Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Inductance of 3-Phase Transmission Lines
Transféré par
JPR EEEDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Inductance of 3-Phase Transmission Lines
Transféré par
JPR EEEDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
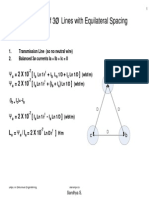
Inductance of 3-phase
Transmission Lines
Inductance of 3-phase Unsymmetrically spaced
Untransposed Transmission line
120
120
120
I
a
I
b
I
c
D
bc
D
ac
D
ab
I
a
I
b
I
c
(
+ + =
(
+ + =
(
+ + =
'
7
'
7
'
7
1
ln
1
ln
1
ln 10 2
1
ln
1
ln
1
ln 10 2
1
ln
1
ln
1
ln 10 2
R
I
D
I
D
I
D
I
R
I
D
I
D
I
D
I
R
I
c
bc
b
ac
a c
bc
c b
ab
a b
ac
c
ab
b a a
( )
) 3 ( ln
2
3 1
ln
1
ln 10 2
) 2 ( ln
2
3 1
ln
1
ln 10 2
,
) 1 ( ln
2
3 1
ln
1
ln 10 2
ln
2
3 1
ln 5 . 0
1
ln 10 2
1
ln
1
ln 866 . 0
1
ln
1
ln 5 . 0
1
ln 10 2
1
ln ) 866 . 0 5 . 0 (
1
ln 866 . 0 5 . 0
1
ln 10 2
'
7
'
7
'
7
'
7
'
7
'
7
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
(
+ + + =
bc
ac
bc ac
c
ab
bc
ab bc
b
ac
ab
ac ab
a
ac
ab
ac ab
a a
ab ac
a
ac ab
a a a
ac
a
ab
a a a
D
D
j
D D R
L
D
D
j
D D R
L
similarly
D
D
j
D D R
L
D
D
j
D D R
I
D D
I j
D D
I
R
I
D
I j
D
I j
R
I
120
120
120
I
a
I
b
I
c
From eqns (1) to (3), it is seen that inductance of conductors a,b and c are
unequal and have imaginary part which is due to mutual inductances.
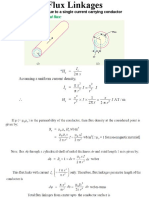
GMD and GMR approach
Self GMD (D
s
)and Mutual GMD
(D
m
)
The inductance calculations relating to
multiconductor arrangements can be
simplified by the use of self geometrical mean
distance and mutual geometrical distance
Self GMD (D
s
) = Geometric Mean Radius
(GMR)
Inductance per conductor per metre length is
given by,
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
r
D
ln
4
1
10 2 L
7 -
conductors e between th spacing the of t independen is and conductor the of shape
and size upon the depends conductor a of GMD - self that noted be may It
r' by denoted is GMR sometimes
0.7788r GMR or D where,
ln 10 2 L : to reduces eqn(i) the GMD - self Using
0.7788r. GMR or GMD - self the
r, radius of conductor round solid a for ally that mathematic proved be can It
purposes. several for
term this eliminate to introduced is GMR or GMD self of concept The
conductor. solid
n the flux withi to due inductance the is
4
1
10 2 eqn, above In the
ln 10 2
4
1
10 2 L
s
7 -
7
7 7
= =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
=
(
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
=
GMD Self
D
D
r
D
s
Mutual GMD (D
m
)
The mutual GMD is the geometrical mean of
the distances from one conductor to the
others, must be between the largest and
smallest such distances. It simply represents
the equivalent geometrical spacing.
- Assuming the spacing between the conductors to be large
compared to the diameter of each conductor, the mutual
GMD between two conductors is equal to the distances
between their centres. i.e D
m
= D
- For a single circuit 3-phase transmission line, the mutual
GMD is equal to the equivalent equilateral spacing,
D
m
=(D
AB
X D
BC
X D
CA
)^(1/3)
Two wire line
D
R
R
- I
I
H/m ln 10 4 L
L L line the of inductance Total
ln 10 2 L
ln 10 2 L B, conductor of inductance
ln 10 2 L
ln 10 2 L A, conuductor of Inductance
D ,
'
7 -
A
'
7
B
7
B
'
7
A
7
A
'
SL
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
= =
R
D
L
R
D
D
D
similarly
R
D
D
D
R D D
B
m
SLB
m
m
SLA
m
m
What is transposition?
interchange the positions of the conductors at regular
intervals along the line so that each conductor occupies the
original position of every other conductor over an equal
distance. Such an exchange of conductor positions is called
transposition.
