Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Managing Service Projects
Transféré par
rabalajiDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Managing Service Projects
Transféré par
rabalajiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Managing Service Projects
Learning Objectives
Describe the nature of project management.
Illustrate the use of a Gantt chart.
Construct a project network.
Perform critical path analysis on a project network.
Allocate limited resources to a project.
Crash activities to reduce the project completion time.
Analyze a project with uncertain activity times.
Use the earned value chart to monitor a project.
Discuss the reasons why projects fail to meet
performance, time, and cost objectives.
The Nature of Project
Management
Characteristics of Projects: purpose, life cycle,
interdependencies, uniqueness, and conflict.
Project Management Process: planning (work
breakdown structure), scheduling, and controlling.
Selecting the Project Manager: credibility, sensitivity,
ability to handle stress, and leadership.
Building the Project Team: Forming, Storming, Norming,
and Performing.
Principles of Effective Project Management: direct
people individually and as a team, reinforce excitement,
keep everyone informed, manage healthy conflict,
empower team, encourage risk taking and creativity.
Project Metrics: Cost, Time, Performance
Work Breakdown Structure
1.0 Move the hospital (Project)
1.1 Move patients (Task)
1.1.1 Arrange for ambulance (Subtask)
1.1.1.1 Prepare patients for move
1.1.1.2 Box patients personnel effects
1.2 Move furniture
1.2.1. Contract with moving company
Project Management Questions
What activities are required to complete a
project and in what sequence?
When should each activity be scheduled to
begin and end?
Which activities are critical to completing the
project on time?
What is the probability of meeting the project
completion due date?
How should resources be allocated to
activities?
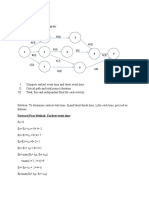
Tennis Tournament Activities
ID Activity Description Network Immediate Duration
Node Predecessor (days)
1 Negotiate for Location A - 2
2 Contact Seeded Players B - 8
3 Plan Promotion C 1 3
4 Locate Officials D 3 2
5 Send RSVP Invitations E 3 10
6 Sign Player Contracts F 2,3 4
7 Purchase Balls and Trophies G 4 4
8 Negotiate Catering H 5,6 1
9 Prepare Location I 5,7 3
10 Tournament J 8,9 2
Notation for Critical Path Analysis
Item Symbol Definition
Activity duration t The expected duration of an activity
Early start ES The earliest time an activity can begin if all previous
activities are begun at their earliest times
Early finish EF The earliest time an activity can be completed if it
is started at its early start time
Late start LS The latest time an activity can begin without
delaying the completion of the project
Late finish LF The latest time an activity can be completed if it
is started at its latest start time
Total slack TS The amount of time an activity can be delayed
without delaying the completion of the project
Scheduling Formulas
ES = EFpredecessor (max) (1)
EF = ES + t (2)
LF = LSsuccessor (min) (3)
LS = LF - t (4)
TS = LF - EF (5)
TS = LS - ES (6)
or
Tennis Tournament Activity on
Node Diagram
J
2
B
8
START
A
2
C
3
D
2
G
4
E
10
I
3
F
4
H
1
TS
ES EF
LS LF
Early Start Gantt Chart for Tennis
Tournament
ID Activity Days Day of Project Schedule
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
A Negotiate for 2
Location
B Contact Seeded 8
Players
C Plan Promotion 3
D Locate Officials 2
E Send RSVP 10
Invitations
F Sign Player 4
Contracts
G Purchase Balls 4
and Trophies
H Negotiate 1
Catering
I Prepare Location 3
J Tournament 2
Personnel Required 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1
Critical Path Activities
Activities with Slack
Resource Leveled Schedule for
Tennis Tournament
ID Activity Days Day of Project Schedule
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
A Negotiate for 2
Location
B Contact Seeded 8
Players
C Plan Promotion 3
D Locate Officials 2
E Send RSVP 10
Invitations
F Sign Player 4
Contracts
G Purchase Balls 4
and Trophies
H Negotiate 1
Catering
I Prepare Location 3
J Tournament 2
Personnel Required 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 1 1
Critical Path Activities
Activities with Slack
Incorporating Uncertainty in
Activity times
A M D B
F(D)
P(D<A) = .01
P(D>B) = .01
optimistic most pessimistic
likely
TIME
Formulas for Beta Distribution of
Activity Duration
Expected Duration
D
A M B
_
=
+ + 4
6
Variance
V
B A
=
(
6
2
Note: (B - A )= Range or 6o
Activity Means and Variances for
Tennis Tournament
Activity A M B D V
A 1 2 3
B 5 8 11
C 2 3 4
D 1 2 3
E 6 9 18
F 2 4 6
G 1 3 11
H 1 1 1
I 2 2 8
J 2 2 2
Uncertainly Analysis
Assumptions
1. Use of Beta Distribution and Formulas For D and V
2. Activities Statistically Independent
3. Central Limit Theorem Applies ( Use student t if less than
30 activities on CP)
4. Use of Critical Path Activities Leading Into Event Node
Result
Project Completion Time Distribution is Normal With:
For Critical Path Activities
For Critical Path Activities
=
D
_
o
2
=
V
Completion Time Distribution for
Tennis Tournament
Critical Path
Activities D V
A 2 4/36
C 3 4/36
E 10 144/36
I 3 36/36
J 2 0
= 20 188/36 = 5.2 =
o
2
Question
What is the probability of an overrun if a 24 day completion time
is promised?
