water, etc). Exceptions: o Congress approves of it o Market participant exception state can favor its own citizens for government services If state law discriminates on its face against out-of-staters and interferes with their ability to make a living: It violates Article 4 P&I unless necessary to achieve an important governmental purpose. Criteria: o Law must discriminate against out of staters o Discrimination must affect civil liberties or affect important economic activities o Discrimination must be necessary to achieve important government purpose. State taxation of interstate commerce o States cant use their tax systems to favor in-state business over out-of-state ones o States may only tax businesses with sufficient nexus/presence in the state o If sufficient nexus exists, state can only tax the business an amount proportionate to that nexus/presence Full faith and credit o The out-of-state deciding court had proper subject matter and personal jurisdiction o The judgment was on the merits o The judgment was final.
INDIVIDUAL LIBERTIES
o o
Constitution technically only applies to state action Exceptions o De facto state action via statute Congress can impose constitutional standard on private actors by statute and by using various parts of the Constitution itself (13th amendment, Commerce clause, etc) o Public function exception o Entanglement exception Essentially that the Constitution automatically applies in any affair that the government is involved in. Examples: Courts cannot enforce racially-restrictive covenants State cant lease land to a business that discriminates on race State cant provide free supplies to a school that discriminate on race State can provide money to fund a school that restricts freedom of speech. Collection of state athletic programs can suspend a basketball coach without due process State action when a private agency regulates all school sports in a state
No state action when a private club with a state liquor license discriminates on race o General themes Mere government financial support is not enough to constitute state action State action is more likely to apply if racial discrimination is involved. Bill of Rights o Technically applies only to the federal government o What hasnt been selectively incorporated 2nd right to bear arms, although this does apply to Washington DC 3rd right to not have to house a solider in your house. 5th amendment right to criminal grand jury indictments in state court 7th amendment right to jury trial in civil cases 8th amendment right against excessive fines. Scrutiny o Strict Means chosen are necessary (i.e. narrowly tailored) to accomplish a compelling governmental interest. Government bears burden o Intermediate Means chosen are substantially-related to an important government purpose. Government bears burden o Rational-basis Means chosen are rationally-related to a legitimate government purpose. Any conceivable governmental purpose will work. Challenger bears burden
DUE PROCESS
o o o
Procedural Due Process o Sufficiency of procedures afforded Substantive Due Process Economic liberties o Takings Possessory taking Regulatory taking Temporary taking is not compensable so long as government action reasonable. o Contracts clause General Does not apply to federal government Intermediate scrutiny Government scrutiny Privacy o Fundamental rights (strict scrutiny to restrict) marry
o o
procreate to have custody of ones kids to control upbringing of ones kids to purchase and use contraceptives To abortion For adults to engage in private, consensual sex. To refuse medical treatment State can require clear and convincing evidence of patients wishes o No fundamental right to physician-assisted suicide 2nd amendment right to bear arms Right to travel domestically (strict scrutiny) o Covered under 14th amendment P&I o Right to foreign travel invokes only rational-basis. Right to vote (strict scrutiny) o Covered under 14th amendment P&I o If the restriction on right to vote is meant to prevent voter fraud, the restriction need only be desirable in totality. o 1:1 representation must be maintained. o At large elections are allowed unless a discriminatory purpose is shown. o Drawing election districts based on race must meet strict scrutiny. No fundamental right to an education
EQUAL PROTECTION (5th feds only; 14th state and local govts only)
o
Sieving questions o What is the classification based on? o What scrutiny does the classification invoke? o Has the government met that scrutiny standard? Strict scrutiny o Racial classifications o National origin (what country youre from) o Alienage classifications (citizen v. non-citizen) Intermediate scrutiny o Legitimate vs. illegitimate children o Gender classifications o Undocumented alien children Rational basis everything else, including, o Age, disability, wealth, economic, or sexual orientation discrimination
FIRST AMENDMENT
o
Permissible speech restrictions o Content restrictions Intermediate scrutiny content-neutral restrictions Strict scrutiny content or viewpoint-based restrictions o Prior restraint
Strict scrutiny Must comply with or appeal a prior restraint order, like an injunction. Criteria: Criteria for restraint must be specified; only limited discretion Injunction must be properly sought and be no broader than necessary Final merits of the restraint claim must be quickly resolved so restraint is no longer than necessary o Vagueness Reasonable person cant tell what a law prohibits and allows. Results in a notice problem for Due Process purposes. o Overbreadth Regulation prohibits illegal speech, but also prohibits a lot of legal and permissible speech too. Protectable speech o Symbolic speech Government can sometimes regulate conduct intended as speech Examples Flag-burning is constitutionally-protected speech that is political protest Draft card burning is not constitutionally-protected speech because there is an important government purpose in having people have their draft cards. Nude dancing is not constitutionally-protected speech. Burning a cross is protected speech, unless it is done with the intent to threaten or intimidate. Contribution limits to candidate election campaigns are constitutional. Limits on expenditure are, however, unconstitutional. o Thus, contributions to Obamas campaign are limited. Expenditures on Obamas behalf are not. o For ballot initiative campaigns, contribution limits are not allowed. Give as much as you want. o Anonymous speech is protected. The right to speech also includes the right not to disclose ones identity. Thus, anonymous speech is protected. Unprotected speech o Incitement Elements: Imminent illegal conduct is likely Speaker intended to cause it o Fighting Words Threats or words likely to incite immediate physical reaction. Fighting words restrictions: Are often vulnerable on vagueness grounds, cannot discriminate on viewpoint.