Position 2
Position 3
b
c
a
a b
c
L / 3 L / 3 L / 3
Position 1
Why Transposition of lines is needed?
The conductor spacing in a 3-phase transmission line is said to be
unsymmetrical if the conductors are not equidistant form each
other. Under such conditions, the flux linkages and inductances of
each phase are not the same and subsequently voltage drops in
three phases are unequal even if the currents in the conductors
are balanced. In order to make voltage drops equal in all
conductors, transposition is done. This arrangement causes each
conductor to have the same average inductance over the
transposition cycle.
About Transpositioned lines
Transposition of lines reduce the inductive
interference with the nearby communication lines
However it suffers from a serious drawback that
faults due to lightning have got tendency to get
concentrated in transposition structures
Transposition is a costly scheme
The risk of outages is increased due to transposition
For these reasons transposition is avoided in
practice,and that if at all it is done, the line is
transposed in the switching stations or their
neighbourhood for a small distance
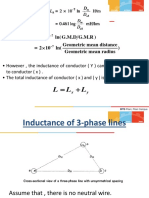
Symmetrical 3-phase Line
D
D
D
a
b
The mutual geometric mean
distance between conductor a and
conductors b and c is
The self geometric mean distance
Therefore,
( ) D D D D
m
= = .
'
R D D
aa s
= =
|
.
|
\
|
= = =
'
7
ln 10 2
R
D
L L L
c b a
Transposition of Lines
D
12
D
13
D
23
a
b
c
Position
1
a b
c
Position
2
Position
3
b
c
a
a b
c
L /
3
L /
3
L /
3
When phase a is in position 1, the value of D
m
is the geometric mean of all the
distances from a to other conductors
( )
( )
( )
H/m ln 10 2 phase any of inductance Average
L
ln 10 2 L
ln 10 2 L
is cycle tion transposi a over a' ' phase of Inductance
) ( D GMD self Equivalent
D 2 position in a phase of GMD Self
D 2 position in a phase of GMD Self
Re D 1 position in a phase of GMD Self
D
D GMD Equivalent
D is GMD 3 position In
D is GMD 2 position In
D is GMD 1 position In
'
3
1
31 23 12 7
a
'
3
1
31 23 12 7
a
7
a
' 3 '
3
3 2 1 s
'
s3
'
s2
'
4
1
s1
6
1
23 31 12 23 31 12
3
3 2 1 m
23 31 m3
12 23 m2
31 12 m1
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
= =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
= = =
=
=
= = =
=
=
=
=
=
R
D D D
L L and
R
D D D
D
D
R R D D D
R
R
R D
D D D D D
D D D
D D
D D
D D
c b
SL
m
s s s
aa
m m m
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Linear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionD'EverandLinear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionPas encore d'évaluation
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterD'EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterPas encore d'évaluation
- Parameters in The Transmission LineDocument30 pagesParameters in The Transmission LineRaju ShanPas encore d'évaluation
- Psa Lab Ex - 1Document22 pagesPsa Lab Ex - 1samkousPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line Parameters ExplainedDocument11 pagesTransmission Line Parameters ExplainedSwechhya kaflePas encore d'évaluation
- Power SystemsDocument54 pagesPower SystemsShyam VimalKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Inductive Loads and Capacitance on Power Transmission LinesDocument10 pagesEffects of Inductive Loads and Capacitance on Power Transmission LinesArslan Bin ShabeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Power SystemsDocument19 pagesPower SystemsMary Rose OleaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power SystemsDocument19 pagesPower SystemsjredfrondaeePas encore d'évaluation
- Power Systems K-NotesDocument36 pagesPower Systems K-NotesAkashGaurav100% (1)
- Power System Simulation Lab ManualDocument41 pagesPower System Simulation Lab ManualArivumani86% (14)
- Docs EEEPSLNotes2013 PDFDocument46 pagesDocs EEEPSLNotes2013 PDFHtet Mrak AungPas encore d'évaluation
- LCP LabDocument13 pagesLCP Labapi-3831923100% (1)
- Transmission and Distribution (Unit 2)Document36 pagesTransmission and Distribution (Unit 2)Jain Marshel BPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Ii Transmission Line Parameters ObjectivesDocument56 pagesUnit Ii Transmission Line Parameters Objectivesmanikandan trPas encore d'évaluation