24
P (Time > 24) = .5 - .4599 = .04 or 4%
Days
o
2
52 = .
Z
X
Z
Z
=
=
=
o
24 20
52
175
.
.
Costs for Hypothetical Project
C
o
s
t
(0,0)
Schedule with Minimum Total Cost
Duration of Project
Total Cost
Indirect Cost
Opportunity Cost
Direct Cost
Activity Cost-time Tradeoff
C
C
*
D
*
D
Activity Duration (Days)
Normal
Crash
Slope is cost to expedite per day
Cost
Cost-Time Estimates for Tennis
Tournament
Time Estimate Direct Cost Expedite Cost
Activity Normal Crash Normal Crash Slope
A 2 1 5 15
B 8 6 22 30
C 3 2 10 13
D 2 1 11 17
E 10 6 20 40
F 4 3 8 15
G 4 3 9 10
H 1 1 10 10
I 3 2 8 10
J 2 1 12 20
Total 115
Progressive Crashing
Project Activity Direct Indirect Opportunity Total
Duration Crashed Cost Cost Cost Cost
20 Normal 115 45 8 168
19 41 6
18 37 4
17 33 2
16 29 0
15 25 -2
14 21 -4
13 17 -6
12 13 -8
Normal Duration After Crashing Activity
Project Paths Duration
A-C-D-G-I-J 16
A-C-E-I-J 20
A-C-E-H-J 18
A-C-F-H-J 12
B-F-H-J 15
Applying Theory of Constraints to
Project Management
Why does activity safety time exist and is subsequently lost?
1. The student syndrome procrastination phenomena.
2. Multi-tasking muddles priorities.
3. Dependencies between activities cause delays to accumulate.
The Critical Chain is the longest sequence of dependent
activities and common (contended) resources.
Measure Project Progress as % of Critical Chain completed.
Replacing safety time with buffers
- Feeding buffer (FB) protects the critical chain from delays.
- Project buffer (PB) is a safety time added to the end of the
critical chain to protect the project completion date.
- Resource buffer (RB) ensures that resources (e.g. rental
equipment) are available to perform critical chain activities.
Accounting for Resource
Contention Using Feeding Buffer
J
2
B
8
START
A
2
C
3
D
2
G
4
E
10
I
3
F
4
H
1
FB=7
FB=5
NOTE: E and G cannot be performed simultaneously (same person)
Set feeding buffer (FB) to allow one day total slack
Project duration based on Critical Chain = 24 days
Incorporating Project Buffer
J
2
B
4
START
A
2
C
3
D
2
G
2
E
5
I
3
F
2
H
1
FB=2
FB=3
NOTE: Reduce by all activity durations > 3 days to eliminate safety time
Redefine Critical Chain = 17 days
Reset feeding buffer (FB) values
Project buffer (PB) = (Original Critical Chain-Redefined Critical Chain)
PB=4
Sources of Unexpected Problems
Cost Time Performance
- Difficulties require
more resources
- Scope of work
increases
- Initial bids or
estimates were too
low
- Reporting was poor
or untimely
- Budgeting was
inadequate
- Corrective control
was not exercised in
time
- Price changes of
inputs
- Delay owing to
technical difficulties
- Initial time estimates
were optimistic
- Task sequencing
was incorrect
- Required resources
not available as
needed
- Necessary preceding
tasks were
incomplete
- Client-generated
changes
- Unforeseen
government
regulations
- Unexpected
technical problems
arise
- Insufficient
resources are
available
- Insurmountable
technical difficulties
- Quality or reliability
problems occur
- Client requires
changes in
specifications
- Complications with
functional areas
- A technological
breakthrough occurs
Earned Value Chart
Actual
Cost
Today
Dollars
Value
Completed
Budgeted Cost
(Baseline)
Days
ACWP
BCWS
BCWP
C
o
s
t
V
a
r
i
a
n
c
e
S
c
h
e
d
u
l
e
V
a
r
i
a
n
c
e
Time
Variance
A
T
W
P
S
T
W
P
Figure 16.17 Earned Value Chart
Topics for Discussion
Give an example that demonstrates trade-off inherent in
projects among cost, time, and performance.