Obscenity Elements Appeal to prurient interest (community standard) Patently offensive under laws that specifically outlaw the behavior (community standard) Work lacks SLAP value (national standard) Child porn is per-se illegal in order to protect kids involved in the production. However, computer-generated child porn or child porn featuring child-like adults is okay. o Profane and indecent speech (like cussing) is protectable because it communicates emotion. Commercial speech o Intermediate scrutiny o Restrict if: Intermediate scrutiny is met, or Speech advertises unlawful activity, or Speech is misleading or fraudulent. Defamation o Plaintiff is a public figure Recovery if prove statement was false and was made with actual malice (knowing falsity or reckless disregard for truth) o Plaintiff is a private figure; matter is of public concern Recovery if prove statement was false and was made negligently o Plaintiff is a private figure, matter not one of public concern Recover presumed and punitive damages without showing malice. Privacy o Govt cant penalize the truthful reporting of information that was lawfullyobtained from governemtn. o Govt cant prevent media from disclosing an illegally intercepted phone call if: The media did not intercept it, and The call regards a matter of public importance. o Government workers have diminished First Amendment protections while on the job. Places o Public forum (street, sidewalk, park) Regulation must be content-neutral, unless strict scrutiny is met. If content-neutral, the regulations must: be a time, place, or manner restriction that serves an important governmental purpose, leave open alternate means of communication need not be the least restrictive means available. o Limited public forum Government can close this to speech, but choose not to. Treated same as public forum. Content-based restriction only if strict scrutiny met.
Content-neutral if it is a time, place, or manner restriction. Means need not be the least restrictive available. o Non-public forum Speech restrictions must: Be viewpoint neutral, and Reasonably relate to a legitimate governmental purpose. Freedom of association (strict scrutiny for any restrictions) o A restriction on association that meets strict scrutiny must also prove the person: Was actively affiliated with the group, and Knew of the groups activities with the specific intent of Furthering those activities o Strict scrutiny for any requirement that groups disclose their membership if doing so would chill association. o Groups cannot be forbidden from discriminating if the exclusion would interfere with the intimate association or the groups expressive activities. Example the KKK can keep blacks out. Freedom of religion o Free exercise (strict scrutiny) Govt cant punish you for your religious beliefs, but can regulate conduct as long as the law is generally applicable. Free exercise cannot be used to challenge a neutral law that is generally applicable. Free exercise does not require religions be exempt from laws that are generally applicable. Govt cannot deny you benefits if you quit your job for religious reasons. Amish people are exempt from having to send their kids to school. o Establishment Govt cant prefer one religion over another unless strict scrutiny is met. Lemon v. Kurtzman test Establishment not violated if: Law has a secular purpose, The laws primary effect neither advances or retards religion, The law does not excessively entangle government with religion. School-sponsored religious activity is invalid, but school accommodation of religious activity is valid, and possibly required. Government can support religious schools, so long as the support is not for the teaching of religion. Government must provide all religious groups the same access to school facilities as non-religious groups have. Freedom of Press o Overriding inquiry is the publics right to receive information of public concern. 1st amendment gives public and press the right to attend criminal trials, subject to trial judges protection of an overriding interest (providing fair trial, protecting minor victims, etc) o General hierarchy Restrictions on newspapers most scrutiny (i.e. strict)
o o
