Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine Presentation
Transféré par
Kimberly Etulle CellonaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Endocrine Presentation
Transféré par
Kimberly Etulle CellonaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
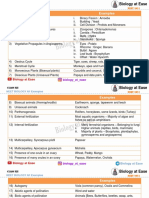
The Endocrine System
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems | The pituitary gland (often called the master gland) is located in a small bony cavity at the base of the brain. A stalk links the pituitary to the hypothalamus, which controls release of pituitary hormones. The pituitary gland has two lobes: the anterior and posterior lobes. The anterior pituitary is glandular. The endocrine system in females and males. .
Hormones | The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete chemical messages we call hormones. These signals are passed through the blood to arrive at a target organ, which has cells possessing the appropriate receptor. Exocrine glands (not part of the endocrine system) secrete products that are passed outside the body. Sweat glands, salivary glands, and digestive glands are examples of exocrine glands
But What is the role of hormones ?
The roles of hormones is selecting target cells and delivering the hormonal message.
And also Hormones are grouped into three classes based on their structure: steroids peptides amines
Steroids ???
Steroids Steroids are lipids derived from cholesterol. Testosterone is the male sex hormone. Estradiol, similar in structure to testosterone, is responsible for many female sex characteristics. Steroid hormones are secreted by the gonads, adrenal cortex, and placenta.
But how about Peptides ?? Amines ??
Peptides and Amines Peptides are short chains of amino acids; most hormones are peptides. They are secreted by the pituitary, parathyroid, heart, stomach, liver, and kidneys. Amines are derived from the amino acid tyrosine and are secreted from the thyroid and the adrenal medulla. Solubility of the various hormone classes
Synthesis, Storage, and Secretion Steroid hormones are derived from cholesterol by a biochemical reaction series. Defects along this series often lead to hormonal imbalances with serious consequences. Once synthesized, steroid hormones pass into the bloodstream; they are not stored by cells, and the rate of synthesis controls them. Peptide hormones are synthesized as precursor molecules and processed by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi where they are stored in secretory granules. When needed, the granules are dumped into the bloodstream. Different hormones can often be made from the same precursor molecule by cleaving it with a different enzyme. Amine hormones (notably epinephrine) are stored as
Evolution of Endocrine Systems | Most animals with well-developed nervous and circulatory systems have an endocrine system. Most of the similarities among the endocrine systems of crustaceans, arthropods, and vertebrates are examples of convergent evolution. The vertebrate endocrine system consists of glands (pituitary, thyroid, adrenal), and diffuse cell groups scattered in epithelial tissues. More than fifty different hormones are secreted. Endocrine glands arise during development for all three embryologic tissue layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm). The type of endocrine product is determined by which tissue layer a gland originated in. Glands of ectodermal and endodermal origin produce peptide and amine hormones; mesodermalorigin glands secrete hormones based on lipids.
Endocrine Systems and Feedback Cycles | The endocrine system uses cycles and negative feedback to regulate physiological functions. Negative feedback regulates the secretion of almost every hormone. Cycles of secretion maintain physiological and homeostatic control. These cycles can range from hours to months in duration.
Negative feedback in the thyroxine release reflex.