- Computation of TR Line Parameters & ModellingDocument18 pagesComputation of TR Line Parameters & ModellingVibin NivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual NewDocument50 pagesLab Manual NewRahul MeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating Sequence Line Constants for Transmission LinesDocument5 pagesCalculating Sequence Line Constants for Transmission LinesRafat ThongPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 Computation of Parameters and Modelling of Transmission LinesDocument13 pagesExperiment 1 Computation of Parameters and Modelling of Transmission LinesshimymbPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2.2Document16 pagesUnit 2.2JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee2404 ManualDocument92 pagesEe2404 ManualsakkuumhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 9Document6 pagesLab 9elen19111036 KFUEITPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3.1Document52 pagesModule 3.1JASPER PAYAPAYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line Parameters: Power Systems EngineeringDocument21 pagesTransmission Line Parameters: Power Systems EngineeringDeepak Srinivas YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System 2Document46 pagesPower System 2Prakash Chandran CPas encore d'évaluation
- Pos Neg ZeroDocument5 pagesPos Neg ZerosankalptiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- EE525 Power Analysis and Design Lecture 1Document74 pagesEE525 Power Analysis and Design Lecture 1Fremon RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee6711 Pss Lab MaualDocument23 pagesEe6711 Pss Lab MaualJaya ShreePas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Institute of Technology, Bhubaneswar, India School of Electrical Sciences B.Tech, 6 Semester (Power System) Laboratory Experiment No-01Document6 pagesIndian Institute of Technology, Bhubaneswar, India School of Electrical Sciences B.Tech, 6 Semester (Power System) Laboratory Experiment No-01Bhoomika R ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Lines CharacteristicsDocument14 pagesTransmission Lines Characteristicsmanda_reeva100% (1)
- JJDocument17 pagesJJVibin NivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ampacity: D D L R R L GMRDocument6 pagesAmpacity: D D L R R L GMRMierdaPas encore d'évaluation
- PS Simulation LabDocument41 pagesPS Simulation LabviksoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 Sequence Impedance of Transmission LinesDocument48 pagesLecture 2 Sequence Impedance of Transmission LinesCatrina FedericoPas encore d'évaluation
- Class19 Crosstalk OverviewDocument32 pagesClass19 Crosstalk OverviewNag ArjunPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 1404 Power System Lab ManualDocument63 pagesEe 1404 Power System Lab ManualSuhas Altruistic100% (1)
- 2.2 XLine Parameters - Inductance Part 2Document15 pages2.2 XLine Parameters - Inductance Part 2Kyla BelgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.feeder Analysis & ModelingDocument117 pages10.feeder Analysis & ModelingNamiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix B: Calculation of Line and Cable ConstantsDocument20 pagesAppendix B: Calculation of Line and Cable ConstantsGilang SamudraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 1404 Power System Lab ManualDocument64 pagesEe 1404 Power System Lab ManualjayamanikandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept of GMD and GMRDocument4 pagesConcept of GMD and GMRyethwePas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line Models and Inductance CalculationsDocument40 pagesTransmission Line Models and Inductance CalculationsA. HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Inductance of 3 Phase LineDocument50 pagesInductance of 3 Phase LineFemi PrincePas encore d'évaluation
- Power Systems IntermediateDocument23 pagesPower Systems IntermediateAbhishek GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- EPS Lab ManualDocument7 pagesEPS Lab ManualJeremy Hensley100% (1)
- End SemDocument29 pagesEnd SemVaskar Ray KarmakarPas encore d'évaluation
- EIE 321 MODULE IV PART 2: CALCULATING TRANSMISSION LINE INDUCTANCE AND CAPACITANCEDocument24 pagesEIE 321 MODULE IV PART 2: CALCULATING TRANSMISSION LINE INDUCTANCE AND CAPACITANCELifeLong SkillsPas encore d'évaluation