Restrictions on cable TV less scrutiny Restrictions on radio and TV broadcasters least scrutiny Press can be required to testify before Grand Juries. Broadcasters do not have to accept political ads, but radio broadcasters can be required to provide free airtime to certain people, like those who have been attacked on air or those who oppose positions the radio station has taken.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- MBE & MEE Essentials: Governing Law for UBE Bar Exam ReviewD'EverandMBE & MEE Essentials: Governing Law for UBE Bar Exam ReviewPas encore d'évaluation
- MPRE Unpacked: Professional Responsibility Explained & Applied for Multistate Professional Responsibility ExamD'EverandMPRE Unpacked: Professional Responsibility Explained & Applied for Multistate Professional Responsibility ExamPas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law OutlineDocument22 pagesCon Law OutlineslavichorsePas encore d'évaluation
- State Action and Equal Protection Judicial ReviewDocument24 pagesState Action and Equal Protection Judicial ReviewNate Enzo100% (1)
- Family Law OutlineDocument18 pagesFamily Law OutlineBill TrecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law OutlineDocument23 pagesCon Law OutlineJonathan EspPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 6 NotesNana Mireku-BoatengPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Judicial Review: Master Constitutional Law Outline Professor BurrisDocument74 pagesI. Judicial Review: Master Constitutional Law Outline Professor BurrisDavid YergeePas encore d'évaluation
- Torts OutlineDocument43 pagesTorts OutlineskjdnaskdjnPas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law I Final Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCon Law I Final Cheat SheetKathryn CzekalskiPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Federal Judicial Power: Future Harm. City of Los Angelas v. LionsDocument21 pagesI. Federal Judicial Power: Future Harm. City of Los Angelas v. LionsGrant StringhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law OutlineDocument72 pagesCon Law OutlineAdam DippelPas encore d'évaluation
- Civ Pro I Outline (Cooley)Document28 pagesCiv Pro I Outline (Cooley)sobethebeardiePas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law OutlineDocument48 pagesCon Law OutlineSeth WalkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: The Federal Judicial Power A. The Authority For Judicial ReviewDocument28 pagesChapter 1: The Federal Judicial Power A. The Authority For Judicial ReviewNicole AmarantePas encore d'évaluation
- DOMESTIC ASPECTS OF SEPARATION OF POWERS - Con Law IDocument10 pagesDOMESTIC ASPECTS OF SEPARATION OF POWERS - Con Law IKeiara PatherPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts OutlineDocument55 pagesTorts OutlineLeah Gaydos100% (1)
- KENS5 Press Release-HB 3554Document1 pageKENS5 Press Release-HB 3554Andrea CardenPas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law Road Map and Standards of ReviewDocument2 pagesCon Law Road Map and Standards of Reviewsuperxl2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Family Law and its DefinitionsDocument93 pagesIntroduction to Family Law and its Definitionsbiglank99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law II NotesDocument190 pagesCon Law II NotesBPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Procedure Brief/Notes 9-6 Federal Question JurisdictionDocument4 pagesCivil Procedure Brief/Notes 9-6 Federal Question JurisdictionRebecca LopesPas encore d'évaluation
- Remedies OutlineDocument14 pagesRemedies OutlineDaria IourtchenkoPas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law Outline - Fall 2011 SeamanDocument30 pagesCon Law Outline - Fall 2011 Seamanzoti_lejdi100% (1)
- Con Law II - Final OutlineDocument27 pagesCon Law II - Final OutlineKeiara Pather100% (1)
- Introduction to Studying the FL ConstitutionDocument157 pagesIntroduction to Studying the FL Constitutionomaidadelgado100% (3)
- Con Law OutlineDocument59 pagesCon Law OutlineAgguy7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Property I Outline Fall19Document46 pagesProperty I Outline Fall19Amelia PoorePas encore d'évaluation
- Federalism Values Rarely Discussed in Supreme Court CasesDocument42 pagesFederalism Values Rarely Discussed in Supreme Court CasesGustavo LiberatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fourth Amendment: 1. Katz and Early CasesDocument29 pagesFourth Amendment: 1. Katz and Early CasesGabbie ByrnePas encore d'évaluation
- ScrutiniesDocument2 pagesScrutiniesmkreese0100% (1)