The Adrenal Glands Each kidney has an adrenal gland located above it. The adrenal gland is divided into an inner medulla and an outer cortex. The medulla synthesizes amine hormones, the cortex secretes steroid hormones. The adrenal medulla consists of modified neurons that secrete two hormones: epinephrine and norepinephrine. Stimulation of the cortex by the sympathetic nervous system causes release of hormones into the blood to initiate the "fight or flight" response. The adrenal cortex produces several steroid hormones in three classes:mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and sex hormones. Mineralocorticoids maintain electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids produce a long-term, slow response to stress by raising blood glucose levels through the breakdown of fats and proteins; they also suppress the immune response and inhibit the inflammatory response.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Chapter 1 Advanced Acctg. SolmanDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Advanced Acctg. SolmanLaraPas encore d'évaluation
- FAR Test BankDocument36 pagesFAR Test BankMangoStarr Aibelle VegasPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Costing PDFDocument36 pagesStandard Costing PDFRamesh ShriPas encore d'évaluation
- EndocrineDocument6 pagesEndocrineKimberly Etulle CellonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Significant Digits WorksheetDocument1 pageSignificant Digits WorksheetKimberly Etulle CellonaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- CHAPTER 30 - Pituitary DrugsDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 30 - Pituitary DrugsBre BistanyPas encore d'évaluation
- ADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine Systembernadil01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Notes CHPTR 12Document14 pagesBiology Notes CHPTR 12Wan HasliraPas encore d'évaluation
- How Animals SurviveDocument35 pagesHow Animals SurvivedhonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Physioloy Lecture 1 PDFDocument33 pagesOral Physioloy Lecture 1 PDFHabeeb AL-AbsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Neet Biology All ExamplesDocument27 pagesNeet Biology All Exampleschannel of dhyana97% (32)
- M.SC TYC ZoologyDocument35 pagesM.SC TYC Zoologyprince1900Pas encore d'évaluation
- EndocrinologyDocument46 pagesEndocrinology[161]Shuaib AktherPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid HormoneDocument396 pagesThyroid HormoneuiliftengPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormones Study GuideDocument4 pagesHormones Study GuideSebastien Berka100% (1)
- Course SyllabusDocument51 pagesCourse Syllabusdahiphale1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organ System and FunctionDocument17 pagesOrgan System and FunctionLajilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Descriptive EssayDocument8 pagesSample Descriptive EssayfarahshazwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Progesterone in Orthomolecular Medicine by Ray PeatDocument66 pagesProgesterone in Orthomolecular Medicine by Ray PeatJulian MiñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Physiology Test PaperDocument3 pagesAnimal Physiology Test PaperRenjith Moorikkaran MPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormonal Imbalance - What It Is, and Why You Should CareDocument74 pagesHormonal Imbalance - What It Is, and Why You Should CareFrankPas encore d'évaluation
- Receent Syllabus of M.sc. Zoology - 19Document39 pagesReceent Syllabus of M.sc. Zoology - 19abdul haseebPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine System - Part 1 (Robbins)Document28 pagesEndocrine System - Part 1 (Robbins)sarguss14100% (2)
- Homeostasis, AnatomyDocument16 pagesHomeostasis, AnatomyKapemba White BothaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Quarter ExamDocument7 pages3rd Quarter ExamHarold HusayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet BiologyDocument2 pagesWorksheet BiologyRidham JainPas encore d'évaluation
- (L-1) - Endocrine System - CCC - Nov 26, 2019Document41 pages(L-1) - Endocrine System - CCC - Nov 26, 2019Omar GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormones and BehaviourDocument16 pagesHormones and BehaviourSushmit KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- 10 TH Science Practical Guide EM PDFDocument15 pages10 TH Science Practical Guide EM PDFSRI VISHNUPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Endocrine Glands, The Hormone They Secrete & Their FunctionDocument50 pagesImportant Endocrine Glands, The Hormone They Secrete & Their FunctionSiva SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Cell Communication Part 1Document40 pagesChapter 9 Cell Communication Part 1MARK BRIAN FLORESPas encore d'évaluation
- HormonesDocument25 pagesHormonesapi-309893409Pas encore d'évaluation
- Testosterone Levels in Healthy Men and The Relation To Behavioural and Physical Characteristics: Facts and ConstructsDocument15 pagesTestosterone Levels in Healthy Men and The Relation To Behavioural and Physical Characteristics: Facts and ConstructsTUẤN TRẦN MINHPas encore d'évaluation
- 22 ZoologyDocument33 pages22 ZoologyMalsawmkima Maski-aPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio - SSC - 2 - Model - Paper 20-9Document9 pagesBio - SSC - 2 - Model - Paper 20-9mughishassan0Pas encore d'évaluation