- 3450 1 PDFDocument20 pages3450 1 PDFKen WalkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 CapacitanceDocument23 pagesChapter 6 Capacitanceahmad abufaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Dual Fed Distributed Amplifier With ContDocument17 pagesDual Fed Distributed Amplifier With ContAmador Garcia IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis and Design of Transmission Line Structures by Means of The Geometric Mean Distance - IEEEDocument4 pagesAnalysis and Design of Transmission Line Structures by Means of The Geometric Mean Distance - IEEEJayson PatrickPas encore d'évaluation
- Path Loss Definition and ModelsDocument4 pagesPath Loss Definition and ModelsSaMs DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Line Parameters ComputationDocument4 pagesLine Parameters Computationswathi_grenPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1D'EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- VLF Radio Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Electromagnetic WavesD'EverandVLF Radio Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Electromagnetic WavesPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Questions LabDocument1 pageList of Questions LabJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Nov Dec 2011Document2 pagesNov Dec 2011JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- ProgramsDocument3 pagesProgramsJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- OOPS Prev. QPDocument2 pagesOOPS Prev. QPJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 1 NotesDocument38 pagesUNIT 1 NotesJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Oops - FilesDocument14 pagesOops - FilesJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- QB 2Document3 pagesQB 2JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Class: III EEE Subject Code: CS2311 Subject: Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument35 pagesClass: III EEE Subject Code: CS2311 Subject: Object Oriented ProgrammingJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Explicit ConstructorsDocument3 pagesExplicit ConstructorsJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Oops Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesOops Important QuestionsJPR EEE100% (1)
- OopsDocument14 pagesOopsJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- CS1015 QBDocument4 pagesCS1015 QBdivyamk02Pas encore d'évaluation
- CS1204 Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument59 pagesCS1204 Object Oriented ProgrammingNaleena SaravananPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5Document44 pagesUnit 5JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee Nov 2012 Timetable CompleteDocument3 pagesEee Nov 2012 Timetable CompleteJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2.2Document16 pagesUnit 2.2JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Interference With Communication CircuitsDocument11 pagesInterference With Communication CircuitsJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- AnnaDocument7 pagesAnnaJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document54 pagesUnit 1JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2.3Document19 pagesUnit 2.3JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2.4Document8 pagesUnit 2.4JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Medium Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesMedium Transmission LinesJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Generalized Circuit ConstantsDocument10 pagesGeneralized Circuit ConstantsJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2.2Document16 pagesUnit 2.2JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1.2Document26 pagesUnit 1.2JPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance of Transmission LineDocument10 pagesPerformance of Transmission LineJPR EEE100% (1)
- Power Flow Through Transmission LinesDocument9 pagesPower Flow Through Transmission LinesJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- CoronaDocument14 pagesCoronaJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Cables For 3 Phase ServiceDocument22 pagesCables For 3 Phase ServiceJPR EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Risc Cisc in Microcontroller and MicroprocessorDocument31 pagesRisc Cisc in Microcontroller and Microprocessormanvir kaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard For Safety UL ADocument49 pagesStandard For Safety UL ANhất NgônPas encore d'évaluation