- Classifying Arguments Activity-Answer Key: Obergefell v. Hodges (And Consolidated Cases)Document6 pagesClassifying Arguments Activity-Answer Key: Obergefell v. Hodges (And Consolidated Cases)zombielibraryPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitutional Law OutlineDocument48 pagesConstitutional Law Outlinehammurabi11100% (1)
- Property Attack OutlineDocument9 pagesProperty Attack OutlineAshley MeredithPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitutional Law - Long NotesDocument106 pagesConstitutional Law - Long NotesstaceyPas encore d'évaluation
- Evidence Questions For FinalDocument5 pagesEvidence Questions For FinalNaderPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Analysis For IntestacyDocument10 pagesBasic Analysis For IntestacyVictoria ZingerPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitutional Law OutlineDocument15 pagesConstitutional Law Outlinemarciagray15514Pas encore d'évaluation
- Negligence v. Strict Liability ComparedDocument78 pagesNegligence v. Strict Liability Comparedblair_bartonPas encore d'évaluation
- Real Property: Future Interests ExplainedDocument1 pageReal Property: Future Interests ExplainedJulie GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Domestic Relations OutlineDocument13 pagesDomestic Relations Outlinedcwashin100% (1)
- Constitutional Law OutlineDocument41 pagesConstitutional Law OutlineLaura SkaarPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts Roberts Final OutlineDocument65 pagesTorts Roberts Final OutlineJon EichtenPas encore d'évaluation
- Pawnbroker Waives Right to Demand by Claiming TitleDocument153 pagesPawnbroker Waives Right to Demand by Claiming TitleAaron WarnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Relevance and Admissibility of EvidenceDocument18 pagesRelevance and Admissibility of EvidenceksskelsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Civ Pro OutlineDocument21 pagesCiv Pro OutlineAGreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Law School Outline - Property - NYU School of Law - EstlundDocument55 pagesLaw School Outline - Property - NYU School of Law - Estlundeagleal5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dministrative AW Utline: I. D A SDocument45 pagesDministrative AW Utline: I. D A Snak75Pas encore d'évaluation
- Agent Otoya's Testimony on Denial of FOIA RequestDocument12 pagesAgent Otoya's Testimony on Denial of FOIA Requestmschrein8480Pas encore d'évaluation
- Controversy Over A National Bank (I)Document42 pagesControversy Over A National Bank (I)Kyle OhPas encore d'évaluation
- Negligence, Intentional Torts, and Property Damage ExplainedDocument2 pagesNegligence, Intentional Torts, and Property Damage Explaineddeenydoll4125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law WinDocument117 pagesCon Law WinAdam JacobsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Crim OutlineDocument4 pagesCrim OutlineAaron FlemingPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts Outline Mortazavi 2013Document19 pagesTorts Outline Mortazavi 2013deenydoll4125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clear and Present Danger Test: Advocacy of Illegal ActionDocument98 pagesClear and Present Danger Test: Advocacy of Illegal ActionDavid YergeePas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 1 Judicial Review and Constitutional StructureDocument18 pagesCh. 1 Judicial Review and Constitutional StructureLaura SkaarPas encore d'évaluation
- Outline-The Commerce ClauseDocument23 pagesOutline-The Commerce ClauseJonnie_TPas encore d'évaluation
- Judges and DiscriminationDocument365 pagesJudges and DiscriminationYun YiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Legal Lynching...: From Which the Legacies of Three Black Houston Lawyers BlossomedD'EverandA Legal Lynching...: From Which the Legacies of Three Black Houston Lawyers BlossomedPas encore d'évaluation
- Justice Thomas Lecture on Why Federalism MattersDocument8 pagesJustice Thomas Lecture on Why Federalism MattersDionisioPas encore d'évaluation