Illustrate the four stages of team building from your
own experience.
Are Gantt charts still viable project management tools?
Explain.
Explain why the PERT estimate of expected project
duration is always optimistic.
What purpose does a project history report serve?
Discuss the differences among time variance, cost
variance, and schedule variance.
Interactive Exercise
Prepare a work breakdown structure
(WBS) for a homecoming dance.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Project ManagementDocument23 pagesProject ManagementMuthusamy SenthilkumaarPas encore d'évaluation
- MGT 3121 Chapter 16Document6 pagesMGT 3121 Chapter 16AmandaPas encore d'évaluation
- CPM PertDocument39 pagesCPM Pertapi-19916368Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment CM Final PDFDocument9 pagesAssignment CM Final PDFRefisa JiruPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimas Dwi Risandi - 7 - Manajeman Proyek Lat 2Document17 pagesDimas Dwi Risandi - 7 - Manajeman Proyek Lat 2Melatih eskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Operations Management Lect 15-20Document64 pagesOperations Management Lect 15-20haleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Planning and Scheduling: Me 479 Project Planning Richard B. Hathaway, PHD, P.EDocument27 pagesProject Planning and Scheduling: Me 479 Project Planning Richard B. Hathaway, PHD, P.Eriyaz10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project Schedule - 4Document40 pagesProject Schedule - 4Fahmi SyakurPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Session 4 RevisedDocument33 pages2015 Session 4 RevisedArslan LatifPas encore d'évaluation
- Deeti MathDocument6 pagesDeeti MathDeeti SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Planning Scheduling Pert CPMDocument34 pagesPlanning Scheduling Pert CPMlorraine atienzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 17 Lecture SlidesDocument42 pagesChapter 17 Lecture SlidesTedy MonevPas encore d'évaluation
- Path AnalysisDocument3 pagesPath AnalysisRakesh bhukyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro PMDocument26 pagesIntro PMekoinPas encore d'évaluation
- 9-Construction Management - Optimizing Resource ScheduleDocument46 pages9-Construction Management - Optimizing Resource Scheduleمحمد بركات0% (1)
- OPER 576 - S04 - Project CrashingDocument30 pagesOPER 576 - S04 - Project Crashingmoondonoo7100% (2)
- Project Scheduling: Prof. Jiang Zhibin Dept. of IE, SJTUDocument40 pagesProject Scheduling: Prof. Jiang Zhibin Dept. of IE, SJTUNavneet Chugh100% (2)
- 2 - Project Planning & SchedulingDocument17 pages2 - Project Planning & SchedulingRedwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Analysis Questions and WorksheetDocument3 pagesNetwork Analysis Questions and WorksheetMarc WrightPas encore d'évaluation
- PM Essentials: Project Definition, Lifecycle & ManagementDocument29 pagesPM Essentials: Project Definition, Lifecycle & ManagementVaishnavi MandhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Operations Research Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesOperations Research Exam QuestionsRaj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- BC 170400916Document4 pagesBC 170400916aqsa ranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of PERT & CPMDocument19 pagesApplication of PERT & CPMabu1sayeed1chowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ManaDocument41 pagesProject Manaom_mohit11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management Critical Path MethodDocument13 pagesProject Management Critical Path MethodNUR RABIATUL ALYA AMRULNIZAMPas encore d'évaluation
- PERT:Programme Evaluation and Review Technique". and CPMDocument39 pagesPERT:Programme Evaluation and Review Technique". and CPMakant_chandrakar6246Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6-2223Document32 pagesUnit 6-2223ali awaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation Scheduling PDFDocument26 pagesOperation Scheduling PDFMd. Mahbub-ul- Huq Alvi, 170021144Pas encore d'évaluation
- Network Analysis Critical Paths and Float CalculationsDocument20 pagesNetwork Analysis Critical Paths and Float CalculationsImransk401Pas encore d'évaluation
- PM - Network Analysis CasesDocument20 pagesPM - Network Analysis CasesImransk401Pas encore d'évaluation