- DiGas 4000 Light E 08.02Document2 pagesDiGas 4000 Light E 08.02manit1963Pas encore d'évaluation
- Proposed Rule: Domestic Mail Manual: Domestic Mailing Services New StandardsDocument45 pagesProposed Rule: Domestic Mail Manual: Domestic Mailing Services New StandardsJustia.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pagesDigital Logic DesignkiranPas encore d'évaluation
- SSP 099 18 Tfsi 132kw 20 Tfsi 162kw Ea888Document60 pagesSSP 099 18 Tfsi 132kw 20 Tfsi 162kw Ea888Jose Ramón Orenes ClementePas encore d'évaluation
- Calibration of A Pressure GaugeDocument6 pagesCalibration of A Pressure GaugeThapelo100% (2)
- Rectify Binary Plate Efficiency BubblesDocument4 pagesRectify Binary Plate Efficiency BubblesCsaba AndrásPas encore d'évaluation
- Plasticizer From Vegetable Oil DerivativesDocument8 pagesPlasticizer From Vegetable Oil Derivativesilan chertokPas encore d'évaluation
- CS As Corporate Saviour - Oil and Gas Industry PDFDocument48 pagesCS As Corporate Saviour - Oil and Gas Industry PDFBalraj JPas encore d'évaluation
- Software TestingDocument3 pagesSoftware TestingDr. P. N. Renjith Associate Professor - CSEPas encore d'évaluation
- DTH Equipment - Product - Catalogue - tcm45-3560033 PDFDocument48 pagesDTH Equipment - Product - Catalogue - tcm45-3560033 PDFJALFAROROPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo - CATUDocument132 pagesCatalogo - CATUxis-zeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation of Caffeine from TeaDocument6 pagesIsolation of Caffeine from TeaDaisy Joyce Seroje BuslonPas encore d'évaluation
- NASA ERAST Program Develops High-Altitude UAVsDocument17 pagesNASA ERAST Program Develops High-Altitude UAVsEgz AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fall Protection Marking GuidelinesDocument2 pagesFall Protection Marking GuidelinescuervohijoguachoPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Valve and Steam Line PDFDocument19 pagesControl Valve and Steam Line PDFRofi MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Semi Circular Bending Test To Evaluate Low Temperature Fracture Resistance For Asphalt ConcreteDocument10 pagesUsing Semi Circular Bending Test To Evaluate Low Temperature Fracture Resistance For Asphalt Concreteappu140688Pas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler MaintenanceDocument144 pagesBoiler Maintenanceaziz100% (2)
- Vernier, Dial, and Electronic Digital Calipers: Session 3Document40 pagesVernier, Dial, and Electronic Digital Calipers: Session 3Emman Bosito100% (1)
- Quick Union Reference Tables: Pressure Control EquipmentDocument1 pageQuick Union Reference Tables: Pressure Control EquipmentMiguel FPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Report PDFDocument184 pagesTechnical Report PDFSrinivasan RajenderanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ieee 1346-1998Document45 pagesIeee 1346-1998pepitorodirguez100% (1)
- Scallops Are Cut Outs in Weld Corners Which Are Used in Many Structures As in BridgesDocument3 pagesScallops Are Cut Outs in Weld Corners Which Are Used in Many Structures As in BridgesJanuel BorelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrostatic and Electromagnetic Forces: Electronic Address: Tim - Henley@mail - Utoronto.caDocument9 pagesElectrostatic and Electromagnetic Forces: Electronic Address: Tim - Henley@mail - Utoronto.caTimothy Murray HenleyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 Can Am Off Road - Apache Track Kits Leaflet - enDocument7 pages2020 Can Am Off Road - Apache Track Kits Leaflet - enNicolas VillamayorPas encore d'évaluation
- HCIE-R&S Huawei Certified Internetwork Expert-Routing and Switching Training Lab Guide PDFDocument228 pagesHCIE-R&S Huawei Certified Internetwork Expert-Routing and Switching Training Lab Guide PDFliviuemanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- International Tubulars MSDS RegisterDocument4 pagesInternational Tubulars MSDS RegisterMuhammad SuhaibPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Metal Cutting-Module 1Document116 pagesTheory of Metal Cutting-Module 1rejeesh_rajendranPas encore d'évaluation
- PRJCTDocument10 pagesPRJCTrpkn541Pas encore d'évaluation