- United States Court of Appeals Third CircuitDocument35 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals Third CircuitScribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- The U.S. Constitution and Money Part 4 The First and Second Banks of The United StatesDocument39 pagesThe U.S. Constitution and Money Part 4 The First and Second Banks of The United Statesmichael s rozeffPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test 300 QuestionsDocument48 pagesPractice Test 300 QuestionsarippeePas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 3 Federalism: Balancing Power, Balancing RightsDocument21 pagesCHAPTER 3 Federalism: Balancing Power, Balancing RightsLa BombaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exxonmobil'S Complaint For Declaratory and Injunctive ReliefDocument33 pagesExxonmobil'S Complaint For Declaratory and Injunctive ReliefBob PricePas encore d'évaluation
- Sisyphus Lament (Philippine Law Journal Chair Essays On Journal Management)Document102 pagesSisyphus Lament (Philippine Law Journal Chair Essays On Journal Management)Facebook.com/OscarFranklinTan100% (1)
- Outline Without CasesDocument38 pagesOutline Without CasesLeah PybasPas encore d'évaluation
- Schuyler Barbeau Motion To Dismiss (Denied)Document47 pagesSchuyler Barbeau Motion To Dismiss (Denied)John P CapitalistPas encore d'évaluation
- United States v. Redmond, 10th Cir. (1997)Document9 pagesUnited States v. Redmond, 10th Cir. (1997)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Munn v. IllinoisDocument7 pagesMunn v. Illinoisalexis_beaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2 NOTES ChemerinskyDocument33 pagesCH 2 NOTES ChemerinskyNana Mireku-BoatengPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study: Petitioners RespondentsDocument5 pagesCase Study: Petitioners RespondentsJabar SabdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Mcculloch V. Maryland:: Theories of Constitutional InterpretationDocument14 pagesMcculloch V. Maryland:: Theories of Constitutional Interpretationfbarber13Pas encore d'évaluation
- PublishedDocument20 pagesPublishedScribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cengage Advantage Books Business Law Text and Cases An Accelerated Course 1st Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesCengage Advantage Books Business Law Text and Cases An Accelerated Course 1st Edition Miller Solutions Manualceromakeslopi8hwcy100% (18)
- Dwnload Full Legal Environment of Business A Managerial Approach Theory To Practice 3rd Edition Melvin Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Legal Environment of Business A Managerial Approach Theory To Practice 3rd Edition Melvin Test Bank PDFjacksonf9wuva100% (9)
- HP Hood & Sons, Inc. v. Du Mond, 336 U.S. 525 (1949)Document39 pagesHP Hood & Sons, Inc. v. Du Mond, 336 U.S. 525 (1949)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- (Please Make This Viral) "THE PRESENT LAW FORBIDS" Member Banks of The Federal Reserve System To Transact Banking Business, Except...Document2 pages(Please Make This Viral) "THE PRESENT LAW FORBIDS" Member Banks of The Federal Reserve System To Transact Banking Business, Except...in1or95% (20)
- Wine Express Motion To DismissDocument19 pagesWine Express Motion To DismissRuss LatinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Barrett v. United States, 423 U.S. 212 (1976)Document15 pagesBarrett v. United States, 423 U.S. 212 (1976)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Bensusan Restaurant Corporation v. Richard B. King, Individually and Doing Business As The Blue Note, 126 F.3d 25, 2d Cir. (1997)Document6 pagesBensusan Restaurant Corporation v. Richard B. King, Individually and Doing Business As The Blue Note, 126 F.3d 25, 2d Cir. (1997)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Management Leading and Collaborating in A Competitive World 12th Edition Bateman Snell Konopaske 1259546942 9781259546945Document36 pagesTest Bank For Management Leading and Collaborating in A Competitive World 12th Edition Bateman Snell Konopaske 1259546942 9781259546945AndrewJonessbdxPas encore d'évaluation
- Con Law FlowchartsDocument11 pagesCon Law Flowchartstdickson1597% (74)
- Montano v. Insular Government 12 Phil 57Document10 pagesMontano v. Insular Government 12 Phil 57REJFREEFALLPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitutional Law NotesDocument14 pagesConstitutional Law NotesKJPas encore d'évaluation
- AnswerDocument16 pagesAnsweratty. domiciano PagulayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Document 1406 Filed 02.28.11Document41 pagesDocument 1406 Filed 02.28.11jediparalegalPas encore d'évaluation
- Regulation: A PrimerDocument128 pagesRegulation: A PrimerMercatus Center at George Mason UniversityPas encore d'évaluation
- Brief A CaseDocument2 pagesBrief A CaseClara BatocchiPas encore d'évaluation