- MTH601 Spring MidTermDocument7 pagesMTH601 Spring MidTermyobayi5874Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - OR (CPM, PERT) PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment - OR (CPM, PERT) PDFranjeet singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessing Resources: by Dr. Mahdi DamghaniDocument28 pagesAssessing Resources: by Dr. Mahdi DamghaniallahmahdialiPas encore d'évaluation
- CB510 Ch3Document36 pagesCB510 Ch3Mohamed KadryPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Path Analysis and Scheduling TechniquesDocument5 pagesCritical Path Analysis and Scheduling TechniquesPeña Tahiris100% (2)
- Variability in The Project Completion DateDocument12 pagesVariability in The Project Completion DateNguyễn Quốc ViệtPas encore d'évaluation
- MTH 601 Assignment 1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesMTH 601 Assignment 1 SolutionsHusnain SajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Pert / CPM by Prof. Richard B. Goldstein: Pert Program Evaluation & Review Technique CPM Critical Path MethodDocument16 pagesPert / CPM by Prof. Richard B. Goldstein: Pert Program Evaluation & Review Technique CPM Critical Path MethodvenkycoolsterPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Management 01 Dr. Emad ElbeltagiDocument21 pagesConstruction Management 01 Dr. Emad Elbeltagishambel asfawPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.A. Network ModelsDocument30 pages7.A. Network ModelsAsh LyPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGINEERING PROJECT MANAGEMENT TOOLSDocument52 pagesENGINEERING PROJECT MANAGEMENT TOOLSTalha Bin SaeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6 Project Planning and SchedulingDocument30 pagesModule 6 Project Planning and SchedulingOkita SoujiPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ManagementDocument6 pagesProject ManagementJacky0% (1)
- Project Scheduling PERT/CPMDocument43 pagesProject Scheduling PERT/CPMAjay KaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- Pert & CPMDocument23 pagesPert & CPMtarbooz kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PERT Chart and CPM Project PlanningDocument2 pagesPERT Chart and CPM Project PlanningDeepak PooranachandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Project ManagementDocument19 pagesCharacteristics of Project Managementkccrseyer03Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 - Time ManagementDocument46 pages6 - Time ManagementMuhammad SajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management PERT/CPM GuideDocument11 pagesProject Management PERT/CPM GuideOji ArashibaPas encore d'évaluation
- O.r-Ques BankDocument17 pagesO.r-Ques Bankshashank1989Pas encore d'évaluation
- 8 A SchedulingDocument45 pages8 A Schedulingpranav guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- ResourcesDocument11 pagesResourcesMontaser El DadahPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheduling The Project-Chapter-Five 03Document77 pagesScheduling The Project-Chapter-Five 03geachew mihiretuPas encore d'évaluation
- QMDM Assignment TwoDocument4 pagesQMDM Assignment TwoTeke TarekegnPas encore d'évaluation
- Precidance Network1Document26 pagesPrecidance Network1Rajesh ThoratPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Path Analysis EXERCISEDocument13 pagesCritical Path Analysis EXERCISEnailofarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 9Document35 pagesLecture 9Dina Saad EskanderePas encore d'évaluation
- Project Scheduling MethodDocument16 pagesProject Scheduling MethodEngineermsabryPas encore d'évaluation
- CSCI380-Week 4-Lecture 2-Gantt ChartDocument3 pagesCSCI380-Week 4-Lecture 2-Gantt Chart12110159Pas encore d'évaluation
- 13 WaitingDocument25 pages13 WaitingrabalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 DemandDocument15 pages12 DemandrabalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Huff's ModelDocument22 pagesHuff's ModelVipul SachdevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Creating the Right Environment for Customers and EmployeesDocument16 pagesCreating the Right Environment for Customers and EmployeesrabalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Forecasting Demand For ServicesDocument14 pagesForecasting Demand For ServicesrabalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Browser BugsDocument3 pagesBrowser BugsrabalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- BacklogDocument65 pagesBacklograbalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- BacklogDocument65 pagesBacklograbalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- TestDocument3 pagesTestrabalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- NBCDocument186 pagesNBCrabalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Stray Current CorrosionDocument21 pagesStray Current CorrosionPaolo Mogollon AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- 16CE125-Structural Analysis - IIDocument12 pages16CE125-Structural Analysis - IIAnkur SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elsa CableDocument2 pagesElsa CableJay WangPas encore d'évaluation
- ABS Thickness Measurement Requirement For Ship in Operation PDFDocument2 pagesABS Thickness Measurement Requirement For Ship in Operation PDFMohd Fouzi AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Furuno GMDSS Installation Manual PDFDocument64 pagesFuruno GMDSS Installation Manual PDFEric PskdPas encore d'évaluation
- Tank Size CalculatorDocument6 pagesTank Size CalculatorVijayakumar Chandrasekaran100% (2)
- Coal Drying Technology and Plant DesignDocument12 pagesCoal Drying Technology and Plant DesignJigar M. UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Software MetricsDocument253 pagesSoftware MetricsAditya ChourasiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- K1 RootingDocument20 pagesK1 RootingHassan BallouzPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Industrial Revolution & French, Russian Revolution?Document10 pagesDifference Between Industrial Revolution & French, Russian Revolution?Anonymous 3owUL0ksVPas encore d'évaluation
- Multisite ErpDocument5 pagesMultisite ErparavindhsekarPas encore d'évaluation
- 03-2ezii (Ex-Lx-Dx) Codde 3 QRH1 V1Document352 pages03-2ezii (Ex-Lx-Dx) Codde 3 QRH1 V1sadh94Pas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IVDocument12 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science IVAgnes DumlaoPas encore d'évaluation
- NUVE EN 032-055-120 Incubators BrochureDocument2 pagesNUVE EN 032-055-120 Incubators BrochureDinhtrung TruongPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Desalination PlantDocument28 pagesSolar Desalination PlantAnonymous TETH310% (1)
- HYDRO VesselsDocument5 pagesHYDRO VesselsMarvinPatricioNarca0% (1)
- Qa & QC Manual - DraftDocument15 pagesQa & QC Manual - DraftNayla Shafea Azzahra100% (1)
- Assessment 1 - Questioning - Written Assessment: Satisfactory or Not YetsatisfactoryDocument38 pagesAssessment 1 - Questioning - Written Assessment: Satisfactory or Not YetsatisfactoryAbhishek Kumar0% (1)
- Especificaciones Discos de Embrague Transmision - Cat 140HDocument6 pagesEspecificaciones Discos de Embrague Transmision - Cat 140HSergio StockmansPas encore d'évaluation
- SHIP HANDLING WITH ESCORT TUGS A REFERENCE MANUAL FOR MASTERS PILOTS GIANO Tug SpecsDocument8 pagesSHIP HANDLING WITH ESCORT TUGS A REFERENCE MANUAL FOR MASTERS PILOTS GIANO Tug SpecsMahmoud ElsherifPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitsubishi forklift manual pdf downloadDocument3 pagesMitsubishi forklift manual pdf downloadDwi Putra33% (12)
- Kali Linux For BeginnersDocument13 pagesKali Linux For Beginnersnihal0% (1)
- Catalogo-Wellhead-Marvic (Valvulas WKM EXPANDING)Document41 pagesCatalogo-Wellhead-Marvic (Valvulas WKM EXPANDING)mantilla7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Methodology for La Vella ResidencesDocument16 pagesConstruction Methodology for La Vella ResidencesEugene Luna100% (1)
- Making Your Chain Run For Longer: Effective Chain Maintenance Advice From Renold JeffreyDocument2 pagesMaking Your Chain Run For Longer: Effective Chain Maintenance Advice From Renold JeffreyCương Phạm NgọcPas encore d'évaluation
- Capitulos 10 y 11Document34 pagesCapitulos 10 y 11mlpz188669Pas encore d'évaluation
- 15 Suspensions PDFDocument57 pages15 Suspensions PDFSASWAT MISHRAPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Development of Swashplate-Less HelicopterDocument68 pagesDesign and Development of Swashplate-Less HelicopterNsv DineshPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Analysis Software of Downhole Operation Pipe Strings and Its ApplicationDocument4 pagesMechanical Analysis Software of Downhole Operation Pipe Strings and Its ApplicationDarya Khan BhuttoPas encore d'évaluation